CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for CD4 monitoring and viral load. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He was diagnosed with HIV infection 2 weeks ago. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 162/mm3 (N ≥ 500). An interferon-gamma release assay is negative. Prophylactic treatment against which of the following pathogens is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Cytomegalovirus
- B. Toxoplasma gondii
- C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- D. Aspergillus fumigatus
- E. Pneumocystis jirovecii (Correct Answer)
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***Pneumocystis jirovecii***
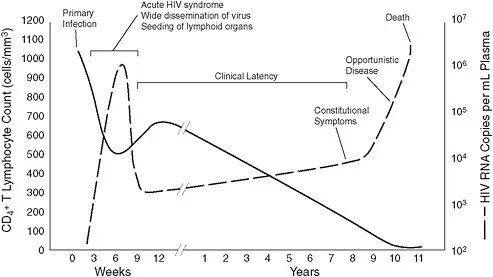
- This patient's **CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of 162/mm3** is below the threshold of 200/mm3, indicating a significant risk for **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**, an opportunistic infection in HIV.
- Prophylaxis with **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is highly effective and recommended for HIV patients with CD4 counts less than 200/mm3.
*Cytomegalovirus*
- **CMV prophylaxis** is generally not recommended for all HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is evidence of active disease or extremely low CD4 counts (e.g., <50/mm3) with high viral loads.
- While CMV can cause end-organ disease in advanced HIV, routine primary prophylaxis is not standard for this CD4 level.
*Toxoplasma gondii*
- **Toxoplasma prophylaxis** is indicated for HIV patients with **CD4 counts less than 100/mm3** who are also seropositive for *Toxoplasma gondii*.
- The patient's CD4 count is 162/mm3, and there's no mention of *Toxoplasma* serostatus, making it less appropriate than PCP prophylaxis.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
- The patient's **interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) is negative**, which suggests no **latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)**, thus making primary prophylaxis unnecessary at this time.
- While HIV patients are at high risk for TB, prophylaxis is typically given for LTBI or as secondary prophylaxis for those who have completed treatment for active TB.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- **Aspergillus infections** are typically seen in patients with severe **neutropenia** or those receiving high-dose corticosteroids, not primarily in HIV patients based solely on CD4 count.
- Routine prophylaxis for Aspergillus is not recommended for HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is a specific risk factor.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 2: A 2300-g (5-lb 1-oz) male newborn is delivered to a 29-year-old primigravid woman. The mother has HIV and received triple antiretroviral therapy during pregnancy. Her HIV viral load was 678 copies/mL 1 week prior to delivery. Labor was uncomplicated. Apgar scores are 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes respectively. Physical examination of the newborn shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this infant?
- A. Administer lamivudine and nevirapine
- B. Administer zidovudine, lamivudine and nevirapine (Correct Answer)
- C. Administer nevirapine
- D. Administer zidovudine
- E. HIV antibody testing
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***Administer zidovudine, lamivudine and nevirapine***
- The mother has a **viral load of 678 copies/mL**, which falls into the **intermediate-risk category** (50-999 copies/mL) for HIV transmission.
- Current guidelines recommend **combination antiretroviral prophylaxis** (zidovudine + lamivudine + nevirapine) for infants born to mothers with viral loads in this range, typically given for 2 weeks followed by zidovudine alone to complete 4-6 weeks.
- This enhanced regimen provides better protection than monotherapy when maternal viral suppression is suboptimal.
*Administer zidovudine*
- Zidovudine monotherapy is reserved for **low-risk infants** whose mothers have viral loads **<50 copies/mL** at delivery with documented adherence to ART during pregnancy.
- With a maternal viral load of 678 copies/mL, monotherapy alone is **insufficient** and would not meet current standard of care for HIV prophylaxis.
*Administer lamivudine and nevirapine*
- This regimen omits **zidovudine**, which remains the **backbone of neonatal HIV prophylaxis** and should always be included.
- Using only lamivudine and nevirapine without zidovudine is not consistent with established guidelines.
*Administer nevirapine*
- Nevirapine monotherapy is **not adequate** for HIV prophylaxis in developed countries with access to combination therapy.
- While nevirapine may be used as a single dose in resource-limited settings, it should be part of a multi-drug regimen when other agents are available.
*HIV antibody testing*
- HIV antibody testing in newborns will detect **maternal antibodies** that crossed the placenta and cannot determine the infant's true infection status at birth.
- While HIV diagnostic testing using **PCR or viral load assays** will be performed at 14-21 days, 1-2 months, and 4-6 months of age, **antiretroviral prophylaxis must be initiated immediately** after birth to prevent transmission.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old HIV-positive male is seen in clinic for follow-up care. When asked if he has been adhering to his HIV medications, the patient exclaims that he has been depressed, thus causing him to not take his medication for six months. His CD4+ count is now 33 cells/mm3. What medication(s) should he take in addition to his anti-retroviral therapy?
- A. Azithromycin and fluconazole
- B. Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole
- C. Dapsone
- D. Fluconazole
- E. Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Correct Answer)
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole***
- With a **CD4+ count of 33 cells/mm3**, this patient is at high risk for **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)** and **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis**, for which **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is the prophylaxis of choice.
- He is also at very high risk for **Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection**, for which **azithromycin** is the recommended preventative treatment when the CD4 count is below 50 cells/mm3.
*Azithromycin and fluconazole*
- While **azithromycin** is indicated for MAC prophylaxis, **fluconazole** is typically used for **cryptococcal meningitis** or **candidiasis**, which are not the primary, immediate prophylactic concerns at this specific CD4 count unless there's evidence of these infections.
- The most critical opportunistic infections to prevent at a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3 are PJP, Toxoplasmosis, and MAC.
*Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole*
- **Dapsone** can be used as an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** if TMP-SMX is contraindicated, but it is not the first-line choice and does not cover toxoplasmosis as effectively as TMP-SMX alone.
- **Fluconazole** again is not a primary prophylactic agent at this CD4 count in the absence of specific indications.
*Dapsone*
- **Dapsone** is an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** and can also prevent **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis** when combined with pyrimethamine, but it is not the first-line recommendation.
- It does not provide coverage against **MAC infection**, which is a significant risk at this CD4 count.
*Fluconazole*
- **Fluconazole** is primarily used for **fungal infections** like **candidiasis** or **cryptococcosis**.
- It does not prevent **PJP, Toxoplasmosis, or MAC**, which are the most critical prophylactic concerns for a patient with a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 4: A 27-year-old G2P1 woman is diagnosed with an HIV infection after undergoing routine prenatal blood work testing. Her estimated gestational age by first-trimester ultrasound is 12 weeks. Her CD4 count is 150 cells/mm^3 and her viral load is 126,000 copies/mL. She denies experiencing any symptoms of HIV infection. Which of the following is appropriate management of this patient's pregnancy?
- A. HAART (Correct Answer)
- B. Breastfeeding
- C. Vaginal delivery
- D. HAART after delivery
- E. Avoidance of antibiotic prophylaxis
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***HAART***
- **Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)** is recommended immediately for pregnant women with HIV, regardless of CD4 count or viral load, to reduce maternofetal transmission.
- Starting HAART early in pregnancy significantly lowers the **viral load**, protecting the fetus from HIV infection.
*Breastfeeding*
- **Breastfeeding** is contraindicated in HIV-positive mothers in developed countries because it carries a risk of HIV transmission to the infant.
- Formula feeding is recommended to prevent **postnatal HIV transmission**.
*Vaginal delivery*
- A **vaginal delivery** may be considered if the viral load is undetectable or very low (<1,000 copies/mL) at the time of delivery.
- Given this patient's **high viral load** (126,000 copies/mL), a scheduled cesarean section would be indicated to minimize the risk of perinatal transmission.
*HAART after delivery*
- Delaying **HAART until after delivery** would increase the risk of maternofetal HIV transmission during pregnancy and delivery.
- Prompt initiation of HAART is crucial for both maternal health and **fetal protection**.
*Avoidance of antibiotic prophylaxis*
- **Antibiotic prophylaxis** is commonly used in combination with antiretroviral agents to prevent opportunistic infections, especially when the **CD4 count is low** (<200 cells/mm³).
- Given a CD4 count of 150 cells/mm³, prophylaxis against opportunistic infections like **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia** might be indicated, making avoidance inappropriate.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old man interested in pre-exposure therapy for HIV (PrEP) is being evaluated to qualify for a PrEP study. In order to qualify, patients must be HIV- and hepatitis B- and C-negative. Any other sexually transmitted infections require treatment prior to initiation of PrEP. The medical history is positive for a prior syphilis infection and bipolar affective disorder, for which he takes lithium. On his next visit, the liver and renal enzymes are within normal ranges. HIV and hepatitis B and C tests are negative. Which of the following about the HIV test is true?
- A. It is a quantitative test used for screening purposes.
- B. It is a qualitative test used for screening purposes. (Correct Answer)
- C. A secondary reagent is needed to interpret the results.
- D. A known antigen binds directly to the patient's serum.
- E. An unknown antigen binds to the known serum.
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***It is a qualitative test used for screening purposes.***
- **HIV screening tests** (e.g., 4th generation antibody/antigen combination assays) are typically **qualitative**, meaning they detect the presence or absence of HIV markers, not their exact amount.
- These tests are primarily used for broad **screening** of populations to identify potential cases of HIV infection.
*It is a quantitative test used for screening purposes.*
- **Quantitative tests** for HIV, such as viral load tests, measure the amount of virus in the blood and are typically used for monitoring disease progression or treatment effectiveness, not for initial screening.
- Screening tests are designed for high sensitivity to detect infection, even with low viral loads or early antibody responses, making a quantitative measurement less relevant for initial screening.
*A secondary reagent is needed to interpret the results.*
- While some complex immunoassays might involve multiple steps, modern **HIV screening tests** often use advanced technologies that directly yield results, making a separate secondary reagent for interpretation generally unnecessary.
- The results are typically indicated by a color change or a signal detected by an instrument, without requiring an additional interpretive reagent.
*A known antigen binds directly to the patient's serum.*
- **HIV antibody tests** detect **antibodies** produced by the patient's immune system in response to HIV infection.
- In such tests, **known HIV antigens** (from the test kit) bind to **HIV-specific antibodies present in the patient's serum**, not to serum components directly.
- This option is incorrect because it omits the critical role of antibodies as the target molecules being detected.
*An unknown antigen binds to the known serum.*
- This statement describes a different type of immunological assay where an unknown antigen is being identified using a known antibody, which is contrary to how **HIV screening tests** for infection are typically structured.
- **HIV screening tests** use known components (e.g., HIV antigens or antibodies) in the test kit to detect unknown components (e.g., HIV antibodies or viral antigens) in the patient's sample.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 6: A student health coordinator plans on leading a campus-wide HIV screening program that will be free for the entire undergraduate student body. The goal is to capture as many correct HIV diagnoses as possible with the fewest false positives. The coordinator consults with the hospital to see which tests are available to use for this program. Test A has a sensitivity of 0.92 and a specificity of 0.99. Test B has a sensitivity of 0.95 and a specificity of 0.96. Test C has a sensitivity of 0.98 and a specificity of 0.93. Which of the following testing schemes should the coordinator pursue?
- A. Test A on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive
- B. Test A on the entire student body followed by Test C on those who are positive
- C. Test C on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive
- D. Test C on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive (Correct Answer)
- E. Test B on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***Test C on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive***
- To "capture as many correct HIV diagnoses as possible" (maximize true positives), the initial screening test should have the **highest sensitivity**. Test C has the highest sensitivity (0.98).
- To "capture as few false positives as possible" (maximize true negatives and confirm diagnoses), the confirmatory test should have the **highest specificity**. Test A has the highest specificity (0.99).
*Test A on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive*
- Starting with Test A (sensitivity 0.92) would miss more true positive cases than starting with Test C (sensitivity 0.98), failing the goal of **capturing as many cases as possible**.
- Following with Test B (specificity 0.96) would result in more false positives than following with Test A (specificity 0.99).
*Test A on the entire student body followed by Test C on those who are positive*
- This scheme would miss many true positive cases initially due to Test A's lower sensitivity compared to Test C.
- Following with Test C would introduce more false positives than necessary, as it has a lower specificity (0.93) than Test A (0.99).
*Test C on the entire student body followed by Test B on those who are positive*
- While Test C is a good initial screen for its high sensitivity, following it with Test B (specificity 0.96) is less optimal than Test A (specificity 0.99) for minimizing false positives in the confirmation step.
- This combination would therefore yield more false positives in the confirmatory stage than using Test A.
*Test B on the entire student body followed by Test A on those who are positive*
- Test B has a sensitivity of 0.95, which is lower than Test C's sensitivity of 0.98, meaning it would miss more true positive cases at the initial screening stage.
- While Test A provides excellent specificity for confirmation, the initial screening step is suboptimal for the goal of capturing as many diagnoses as possible.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 7: A 44-year-old man with HIV comes to the physician for a routine follow-up examination. He has been noncompliant with his antiretroviral medication regimen for several years. He appears chronically ill and fatigued. CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 180/mm³ (N ≥ 500). Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Multifocal demyelination on brain MRI
- B. Violaceous lesions on skin exam (Correct Answer)
- C. Ring-enhancing lesions on brain MRI
- D. Cotton-wool spots on fundoscopy
- E. Ground-glass opacities on chest CT
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***Violaceous lesions on skin exam***
- A CD4 count of 180/mm³ indicates severe **immunosuppression**, making the patient highly susceptible to **opportunistic infections** and cancers, such as Kaposi sarcoma.
- **Kaposi sarcoma** typically presents with violaceous (purple-blue) cutaneous lesions, which are often the initial manifestation of the disease in HIV-positive patients.
*Multifocal demyelination on brain MRI*
- This finding is characteristic of **progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)**, caused by the **JC virus**.
- PML typically occurs at **CD4 counts below 100/mm³**, lower than the patient's current count, although still possible with severe immunosuppression.
*Ring-enhancing lesions on brain MRI*
- **Ring-enhancing lesions** on brain MRI are often seen in cerebral **toxoplasmosis** or CNS **lymphoma** in HIV patients.
- Toxoplasmosis usually presents with focal neurological deficits and seizures, and is more common with CD4 counts below 100/mm³.
*Cotton-wool spots on fundoscopy*
- **Cotton-wool spots** are a common finding in **HIV retinopathy** due to retinal ischemia.
- While possible, they are non-specific and are usually asymptomatic, whereas the patient's presentation suggests a more prominent and diagnosable condition.
*Ground-glass opacities on chest CT*
- **Ground-glass opacities** on chest CT are characteristic of **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)**, a common opportunistic infection in HIV patients.
- While PJP is a strong possibility with a CD4 count <200/mm³, the question asks for a finding that is *most likely* given the patient's general appearance and the option of Kaposi sarcoma, which manifests directly on examination.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator is studying the mechanism of HIV infection in cells obtained from a human donor. The effect of a drug that impairs viral fusion and entry is being evaluated. This drug acts on a protein that is cleaved off of a larger glycosylated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum of the host cell. The protein that is affected by the drug is most likely encoded by which of the following genes?
- A. gag
- B. env (Correct Answer)
- C. tat
- D. pol
- E. rev
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***env***
- The **env (envelope) gene** of HIV encodes for the precursor protein **gp160**, which is then cleaved by host cellular proteases into **gp120** and **gp41** within the endoplasmic reticulum.
- **gp120** and **gp41** together form the viral envelope glycoproteins responsible for viral binding to host cells and **fusion/entry**, making them the target of drugs that impair these processes.
*gag*
- The **gag (group-specific antigen) gene** encodes for structural proteins of the viral core, such as **p24 (capsid protein)**, p17 (matrix protein), and p7 (nucleocapsid protein).
- These proteins are primarily involved in the assembly of new virions and do not directly mediate viral fusion and entry.
*tat*
- The **tat (trans-activator of transcription) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that significantly enhances the transcription of viral genes.
- It plays a crucial role in the viral life cycle by increasing the efficiency of HIV gene expression, but it is not directly involved in viral fusion or entry.
*pol*
- The **pol (polymerase) gene** encodes for essential viral enzymes, including **reverse transcriptase**, integrase, and protease.
- These enzymes are critical for converting viral RNA into DNA, integrating viral DNA into the host genome, and cleaving viral polyproteins, respectively, but they are not involved in mediating viral entry.
*rev*
- The **rev (regulator of virion expression) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that facilitates the transport of unspliced and partially spliced viral RNAs from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- This transport is crucial for the synthesis of structural and enzymatic proteins and for packaging viral RNA into new virions, but it does not directly participate in viral fusion and entry.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old woman tests positive for HIV during pregnancy screening. She is concerned about transmission to her baby. Which of the following interventions most significantly reduces the risk of vertical transmission?
- A. Avoiding breastfeeding only
- B. Cesarean delivery only
- C. Antiretroviral therapy during pregnancy and labor (Correct Answer)
- D. Maternal immunization
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***Antiretroviral therapy during pregnancy and labor***
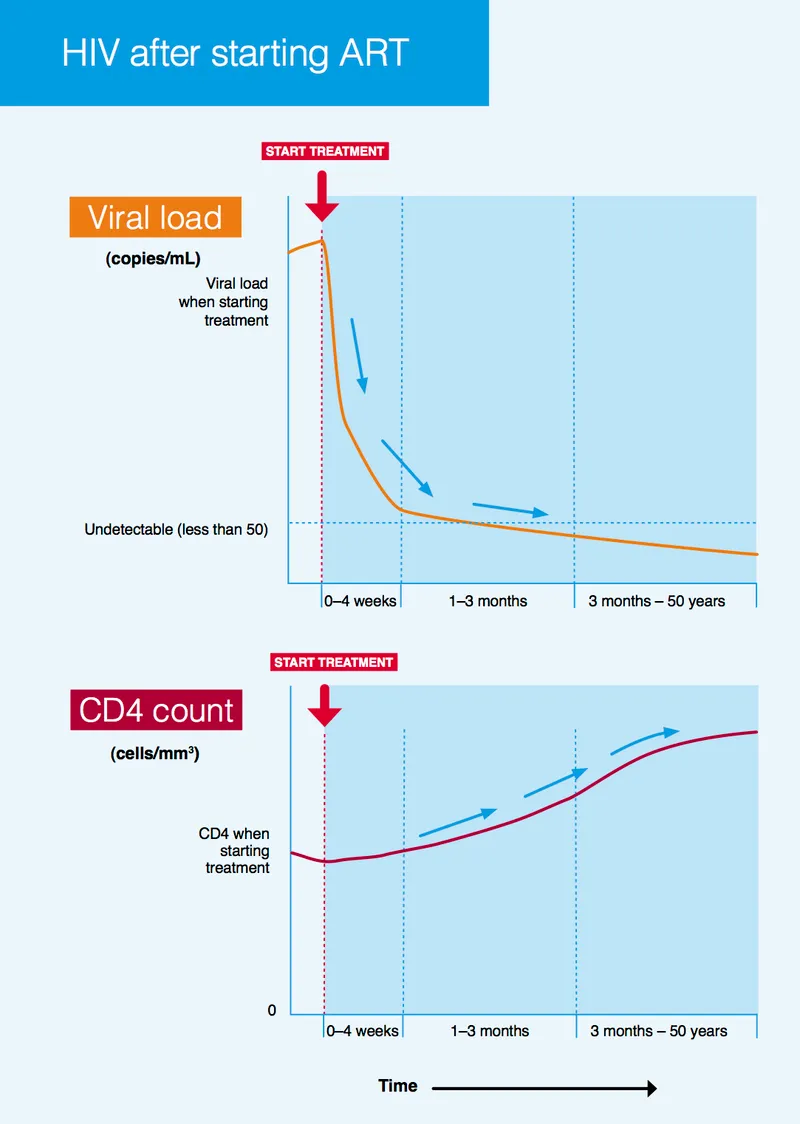
- **Antiretroviral therapy (ART)** significantly reduces the **viral load** in the mother, thereby minimizing the risk of HIV transmission to the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth.
- When combined with other strategies like **cesarean section** and **avoidance of breastfeeding** in developed countries, ART can reduce vertical transmission rates to less than 1%.
*Avoiding breastfeeding only*
- While **avoiding breastfeeding** is a crucial intervention, especially in settings where safe alternatives are available, it addresses only one mode of transmission (postnatal).
- It does not prevent **in-utero** or **intrapartum transmission**, which are primary routes of vertical transmission if the viral load is high.
*Cesarean delivery only*
- **Cesarean delivery** can reduce the risk of transmission by avoiding exposure to maternal blood and secretions during vaginal delivery.
- However, it is most effective when the maternal **viral load is high** and is often combined with ART for maximum efficacy; it's less effective without ART.
*Maternal immunization*
- **Maternal immunization** involves administering vaccines to the mother to protect against specific infections, primarily bacterial or viral diseases like influenza or tetanus.
- It has **no direct impact** on the risk of HIV transmission, as there is currently no vaccine available for HIV.
CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old pregnant woman presents to an obstetrician at 35 weeks gestation reporting that she noted the presence of a mucus plug in her vaginal discharge this morning. The obstetrician performs an examination and confirms that she is in labor. She was diagnosed with HIV infection 1 year ago. Her current antiretroviral therapy includes abacavir, lamivudine, and nevirapine. Her last HIV RNA level was 2,000 copies/mL 3 weeks ago. Which of the following anti-retroviral drugs should be administered intravenously to the woman during labor?
- A. Enfuvirtide
- B. Nevirapine
- C. Abacavir
- D. Rilpivirine
- E. Zidovudine (Correct Answer)
CD4 monitoring and viral load Explanation: ***Zidovudine***
- Intravenous **zidovudine** is recommended during labor for HIV-positive pregnant women, especially when the viral load is **>1000 copies/mL**, to reduce the risk of **mother-to-child transmission (MTCT)**.
- This intervention significantly lowers the viral load in the maternal blood and reduces fetal exposure to the virus during delivery.
*Enfuvirtide*
- **Enfuvirtide** is a **fusion inhibitor** administered subcutaneously, not intravenously, and is reserved for treatment-experienced patients with multi-drug resistant HIV.
- It is not a standard recommendation for intrapartum prophylaxis against MTCT.
*Nevirapine*
- **Nevirapine** is an **NNRTI** that is typically given orally, and while it has been used for MTCT prophylaxis, intravenous administration is not standard for intrapartum use.
- The woman is already on oral nevirapine as part of her ART regimen.
*Abacavir*
- **Abacavir** is an **NRTI** given orally and is part of the patient's current ART regimen.
- It is not administered intravenously for intrapartum MTCT prophylaxis.
*Rilpivirine*
- **Rilpivirine** is an **NNRTI** that is taken orally and is not indicated for intravenous administration during labor to prevent MTCT.
- Its use is limited by potential drug interactions and efficacy in patients with high viral loads.
More CD4 monitoring and viral load US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.