Skin microbiome US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Skin microbiome. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
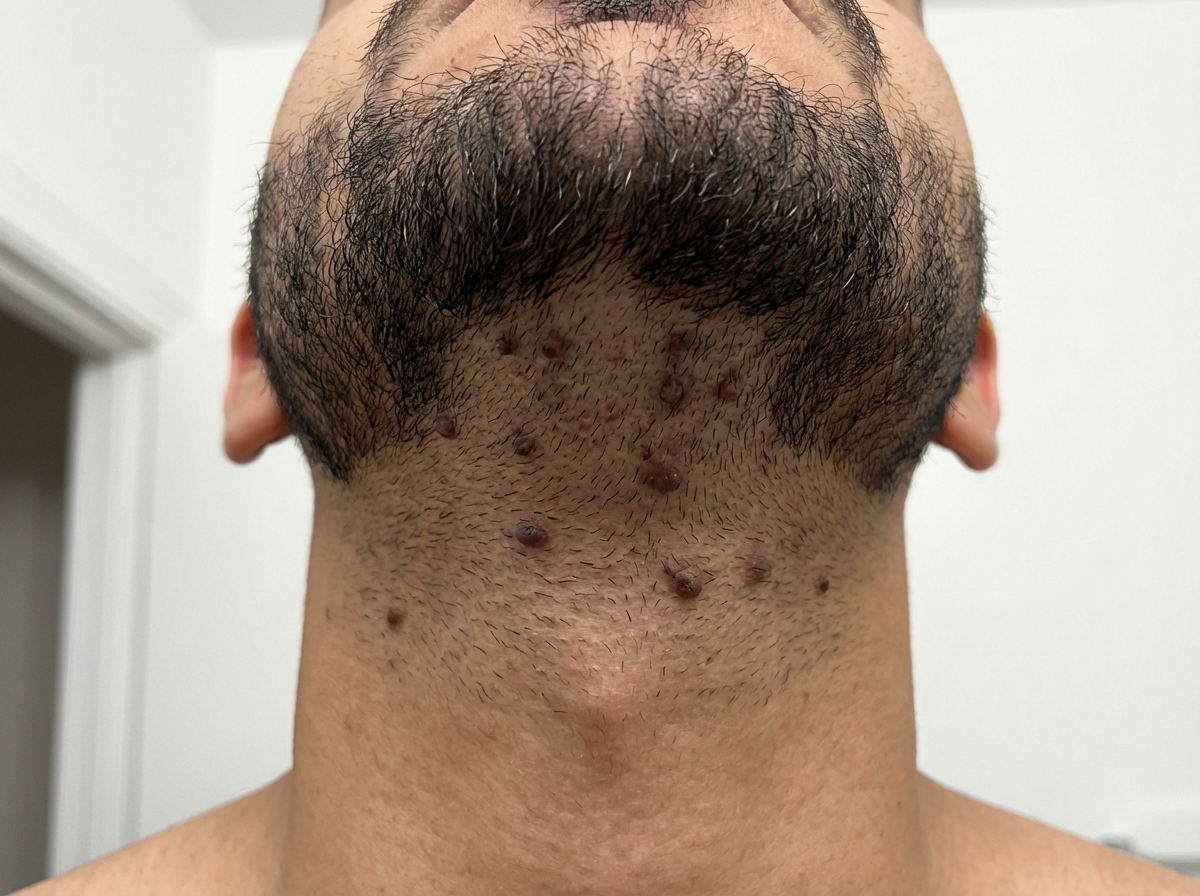
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 1: A 21-year-old man comes to the physician because of painful, firm, dark bumps on his neck and jawline. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. His brother had a similar rash. A photograph of the rash is shown. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's condition?
- A. Trichophyton infection of the superficial hair follicle
- B. Interfollicular penetration of the skin by distal end of hair (Correct Answer)
- C. Bacterial infection of the superficial or deep hair follicle
- D. Follicular obstruction with subsequent duct rupture
- E. Cutibacterium acnes colonization of the pilosebaceous unit
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Interfollicular penetration of the skin by distal end of hair***
- The description of painful, firm, dark bumps on the neck and jawline, particularly in a young man, is classic for **pseudofolliculitis barbae**, often caused by the distal end of hair penetrating the skin after shaving.
- This condition is common in individuals with **curly hair** where shaved hairs re-enter the skin, causing a foreign body inflammatory reaction.
*Trichophyton infection of the superficial hair follicle*
- This would typically present as **tinea barbae** or **tinea capitis**, characterized by scaling, erythema, and pustules, often with hair breakage, not firm dark bumps from embedded hairs.
- While fungal infections can cause folliculitis, the clinical presentation and family history of improvement with erythromycin (an antibacterial) make this less likely.
*Bacterial infection of the superficial or deep hair follicle*
- **Bacterial folliculitis** (e.g., *Staphylococcus aureus*) usually presents as pustules, papules, and sometimes carbuncles, which are typically red, inflamed, and often pus-filled.
- The family history of improvement with erythromycin might suggest a bacterial component, but the primary mechanism described (firm, dark bumps) points away from primary bacterial infection and more towards a physical cause like pseudofolliculitis barbae, which can then become secondarily infected.
*Follicular obstruction with subsequent duct rupture*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **acne vulgaris** (comedones, papules, pustules, cysts) or **hidradenitis suppurativa** (deep-seated nodules, abscesses affecting intertriginous areas), which are different in appearance and location from the described lesions.
- While related to follicular issues, the specific description of "dark bumps" and the context of shaving make embedded hairs more likely than a primary obstruction and rupture.
*Cutibacterium acnes colonization of the pilosebaceous unit*
- This is the primary bacterial contributor to **acne vulgaris**, leading to comedones, inflamed papules, and pustules, often affecting the face, chest, and back.
- Although the jawline is a common area for acne, the "firm, dark bumps" are less typical of classic acne and more consistent with ingrown hairs.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 2: A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a complaint of intense pain in his right foot for the past month, along with fever and chills. He denies any traumatic injury to his foot in recent memory. He has a medical history of poorly-controlled type II diabetes and is a former smoker with extensive peripheral vascular disease. On physical exam, the area of his right foot around the hallux is swollen, erythematous, tender to light palpation, and reveals exposed bone. Labs are notable for elevated C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The physician obtains a biopsy for culture. What is the most likely causative organism for this patient’s condition?
- A. Pasteurella multocida
- B. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- C. Staphylococcus aureus (Correct Answer)
- D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- E. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Staphylococcus aureus***
- This patient presents with signs of **osteomyelitis** (foot pain, fever, chills, exposed bone, elevated inflammatory markers) in the setting of **diabetes** and **peripheral vascular disease (PVD)**.
- **_S. aureus_** is the most common cause of osteomyelitis, especially in patients with diabetes and PVD where skin integrity is compromised or there's hematogenous spread.
*Pasteurella multocida*
- **_Pasteurella multocida_** is typically associated with infections following **animal bites**, specifically cat or dog bites.
- There is no history of animal bite in this patient, making this organism less likely.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
- **_Mycobacterium tuberculosis_** can cause osteomyelitis, known as **Pott's disease** when affecting the spine, but it's typically a **chronic, granulomatous infection** often without acute purulence or the rapid progression seen here.
- It usually occurs in patients with active tuberculosis elsewhere or those from endemic regions, and the clinical presentation is not as acute as described.
*Pseudomonas aeruginosa*
- **_Pseudomonas aeruginosa_** is a common cause of osteomyelitis in specific contexts, such as **puncture wounds** through footwear (especially in diabetic patients) or in **IV drug users**.
- While possible in diabetic foot infections, **_S. aureus_** remains overwhelmingly more common given the general presentation of osteomyelitis without a specific puncture wound history.
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae*
- **_Neisseria gonorrhoeae_** causes **gonococcal arthritis** or disseminated gonococcal infection, which can affect joints.
- However, it typically presents with migratory polyarthralgia, tenosynovitis, or dermatitis, rather than localized acute osteomyelitis with exposed bone in the foot as described.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 3: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-week history of fatigue and low-grade fever. She has no history of serious illness except for a bicuspid aortic valve, diagnosed 10 years ago. She does not use illicit drugs. Her temperature is 37.7°C (99.9°F). Physical examination shows petechiae under the fingernails and multiple tender, red nodules on the fingers. A new grade 2/6 diastolic murmur is heard at the right second intercostal space. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Staphylococcus epidermidis
- B. Streptococcus pyogenes
- C. Streptococcus sanguinis (Correct Answer)
- D. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- E. Enterococcus faecalis
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Streptococcus sanguinis***
- The patient's presentation with **fatigue, low-grade fever, petechiae, tender nodules (Osler nodes)**, and a **new diastolic murmur** in a patient with a **bicuspid aortic valve** is highly suggestive of **infective endocarditis**.
- **Streptococcus sanguinis** (and other viridans streptococci) are common causes of subacute bacterial endocarditis, often associated with **oral flora** and pre-existing valvular heart disease.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- This organism is a common cause of **prosthetic valve endocarditis** and **nosocomial infections** but is less likely to cause endocarditis in a native valve without a history of recent surgery or intravenous lines.
- While it can cause endocarditis, the clinical features here, especially the lack of recent medical interventions, point away from *S. epidermidis* as the primary cause.
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
- **Streptococcus pyogenes** is primarily known for causing **strep throat, scarlet fever, and rheumatic fever**, which can lead to rheumatic heart disease but rarely causes acute or subacute infective endocarditis directly.
- It typically causes more acute and severe infections, which doesn't align with the 6-week history of low-grade fever and fatigue.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- **Streptococcus pneumoniae** is a common cause of **pneumonia, meningitis, and otitis media** but is an uncommon cause of infective endocarditis, accounting for a very small percentage of cases.
- Endocarditis due to *S. pneumoniae* tends to be **acute and fulminant**, often associated with severe systemic illness, which is not fully consistent with the subacute presentation here.
*Enterococcus faecalis*
- **Enterococcus faecalis** is a common cause of **nosocomial urinary tract infections** and can cause endocarditis, especially in older patients or those with gastrointestinal or genitourinary procedures.
- While it's a possibility for endocarditis, the oral flora association with viridans streptococci (like *S. sanguinis*) in the context of a bicuspid aortic valve makes it a more direct fit.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old woman undergoes an abdominal hysterectomy. She develops pain and discharge at the incision site on the fourth postoperative day. The past medical history is significant for diabetes of 12 years duration, which is well-controlled on insulin. Pus from the incision site is sent for culture on MacConkey agar, which shows white-colorless colonies. On blood agar, the colonies were green. Biochemical tests reveal an oxidase-positive organism. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
- A. Staphylococcus aureus
- B. Enterococcus faecalis
- C. Streptococcus pyogenes
- D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Correct Answer)
- E. Staphylococcus epidermidis
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Pseudomonas aeruginosa***
- The combination of **white, colorless colonies on MacConkey agar** (indicating a non-lactose fermenter), **green colonies on blood agar** (due to pigment production), and a **positive oxidase test** is highly characteristic of *Pseudomonas aeruginosa*.
- This organism is a common cause of **nosocomial infections**, particularly in immunocompromised patients (like those with diabetes) and in postoperative wound infections.
*Staphylococcus aureus*
- This bacterium would typically produce **golden-yellow colonies** on blood agar and **no growth on MacConkey agar**.
- It is **oxidase-negative** and a common cause of surgical site infections, but its colonial morphology and biochemical tests do not match the description.
*Enterococcus faecalis*
- This organism is a **Gram-positive coccus** that would not grow well on MacConkey agar and would not produce green colonies on blood agar or be oxidase-positive.
- It is a common cause of urinary tract and wound infections, especially in hospitalized patients.
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
- This is a **beta-hemolytic Streptococcus** that typically produces small, clear colonies with a zone of complete hemolysis on blood agar and would not grow on MacConkey agar.
- It is also **oxidase-negative**, making it inconsistent with the findings.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- This organism forms **white colonies** on blood agar and would not grow on MacConkey agar or produce green pigment.
- It is **coagulase-negative** and **oxidase-negative**, and while it can cause surgical site infections, its colonial characteristics differ.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old female recovering from a total shoulder arthroplasty completed 6 days ago presents complaining of joint pain in her repaired shoulder. Temperature is 39 degrees Celsius. Physical examination demonstrates erythema and significant tenderness around the incision site. Wound cultures reveal Gram-positive cocci that are resistant to nafcillin. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Streptococcus pyogenes
- B. Escherichia coli
- C. Streptococcus viridans
- D. Staphylococcus epidermidis
- E. Staphylococcus aureus (Correct Answer)
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Staphylococcus aureus***
- The combination of **post-surgical infection**, **erythema**, and fever with **Gram-positive cocci** that are **nafcillin-resistant** is highly indicative of **Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)**.
- *S. aureus* is a common cause of **surgical site infections**, and its resistance to nafcillin implies it is MRSA, a significant clinical concern for its difficulty in treatment.
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
- While *S. pyogenes* is a Gram-positive coccus that can cause skin and soft tissue infections, it is typically **susceptible to penicillin** and related antibiotics like nafcillin, unlike the organism described.
- It is more commonly associated with **streptococcal pharyngitis** or **cellulitis**, and while it can cause severe disease, its resistance profile doesn't match the clinical picture.
*Escherichia coli*
- *E. coli* is a **Gram-negative rod**, not a Gram-positive coccus.
- It is a common cause of **urinary tract infections** and **gastrointestinal infections**, making it an unlikely pathogen for a post-surgical joint infection unless contaminated from a visceral source.
*Streptococcus viridans*
- **Viridans streptococci** are Gram-positive cocci but are typically associated with **endocarditis** or dental infections, especially after poor dental hygiene or procedures.
- They are usually **susceptible to penicillin** and do not typically exhibit nafcillin resistance as the primary feature in a post-arthroplasty infection.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- *S. epidermidis* is a **coagulase-negative Staphylococcus** known for forming **biofilms on prosthetic devices**, leading to chronic, low-grade infections.
- While it can be nafcillin-resistant, the **acute presentation** with fever and significant inflammation suggests a more virulent pathogen like *S. aureus*, as *S. epidermidis* infections are typically indolent.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 6: Blood cultures are sent to the laboratory. Intravenous antibiotic therapy is started. Transesophageal echocardiography shows a large, oscillating vegetation attached to the tricuspid valve. There are multiple small vegetations attached to tips of the tricuspid valve leaflets. There is moderate tricuspid regurgitation. The left side of the heart and the ejection fraction are normal. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism of this patient's condition?
- A. Streptococcus sanguinis
- B. Staphylococcus aureus (Correct Answer)
- C. Enterococcus faecalis
- D. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- E. Staphylococcus epidermidis
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Staphylococcus aureus***
- **_Staphylococcus aureus_** is the most common cause of **acute infective endocarditis**, particularly in intravenous drug users, which often affects the **tricuspid valve**.
- The presence of large, oscillating vegetations and **multiple small vegetations** on the tricuspid valve strongly suggests an aggressive infection, typical of _S. aureus_.
*Streptococcus sanguinis*
- _Streptococcus sanguinis_ is a common cause of **subacute infective endocarditis** in patients with pre-existing valvular disease but rarely causes acute, aggressive right-sided endocarditis.
- It's typically associated with **dental procedures** and usually affects the left side of the heart.
*Enterococcus faecalis*
- _Enterococcus faecalis_ can cause endocarditis, often associated with **genitourinary or gastrointestinal procedures**, and typically affects older men.
- While it can cause virulent endocarditis, it is less commonly associated with acute right-sided disease in this demographic compared to _S. aureus_.
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae*
- **_Neisseria gonorrhoeae_** is a rare cause of endocarditis, usually seen in younger, sexually active individuals, and often involves the aortic valve.
- While it can be acute, it is an extremely uncommon cause of **tricuspid valve endocarditis**.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- **_Staphylococcus epidermidis_** is primarily associated with **prosthetic valve endocarditis** or foreign bodies, often presenting as a subacute infection.
- It rarely causes natural valve endocarditis, especially acute right-sided disease in this context.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old female presents to her primary care physician because she is concerned about lighter colored patches on her skin. She recently went sunbathing and noticed that these areas also did not tan. Her doctor explains that she has a fungal infection of the skin that damages melanocytes by producing acids. She is prescribed selenium sulfide and told to follow-up in one month. Which of the following describes the appearance of the most likely infectious organism under microscopy?
- A. Broad based budding yeast
- B. "Captain's wheel" yeast
- C. Germ tube forming fungus
- D. Branching septate hyphae
- E. "Spaghetti and meatballs" fungus (Correct Answer)
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***"Spaghetti and meatballs" fungus***
- The "spaghetti and meatballs" appearance on microscopy, referring to a mixture of short, septate hyphae and spherical yeast forms, is characteristic of **Malassezia globosa** or other *Malassezia* species, which cause **tinea versicolor**.
- **Tinea versicolor** presents as hypopigmented patches, especially after sun exposure, because the fungus produces **azelaic acid** that inhibits melanin synthesis.
*Broad based budding yeast*
- This description is characteristic of **Blastomyces dermatitidis**, which causes **blastomycosis**, a deep fungal infection.
- Blastomycosis typically manifests as pulmonary disease or disseminated lesions, not superficial hypopigmented skin patches.
*"Captain's wheel" yeast*
- The "captain's wheel" or multi-budding yeast appearance is characteristic of **Paracoccidioides brasiliensis**, the causative agent of **paracoccidioidomycosis**.
- This is a systemic mycosis primarily affecting the lungs and mucocutaneous areas, not a superficial skin infection like tinea versicolor.
*Germ tube forming fungus*
- The formation of **germ tubes** when incubated in serum at 37°C is a characteristic feature used to identify **Candida albicans**.
- *Candida* most commonly causes mucocutaneous candidiasis (e.g., thrush, vaginitis) or invasive infections, not hypopigmented skin patches that fail to tan.
*Branching septate hyphae*
- **Branching septate hyphae** are a general microscopic feature seen in many filamentous fungi, including dermatophytes like *Trichophyton* and *Microsporum*, which cause **tinea corporis** or **tinea pedis**.
- While dermatophytes cause skin infections, they typically result in erythematous, scaly, and often pruritic lesions and do not usually present as hypopigmented patches that fail to tan due to melanin inhibition, as seen in tinea versicolor.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 8: A 36-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of malaise and a painful, pruritic rash on his lower back and thighs. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F). Physical examination shows the findings in the photograph. Skin scrapings from the thigh grow neutral colonies on MacConkey agar. The colony-producing bacteria are oxidase-positive. Which of the following is the greatest risk factor for the patient's condition?
- A. Swimming in pool (Correct Answer)
- B. Skin-to-skin contact
- C. Rose pruning
- D. Unprotected sexual intercourse
- E. Outdoor camping
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Swimming in pool***
- The description of a **painful, pruritic rash** on the lower back and thighs, growing **oxidase-positive, neutral colonies on MacConkey agar**, is highly suggestive of **hot tub folliculitis** caused by *Pseudomonas aeruginosa*.
- *Pseudomonas aeruginosa* thrives in **warm, moist environments** like inadequately chlorinated hot tubs and swimming pools, making swimming a major risk factor.
*Skin-to-skin contact*
- While various skin infections can spread via skin-to-skin contact, *Pseudomonas aeruginosa* folliculitis is predominantly linked to **water exposure** rather than direct person-to-person spread.
- Infections like impetigo or herpes simplex virus are more typically associated with this mode of transmission.
*Rose pruning*
- **Rose gardener's disease** (sporotrichosis) is caused by the fungus *Sporothrix schenckii*, which is introduced through skin trauma, often from handling thorny plants like roses.
- The clinical presentation and causative organism are distinct from the described bacterial folliculitis.
*Unprotected sexual intercourse*
- This is a risk factor for **sexually transmitted infections (STIs)**, which typically present with genital lesions, urethritis, cervicitis, or systemic symptoms, rather than generalized folliculitis on the back and thighs.
- Examples include syphilis, gonorrhea, or herpes simplex virus.
*Outdoor camping*
- Outdoor camping can increase exposure to various pathogens, such as those causing **Lyme disease** (from ticks) or **leptospirosis** (from contaminated water/soil).
- These conditions have distinct clinical presentations and are not characterized by *Pseudomonas aeruginosa* folliculitis from water exposure.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 9: A 24-year-old man presents with low-grade fever and shortness of breath for the last 3 weeks. Past medical history is significant for severe mitral regurgitation status post mitral valve replacement five years ago. His temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F) and respiratory rate is 18/min. Physical examination reveals vertical hemorrhages under his nails, multiple painless erythematous lesions on his palms, and two tender, raised nodules on his fingers. Cardiac auscultation reveals a new-onset 2/6 holosystolic murmur loudest at the apex with the patient in the left lateral decubitus position. A transesophageal echocardiogram reveals vegetations on the prosthetic valve. Blood cultures reveal catalase-positive, gram-positive cocci. Which of the following characteristics is associated with the organism most likely responsible for this patient’s condition?
- A. Coagulase positive
- B. DNAse positive
- C. Hemolysis
- D. Novobiocin sensitive (Correct Answer)
- E. Optochin sensitive
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Novobiocin sensitive***
- The patient has **prosthetic valve endocarditis** caused by a **catalase-positive, gram-positive coccus**, which is most likely **_Staphylococcus epidermidis_** due to its association with foreign bodies and prosthetic devices.
- _Staphylococcus epidermidis_ is a **coagulase-negative staphylococcus** that is **novobiocin sensitive**, helping to differentiate it from other coagulase-negative staphylococci like **_Staphylococcus saprophyticus_** (novobiocin resistant).
- Although this is late prosthetic valve endocarditis (5 years post-surgery), _S. epidermidis_ remains a common pathogen due to biofilm formation on prosthetic materials.
*Coagulase positive*
- **Coagulase-positive** gram-positive cocci, such as **_Staphylococcus aureus_**, are a common cause of endocarditis, especially in intravenous drug users and can also cause prosthetic valve endocarditis.
- However, the correct answer requires identifying the characteristic that differentiates the most likely organism, and **coagulase-negative** staphylococci like _S. epidermidis_ are more characteristically associated with prosthetic device infections due to their biofilm-forming capabilities.
- A positive coagulase test differentiates _S. aureus_ from coagulase-negative staphylococci.
*DNAse positive*
- **DNAse positivity** is characteristic of **_Staphylococcus aureus_** and group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (_Streptococcus pyogenes_).
- While _S. aureus_ can cause prosthetic valve endocarditis, the question asks for the characteristic most associated with the likely organism, which in the context of prosthetic devices is typically **_S. epidermidis_** (DNAse negative).
*Hemolysis*
- **Hemolysis patterns** are primarily used to differentiate **streptococcal species**, not staphylococci. For example, **beta-hemolytic streptococci** cause complete hemolysis.
- While some staphylococci can show hemolytic activity, it is not a primary characteristic used to differentiate between the most likely staphylococcal causes of prosthetic valve endocarditis.
*Optochin sensitive*
- **Optochin sensitivity** is a key characteristic used to identify **_Streptococcus pneumoniae_**.
- _S. pneumoniae_ is **catalase-negative**, while the described organism is **catalase-positive**, ruling out _S. pneumoniae_ as the causative agent.
Skin microbiome US Medical PG Question 10: A hospital implements a bundle to reduce catheter-associated bloodstream infections. Components include: chlorhexidine bathing, antibiotic-impregnated catheters, antiseptic catheter site dressings, and daily line necessity assessment. After implementation, bloodstream infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci decrease by 60%, but Candida bloodstream infections increase by 40%. Evaluate the microbiological mechanisms underlying these divergent outcomes and synthesize an optimal prevention strategy.
- A. Antibiotic-impregnated catheters select for resistant Candida; use non-antibiotic catheters
- B. The bundle successfully reduced bacterial infections, revealing underlying fungal infections; add antifungal prophylaxis
- C. Multiple interventions disrupted skin flora creating ecological niche for Candida; modify bundle to preserve some commensal bacteria while maintaining antisepsis (Correct Answer)
- D. Chlorhexidine bathing eliminates bacterial skin flora but promotes fungal colonization; discontinue chlorhexidine
- E. Candida increase represents surveillance bias from increased culturing; no change needed
Skin microbiome Explanation: ***Multiple interventions disrupted skin flora creating ecological niche for Candida; modify bundle to preserve some commensal bacteria while maintaining antisepsis***
- Aggressive use of **chlorhexidine bathing** and **antibiotic-impregnated catheters** eliminates commensal bacterial flora that provide **colonization resistance** against opportunistic fungi.
- The reduction in **Coagulase-negative staphylococci** creates an available **ecological niche**, allowing *Candida* species to proliferate and colonize the catheter site more effectively.
*Antibiotic-impregnated catheters select for resistant Candida; use non-antibiotic catheters*
- While **antibiotic-impregnated catheters** reduce bacterial biofilm, they do not directly "select" for resistance in fungi, as antibiotics have no biochemical target in *Candida*.
- Removing them entirely may lead to a rebound in **staphylococcal infections**, failing to address the need for a balanced antiseptic strategy.
*The bundle successfully reduced bacterial infections, revealing underlying fungal infections; add antifungal prophylaxis*
- Adding **antifungal prophylaxis** as a routine measures increases the risk of developing **drug-resistant fungal strains** like *Candida auris*.
- This approach ignores the ecological disruption caused by the bundle and instead layers on more **antimicrobial pressure**, which is rarely a sustainable prevention strategy.
*Chlorhexidine bathing eliminates bacterial skin flora but promotes fungal colonization; discontinue chlorhexidine*
- Discontinuing **chlorhexidine bathing** would likely reverse the 60% reduction in **coagulase-negative staphylococcal** infections, which are a major source of morbidity.
- The goal should be optimization (e.g., targeted use or modified frequency) rather than total discontinuation of an effective **infection control** tool.
*Candida increase represents surveillance bias from increased culturing; no change needed*
- A 40% increase in **Candida bloodstream infections** is a significant clinical shift that requires a root-cause analysis rather than dismissal as **surveillance bias**.
- "No change needed" is incorrect because the bundle has created a new, clinically significant risk for **iatrogenic candidemia**.
More Skin microbiome US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.