HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for HIV prevention strategies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 1 week after being admitted to the hospital for oral candidiasis and esophagitis. His CD4+ T lymphocyte count is 180 cells/μL. An HIV antibody test is positive. Genotypic resistance assay shows the virus to be susceptible to all antiretroviral therapy regimens and therapy with dolutegravir, tenofovir, and emtricitabine is initiated. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings would be most likely on follow-up evaluation 3 months later?
$$$ CD4 +/CD8 ratio %%% HIV RNA %%% HIV antibody test $$$
- A. ↓ ↓ negative
- B. ↑ ↑ negative
- C. ↓ ↑ negative
- D. ↑ ↓ positive (Correct Answer)
- E. ↓ ↑ positive
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***↑ ↓ positive***
- With effective **antiretroviral therapy (ART)**, the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would increase as **CD4+ T cell counts rise** and **CD8+ T cell counts decrease**.
- **HIV RNA (viral load)** would significantly decrease (ideally to undetectable levels) due to the suppression of viral replication, but HIV antibodies would remain positive indefinitely.
*↓ ↓ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** and **HIV RNA** (viral load) along with a negative **HIV antibody test** is inconsistent with successful ART.
- A negative HIV antibody test would mean the patient was never infected, which contradicts the initial positive result and symptoms.
*↑ ↑ negative*
- An increase in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** is expected with ART, but an increase in **HIV RNA** (viral load) indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is impossible after a confirmed positive result, regardless of treatment success.
*↓ ↑ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would suggest worsening immune function, while an increase in **HIV RNA** indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is not possible once a patient has developed antibodies to HIV.
*↓ ↑ positive*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would indicate immune decline, contrary to the expected improvement with effective ART.
- An increase in **HIV RNA (viral load)** would signify treatment failure, even if HIV antibodies remain positive.
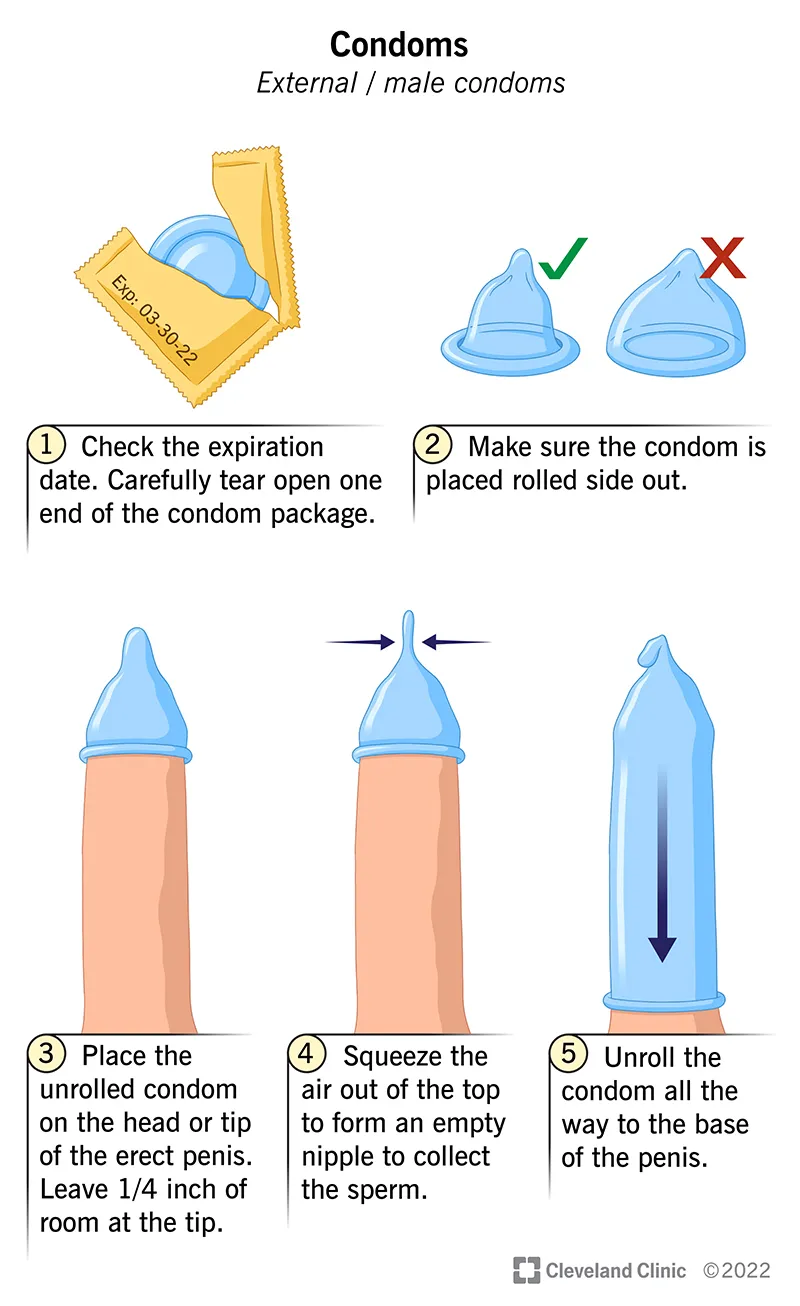
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 2: A 23-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for a wellness checkup. She has been treated for gonorrhea and chlamydia 3 times in the past 6 months but is otherwise healthy. She smokes cigarettes, drinks alcohol regularly, and wears a helmet while riding her bicycle. The patient is generally healthy and has no acute complaints. Her vitals and physical exam are unremarkable. She is requesting advice regarding contraception. The patient is currently taking oral contraceptive pills. Which of the following would be the most appropriate recommendation for this patient?
- A. Intrauterine device
- B. Tubal ligation
- C. Etonogestrel implant
- D. Condoms (Correct Answer)
- E. Pull out method
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***Condoms***
- The patient has a history of **recurrent STIs**, indicating a need for barrier protection in addition to contraception to prevent future infections.
- **Condoms** are the only contraceptive method listed that provides significant protection against STIs, making them the most appropriate recommendation for this patient's overall health and sexual practices.
*Intrauterine device*
- While a highly effective contraceptive, an **IUD** does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and the patient's history suggests a high risk for contracting STIs.
- Additionally, some IUDs (like copper IUDs) can **increase menstrual bleeding**, and hormonal IUDs have their own systemic effects.
*Tubal ligation*
- This is a permanent sterilization method that, while highly effective for contraception, offers **no protection against STIs**.
- It is generally considered for women who have completed childbearing or are certain they do not desire future pregnancies, which may not be the case for a 23-year-old.
*Etonogestrel implant*
- The **etonogestrel implant** is an effective form of contraception but offers **no protection against STIs**.
- The patient's history of recurrent STIs indicates that a method also providing STI prevention is crucial.
*Pull out method*
- The **pull-out method** is an unreliable form of contraception with a high failure rate, offering minimal protection against pregnancy and **no protection against STIs**.
- Given the patient's history of STIs and desire for effective contraception, this method is entirely inappropriate.
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old sexually active male presents to an internal medicine physician for a routine health check up after having several unprotected sexual encounters. After appropriate testing the physician discusses with the patient that he is HIV+ and must be started on anti-retroviral treatment. Which of the following medications prescribed acts on the gp41 subunit of the HIV envelope glycoprotein?
- A. Zidovudine
- B. Saquinavir
- C. Enfuvirtide (Correct Answer)
- D. Amantadine
- E. Rimantadine
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***Enfuvirtide***
- **Enfuvirtide** is a **fusion inhibitor** that binds specifically to the **gp41 subunit** of the HIV envelope glycoprotein.
- By binding to gp41, Enfuvirtide prevents the **fusion of the viral and host cell membranes**, thereby blocking viral entry and replication.
*Zidovudine*
- **Zidovudine** is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)**.
- It works by inhibiting the enzyme **reverse transcriptase**, which is responsible for converting viral RNA into DNA.
*Saquinavir*
- **Saquinavir** is a **protease inhibitor (PI)**.
- This drug works by inhibiting the **HIV protease enzyme**, which is crucial for cleaving viral polyproteins into functional proteins required for viral assembly and maturation.
*Amantadine*
- **Amantadine** is an **antiviral agent** primarily used to treat **influenza A**.
- It works by interfering with the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, thus inhibiting viral uncoating.
*Rimantadine*
- **Rimantadine** is another **antiviral agent** used for **influenza A treatment and prophylaxis**.
- Similar to amantadine, it targets the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, preventing the uncoating step necessary for viral replication.
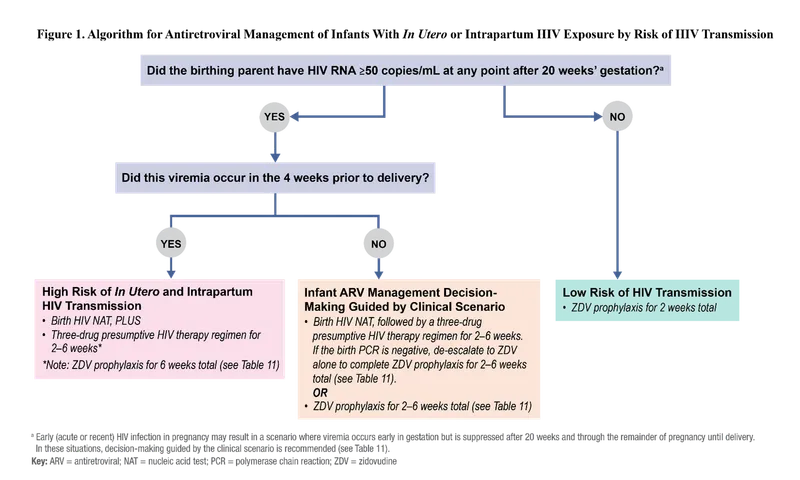
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 4: A 27-year-old G2P1 woman is diagnosed with an HIV infection after undergoing routine prenatal blood work testing. Her estimated gestational age by first-trimester ultrasound is 12 weeks. Her CD4 count is 150 cells/mm^3 and her viral load is 126,000 copies/mL. She denies experiencing any symptoms of HIV infection. Which of the following is appropriate management of this patient's pregnancy?
- A. HAART (Correct Answer)
- B. Breastfeeding
- C. Vaginal delivery
- D. HAART after delivery
- E. Avoidance of antibiotic prophylaxis
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***HAART***
- **Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)** is recommended immediately for pregnant women with HIV, regardless of CD4 count or viral load, to reduce maternofetal transmission.
- Starting HAART early in pregnancy significantly lowers the **viral load**, protecting the fetus from HIV infection.
*Breastfeeding*
- **Breastfeeding** is contraindicated in HIV-positive mothers in developed countries because it carries a risk of HIV transmission to the infant.
- Formula feeding is recommended to prevent **postnatal HIV transmission**.
*Vaginal delivery*
- A **vaginal delivery** may be considered if the viral load is undetectable or very low (<1,000 copies/mL) at the time of delivery.
- Given this patient's **high viral load** (126,000 copies/mL), a scheduled cesarean section would be indicated to minimize the risk of perinatal transmission.
*HAART after delivery*
- Delaying **HAART until after delivery** would increase the risk of maternofetal HIV transmission during pregnancy and delivery.
- Prompt initiation of HAART is crucial for both maternal health and **fetal protection**.
*Avoidance of antibiotic prophylaxis*
- **Antibiotic prophylaxis** is commonly used in combination with antiretroviral agents to prevent opportunistic infections, especially when the **CD4 count is low** (<200 cells/mm³).
- Given a CD4 count of 150 cells/mm³, prophylaxis against opportunistic infections like **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia** might be indicated, making avoidance inappropriate.
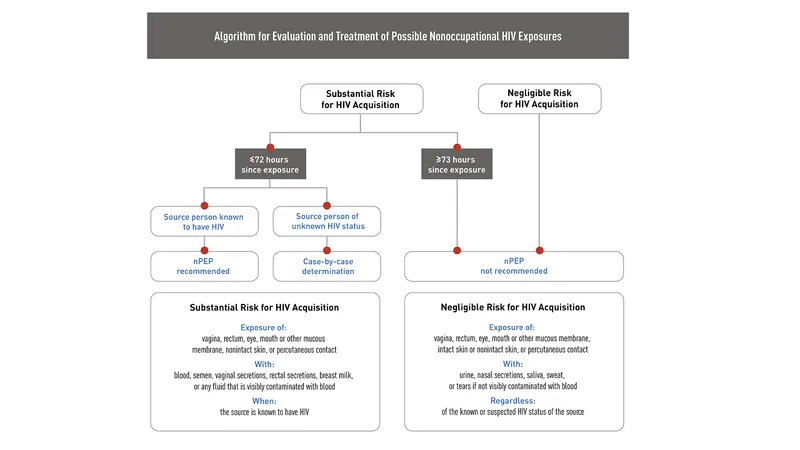
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 5: A 26-year-old nurse presents 12 hours after she accidentally stuck herself with a blood-contaminated needle. She reported the accident appropriately and now seeks post-exposure prophylaxis. She does not have any complaints at the moment of presentation. Her vital signs include: blood pressure 125/80 mm Hg, heart rate 71/min, respiratory rate 15/min, and temperature 36.5℃ (97.7℉). Physical examination is unremarkable. The nurse has prescribed a post-exposure prophylaxis regimen which includes tenofovir, emtricitabine, and raltegravir. How will tenofovir change the maximum reaction rate (Vm) and Michaelis constant (Km) of the viral reverse transcriptase?
- A. Vm will decrease, Km will increase
- B. Vm and Km will both decrease
- C. Vm will stay the same, Km will increase
- D. Vm and Km will both increase
- E. Vm will decrease, Km will stay the same (Correct Answer)
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***Vm will decrease, Km will stay the same***
- **Tenofovir** is a **nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NtRTI)** that acts as a **competitive substrate analog**. Once phosphorylated to **tenofovir diphosphate**, it competes with natural deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) for incorporation into the viral DNA chain.
- Upon incorporation, tenofovir acts as a **chain terminator** because it lacks a 3'-hydroxyl group necessary for further DNA elongation. This **irreversibly inactivates** the enzyme-DNA complex, effectively reducing the **maximum reaction rate (Vm)** by decreasing the amount of functional enzyme available.
- Since tenofovir competes with natural nucleotides but doesn't affect the enzyme's affinity for its natural substrates, the **Michaelis constant (Km) remains unchanged**. The inhibition pattern shows characteristics of competitive inhibition with irreversible chain termination.
*Vm will decrease, Km will increase*
- This pattern is characteristic of a **mixed inhibitor**, where the inhibitor can bind to both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex, reducing Vm while also decreasing substrate affinity (increasing Km).
- While tenofovir does reduce Vm through chain termination, it does not significantly alter the enzyme's affinity for natural nucleotide substrates. Tenofovir diphosphate **competes directly** with dATP rather than binding to an allosteric site, so Km remains unchanged rather than increasing.
*Vm and Km will both decrease*
- This effect is typical of an **uncompetitive inhibitor**, which binds only to the **enzyme-substrate complex**. Uncompetitive inhibitors decrease both Vm and Km, implying increased apparent substrate affinity.
- Tenofovir does not function as an uncompetitive inhibitor. As a **nucleotide analog**, it competes for the active site and gets incorporated into DNA, causing chain termination. This mechanism does not involve preferential binding to the enzyme-substrate complex that would decrease Km.
*Vm will stay the same, Km will increase*
- This describes **pure reversible competitive inhibition**, where the inhibitor competes with substrate for the active site but can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration, leaving Vm unchanged.
- While tenofovir diphosphate does **compete with natural nucleotides**, it acts as a **suicide substrate** that causes irreversible chain termination once incorporated. This **permanently inactivates** the enzyme-DNA complex, reducing the pool of functional enzyme and thus decreasing Vm, distinguishing it from simple reversible competitive inhibition.
*Vm and Km will both increase*
- An increase in both Vm and Km is not a standard pattern for enzyme inhibition and would suggest **reduced substrate affinity** with paradoxically increased catalytic capacity, which is inconsistent with any inhibitory mechanism.
- This scenario contradicts the **intended therapeutic effect** of tenofovir, which is to inhibit HIV reverse transcriptase activity and prevent viral replication, not to enhance enzyme function.
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 6: A 23-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician at 36 weeks' gestation for her first prenatal visit. She confirmed the pregnancy with a home urine pregnancy kit a few months ago but has not yet followed up with a physician. She takes no medications. Vital signs are within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 36-week gestation. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.6 g/dL
Serum
Glucose 88 mg/dL
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Hepatitis C antibody negative
HIV antibody positive
HIV load 11,000 copies/mL (N < 1000 copies/mL)
Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine fetus consistent in size with a 36-week gestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
- A. Intrapartum zidovudine and vaginal delivery when labor occurs
- B. Intrapartum zidovudine and cesarean delivery at 38 weeks' gestation
- C. Start cART and prepare for vaginal delivery at 38 weeks' gestation
- D. Conduct cesarean delivery immediately
- E. Start cART and schedule cesarean delivery at 38 weeks' gestation (Correct Answer)
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***Start cART and schedule cesarean delivery at 38 weeks' gestation***
- This patient presents at 36 weeks with a **newly diagnosed HIV infection** and a **viral load of 11,000 copies/mL**, which is considered high. Starting **combination antiretroviral therapy (cART)** immediately is crucial to reduce the viral load and the risk of **mother-to-child transmission (MTCT)**.
- For patients with **HIV viral loads > 1,000 copies/mL** near term, a **scheduled cesarean delivery at 38 weeks** is recommended to minimize fetal exposure to maternal blood and secretions during labor, further reducing the risk of MTCT.
*Intrapartum zidovudine and vaginal delivery when labor occurs*
- This approach is appropriate for HIV-positive mothers with a **low viral load (< 1,000 copies/mL)** at or near delivery, as a scheduled cesarean section would not significantly further reduce the risk of transmission.
- Given the patient's **high viral load (11,000 copies/mL)**, **only intrapartum zidovudine** would be insufficient to adequately reduce the risk of MTCT during a vaginal delivery.
*Intrapartum zidovudine and cesarean delivery at 38 weeks' gestation*
- While a **scheduled cesarean delivery at 38 weeks** is indicated for a high viral load, simply administering **intrapartum zidovudine without prior cART** misses the opportunity to significantly reduce viral load before delivery.
- Starting **cART immediately** offers the best chance to lower viral load and optimize outcomes for both mother and child, which is superior to only intrapartum prophylaxis.
*Start cART and prepare for vaginal delivery at 38 weeks' gestation*
- Starting **cART is essential**, but preparing for a vaginal delivery with a **viral load of 11,000 copies/mL** at 36 weeks is inappropriate.
- A **high viral load** necessitates a ** scheduled cesarean delivery** to minimize the risk of MTCT, regardless of cART initiation at this late stage.
*Conduct cesarean delivery immediately*
- While immediate action is needed, an **emergency cesarean delivery** is not indicated at 36 weeks unless there are other obstetric complications or rapid deterioration.
- The primary goal is to **reduce viral load through cART** and then perform a **scheduled cesarean at 38 weeks**, balancing safety for both mother and fetus with the greatest reduction in HIV transmission risk.
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old female medical student presents to occupational health after sustaining a needlestick injury. She reports that she was drawing blood from an HIV-positive patient when she stuck herself percutaneously while capping the needle. She immediately washed the puncture wound with betadine. The medical student has a negative HIV serology from the beginning of medical school two years ago. She is monogamous with one male partner and denies any intravenous drug use. The source patient was recently diagnosed with HIV, and has a CD4 count of 550 cells/µL. His most recent viral load is 1,800,000 copies/mL, and he was started on HAART three days ago.
Which of the following is the best next step to manage the female medical student’s exposure?
- A. Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if positive
- B. Perform genotype testing on source patient and initiate antiretroviral therapy tailored to results
- C. Immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy
- D. Draw her repeat HIV serology and immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy (Correct Answer)
- E. Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if negative
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***Draw her repeat HIV serology and immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy***
- This approach ensures that baseline **HIV status** is established while simultaneously providing **post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)** as quickly as possible. Time is critical for PEP efficacy.
- The patient has a high-risk exposure (percutaneous injury, high viral load source) warranting immediate initiation of a **three-drug antiretroviral regimen** to prevent seroconversion.
*Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if positive*
- Waiting for serology results before initiating therapy would delay PEP, significantly reducing its effectiveness in potentially preventing **HIV transmission**.
- If the student is already HIV-positive from a prior undisclosed exposure, PEP for a new exposure is not the primary concern; rather, she would need full **HIV treatment**. However, the immediate concern after an exposure is always prevention.
*Immediately initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy*
- While immediate initiation of PEP is correct, it is still crucial to obtain a **baseline HIV serology** for the exposed individual.
- This baseline allows for clear documentation of the pre-exposure HIV status, which is vital for any future testing and counseling following the exposure.
*Draw her repeat HIV serology and initiate three-drug antiretroviral therapy if negative*
- Waiting for serology results to return before starting PEP is incorrect as this would significantly delay the initiation of therapy.
- The critical window for effective PEP is within hours of exposure, ideally within 72 hours.
*Perform genotype testing on source patient and initiate antiretroviral therapy tailored to results*
- While **genotype testing** on the source patient provides valuable information about drug resistance, it should not delay the immediate initiation of **empiric PEP** for the exposed individual.
- PEP must be started as soon as possible, and the regimen can be adjusted later if the genotype results indicate resistance to the initial drugs.
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old woman G1P0 presents at 38 weeks of gestation for a standard prenatal visit. She endorses occasional mild lower back pain but otherwise remains asymptomatic. Her past medical history is significant for HIV for which she is treated with azidothymidine (AZT). Her vital signs and physical exam are unremarkable. Her current HIV viral titer level is 1,400 copies. If she were to go into labor today, what would be the next and most important step for the prevention of vertical HIV transmission to the newborn?
- A. Urge the patient to have a cesarean section delivery (Correct Answer)
- B. Add nevirapine to the patient’s AZT
- C. Treat the newborn with AZT following delivery
- D. Increase AZT dose
- E. Avoid breastfeeding
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***Urge the patient to have a cesarean section delivery***
- A **high viral load** (>1000 copies/mL) at 38 weeks gestation is an indication for a **scheduled cesarean section** to reduce the risk of vertical HIV transmission.
- This approach minimizes the infant's exposure to maternal blood and genital secretions during vaginal delivery.
*Add nevirapine to the patient’s AZT*
- While adding a second antiretroviral (ARV) medication is generally beneficial in HIV treatment, a single dose of **nevirapine** given to the mother in labor is typically used when **highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)** has not been given prenatally or with unknown viral load status.
- The primary intervention for a known high viral load near term is delivery mode modification.
*Treat the newborn with AZT following delivery*
- This is a standard and essential component of **post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)** for all infants born to HIV-positive mothers, regardless of maternal viral load or delivery route.
- However, it is a post-delivery intervention and not the **next and most important step** for prevention *at the time of labor* with a high viral load.
*Increase AZT dose*
- Increasing the dose of a single ARV medication like **AZT** alone is unlikely to rapidly suppress a viral load of 1,400 copies/mL sufficiently to mitigate transmission risks during labor, and could lead to toxicity.
- Achieving viral suppression before labor is crucial, and if not achieved, a C-section is indicated.
*Avoid breastfeeding*
- **Avoiding breastfeeding** is a critical recommendation for HIV-positive mothers in developed countries to prevent **postnatal vertical transmission**.
- While important for overall prevention, it addresses transmission after birth and is not the immediate and most important step to prevent transmission *at the onset of labor* when a high viral load is present.
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 9: A 24-year-old male presents to the emergency room with a cough and shortness of breath for the past 3 weeks. You diagnose Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP). An assay of the patient's serum reveals the presence of viral protein p24. Which of the following viral genes codes for this protein?
- A. gag (Correct Answer)
- B. pol
- C. rev
- D. env
- E. tat
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***gag***
- The **gag gene** (group-specific antigen) in HIV codes for structural proteins of the virus, including **p24**, which forms the viral capsid.
- The presence of **p24 protein** in the serum is a key marker for **HIV infection**, particularly in the early stages, as it indicates active viral replication.
*pol*
- The **pol gene** codes for essential viral enzymes such as **reverse transcriptase**, **integrase**, and **protease**, which are crucial for the HIV life cycle.
- While vital for viral replication, the **pol gene products** are enzymes involved in processing and replication, not the structural capsid protein p24.
*rev*
- The **rev gene** (regulator of expression of virion proteins) codes for the **Rev protein**, which regulates the export of HIV mRNAs from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- This regulatory protein ensures the efficient synthesis of structural and enzymatic proteins but does not directly code for the p24 capsid protein.
*env*
- The **env gene** (envelope) codes for the viral envelope glycoproteins **gp160**, which is cleaved into **gp120** and **gp41**.
- These proteins are critical for viral entry into host cells by binding to CD4 receptors and co-receptors, but they are distinct from the p24 capsid protein.
*tat*
- The **tat gene** (trans-activator of transcription) codes for the **Tat protein**, a powerful trans-activator that enhances the transcription of HIV RNA.
- Tat plays a crucial role in increasing the efficiency of viral gene expression but does not code for structural components like the p24 capsid.
HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG Question 10: A 44-year-old with a past medical history significant for human immunodeficiency virus infection presents to the emergency department after he was found to be experiencing worsening confusion. The patient was noted to be disoriented by residents and staff at the homeless shelter where he resides. On presentation he reports headache and muscle aches but is unable to provide more information. His temperature is 102.2°F (39°C), blood pressure is 112/71 mmHg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 24/min. Knee extension with hips flexed produces significant resistance and pain. A lumbar puncture is performed with the following results:
Opening pressure: Normal
Fluid color: Clear
Cell count: Increased lymphocytes
Protein: Slightly elevated
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Herpes simplex virus
- B. Group B streptococcus
- C. Cryptococcus (Correct Answer)
- D. Tuberculosis
- E. Neisseria meningitidis
HIV prevention strategies Explanation: ***Cryptococcus***
- **Cryptococcus neoformans** is the **most common cause of meningitis** in HIV-positive patients, particularly those with CD4 counts <100 cells/μL.
- The CSF findings are **classic for cryptococcal meningitis**: clear fluid, **lymphocytic pleocytosis**, normal or mildly elevated opening pressure, and **slightly elevated protein** with normal or mildly decreased glucose.
- The patient's **subacute presentation** with confusion, fever, and meningeal signs in the context of **HIV infection** strongly suggests cryptococcal meningitis as the most likely diagnosis.
- Diagnosis is confirmed with **CSF cryptococcal antigen**, India ink stain, or fungal culture.
*Herpes simplex virus*
- While HSV can cause meningitis or encephalitis, it is **not the most common cause** of meningitis in HIV-positive patients.
- **HSV encephalitis** typically presents with more prominent temporal lobe involvement, including personality changes, seizures, and focal neurological deficits.
- HSV meningitis is more common in **immunocompetent individuals** and would be less likely than cryptococcal infection in an HIV patient.
*Group B streptococcus*
- This causes **bacterial meningitis** with a **neutrophilic predominance** in CSF, not lymphocytic.
- CSF would show **markedly elevated protein**, **decreased glucose**, and cloudy appearance.
- More common in neonates and elderly patients, not typically associated with HIV.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- This is a cause of **acute bacterial meningitis** with rapid onset and often a **petechial rash**.
- CSF would show **neutrophilic predominance**, **high protein**, **low glucose**, and turbid appearance.
- The lymphocytic pleocytosis rules out typical bacterial meningitis.
*Tuberculosis*
- **Tuberculous (TB) meningitis** is an important consideration in HIV-positive patients and can present with lymphocytic pleocytosis.
- However, TB meningitis typically shows **markedly elevated protein** (often >100 mg/dL, not "slightly elevated"), **low glucose** (<45 mg/dL), and may have a "spider-web clot" on standing CSF.
- The **more subacute to chronic course** (weeks) and absence of very high protein make TB less likely than cryptococcal meningitis in this acute presentation.
More HIV prevention strategies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.