Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Human papillomavirus. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 1: A 56-year-old woman makes an appointment with her physician to discuss the results of her cervical cancer screening. She has been menopausal for 2 years and does not take hormone replacement therapy. Her previous Pap smear showed low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL); no HPV testing was performed. Her gynecologic examination is unremarkable. The results of her current Pap smear is as follows:
Specimen adequacy satisfactory for evaluation
Interpretation low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
Notes atrophic pattern
Which option is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Reflex HPV testing
- B. Colposcopy (Correct Answer)
- C. Repeat HPV testing in 6 months
- D. Immediate loop excision
- E. Intravaginal estrogen therapy followed by repeat Pap smear in 1 week
Human papillomavirus Explanation: **Colposcopy**
- For postmenopausal women with **LSIL**, current guidelines recommend immediate colposcopy due to the slightly increased risk of underlying **high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2+)** compared to premenopausal women.
- The "atrophic pattern" note suggests potential for difficulty in cytology interpretation, making direct visualization and biopsy with colposcopy more appropriate for thorough evaluation.
*Reflex HPV testing*
- While HPV testing is often used with LSIL, in a postmenopausal woman with a persistent LSIL result, immediate colposcopy is preferred over reflex HPV testing due to a higher likelihood of significant pathology and the potential for **false negatives in HPV testing** in this age group.
- The patient already has a history of LSIL, and reflex HPV testing might delay definitive diagnosis or treatment for potential underlying high-grade lesions.
*Intravaginal estrogen therapy followed by repeat Pap smear in 1 week*
- While the Pap smear shows an **atrophic pattern** and estrogen therapy can improve cellular maturation making cytology interpretation easier, this approach is not recommended as the initial management for persistent LSIL in a postmenopausal woman.
- The patient already has a **second LSIL result**, indicating this is not simply atrophic changes causing interpretation difficulty, and colposcopy is warranted regardless of the atrophic pattern.
*Repeat HPV testing in 6 months*
- Repeat HPV testing in 6 months might be considered in younger, premenopausal women with LSIL, but in a 56-year-old postmenopausal woman with a history of LSIL, this approach would delay necessary investigation for potential high-grade lesions.
- The risk profile for CIN2+ is different in postmenopausal women, warranting a more aggressive management approach.
*Immediate loop excision*
- **Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP)** is a therapeutic procedure used to remove high-grade lesions (CIN2, CIN3), not usually indicated as the immediate next step for LSIL.
- A colposcopy with directed biopsies is required first to confirm the presence and grade of any underlying lesion before considering an excisional procedure.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 2: Researchers are investigating a new strain of a virus that has been infecting children over the past season and causing dermatitis. They have isolated the virus and have run a number of tests to determine its structure and characteristics. They have found that this new virus has an outer coating that is high in phospholipids. Protein targeting assays and immunofluorescence images have shown that the outer layer contains numerous surface proteins. On microscopy, these surface proteins are also expressed around the nucleus of cells derived from the infected tissue of the children. This virus’s structure most closely resembles which of the following?
- A. Adenovirus
- B. Papillomavirus
- C. Herpesvirus (Correct Answer)
- D. Poxvirus
- E. Hepadnavirus
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Herpesvirus***
- The presence of an **outer coating high in phospholipids** indicates an **enveloped virus**. Herpesviruses are large, enveloped DNA viruses.
- The detection of surface proteins expressed around the **nucleus** is a key finding that suggests the virus **buds from the nuclear membrane**, a characteristic feature of **herpesviruses**.
- Many herpesviruses cause dermatitis, including **HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV**, and **HHV-6**.
*Adenovirus*
- Adenoviruses are **non-enveloped viruses**, meaning they lack a lipid outer coating, which contradicts the phospholipid-rich coating described.
- Their replication and assembly occur exclusively in the **nucleus**, but they do not acquire an envelope by budding from the nuclear membrane.
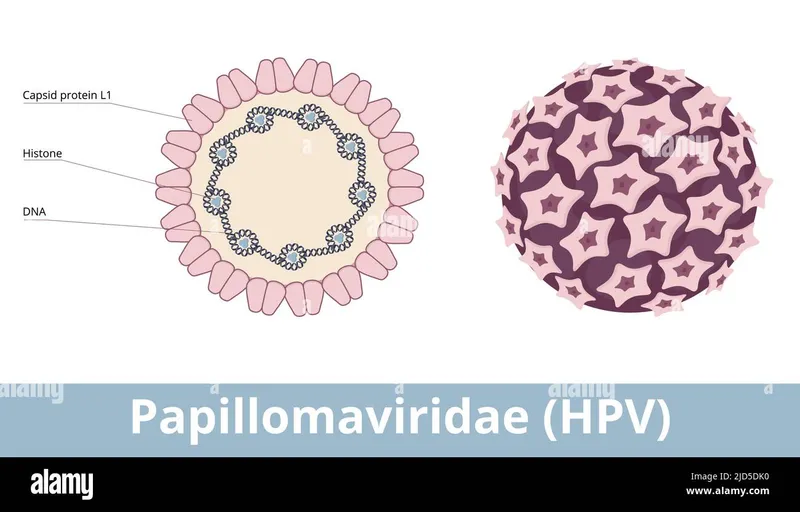
*Papillomavirus*
- Papillomaviruses are also **non-enveloped viruses** with an **icosahedral capsid**, lacking the phospholipid envelope described.
- They replicate and assemble in the nucleus but do not possess the phospholipid-rich outer coating.
*Poxvirus*
- While poxviruses are **enveloped**, they acquire their envelope from the **Golgi apparatus** or **plasma membrane**, not the nuclear membrane.
- They are also distinct from other DNA viruses in that they replicate entirely in the **cytoplasm**, not the nucleus, which does not explain the perinuclear protein expression.
*Hepadnavirus*
- Hepadnaviruses (e.g., **Hepatitis B virus**) are enveloped DNA viruses, but their envelope is acquired by budding through the **endoplasmic reticulum** and **Golgi apparatus**, not the nuclear membrane.
- The perinuclear localization of surface proteins in immunofluorescence is not a characteristic feature of hepadnaviruses.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 3: A 31-year-old female presents to her gynecologist for a routine Pap smear. Her last Pap smear was three years ago and was normal. On the current Pap smear, she is found to have atypical squamous cells of unknown significance (ASCUS). Reflex HPV testing is positive. What is the best next step?
- A. Colposcopy (Correct Answer)
- B. Repeat Pap smear and HPV testing in 5 years
- C. Repeat Pap smear in 3 years
- D. Repeat Pap smear in 1 year
- E. Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP)
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Colposcopy***
- A **colposcopy** is indicated for a patient over 25 with **atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS)** and a **positive high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) test** to evaluate for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
- The positive HPV test suggests a higher risk of underlying cervical disease requiring direct visualization and potentially biopsy of abnormal areas.
*Repeat Pap smear and HPV testing in 5 years*
- This option is incorrect because a **positive HPV test** along with ASCUS indicates a need for more immediate and invasive evaluation than routine screening.
- Waiting five years could allow progression of potential **cervical dysplasia** without intervention.
*Repeat Pap smear in 3 years*
- This timeframe is typically for women aged 21-29 with a normal Pap smear and negative HPV, or for follow-up after low-grade abnormalities, not for ASCUS with positive HPV.
- The presence of **high-risk HPV** mandates a more aggressive follow-up strategy.
*Repeat Pap smear in 1 year*
- This might be an option for ASCUS with a **negative HPV test** or for adolescents, but it is insufficient when high-risk HPV is positive.
- A **high-risk HPV infection** following an ASCUS result requires colposcopy to rule out significant cervical lesions.
*Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP)*
- A **LEEP** is a therapeutic procedure used to remove abnormal cervical tissue, usually performed after a colposcopy and biopsy confirms a high-grade lesion (CIN 2 or 3).
- Performing a LEEP immediately without a preceding colposcopy and biopsy would be **premature** as the diagnosis of the severity of cervical changes is not yet confirmed.
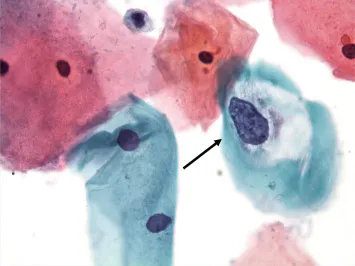
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 4: A 36-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual pelvic examination and Pap smear. Her last Pap smear was 3 years ago. She has been sexually active with multiple male partners and takes an oral contraceptive. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 10 years. Pelvic examination shows no abnormalities. A photomicrograph of cervical cells from the Pap smear specimen is shown. Cells similar to the one indicated by the arrow are most likely to be seen in which of the following conditions?
- A. Condylomata acuminata (Correct Answer)
- B. Bacterial vaginosis
- C. Trichomoniasis
- D. Genital herpes
- E. Syphilitic chancre
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Condylomata acuminata***
- The image likely depicts a **koilocyte**, a key indicator of **Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection**, which causes condylomata acuminata.
- Koilocytes are characterized by **perinuclear cytoplasmic vacuolization** and nuclear atypia, directly linked to HPV.
*Bacterial vaginosis*
- Characterized by a **shift in vaginal flora**, presenting with "clue cells" (vaginal epithelial cells covered in bacteria) and discharge, not koilocytes.
- While common, bacterial vaginosis does not cause the **cytopathic changes** seen with HPV infection.
*Trichomoniasis*
- Caused by the **protozoan parasite** *Trichomonas vaginalis*, leading to a frothy, green-yellow discharge and cervical inflammation (strawberry cervix).
- Diagnosis involves identifying the **motile trichomonads** on wet mount, not koilocytes on a Pap smear.
*Genital herpes*
- Caused by **herpes simplex virus (HSV)**, resulting in painful vesicular lesions that ulcerate.
- Cytologic findings include **multinucleated giant cells** with nuclear molding and intranuclear inclusions, distinctly different from koilocytes.
*Syphilitic chancre*
- A primary lesion of syphilis caused by **_Treponema pallidum_**, presenting as a painless ulcer.
- Diagnosis is made by **darkfield microscopy** or serologic tests; cytology is not used to identify syphilitic chancres.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 5: A 55-year-old postmenopausal woman comes to the physician for a screening Pap smear. She has no history of serious illness. Her last Pap smear was 10 years ago and showed no abnormalities. She has smoked one-half pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years and drinks 3 bottles of wine per week. She is sexually active with multiple male partners and uses condoms inconsistently. Her paternal grandmother had ovarian cancer and her maternal aunt had breast cancer. Pelvic examination shows multiple red, fleshy polypoid masses on the anterior vaginal wall. A biopsy is obtained and histology shows large cells with abundant clear cytoplasm. Which of the following is the most significant risk factor for this diagnosis?
- A. Family history of breast and ovarian cancer
- B. Human papillomavirus infection
- C. Alcohol consumption
- D. Diethylstilbestrol exposure in utero (Correct Answer)
- E. Cigarette smoking
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Diethylstilbestrol exposure in utero***
- The patient's presentation with **clear cell carcinoma of the vagina**, characterized by **red, fleshy polypoid masses** and **large cells with abundant clear cytoplasm**, is highly suggestive of this diagnosis.
- **In utero exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES)** is a classic and significant risk factor for the development of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and cervix.
*Family history of breast and ovarian cancer*
- While a family history of breast and ovarian cancer may indicate an increased risk for other gynecological cancers (e.g., BRCA mutations), it is **not directly linked** to clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina.
- This family history points more towards **hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes**, not the specific pathology described.
*Human papillomavirus infection*
- **HPV infection** is a major risk factor for most cases of **squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina and cervix**, and also increases the risk of adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
- However, HPV is **not a primary risk factor for clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina**, which has a distinct etiology.
*Alcohol consumption*
- While excessive **alcohol consumption** can be associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, it is **not a specific or significant risk factor** for clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina.
- It generally contributes to a broad range of cancers rather than specific rare forms.
*Cigarette smoking*
- **Cigarette smoking** is a well-established risk factor for **squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix and vagina**, among other cancers.
- However, it is **not a recognized significant risk factor** for the development of **clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina**.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 6: A 34-year-old G2P2 undergoes colposcopy due to high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia detected on a Pap smear. Her 2 previous Pap smears showed low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia. She has had 2 sexual partners in her life, and her husband has been her only sexual partner for the last 10 years. She had her sexual debut at 16 years of age. She had her first pregnancy at 26 years of age. She uses oral contraceptives for birth control. Her medical history is significant for right ovary resection due to a large follicular cyst and cocaine abuse for which she completed a rehabilitation program. Colposcopy reveals an acetowhite lesion with distorted vascularity at 4 o'clock. Which of the following factors present in this patient is a risk factor for the detected condition?
- A. Age of sexual debut (Correct Answer)
- B. Ovarian surgery
- C. History of cocaine abuse
- D. Patient age
- E. Age at first pregnancy
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Age of sexual debut***
- An early **age of sexual debut** (before 17 years old) is a significant risk factor for **HPV infection** and subsequently, cervical dysplasia. This patient's sexual debut at 16 years old falls within this high-risk category.
- Early sexual activity, especially with multiple partners, increases the likelihood of exposure to **human papillomavirus (HPV)**, the primary cause of cervical cancer and its precursor lesions.
*Ovarian surgery*
- **Ovarian surgery**, such as a right ovary resection for a follicular cyst, is not a known risk factor for **cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)** or **cervical cancer**.
- This aspect of her medical history is unrelated to the development of cervical dysplasia.
*History of cocaine abuse*
- While **cocaine abuse** can be associated with other health complications and risky behaviors, it is not a direct or independent **risk factor** for **cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)**.
- There is no established physiological link between cocaine use and the development of cervical dysplasia.
*Patient age*
- Although the incidence of HPV infection peaks in younger women, the risk of developing **high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (HGSIL)** and invasive cancer increases with age, particularly after 30 due to persistent HPV infection.
- However, at 34, her age is not as strong a contributing risk factor as an early **age of sexual debut** for the initial development of the underlying condition.
*Age at first pregnancy*
- **Early age at first pregnancy** (before 20) can increase the risk of cervical cancer in some studies, possibly due to hormonal changes in the cervix making it more vulnerable to **HPV infection**.
- This patient's first pregnancy at 26 is not considered an early age at first pregnancy and therefore is not a significant risk factor in this context.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old woman comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. She feels well. She had a chlamydia infection at the age of 22 years that was treated. Her only medication is an oral contraceptive. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 6 years. She has recently been sexually active with 3 male partners and uses condoms inconsistently. Her last Pap test was 4 years ago and results were normal. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. A Pap test shows atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Repeat cytology in 6 months
- B. Perform laser ablation
- C. Perform loop electrosurgical excision procedure
- D. Perform HPV testing (Correct Answer)
- E. Perform cervical biopsy
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Perform HPV testing***
- For women aged 25-29 with **Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance (ASC-US)**, **HPV co-testing** is the preferred next step to risk-stratify for high-grade lesions.
- If **HPV is positive**, the patient should proceed to **colposcopy**; if HPV is negative, she can return to routine screening.
*Repeat cytology in 6 months*
- This approach is typically recommended for adolescents (age <21) with ASC-US or for women aged 21-24 where HPV testing is often not performed due to the high rate of transient HPV infections.
- For women aged ≥25 years with ASC-US, **reflex HPV testing** or **HPV co-testing** (if not done with the initial Pap) is generally preferred over repeat cytology alone.
*Perform laser ablation*
- **Laser ablation** is a treatment for **high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2/3)** identified after colposcopy and biopsy, not for initial ASC-US findings.
- Initiating a destructive procedure without further diagnostic evaluation would be premature and over-treatment for ASC-US.
*Perform loop electrosurgical excision procedure*
- **LEEP (loop electrosurgical excision procedure)** is a **diagnostic and therapeutic procedure** typically reserved for confirmed **high-grade CIN (CIN2 or CIN3)** or adenocarcinoma in situ.
- It is an invasive procedure and not appropriate as the initial management step for an ASC-US Pap result.
*Perform cervical biopsy*
- A **cervical biopsy** is performed during a **colposcopy** if abnormal areas are identified, usually following a positive HPV test or higher-grade abnormal cytology (e.g., LSIL, HSIL).
- ASC-US alone does not automatically warrant an immediate colposcopy and biopsy without prior **HPV risk stratification**.
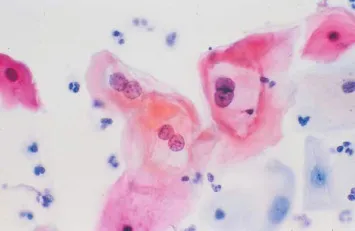
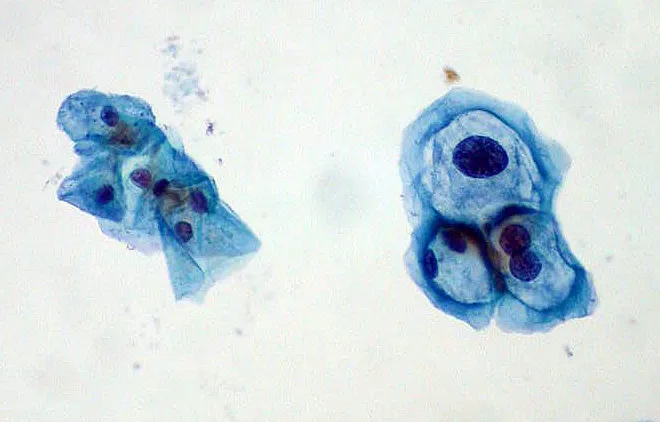
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 8: A 31-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist for a routine well-visit. She is sexually active with multiple male partners and uses an intrauterine device for contraception. Her last menstrual period was two weeks ago. She denies abnormal vaginal discharge or sensations of burning or itching. Pelvic exam is normal. Routine Pap smear shows the following (see Image A). Which organism is most likely responsible for her abnormal Pap smear?
- A. Trichomonas vaginalis
- B. Human papillomavirus (Correct Answer)
- C. Herpes simplex virus 1
- D. Treponema pallidum
- E. Chlamydia trachomatis
Human papillomavirus Explanation: **Human papillomavirus**
- The image illustrates **koilocytes**, which are squamous epithelial cells with perinuclear halos and enlarged, hyperchromatic, and often irregular nuclei. These are pathognomonic for **human papillomavirus (HPV) infection**.
- HPV is a sexually transmitted infection, and the patient's history of being **sexually active with multiple partners** increases her risk of exposure to HPV.
*Trichomonas vaginalis*
- *Trichomonas vaginalis* typically causes a **foamy, green-yellow vaginal discharge** and can lead to a "strawberry cervix" on speculum exam, neither of which are mentioned or depicted.
- Pap smears infected with *Trichomonas* often show flagellated organisms and an inflammatory response, but not the characteristic koilocytes.
*Herpes simplex virus 1*
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection on a Pap smear would typically show **multinucleated giant cells** with nuclear molding and intranuclear inclusions, not koilocytes.
- Patients often present with painful genital lesions, which are absent in this case.
*Treponema pallidum*
- *Treponema pallidum* (syphilis) is a bacterial infection that would not be diagnosed via Pap smear cytology and does not cause koilocytes.
- Primary syphilis presents as a **painless chancre**, while secondary syphilis involves a rash and systemic symptoms.
*Chlamydia trachomatis*
- *Chlamydia trachomatis* is a bacterial infection that can cause cervicitis, but it does not lead to koilocytic changes on a Pap smear.
- Diagnosis relies on **nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)**, and symptoms, if present, might include abnormal discharge or post-coital bleeding.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 9: A 62-year-old man comes to the physician because of a growth on his penis that has been gradually increasing in size over the last year. He was diagnosed with HIV 10 years ago. He has been divorced for 25 years and has had “at least 30 sexual partners” since. Physical examination shows a nontender 2.5-cm ulcerated lesion with an erythematous base on the dorsum of the glans. There is firm left inguinal lymphadenopathy. A biopsy of the lesion shows small uniform basophilic cells with central necrosis that invade into the corpus cavernosum. This patient's condition is most likely associated with which of the following pathogens?
- A. Chlamydia trachomatis
- B. Haemophilus ducreyi
- C. Epstein-Barr virus
- D. Human papillomavirus (Correct Answer)
- E. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Human papillomavirus***
- The description of a slowly growing, ulcerated penile lesion with inguinal lymphadenopathy in an HIV-positive man with multiple sexual partners is highly suggestive of **penile squamous cell carcinoma**, which is strongly associated with **human papillomavirus (HPV)** infection.
- The biopsy findings of "small uniform basophilic cells with central necrosis invading into the corpus cavernosum" are consistent with a poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, often linked to high-risk HPV types.
*Chlamydia trachomatis*
- This pathogen causes **urethritis**, **cervicitis**, and **lymphogranuloma venereum**, which presents with painful lymphadenopathy and anogenital ulcers, but typically not a slowly growing, ulcerated mass like the one described.
- The histological description does not fit the typical presentation of complications from *Chlamydia trachomatis* infection.
*Haemophilus ducreyi*
- This bacterium is the cause of **chancroid**, which presents as painful, ragged ulcers with tender inguinal lymphadenopathy.
- While it causes ulcers and lymphadenopathy, the clinical presentation and biopsy findings of a chronic, slowly enlarging, infiltrative lesion are not typical of chancroid.
*Epstein-Barr virus*
- While Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is associated with several cancers, including **nasopharyngeal carcinoma**, **Burkitt lymphoma**, and **post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder**, it is not a known cause of penile squamous cell carcinoma.
- The clinical and histological features do not align with EBV-associated malignancies.
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae*
- This bacterium primarily causes **urethritis**, **cervicitis**, and **disseminated gonococcal infection**.
- It does not cause chronic, slowly enlarging ulcerated lesions on the penis that progress to squamous cell carcinoma.
Human papillomavirus US Medical PG Question 10: A 57-year-old man presents to the office with complaints of perianal pain during defecation and perineal heaviness for 1 month. He also complains of discharge around his anus, and bright red bleeding during defecation. The patient provides a history of having a sexual relationship with other men without using any methods of protection. The physical examination demonstrates edematous verrucous anal folds that are of hard consistency and painful to the touch. A proctosigmoidoscopy reveals an anal canal ulcer with well defined, indurated borders on a white background. A biopsy is taken and the results are pending. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Anal cancer (Correct Answer)
- B. Polyps
- C. Anal fissure
- D. Hemorrhoids
- E. Proctitis
Human papillomavirus Explanation: ***Anal cancer***
- The patient's presentation with **perianal pain**, **bleeding**, **discharge**, and **edematous verrucous anal folds** (suggesting a lesion) are highly suspicious for anal cancer. His history of unprotected sexual relationships with men is a significant risk factor for **HPV infection**, which is a leading cause of anal squamous cell carcinoma.
- The proctosigmoidoscopy findings of an **anal canal ulcer with well-defined, indurated borders** and a white background further point towards a malignant lesion, making anal cancer the most likely diagnosis.
*Polyps*
- While polyps can cause bleeding, they typically do not present with **indurated, painful verrucous lesions** or an ulcer with defined borders.
- Polyps are usually soft and less likely to cause the severe perianal pain and perineal heaviness described.
*Anal fissure*
- An anal fissure is a **linear tear** in the anal canal, causing sharp pain during defecation and bright red blood.
- It would not typically present with **edematous verrucous anal folds**, perineal heaviness, or an indurated ulcer as seen on proctosigmoidoscopy.
*Hemorrhoids*
- Hemorrhoids commonly cause **bright red bleeding** and can cause discomfort or heaviness.
- However, they usually appear as swollen vascular cushions and do not typically present as **indurated, painful verrucous lesions** or an ulcer with defined borders.
*Proctitis*
- Proctitis is an inflammation of the rectum, causing rectal pain, tenesmus, and bleeding, often due to **inflammatory bowel disease** or **infections**.
- While it can cause some of the symptoms, it wouldn't typically manifest as a distinct **indurated, verrucous lesion** or an ulcer with firm borders, which are more indicative of a mass.
More Human papillomavirus US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.