EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for EBV-associated malignancies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 1: An 11-year-old boy who recently emigrated from Nigeria is brought to the physician for evaluation of jaw swelling. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Examination shows a 5-cm solid mass located above the right mandible and significant cervical lymphadenopathy. A biopsy specimen of the mass shows sheets of lymphocytes with interspersed tingible body macrophages. Serology for Epstein-Barr virus is positive. Which of the following chromosomal translocations is most likely present in cells obtained from the tissue mass?
- A. t(8;14) (Correct Answer)
- B. t(12;21)
- C. t(11;22)
- D. t(15;17)
- E. t(11;14)
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***t(8;14)***
- The constellation of **jaw swelling** in a child from **Nigeria**, positive **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)** serology, and a biopsy showing a **"starry sky"** pattern (sheets of lymphocytes with interspersed tingible body macrophages) is classic for **endemic Burkitt lymphoma**.
- **Burkitt lymphoma** is characterized by the **t(8;14) translocation**, which results in the constitutive activation of the **c-MYC oncogene** on chromosome 8 due to its proximity to the **immunoglobulin heavy chain locus** on chromosome 14.
*t(12;21)*
- This translocation is typically associated with **B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)**, particularly in children.
- While ALL can present with bone pain or cytopenias, it does not typically manifest as a localized **jaw mass** with a "starry sky" histology.
*t(11;22)*
- This translocation is characteristic of **Ewing sarcoma**, a **bone tumor** that can affect the jaw.
- However, Ewing sarcoma would typically show small, round, blue cells on histology and would not be associated with **EBV infection** or the "starry sky" pattern.
*t(15;17)*
- This translocation is pathognomonic for **acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML)**, a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia.
- APML presents with signs of bone marrow failure and disseminated intravascular coagulation, not with a localized head and neck mass.
*t(11;14)*
- This translocation is primarily associated with **mantle cell lymphoma**, a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that typically affects older adults.
- Mantle cell lymphoma would have cyclin D1 overexpression, and usually does not present as a localized jaw mass in children, nor is it strongly linked to EBV in this clinical context.
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 2: A 28-year-old male with a history of HIV infection is found to have a CD4+ T lymphocyte count of 68 cells per microliter. As a consequence of his HIV infection, this patient is at increased risk of malignancy due to which of the following?
- A. Pneumocystis jiroveci
- B. Actinomyces israelii
- C. Helicobacter pylori
- D. HHV-6
- E. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) (Correct Answer)
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)***
- **EBV** is a major cause of **AIDS-related malignancies**, particularly **B-cell lymphomas** including **non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)** and **primary CNS lymphoma**, which are common in patients with CD4 counts below 100 cells/µL.
- The severe immunosuppression in **HIV/AIDS** allows for unchecked **EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disorders** due to impaired T-cell surveillance of EBV-infected B cells.
- Among the options listed, **EBV** is the only **oncogenic virus** and represents a significant cause of morbidity in advanced AIDS patients.
- **Note:** While HHV-8 (KSHV) causing Kaposi's sarcoma is also a major AIDS-related malignancy, it is not among the listed options.
*Pneumocystis jiroveci*
- **Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP)** is a common opportunistic **fungal infection** in HIV patients with CD4 < 200 cells/µL, causing severe respiratory illness.
- **PCP** is not oncogenic and does not increase malignancy risk; it causes acute infection, not cellular transformation.
*Actinomyces israelii*
- **Actinomyces israelii** is a gram-positive **bacterium** causing **actinomycosis**, a chronic suppurative infection with abscess formation and sinus tracts.
- While it can cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients, it is **not oncogenic** and not associated with malignancy risk.
*Helicobacter pylori*
- **H. pylori** is a bacterium associated with **gastric adenocarcinoma** and **gastric MALT lymphoma** in the general population through chronic gastric inflammation.
- However, in the context of advanced HIV/AIDS with CD4 < 100, the predominant malignancy risk is from **oncogenic viruses** (EBV, HHV-8), not gastric pathology from **H. pylori**.
- **H. pylori** is not typically considered an AIDS-defining or AIDS-related malignancy.
*HHV-6*
- **Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6)** causes roseola infantum in children and can reactivate in immunocompromised patients, potentially causing encephalitis or pneumonitis.
- **HHV-6** is **not established as oncogenic** and lacks strong evidence linking it to malignancy in HIV patients, unlike **EBV** (lymphomas) or **HHV-8** (Kaposi's sarcoma).
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 3: A 37-year old man is being evaluated due to a recent history of fatigue that started 3 weeks ago. The patient presents with a history of HIV, which was first diagnosed 7 years ago. He has been on an antiretroviral regimen and takes it regularly. His CD4+ count is 350 cells/mm3. According to the patient, his partner passed away from a "blood cancer", and he is worried that his fatigue might be connected to a similar pathology. The physician clarifies that there is an increased risk for HIV patients to develop certain kinds of lymphomas. Which one of the conditions below is the patient more likely to develop based on his medical history?
- A. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- B. Follicular lymphoma
- C. Burkitt’s lymphoma
- D. Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma
- E. Small lymphocytic lymphoma
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***Diffuse large B cell lymphoma***
- **Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)** is the most common type of lymphoma diagnosed in HIV-positive patients, accounting for about 50% of cases.
- The increased risk of DLBCL in HIV patients is related to chronic immune stimulation and dysregulation, often exacerbated by co-infection with viruses like **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**.
*Follicular lymphoma*
- **Follicular lymphoma** is generally *less common* in HIV-positive patients compared to the general population.
- Its incidence does not significantly increase in the context of HIV infection.
*Burkitt’s lymphoma*
- **Burkitt's lymphoma** is also more common in HIV patients, but typically presents in those with *more severe immunosuppression* (lower CD4 counts) and is specifically associated with **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)** co-infection.
- While a possibility, DLBCL is the *overall most likely* lymphoma.
*Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma*
- **Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma** is *not typically associated* with an increased incidence in HIV-positive individuals.
- It often correlates with chronic inflammation or specific infections (e.g., *H. pylori* in gastric MALT lymphoma).
*Small lymphocytic lymphoma*
- **Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)**, which is essentially the nodal form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), is *not increased* in incidence in HIV-positive patients.
- CLL/SLL is generally considered to be *less common* or have no increased risk in HIV-infected individuals.
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 4: A 63-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because he has been having headaches and hearing loss. In addition, he says that he has been having difficulty opening his jaw to eat and recurrent middle ear infections. Physical exam reveals enlarged neck lymph nodes and a mass in the nasopharynx. Biopsy of the mass reveals undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells. The organism that is most likely associated with this patient's disease is also associated with which of the following disorders?
- A. Kaposi sarcoma
- B. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- C. Adult T-cell lymphoma
- D. Burkitt lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Vulvar carcinoma
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***Burkitt lymphoma***
- The patient's symptoms (headaches, hearing loss, difficulty opening jaw, recurrent middle ear infections, nasopharyngeal mass, enlarged neck lymph nodes) and biopsy results (undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells) point to **nasopharyngeal carcinoma**.
- **Nasopharyngeal carcinoma** is strongly associated with the **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**. EBV is also a causative agent in **Burkitt lymphoma**.
*Kaposi sarcoma*
- **Kaposi sarcoma** is caused by **Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)**, not EBV.
- It typically presents as vascular skin lesions and can affect visceral organs, differing from the nasopharyngeal carcinoma described.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma*
- **Hepatocellular carcinoma** is primarily associated with **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** and **Hepatitis C virus (HCV)** infection, as well as cirrhosis from other causes.
- There is no significant association between EBV and hepatocellular carcinoma.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- **Adult T-cell lymphoma** is caused by the **Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)**.
- This is a retrovirus distinct from EBV.
*Vulvar carcinoma*
- **Vulvar carcinoma** is most frequently associated with **Human Papillomavirus (HPV)** infection, especially high-risk strains like HPV 16 and 18.
- It is not typically linked to EBV.
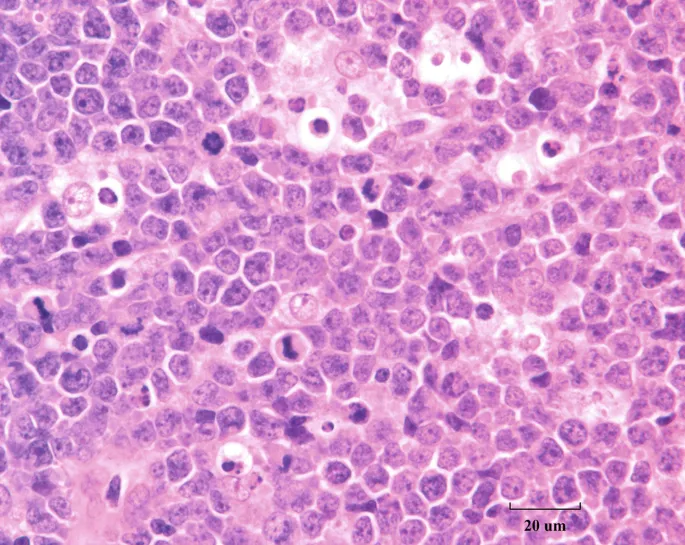
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 5: A 10-year-old boy who recently immigrated to the United States from Africa with his family is brought to the emergency department by his mother for a progressively worsening ulcerative lesion on his jaw. His mother reports that her son’s right jaw has rapidly enlarged over the past few months. He says that it is very tender though he doesn’t recall any trauma to the site. In addition, the mother says her son hasn’t been himself the past few months with intermittent fever, weakness, and fatigue. Physical exam reveals a large, ulcerating right jaw mass that is draining serous fluid and painless cervical and axillary lymphadenopathy. Laboratory results are notable for an elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase. A biopsy of the right jaw mass is shown in the photograph. Which of the following chromosomal translocations is most likely to be found in this patient’s lesion?
- A. t(11;14)
- B. t(15;17)
- C. t(8;14) (Correct Answer)
- D. t(9;22)
- E. t(14;18)
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***t(8;14)***
- The clinical presentation, including a rapidly enlarging jaw mass in an African child, systemic symptoms (fever, weakness, fatigue), and elevated LDH, is highly suggestive of **endemic Burkitt lymphoma**.
- **Burkitt lymphoma** is characterized by the **t(8;14) translocation**, which leads to the overexpression of the *MYC* oncogene.
- The biopsy typically shows a "**starry sky**" pattern due to tingible body macrophages scattered among sheets of rapidly proliferating lymphocytes with a very high mitotic index (Ki-67 approaching 100%).
*t(11;14)*
- This translocation is associated with **Mantle Cell Lymphoma**, which typically affects older adults and presents with generalized lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and bone marrow involvement, not primarily a jaw mass in a child.
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma is characterized by the overexpression of **cyclin D1**, driven by this translocation.
*t(15;17)*
- This translocation is characteristic of **Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL)**, a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia, which presents with symptoms of bone marrow failure (bleeding, infection, anemia) and **DIC risk** rather than a solid jaw mass.
- APL shows abnormal promyelocytes with numerous Auer rods and responds to **all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)** therapy.
*t(9;22)*
- This translocation, also known as the **Philadelphia chromosome**, is characteristic of **Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)** and some cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). CML typically presents with splenomegaly, leukocytosis, and constitutional symptoms, while ALL presents with bone marrow failure, neither of which aligns with this patient's jaw mass.
- The t(9;22) translocation results in the **BCR-ABL fusion gene**, a constitutively active tyrosine kinase targeted by **imatinib** therapy.
*t(14;18)*
- This translocation is characteristic of **Follicular Lymphoma**, which commonly presents as painless generalized lymphadenopathy in older adults. It is rarely seen in children and does not typically present as a rapidly growing jaw mass.
- Follicular lymphoma involves overexpression of the **Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic protein**, promoting cell survival and resulting in an indolent clinical course.
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 6: A pathologist receives a patient sample for analysis. Cells in the sample are first labeled with fluorescent antibodies and then passed across a laser beam in a single file of particles. The light scatter and fluorescent intensity of the particles are plotted on a graph; this information is used to characterize the sample. This laboratory method would be most useful to establish the diagnosis of a patient with which of the following?
- A. Ventricular septal defect and facial dysmorphism with low T-lymphocyte count
- B. Painless generalized lymphadenopathy with monomorphic cells and interspersed benign histiocytes on histology
- C. Pancytopenia and deep vein thrombosis with intermittent hemoglobinuria (Correct Answer)
- D. Multiple opportunistic infections with decreased CD4 counts
- E. Vesicular lesions with dermatomal distribution and dendritic corneal ulcers
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***Pancytopenia and deep vein thrombosis with intermittent hemoglobinuria***
- The described laboratory method is **flow cytometry**, which is the **gold standard for diagnosing paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)** by detecting the absence of **CD55** and **CD59** on red blood cells due to impaired GPI anchor synthesis.
- PNH classically presents with **pancytopenia**, **hemolytic anemia** (leading to hemoglobinuria), and a high risk of **thrombosis** (e.g., deep vein thrombosis).
*Ventricular septal defect and facial dysmorphism with low T-lymphocyte count*
- This clinical picture suggests **DiGeorge syndrome**, which involves a developmental defect of the **third and fourth pharyngeal pouches**, leading to thymic hypoplasia and **T-cell deficiency**.
- While flow cytometry is used to quantify T-lymphocyte subsets (e.g., CD3, CD4, CD8), the primary method for diagnosing DiGeorge syndrome is **fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)** for a **22q11 deletion**, making it less ideal for flow cytometry diagnosis.
*Painless generalized lymphadenopathy with monomorphic cells and interspersed benign histiocytes on histology*
- This description with "**monomorphic cells**" is more consistent with certain **non-Hodgkin lymphomas** (e.g., Burkitt lymphoma) rather than Hodgkin lymphoma, which typically shows a **polymorphic** cellular infiltrate.
- While flow cytometry can be useful in characterizing lymphomas by identifying cell surface markers, the diagnosis is primarily established by **lymph node biopsy and histopathology** with **immunohistochemistry**, making flow cytometry a supplementary rather than primary diagnostic tool.
*Multiple opportunistic infections with decreased CD4 counts*
- This presentation is highly suggestive of **HIV infection leading to AIDS**. The "decreased CD4 counts" are a key diagnostic and prognostic marker.
- While flow cytometry is used to **monitor CD4 cell counts** in HIV patients, the initial diagnosis of HIV is established via **antibody/antigen combination tests** and confirmed by **Western blot** or **PCR for viral load**, not by flow cytometry.
*Vesicular lesions with dermatomal distribution and dendritic corneal ulcers*
- This clinical presentation points to **herpes zoster ophthalmicus** (shingles affecting the eye due to **varicella-zoster virus** reactivation).
- Diagnosis is primarily **clinical** based on the characteristic rash and eye findings, although **PCR** of vesicular fluid can confirm VZV infection. Flow cytometry has no role in this diagnosis.
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 7: A 16-year-old male is brought to the clinic by his mother for the complaints of fever, nonproductive cough, fatigue, lack of appetite, and sore throat for the past 2 months. Several other students at his high school have had similar symptoms. Physical exam shows a whitish membrane in his oropharynx, bilateral enlarged cervical lymphadenopathy, and mild splenomegaly. Which of the following tests is most likely to diagnose his condition?
- A. Monospot test (Correct Answer)
- B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- C. Throat culture
- D. Urine culture
- E. Chest X-ray
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***Monospot test***
- The Monospot test detects **heterophile antibodies**, which are commonly produced during an acute Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, the cause of **infectious mononucleosis**.
- The patient's symptoms (fever, fatigue, nonproductive cough, sore throat, cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) and the epidemiological context (several other students with similar symptoms) are highly suggestive of **infectious mononucleosis**.
*Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)*
- While ELISA can detect antibodies to various pathogens, including EBV-specific antigens, the **Monospot test** is the more common and rapid initial diagnostic tool for infectious mononucleosis.
- ELISA for EBV-specific antibodies (e.g., VCA-IgM, VCA-IgG) might be used if the Monospot test is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, especially in younger children or atypical presentations.
*Throat culture*
- A throat culture is used to identify bacterial infections, such as **Streptococcus pyogenes** (strep throat).
- Although the patient has a sore throat and a whitish membrane, his other systemic symptoms (fatigue, splenomegaly, lack of appetite for 2 months) are not typical for a bacterial pharyngitis which usually responds to antibiotics. A **nonproductive cough** also makes bacterial pharyngitis less likely.
*Urine culture*
- A urine culture is used to diagnose **urinary tract infections**.
- The patient's symptoms are not indicative of a urinary tract infection.
*Chest X-ray*
- A chest X-ray is used to evaluate the lungs for conditions such as **pneumonia**, **bronchitis**, or other respiratory pathologies.
- While the patient has a nonproductive cough, the predominant systemic symptoms (fever, fatigue, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) point towards a systemic viral infection rather than primarily a lung issue that would be definitively diagnosed by a chest X-ray.
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 8: A research lab is investigating the rate of replication of a variety of human cells in order to better understand cancer metastasis. A particular cell line of interest is marked with a high concern for malignant potential due to its chromatin structure characteristics. Which of the following is most closely associated with an increased potential for malignancy?
- A. Methylated DNA
- B. H1 protein
- C. Nucleosomes
- D. Euchromatin (Correct Answer)
- E. Heterochromatin
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***Euchromatin***
- An increased amount of **euchromatin** suggests that the DNA is less condensed and more accessible for transcription and replication, which is characteristic of rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells.
- Cancer cells often exhibit **deregulated gene expression** due to alterations in chromatin structure, leading to an increase in euchromatin and higher rates of protein synthesis necessary for rapid proliferation.
*Methylated DNA*
- While DNA methylation is an important **epigenetic modification** involved in cancer, specific patterns of methylation (e.g., hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes or hypomethylation of oncogenes) are associated with malignancy, not methylation of all DNA.
- Global hypomethylation is linked to genomic instability in cancer, whereas hypermethylation often leads to gene silencing.
*H1 protein*
- **H1 histone protein**, also known as the linker histone, is responsible for compacting nucleosomes and is essential for forming higher-order chromatin structures.
- An abundance of H1 generally indicates a more condensed chromatin state, which would be *less* associated with the active transcription and replication seen in highly malignant cells.
*Nucleosomes*
- **Nucleosomes** are the fundamental building blocks of chromatin, consisting of DNA wrapped around histone proteins. They are present in all eukaryotic cells, irrespective of their malignant potential.
- While alterations in nucleosome positioning and modification can occur in cancer, the presence of nucleosomes themselves is not indicative of malignancy.
*Heterochromatin*
- **Heterochromatin** is a highly condensed form of chromatin that is typically transcriptionally inactive or silenced.
- A high proportion of heterochromatin would suggest a cell with reduced gene expression and replication activity, which is generally *not* characteristic of rapidly dividing malignant cells.
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 9: A 19-year-old woman presents to the family medical center with a 2-week history of a sore throat. She says that she has felt increasingly tired during the day and has a difficult time staying awake during her classes at the university. She appears well-nourished with a low energy level. Her vital signs include the following: the heart rate is 82/min, the respiratory rate is 14/min, the temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F), and the blood pressure is 112/82 mm Hg. Inspection of the pharynx is depicted in the picture. Palpation of the neck reveals posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. The membrane does not bleed upon scraping. What is the most specific finding for detecting the syndrome described in the vignette?
- A. > 10% atypical lymphocytes
- B. Positive rapid strep test
- C. Growth in Loffler’s medium
- D. Increased transaminase levels
- E. Positive monospot test (Correct Answer)
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***Positive monospot test***
- The patient's symptoms (sore throat, fatigue, posterior cervical lymphadenopathy, pharyngitis with exudates, age) are highly suggestive of **infectious mononucleosis**, which is caused by the **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**.
- A **positive monospot test**, which detects **heterophile antibodies**, is the most specific and widely used rapid diagnostic test for infectious mononucleosis.
* > 10% atypical lymphocytes*
- While **atypical lymphocytes** are characteristic of infectious mononucleosis, they are not exclusive to EBV infection and can be seen in other viral infections (e.g., CMV, HIV). Therefore, this finding is less specific than a positive monospot test.
- A definitive diagnosis usually requires a combination of clinical symptoms and specific serological tests like the **monospot test** or **EBV-specific antibodies**.
*Positive rapid strep test*
- A rapid strep test detects **Group A Streptococcus (GAS)**. While bacterial pharyngitis can present with a sore throat, the accompanying fatigue and posterior cervical lymphadenopathy make streptococcal pharyngitis less likely as the primary diagnosis.
- The rapid strep test would be negative in infectious mononucleosis, and therefore, a positive result would rule out mononucleosis as the sole cause.
*Growth in Loffler’s medium*
- **Loffler's medium** is used to culture **Corynebacterium diphtheriae**, the causative agent of diphtheria. Diphtheria presents with a severe sore throat and a tenacious gray membrane that **bleeds upon scraping**, unlike the description in the vignette.
- While it's a specific diagnostic test for diphtheria, the patient's presentation does not align with diphtheria, and this test would not be positive in infectious mononucleosis.
*Increased transaminase levels*
- **Increased transaminase levels** (AST, ALT) indicate liver involvement, which can occur in infectious mononucleosis due to **hepatitis**.
- While this is a common finding in many cases of mononucleosis (and supports the diagnosis), it is an indicator of organ involvement rather than a specific diagnostic test for the presence of the virus or its unique immunological response (like the monospot test).
EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG Question 10: A 20-year-old man presents to the emergency department with complaints of severe malaise, fevers, and sore throat for the past 7 days. He also has had episodes of nausea and vomiting during this period. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. There is no family history of liver disease. His blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, temperature is 38.3℃ (100.9℉), pulse is 102/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. On physical examination, he appears ill with bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy. His tonsils are erythematous and enlarged. There is no jaundice and he is mildly dehydrated. Abdominal examination demonstrates splenomegaly. The laboratory findings are shown below:
Hemoglobin 15 g/dL
Platelet count 95,000/mm³
Leukocytes 13,500/mm³
Neutrophils 50%
Atypical lymphocytes 34%
AST 232 U/L
ALT 312 U/L
ALP 120 U/L
GGT 35 U/L
Total bilirubin 1.2 mg/dL
Direct bilirubin 0.2 mg/dL
PT 12 seconds
The serologic test for hepatitis A, B, and C, CMV, and leptospirosis are negative. Serology for both serum IgM and IgG antibodies for EBV capsid antigen are positive, but the heterophile antibody test is negative. What is the most likely reason for the negative heterophile test?
- A. Concurrent viral hepatitis A infection
- B. CMV infection
- C. Low specificity
- D. Age of the patient
- E. False negative (Correct Answer)
EBV-associated malignancies Explanation: ***False negative***
- The **heterophile antibody test (Monospot test)** has a sensitivity of only **70-92%** for infectious mononucleosis, meaning false negatives occur in **10-25% of cases**.
- Heterophile antibodies typically appear **1-2 weeks after symptom onset**, and this patient has been symptomatic for only **7 days**, making it likely the heterophile antibodies have not yet developed to detectable levels.
- The positive **EBV IgM and IgG for capsid antigen** confirm acute EBV infection, so the negative heterophile test is a **false negative** result.
- False negatives are especially common **early in the course of illness**.
*Age of the patient*
- Age 20 years is actually within the **peak sensitivity range** for heterophile antibody testing (adolescents and young adults 15-25 years have 85-90% sensitivity).
- The heterophile test is **less sensitive in young children (<12 years)**, with sensitivity as low as 30-50% in children under 4 years.
- This patient's age would not explain the negative result.
*Concurrent viral hepatitis A infection*
- Serologic testing for **hepatitis A is negative**, ruling out co-infection.
- Hepatitis A co-infection would not cause a false negative heterophile test.
*CMV infection*
- Serologic testing for **CMV is negative**, and the patient has **positive EBV-specific serology**.
- While CMV can cause heterophile-negative mononucleosis syndrome, the confirmed EBV infection makes this irrelevant.
*Low specificity*
- The heterophile antibody test has **high specificity (95-100%)** for infectious mononucleosis, meaning false positives are rare.
- The limitation of the test is its **low sensitivity**, not low specificity, which explains false negatives but doesn't directly answer why this specific test is negative.
More EBV-associated malignancies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.