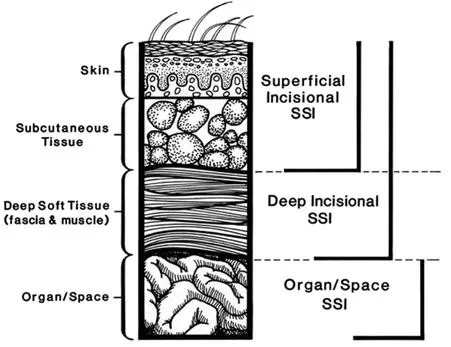
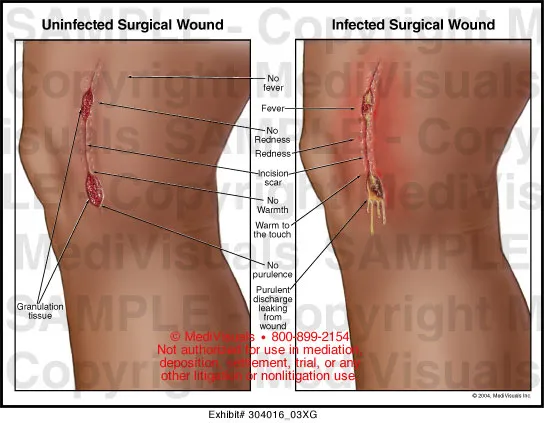
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Surgical site infections. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 1: The surgical equipment used during a craniectomy is sterilized using pressurized steam at 121°C for 15 minutes. Reuse of these instruments can cause transmission of which of the following pathogens?
- A. Non-enveloped viruses
- B. Sporulating bacteria
- C. Prions (Correct Answer)
- D. Enveloped viruses
- E. Yeasts
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Prions***
- Prions are **abnormally folded proteins** that are highly resistant to standard sterilization methods like steam autoclaving at 121°C, making them a risk for transmission through reused surgical instruments.
- They cause transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) like **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease**, where even trace amounts can be highly infectious.
*Non-enveloped viruses*
- Non-enveloped viruses are generally **more resistant to heat and disinfectants** than enveloped viruses but are typically inactivated by recommended steam sterilization protocols.
- Standard autoclaving conditions are effective in destroying most non-enveloped viruses.
*Sporulating bacteria*
- **Bacterial spores**, such as those from *Clostridium* or *Bacillus*, are known for their high resistance to heat and chemicals, but are usually **inactivated by steam sterilization at 121°C** for 15 minutes.
- This method is specifically designed to kill bacterial spores effectively.
*Enveloped viruses*
- Enveloped viruses are the **least resistant to heat and chemical disinfectants** due to their lipid envelope.
- They are readily **inactivated by standard steam sterilization** at 121°C.
*Yeasts*
- **Yeasts** are eukaryotic microorganisms that are typically **susceptible to heat sterilization**.
- They are effectively killed by typical steam autoclaving conditions used for surgical instruments.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 2: A 47-year-old man presents to the emergency department with jaundice and extreme fatigue for the past 4 days. He also noticed that his stool is very pale and urine is dark. Past medical history is unremarkable. The review of systems is significant for a 23 kg (50 lb) weight loss over the last 3 months which he says is due to decreased appetite. He is afebrile and the vital signs are within normal limits. A contrast computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen reveals a mass in the pancreatic head. A blood test for carbohydrate antigen (CA19-9) is positive. The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) and undergoes surgical decompression of the biliary tract. He is placed on total parenteral nutrition (TPN). On day 4 after admission, his intravenous access site is found to be erythematous and edematous. Which of the following microorganisms is most likely responsible for this patient’s intravenous (IV) site infection?
- A. Candida parapsilosis (Correct Answer)
- B. E. coli
- C. Hepatitis B virus
- D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- E. Malassezia furfur
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Candida parapsilosis***
- This yeast is a common cause of **catheter-related bloodstream infections** in patients receiving **total parenteral nutrition (TPN)**, as it can readily grow on lipid emulsions.
- The patient's presentation with an erythematous and edematous intravenous access site, coupled with a history of TPN, strongly points towards a fungal infection, with *C. parapsilosis* being a primary suspect due to its affinity for TPN.
*E. coli*
- While *E. coli* is a common cause of **urinary tract infections** and can cause **bloodstream infections**, it is not a typical cause of IV site infections specifically associated with TPN.
- Its presence at an IV site would usually indicate a more generalized sepsis or contamination, rather than the specific affinity *C. parapsilosis* has for TPN lines.
*Hepatitis B virus*
- **Hepatitis B virus** causes **viral hepatitis** and liver damage, but it does not directly cause localized IV site infections with erythema and edema.
- It is typically spread through blood and body fluids and its clinical manifestations are systemic, primarily involving the liver, rather than local skin signs at an IV access site.
*Pseudomonas aeruginosa*
- **Pseudomonas aeruginosa** is a common opportunistic pathogen, particularly in **immunocompromised patients** and those with medical devices, but it is typically associated with infections in burn wounds, cystic fibrosis, or ventilator-associated pneumonia.
- While it can cause catheter-related infections, it is not as uniquely linked to TPN-associated IV site infections as *Candida parapsilosis*.
*Malassezia furfur*
- *Malassezia furfur* is known to cause **catheter-related infections** in patients receiving **lipid emulsions** via central lines, similar to *C. parapsilosis*.
- However, *C. parapsilosis* is statistically a more common cause of TPN-associated fungemia and IV site infections than *M. furfur*.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 3: A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a complaint of intense pain in his right foot for the past month, along with fever and chills. He denies any traumatic injury to his foot in recent memory. He has a medical history of poorly-controlled type II diabetes and is a former smoker with extensive peripheral vascular disease. On physical exam, the area of his right foot around the hallux is swollen, erythematous, tender to light palpation, and reveals exposed bone. Labs are notable for elevated C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The physician obtains a biopsy for culture. What is the most likely causative organism for this patient’s condition?
- A. Pasteurella multocida
- B. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- C. Staphylococcus aureus (Correct Answer)
- D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- E. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Staphylococcus aureus***
- This patient presents with signs of **osteomyelitis** (foot pain, fever, chills, exposed bone, elevated inflammatory markers) in the setting of **diabetes** and **peripheral vascular disease (PVD)**.
- **_S. aureus_** is the most common cause of osteomyelitis, especially in patients with diabetes and PVD where skin integrity is compromised or there's hematogenous spread.
*Pasteurella multocida*
- **_Pasteurella multocida_** is typically associated with infections following **animal bites**, specifically cat or dog bites.
- There is no history of animal bite in this patient, making this organism less likely.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
- **_Mycobacterium tuberculosis_** can cause osteomyelitis, known as **Pott's disease** when affecting the spine, but it's typically a **chronic, granulomatous infection** often without acute purulence or the rapid progression seen here.
- It usually occurs in patients with active tuberculosis elsewhere or those from endemic regions, and the clinical presentation is not as acute as described.
*Pseudomonas aeruginosa*
- **_Pseudomonas aeruginosa_** is a common cause of osteomyelitis in specific contexts, such as **puncture wounds** through footwear (especially in diabetic patients) or in **IV drug users**.
- While possible in diabetic foot infections, **_S. aureus_** remains overwhelmingly more common given the general presentation of osteomyelitis without a specific puncture wound history.
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae*
- **_Neisseria gonorrhoeae_** causes **gonococcal arthritis** or disseminated gonococcal infection, which can affect joints.
- However, it typically presents with migratory polyarthralgia, tenosynovitis, or dermatitis, rather than localized acute osteomyelitis with exposed bone in the foot as described.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old man presents with low-grade fever and malaise for the last 4 months. He also says he has lost 9 kg (20 lb) during this period and suffers from extreme fatigue. Past medical history is significant for a mitral valve replacement 5 years ago. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F), respirations are 22/min, pulse is 102/min, and blood pressure is 138/78 mm Hg. On physical examination, there is a new onset 2/6 holosystolic murmur loudest in the apical area of the precordium. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
- A. Enterococcus (Correct Answer)
- B. Candida albicans
- C. Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp.
- D. Escherichia coli
- E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Enterococcus***
- This patient has **late prosthetic valve endocarditis (PVE)**, occurring **5 years after mitral valve replacement**.
- Late PVE (>1 year post-surgery) is most commonly caused by **viridans streptococci** and ***Staphylococcus aureus***, followed by **Enterococcus species**.
- Among the given options, ***Enterococcus*** is the most common cause, particularly in **elderly patients**.
- The **subacute presentation** with **4 months of low-grade fever, malaise, weight loss**, and **new-onset murmur** is consistent with enterococcal endocarditis.
- Enterococcus is a common cause of healthcare-associated endocarditis and has increased prevalence in patients with prosthetic valves.
*Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp.*
- Coagulase-negative staphylococci (e.g., *S. epidermidis*) are the **most common cause of early PVE** (within the first year after surgery).
- At **5 years post-surgery**, this represents **late PVE**, where coagulase-negative staph is much less common than streptococci, *S. aureus*, and enterococci.
- While it can occur in late PVE, it is not the most likely organism in this timeframe.
*Escherichia coli*
- *E. coli* is an uncommon cause of endocarditis, typically associated with underlying gastrointestinal or urinary tract sources.
- It generally presents **acutely** rather than with the subacute 4-month course seen here.
- Not a typical cause of prosthetic valve endocarditis.
*Candida albicans*
- Fungal endocarditis is rare and typically seen in **immunocompromised patients, IV drug users**, or those with **prolonged ICU stays** with indwelling catheters.
- While *Candida* can cause PVE, it is much less common than bacterial causes in this clinical context.
*Pseudomonas aeruginosa*
- *Pseudomonas* endocarditis typically occurs in **IV drug users** and commonly affects the **tricuspid valve** (right-sided).
- Usually presents as an **acute infection** rather than the subacute presentation here.
- Not a common cause of late prosthetic valve endocarditis in non-IVDU patients.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old female recovering from a total shoulder arthroplasty completed 6 days ago presents complaining of joint pain in her repaired shoulder. Temperature is 39 degrees Celsius. Physical examination demonstrates erythema and significant tenderness around the incision site. Wound cultures reveal Gram-positive cocci that are resistant to nafcillin. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Streptococcus pyogenes
- B. Escherichia coli
- C. Streptococcus viridans
- D. Staphylococcus epidermidis
- E. Staphylococcus aureus (Correct Answer)
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Staphylococcus aureus***
- The combination of **post-surgical infection**, **erythema**, and fever with **Gram-positive cocci** that are **nafcillin-resistant** is highly indicative of **Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)**.
- *S. aureus* is a common cause of **surgical site infections**, and its resistance to nafcillin implies it is MRSA, a significant clinical concern for its difficulty in treatment.
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
- While *S. pyogenes* is a Gram-positive coccus that can cause skin and soft tissue infections, it is typically **susceptible to penicillin** and related antibiotics like nafcillin, unlike the organism described.
- It is more commonly associated with **streptococcal pharyngitis** or **cellulitis**, and while it can cause severe disease, its resistance profile doesn't match the clinical picture.
*Escherichia coli*
- *E. coli* is a **Gram-negative rod**, not a Gram-positive coccus.
- It is a common cause of **urinary tract infections** and **gastrointestinal infections**, making it an unlikely pathogen for a post-surgical joint infection unless contaminated from a visceral source.
*Streptococcus viridans*
- **Viridans streptococci** are Gram-positive cocci but are typically associated with **endocarditis** or dental infections, especially after poor dental hygiene or procedures.
- They are usually **susceptible to penicillin** and do not typically exhibit nafcillin resistance as the primary feature in a post-arthroplasty infection.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- *S. epidermidis* is a **coagulase-negative Staphylococcus** known for forming **biofilms on prosthetic devices**, leading to chronic, low-grade infections.
- While it can be nafcillin-resistant, the **acute presentation** with fever and significant inflammation suggests a more virulent pathogen like *S. aureus*, as *S. epidermidis* infections are typically indolent.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 7: A 43-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 40 minutes after falling off a 10-foot ladder. He has severe pain and swelling of his right ankle and is unable to walk. He did not lose consciousness after the fall. He has no nausea. He appears uncomfortable. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg. He is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. Examination shows multiple abrasions over both lower extremities. There is swelling and tenderness of the right ankle; range of motion is limited by pain. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An x-ray of the ankle shows an extra-articular calcaneal fracture. Intravenous analgesia is administered. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Short leg splint and orthopedic consultation
- B. Broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
- C. MRI of the right ankle
- D. Open reduction and internal fixation
- E. X-ray of the spine (Correct Answer)
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***X-ray of the spine***
- A **high-energy calcaneal fracture** (especially from a fall from height) is often associated with other injuries, particularly to the **spine**, due to axial loading.
- Approximately **10% of calcaneal fractures** are associated with **lumbar spine compression fractures**, making imaging of the spine an essential next step to rule out this potentially serious concomitant injury.
*Short leg splint and orthopedic consultation*
- While a **short leg splint** is appropriate for initial immobilization and pain control of the ankle fracture, and **orthopedic consultation** is necessary, these steps do not address the immediate need to exclude other critical injuries like spinal fractures in high-impact trauma.
- This option represents definitive management of the ankle rather than comprehensive early trauma assessment in a high-risk patient.
*Broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy*
- **Antibiotic therapy** is primarily indicated for **open fractures** to prevent infection, or in cases of significant soft tissue injury with high contamination risk; the provided information describes an extra-articular fracture with abrasions, but not explicitly an open fracture requiring immediate broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- The focus should first be on skeletal integrity elsewhere and definitive fracture management rather than presumptive infection prevention unless an open fracture is confirmed.
*MRI of the right ankle*
- While an **MRI** can provide detailed imaging of soft tissues, ligaments, and cartilage, and may be useful later for surgical planning or to assess subtle injuries, a plain **X-ray has already confirmed a calcaneal fracture**.
- The immediate priority after a high-energy trauma is to rule out other significant, potentially disabling or life-threatening bony injuries, particularly to the spine, rather than further detailed imaging of the already-identified ankle fracture.
*Open reduction and internal fixation*
- **Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF)** is a surgical procedure for definitive management of certain fractures; however, it is not the **immediate next step** in the emergency department for initial patient assessment following trauma.
- Before surgical intervention, a comprehensive assessment to rule out other injuries (especially spinal fractures) and to thoroughly plan the specific surgical approach is required.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 8: A 27-year-old previously healthy man presents to the clinic complaining of bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain. Sexual history reveals that he has sex with men and women and uses protection most of the time. He is febrile with all other vital signs within normal limits. Physical exam demonstrates tenderness to palpation of the right upper quadrant. Subsequent ultrasound shows a uniform cyst in the liver. In addition to draining the potential abscess and sending it for culture, appropriate medical therapy would involve which of the following?
- A. Supportive therapy
- B. Metronidazole and iodoquinol (Correct Answer)
- C. Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine
- D. Nifurtimox
- E. Amphotericin
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Metronidazole and iodoquinol***
- The patient's symptoms (bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, liver cyst) and risk factors (sexual activity with men and women) are highly suggestive of an **amoebic liver abscess** caused by *Entamoeba histolytica*.
- **Metronidazole** is the drug of choice for invasive amoebiasis (including liver abscess), while **iodoquinol** (or paromomycin) treats the intestinal luminal cysts to prevent recurrence and transmission.
*Supportive therapy*
- While supportive care is important for managing symptoms like fever and dehydration, it does not address the underlying **amoebic infection** or the liver abscess.
- Delaying specific antimicrobial therapy can lead to worsening of the abscess, potential rupture, and increased morbidity.
*Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine*
- This combination is the standard treatment for **toxoplasmosis**, a protozoal infection that typically affects immunocompromised individuals and can cause encephalitis or disseminated disease.
- It is not effective against *Entamoeba histolytica* and would not resolve an amoebic liver abscess.
*Nifurtimox*
- **Nifurtimox** is an antiparasitic medication specifically used to treat **Chagas disease**, caused by *Trypanosoma cruzi*.
- Chagas disease presents with different clinical manifestations and is transmitted by blood-sucking triatomine bugs, which does not fit the patient's presentation.
*Amphotericin*
- **Amphotericin B** is a broad-spectrum **antifungal agent** used to treat severe systemic fungal infections.
- It has no activity against *Entamoeba histolytica* or other protozoal infections causing similar symptoms.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 9: A surgical ICU has implemented multiple interventions over 18 months: chlorhexidine bathing, antibiotic stewardship, contact precautions for MRSA, and environmental cleaning protocols. Despite these efforts, MRSA surgical site infection rates remain unchanged at 8 per 1000 surgical procedures. Universal MRSA screening shows 15% of admitted patients are colonized. Evaluate the most effective evidence-based strategy to reduce MRSA SSI rates further.
- A. Targeted decolonization only for MRSA-positive patients with mupirocin and chlorhexidine
- B. Isolation of all surgical patients in private rooms until discharge
- C. Routine screening and decolonization of all healthcare workers
- D. Extended vancomycin prophylaxis for all surgical patients for 48 hours postoperatively
- E. Universal MRSA decolonization for all surgical patients regardless of screening results (Correct Answer)
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Universal MRSA decolonization for all surgical patients regardless of screening results***
- **Universal decolonization** has been proven more effective than screening-based strategies in high-risk settings like the ICU, significantly reducing **MRSA surgical site infections** and bloodstream infections.
- This approach is superior because it addresses **undetected carriers**, eliminates delays associated with waiting for lab cultures, and is often more **cost-effective** and easier to implement.
*Targeted decolonization only for MRSA-positive patients with mupirocin and chlorhexidine*
- While logical, **targeted decolonization** is less effective than the universal approach because it misses patients who may be **falsely negative** or colonized at levels below detection thresholds.
- Evidence from recent large-scale trials shows that **targeted strategies** do not reduce MRSA infection rates as drastically as treating the entire cohort at risk.
*Isolation of all surgical patients in private rooms until discharge*
- This strategy is **logistically impractical** and extremely expensive, focusing on **containment** rather than the active reduction of the patient's own bacterial load (colonization).
- Research indicates that **contact precautions** and isolation alone are less effective than decolonization protocols in preventing **autoinoculation** during surgery.
*Routine screening and decolonization of all healthcare workers*
- Screening of **healthcare workers (HCWs)** is not recommended as a routine practice; it is typically reserved for **outbreak investigations** where an epidemiological link is suspected.
- Constant recolonization from patients and the environment makes **HCW decolonization** an unsustainable and transient solution for reducing overall SSI rates.
*Extended vancomycin prophylaxis for all surgical patients for 48 hours postoperatively*
- **Extended antibiotic prophylaxis** beyond 24 hours provides no additional protection against SSIs and significantly increases the risk of **C. difficile** and antibiotic resistance.
- Proper surgical prophylaxis involves **timely administration** before the incision, not prolonged courses which violate **antibiotic stewardship** principles.
Surgical site infections US Medical PG Question 10: A 70-year-old man with prosthetic aortic valve develops fever and bacteremia 3 weeks after valve replacement. Blood cultures grow Enterococcus faecium resistant to ampicillin and vancomycin (VRE). Susceptibilities show sensitivity to linezolid and daptomycin. TEE shows a small vegetation on the prosthetic valve. Creatinine is 1.8 mg/dL (baseline 1.0). Evaluate the optimal treatment strategy considering the infection location and drug characteristics.
- A. Combination daptomycin and linezolid (Correct Answer)
- B. Linezolid plus gentamicin for synergy
- C. Daptomycin plus ampicillin despite resistance
- D. Daptomycin monotherapy with high dose (10-12 mg/kg)
- E. Linezolid monotherapy for 6 weeks
Surgical site infections Explanation: ***Combination daptomycin and linezolid***
- For **VRE prosthetic valve endocarditis (PVE)**, monotherapy often fails due to high bacterial inoculum and **biofilm formation**, necessitating synergistic combinations.
- **Daptomycin** provides bactericidal activity, while **linezolid** enhances biofilm penetration; this combination is a salvage strategy to prevent the emergence of **daptomycin resistance** during prolonged therapy.
*Linezolid plus gentamicin for synergy*
- **Gentamicin** synergy is typically reserved for **ampicillin-susceptible** enterococci and requires a cell-wall active agent to facilitate entry, which linezolid (protein synthesis inhibitor) does not provide.
- The patient has an elevated **creatinine (1.8 mg/dL)**, making the use of **nephrotoxic aminoglycosides** like gentamicin highly risky and suboptimal.
*Daptomycin plus ampicillin despite resistance*
- While **ampicillin** can sometimes enhance daptomycin binding by reducing the net negative surface charge of the bacteria, it is generally less effective when high-level **ampicillin resistance** is already confirmed in *E. faecium*.
- This strategy is typically considered when other secondary agents are unavailable or contraindicated, but it is not superior to linezolid-based combinations in VRE endocarditis.
*Daptomycin monotherapy with high dose (10-12 mg/kg)*
- High-dose **daptomycin (10-12 mg/kg)** is recommended for endocarditis, but monotherapy for **prosthetic valve** infections carries a high risk of treatment failure.
- *Enterococcus faecium* can rapidly develop **resistance** (via the LiaFSR system) during daptomycin monotherapy, making a second agent necessary for such a high-burden infection.
*Linezolid monotherapy for 6 weeks*
- **Linezolid** is primarily **bacteriostatic** against enterococci, which is generally insufficient for the definitive treatment of **infective endocarditis** where bactericidal activity is required.
- Long-term use (over 2 weeks) carries significant risks of **bone marrow suppression** (thrombocytopenia) and **mitochondrial toxicity**, making it unsafe as a sole agent for a 6-week course.
More Surgical site infections US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.