Hospital-acquired infections

On this page
🦠 The Hospital Infection Battlefield: Where Healing Meets Hazard
Every year, millions of patients enter hospitals seeking healing but face an invisible threat that turns care settings into infection battlegrounds. You'll master how to identify the pathogens lurking in healthcare environments, trace their transmission pathways through the diagnostic-treatment-prevention cycle, and deploy evidence-based strategies that transform you from bystander to frontline defender. This lesson builds your clinical judgment from recognizing early infection signs to implementing multi-modal prevention systems that save lives. Understanding hospital-acquired infections means protecting your most vulnerable patients when they need safety most.
📌 Remember: HASTE - Healthcare setting, Acquired after 48 hours, Symptoms not present on admission, Transmission via healthcare contact, Evidence of new infection
The epidemiological foundation reveals staggering numbers: HAIs affect 4% of acute care patients, cause 99,000 deaths annually, and generate $28-45 billion in excess healthcare costs. These infections demonstrate 2-4x higher mortality rates compared to community-acquired infections, with surgical site infections leading at 31% of all HAIs, followed by pneumonia at 22% and bloodstream infections at 14%.
- Primary HAI Categories
- Surgical site infections: 31% of total HAIs
- Superficial incisional: 60% of SSIs
- Deep incisional: 25% of SSIs
- Organ/space: 15% of SSIs
- Healthcare-associated pneumonia: 22% of HAIs
- Ventilator-associated: 83% of hospital pneumonias
- Non-ventilator: 17% of hospital pneumonias
- Bloodstream infections: 14% of HAIs
- Central line-associated: 65% of hospital BSIs
- Secondary bloodstream: 35% of hospital BSIs
- Surgical site infections: 31% of total HAIs
| HAI Type | Incidence Rate | Mortality % | Cost per Episode | Prevention Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLABSI | 0.8/1000 line-days | 12-25% | $46,000 | 65-70% reducible |
| VAP | 2.0/1000 vent-days | 20-50% | $40,000 | 55-68% reducible |
| CAUTI | 3.1/1000 cath-days | 2-10% | $13,000 | 65-69% reducible |
| SSI | 1.9% procedures | 3-75% | $25,000 | 60% reducible |
| CDI | 8.2/10,000 days | 6-30% | $11,000 | 30% reducible |
💡 Master This: HAI risk increases exponentially with invasive device duration - CLABSI risk rises 5-7% daily, VAP risk increases 1-3% daily, and CAUTI risk climbs 3-7% daily after initial placement
Understanding these foundational patterns reveals how healthcare environments create unique infection dynamics that demand specialized prevention and management strategies.
🦠 The Hospital Infection Battlefield: Where Healing Meets Hazard
⚔️ The Pathogen Arsenal: Microbial Warfare in Healthcare
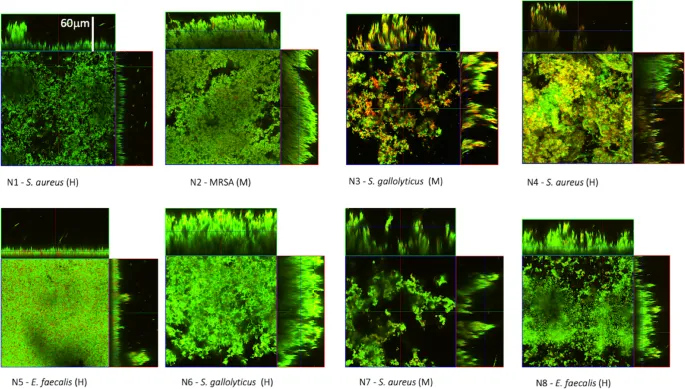
The "Big Six" healthcare pathogens account for 75% of all HAIs, each demonstrating distinct transmission patterns and resistance mechanisms:
📌 Remember: ESCAPE pathogens - Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium difficile, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacteriaceae (CRE)
- Gram-Positive Dominance
- MRSA: 13-15% of all HAIs
- Vancomycin resistance: <1% prevalence
- Biofilm production: 85% of isolates
- Mortality rate: 20-40% in bacteremia
- VRE: 4-6% of all HAIs
- Vancomycin MIC: ≥32 μg/mL
- Environmental survival: 7 days on surfaces
- Colonization rate: 15-20% ICU patients
- C. difficile: 12-15% of all HAIs
- Spore survival: 5 months on surfaces
- Recurrence rate: 20-35% after treatment
- Severe disease: 8-10% of cases
- MRSA: 13-15% of all HAIs

- Gram-Negative Threats
- CRE: 4-5% of all HAIs
- Carbapenem MIC: ≥4 μg/mL
- Mortality rate: 40-50% in bacteremia
- Colistin resistance: 5-15% emerging
- MDR Pseudomonas: 6-8% of all HAIs
- Triple-drug resistance: 13% of isolates
- Biofilm production: 90% of strains
- ICU prevalence: 15-20% of infections
- MDR Acinetobacter: 2-4% of all HAIs
- Carbapenem resistance: 63% of isolates
- Environmental persistence: 12 months
- Outbreak potential: High in ICUs
- CRE: 4-5% of all HAIs
| Pathogen | Resistance Rate | Transmission | Environmental Survival | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA | 46% S. aureus | Contact | 7-90 days | Vancomycin, linezolid |
| VRE | 77% E. faecium | Contact | 7 days-4 months | Linezolid, daptomycin |
| CRE | 4.2% Enterobacteriaceae | Contact | 2-7 months | Colistin, tigecycline |
| C. diff | 29.1% healthcare | Spores | 5 months | Vancomycin, fidaxomicin |
| MDR-PA | 13.1% P. aeruginosa | Contact/droplet | 6 hours-16 months | Ceftolozane, colistin |
💡 Master This: MDRO transmission follows the "5 D's" - Drugs (antibiotic exposure), Devices (invasive procedures), Debilitation (immunocompromise), Duration (length of stay), Dissemination (inadequate infection control)
These pathogen characteristics drive the complex infection control strategies required to prevent healthcare-associated transmission and treatment failures.
⚔️ The Pathogen Arsenal: Microbial Warfare in Healthcare
🎯 The Transmission Triangle: Mapping Infection Pathways
The transmission triad - source, mode, and susceptible host - creates multiple intervention points where prevention strategies can interrupt infection spread:
📌 Remember: DIRECT transmission modes - Direct contact, Indirect contact, Respiratory droplets, Environmental vehicles, Common source, Transmission-based precautions
- Contact Transmission Patterns
- Direct contact: 80% of HAI transmission
- Hand contamination: 40-100% after patient contact
- Glove contamination: 15-30% despite proper use
- Healthcare worker clothing: 65% contamination rate
- Indirect contact: 15% of HAI transmission
- Environmental surfaces: 40-60% contamination
- Medical equipment: 25-50% contamination
- Shared items: 30-70% contamination rate
- Fomite survival varies dramatically:
- MRSA: 7-90 days on surfaces
- VRE: 7 days-4 months on surfaces
- C. diff spores: 5 months on surfaces
- Direct contact: 80% of HAI transmission
- Respiratory Transmission Dynamics
- Droplet transmission: 3-5% of HAIs
- Particle size: >5 micrometers
- Travel distance: 3-6 feet maximum
- Settling time: Minutes to hours
- Airborne transmission: 1-2% of HAIs
- Particle size: <5 micrometers
- Travel distance: >6 feet potential
- Suspension time: Hours in air
- Aerosol-generating procedures increase risk 6-fold:
- Intubation: 6.6x increased transmission
- Bronchoscopy: 5.4x increased transmission
- Suctioning: 3.2x increased transmission
- Droplet transmission: 3-5% of HAIs
| Transmission Mode | HAI Percentage | Key Pathogens | Prevention Strategy | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct contact | 80% | MRSA, VRE, CRE | Hand hygiene, gloves | 40-70% reduction |
| Indirect contact | 15% | C. diff, Norovirus | Environmental cleaning | 30-50% reduction |
| Droplet | 3-5% | Influenza, RSV | Surgical masks | 80-95% reduction |
| Airborne | 1-2% | TB, measles, varicella | N95 respirators, AIIR | 95-99% reduction |
| Vehicle-borne | 1-2% | Legionella, Pseudomonas | Water system control | 70-90% reduction |
💡 Master This: The "5-moment" hand hygiene framework targets highest-risk transmission points - before patient contact, before aseptic procedures, after body fluid exposure, after patient contact, after contact with patient surroundings
Understanding transmission pathways enables precise targeting of prevention interventions based on pathogen-specific characteristics and environmental factors.
🎯 The Transmission Triangle: Mapping Infection Pathways
🔬 The Diagnostic Detective: Identifying Healthcare Infections

The diagnostic framework integrates clinical presentation, laboratory findings, and epidemiological factors through standardized surveillance definitions:
📌 Remember: CLINICAL HAI criteria - Culture positive, Laboratory confirmation, Infection timeline >48h, New signs/symptoms, Imaging consistent, Clinical deterioration, Appropriate specimen, Localized to site
- Laboratory Diagnostic Thresholds
- Blood cultures: ≥1 positive bottle with recognized pathogen
- Coagulase-negative Staph: ≥2 positive cultures required
- Time to positivity: <24 hours suggests high organism load
- Quantitative cultures: ≥15 CFU from catheter tip
- Respiratory cultures: ≥10^4-10^5 CFU/mL threshold
- BAL cultures: ≥10^4 CFU/mL significant
- Endotracheal aspirate: ≥10^5 CFU/mL significant
- Sputum cultures: ≥10^7 CFU/mL significant
- Urine cultures: ≥10^5 CFU/mL traditional threshold
- Catheterized patients: ≥10^3 CFU/mL may be significant
- Symptomatic patients: ≥10^2 CFU/mL can indicate infection
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria: No treatment indicated
- Blood cultures: ≥1 positive bottle with recognized pathogen
- Site-Specific Diagnostic Criteria
- Surgical site infections require ≥1 of:
- Purulent drainage from incision
- Positive culture from wound
- Signs of inflammation plus positive culture
- Surgeon diagnosis of infection
- Pneumonia diagnosis requires ≥2 of:
- New/progressive infiltrate on imaging
- Fever >38°C or hypothermia <36°C
- Leukocytosis >12,000 or leukopenia <4,000
- Purulent respiratory secretions
- Bloodstream infections require:
- ≥1 positive blood culture with recognized pathogen
- Clinical signs of infection
- No other identified source
- Surgical site infections require ≥1 of:
| HAI Type | Primary Criterion | Secondary Criteria | Exclusions | Diagnostic Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLABSI | Positive blood culture | Fever, chills, hypotension | Other BSI source | 85-95% specificity |
| VAP | New infiltrate | Fever, leukocytosis, purulent sputum | CHF, ARDS | 60-70% sensitivity |
| CAUTI | Positive urine culture | Fever, urgency, suprapubic pain | Asymptomatic bacteriuria | 75-85% specificity |
| SSI | Wound drainage | Fever, pain, erythema | Stitch abscess | 90-95% specificity |
| CDI | Positive toxin assay | Diarrhea >3 stools/day | Laxative use | 95-99% specificity |
💡 Master This: The "colonization vs. infection" distinction requires clinical correlation - positive cultures without clinical signs indicate colonization in 30-50% of cases, leading to unnecessary antibiotic therapy if not properly interpreted
Diagnostic precision prevents both missed infections and inappropriate antibiotic use, directly impacting patient outcomes and antimicrobial stewardship goals.
🔬 The Diagnostic Detective: Identifying Healthcare Infections
⚕️ The Treatment Arsenal: Evidence-Based HAI Management
Treatment algorithms prioritize empirical coverage based on local resistance patterns, followed by targeted therapy guided by culture results:
📌 Remember: OPTIMAL therapy principles - Obtain cultures first, Pathogen-directed therapy, Timing within 1 hour for sepsis, Infection source control, Minimize duration, Adjust for renal/hepatic function, Limit broad-spectrum exposure
- Empirical Therapy Selection
- MRSA coverage indicated when:
- ICU location: >20% MRSA prevalence
- Prior MRSA colonization: 40-60% infection risk
- Severe sepsis/shock: Mortality benefit with early coverage
- Risk factors present: >2 major risk factors
- Anti-pseudomonal coverage for:
- Ventilated patients: 15-20% Pseudomonas rate
- Immunocompromised: 25-30% gram-negative rate
- Prior broad-spectrum antibiotics: 3x increased risk
- Structural lung disease: 5x increased risk
- MRSA coverage indicated when:

- Targeted Therapy Optimization
- MRSA bacteremia treatment:
- Vancomycin: 15-20 mg/kg q8-12h, target trough 15-20 μg/mL
- Daptomycin: 8-10 mg/kg daily for bacteremia
- Linezolid: 600 mg q12h, avoid >28 days
- Duration: Minimum 14 days for uncomplicated bacteremia
- CRE infections require combination therapy:
- Colistin: 5 mg/kg loading, then 2.5-5 mg/kg q12h
- Tigecycline: 100 mg loading, then 50 mg q12h
- Carbapenem: High-dose extended infusion if MIC ≤8
- Duration: 14-21 days depending on source control
- MRSA bacteremia treatment:
| Pathogen | First-Line Therapy | Alternative Options | Duration | Cure Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA | Vancomycin 15-20 mg/kg q8-12h | Daptomycin 8-10 mg/kg daily | 7-14 days | 85-95% |
| VRE | Linezolid 600 mg q12h | Daptomycin 8-12 mg/kg daily | 7-14 days | 80-90% |
| CRE | Colistin + carbapenem | Tigecycline + colistin | 14-21 days | 60-75% |
| C. diff | Vancomycin 125 mg q6h PO | Fidaxomicin 200 mg q12h PO | 10-14 days | 80-90% |
| MDR-PA | Ceftolozane/tazobactam | Colistin + carbapenem | 7-14 days | 75-85% |
💡 Master This: Source control remains essential for cure - infected devices must be removed within 48-72 hours for optimal outcomes, as biofilm-associated infections have <30% cure rates with antibiotics alone
Treatment success requires integration of antimicrobial therapy with aggressive source control measures and careful monitoring for treatment response and adverse effects.
⚕️ The Treatment Arsenal: Evidence-Based HAI Management
🛡️ The Prevention Fortress: Multi-Modal Defense Systems
Prevention bundles integrate evidence-based practices into systematic protocols that ensure consistent implementation across all patient encounters:
📌 Remember: BUNDLE components - Best practices combined, Uniform implementation, Non-negotiable elements, Daily assessment, Leadership support, Education ongoing
- Core Prevention Bundles
- CLABSI prevention bundle:
- Hand hygiene: >95% compliance target
- Maximal sterile barriers: Full-body drape during insertion
- Chlorhexidine skin prep: >0.5% concentration
- Optimal catheter site: Subclavian preferred over femoral
- Daily review: Remove unnecessary lines
- VAP prevention bundle:
- Head of bed elevation: 30-45 degrees
- Daily sedation vacation: Assess readiness to wean
- Oral care: Chlorhexidine 0.12% every 12 hours
- Subglottic suctioning: Continuous or intermittent
- Stress ulcer prophylaxis: PPI or H2 blocker
- CLABSI prevention bundle:

- Environmental Prevention Strategies
- Enhanced cleaning protocols:
- High-touch surfaces: Every 4 hours minimum
- Terminal cleaning: UV disinfection or hydrogen peroxide
- Monitoring systems: ATP bioluminescence or fluorescent markers
- Compliance targets: >95% for high-risk areas
- Isolation precautions:
- Contact precautions: Gown and gloves for all contact
- Private rooms: Preferred for MDRO patients
- Cohorting: Acceptable when private rooms unavailable
- Duration: Until discharge or 3 negative cultures
- Enhanced cleaning protocols:
| Prevention Bundle | Target HAI | Key Components | Compliance Target | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLABSI | Central line BSI | 5 evidence-based practices | >95% all elements | 65-70% reduction |
| VAP | Ventilator pneumonia | 4-6 core interventions | >90% all elements | 55-68% reduction |
| CAUTI | Catheter UTI | Insertion/maintenance bundle | >90% compliance | 65-69% reduction |
| SSI | Surgical site infection | Perioperative bundle | >95% compliance | 60% reduction |
| CDI | C. difficile infection | Antimicrobial stewardship | >80% appropriate use | 30% reduction |
💡 Master This: Horizontal prevention strategies (hand hygiene, environmental cleaning) protect against multiple pathogens simultaneously, while vertical strategies (device bundles) target specific HAI types with greater precision
Prevention success requires sustained organizational commitment, continuous monitoring, and rapid cycle improvement to maintain high compliance rates across all prevention interventions.
🛡️ The Prevention Fortress: Multi-Modal Defense Systems
🎯 The Mastery Framework: HAI Prevention Excellence
📌 Remember: MASTER HAI prevention - Measure outcomes continuously, Assess compliance rigorously, Standardize best practices, Train teams systematically, Engage leadership actively, Respond to data rapidly
- Essential HAI Prevention Arsenal
- Surveillance metrics: Real-time monitoring systems
- HAI rates: Monthly trending with statistical process control
- Bundle compliance: Daily measurement with immediate feedback
- Outbreak detection: Automated alerts for rate increases
- Implementation tools: Systematic deployment strategies
- Checklists: Standardized for all high-risk procedures
- Education: Competency-based with annual updates
- Feedback: Unit-specific performance data monthly
- Surveillance metrics: Real-time monitoring systems
| Prevention Priority | Target Metric | Monitoring Frequency | Action Threshold | Intervention Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand hygiene | >90% compliance | Daily observation | <85% compliance | Immediate re-education |
| CLABSI bundle | >95% all elements | Every insertion | <90% compliance | Process review |
| Environmental cleaning | >95% ATP pass rate | Weekly monitoring | <90% pass rate | Enhanced protocols |
| Antimicrobial stewardship | >80% appropriate use | Daily review | <70% appropriate | Prescriber feedback |
| Isolation compliance | >95% PPE use | Daily audit | <90% compliance | Staff re-training |
💡 Master This: HAI prevention return on investment averages $3-7 saved per $1 invested through reduced length of stay, readmissions, and liability costs - making prevention both clinically essential and financially advantageous
Mastery transforms HAI prevention from reactive problem-solving to proactive system optimization that consistently delivers exceptional patient safety outcomes.
🎯 The Mastery Framework: HAI Prevention Excellence
Practice Questions: Hospital-acquired infections
Test your understanding with these related questions
The surgical equipment used during a craniectomy is sterilized using pressurized steam at 121°C for 15 minutes. Reuse of these instruments can cause transmission of which of the following pathogens?













