Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antiretroviral therapy principles. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 1 week after being admitted to the hospital for oral candidiasis and esophagitis. His CD4+ T lymphocyte count is 180 cells/μL. An HIV antibody test is positive. Genotypic resistance assay shows the virus to be susceptible to all antiretroviral therapy regimens and therapy with dolutegravir, tenofovir, and emtricitabine is initiated. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings would be most likely on follow-up evaluation 3 months later?
$$$ CD4 +/CD8 ratio %%% HIV RNA %%% HIV antibody test $$$
- A. ↓ ↓ negative
- B. ↑ ↑ negative
- C. ↓ ↑ negative
- D. ↑ ↓ positive (Correct Answer)
- E. ↓ ↑ positive
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***↑ ↓ positive***
- With effective **antiretroviral therapy (ART)**, the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would increase as **CD4+ T cell counts rise** and **CD8+ T cell counts decrease**.
- **HIV RNA (viral load)** would significantly decrease (ideally to undetectable levels) due to the suppression of viral replication, but HIV antibodies would remain positive indefinitely.
*↓ ↓ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** and **HIV RNA** (viral load) along with a negative **HIV antibody test** is inconsistent with successful ART.
- A negative HIV antibody test would mean the patient was never infected, which contradicts the initial positive result and symptoms.
*↑ ↑ negative*
- An increase in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** is expected with ART, but an increase in **HIV RNA** (viral load) indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is impossible after a confirmed positive result, regardless of treatment success.
*↓ ↑ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would suggest worsening immune function, while an increase in **HIV RNA** indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is not possible once a patient has developed antibodies to HIV.
*↓ ↑ positive*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would indicate immune decline, contrary to the expected improvement with effective ART.
- An increase in **HIV RNA (viral load)** would signify treatment failure, even if HIV antibodies remain positive.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 2: A 37-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of progressive breast enlargement. Two years ago, he was diagnosed with HIV infection and started treatment with antiretroviral medications. Examination shows a soft, non-tender, ill-defined swelling at the nape of the neck. The cheeks appear hollowed. Serum studies show increased total cholesterol and LDL concentration. Which of the following medications is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Nevirapine
- B. Indinavir (Correct Answer)
- C. Enfuvirtide
- D. Abacavir
- E. Raltegravir
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***Indinavir***
- This patient presents with signs of **lipodystrophy**, specifically **lipoaccumulation** (breast enlargement, "buffalo hump" at the nape of the neck) and **lipoatrophy** (hollow cheeks), along with **dyslipidemia**.
- **Protease inhibitors (PIs)**, such as indinavir, are well-known to cause these metabolic complications, including **lipodystrophy** and **hyperlipidemia**, in patients with HIV.
*Nevirapine*
- Nevirapine is a **non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI)**.
- While NNRTIs can be associated with some metabolic side effects, they are less commonly implicated in severe **lipodystrophy** and **dyslipidemia** compared to protease inhibitors.
*Enfuvirtide*
- Enfuvirtide is a **fusion inhibitor** and generally has a favorable metabolic profile.
- It is not typically associated with **lipodystrophy** or significant **dyslipidemia**.
*Abacavir*
- Abacavir is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)**.
- While some NRTIs (especially stavudine and zidovudine) were strongly linked to lipoatrophy, abacavir is much less likely to cause this severe form of **lipodystrophy** or **hyperlipidemia**.
*Raltegravir*
- Raltegravir is an **integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)**.
- INSTIs are increasingly used due to their generally good metabolic profile and are not a common cause of **lipodystrophy** or **dyslipidemia**.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 3: A 35-year-old woman presents to a physician’s office for a follow-up visit. She recently underwent a complete physical examination with routine laboratory tests. She also had a Pap smear and testing for sexually transmitted diseases. Since her divorce 2 years ago, she had sexual encounters with random men at bars or social events and frequently did not use any form of contraception during sexual intercourse. She was shown to be positive for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Combination anti-retroviral treatment is initiated including zidovudine, didanosine, and efavirenz. One week later, she is rushed to the hospital where she is diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. Which of the following precautions will be required after pancreatitis resolves with treatment?
- A. Frequent monitoring of CD4+ cell count
- B. Add ritonavir to the HIV treatment regimen
- C. Replace efavirenz with nevirapine
- D. Replace didanosine with lamivudine (Correct Answer)
- E. Check hemoglobin levels
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***Replace didanosine with lamivudine***
- **Didanosine (ddI)** is known to cause **pancreatitis** as a significant adverse effect and should be discontinued if pancreatitis occurs. Replacing it with **lamivudine** is appropriate because lamivudine is also a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) and does not typically cause pancreatitis.
- This step ensures that the medication causing the adverse reaction is removed while maintaining an effective anti-retroviral regimen
*Frequent monitoring of CD4+ cell count*
- While **CD4+ cell count monitoring** is crucial in HIV management to assess immune status and treatment efficacy, it is a routine part of HIV care and not a specific precaution for resolving pancreatitis.
- Pancreatitis itself does not directly alter the *frequency* of CD4+ monitoring beyond standard HIV care protocols.
*Add ritonavir to the HIV treatment regimen*
- **Ritonavir** is a **protease inhibitor** and a strong pharmacokinetic booster, but adding it without specific indication or considering potential drug interactions is not the appropriate first step for managing pancreatitis.
- It might increase the risk of other side effects or alter the metabolism of other antiretrovirals, and is not directly related to managing didanosine-induced pancreatitis.
*Replace efavirenz with nevirapine*
- **Efavirenz** and **nevirapine** are both **non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)**. Replacing efavirenz with nevirapine is a change within the NNRTI class and is not indicated as a direct result of didanosine-induced pancreatitis.
- Both drugs have their own side effect profiles, and switching between them would be based on issues specific to the NNRTI chosen, not the pancreatitis induced by didanosine.
*Check hemoglobin levels*
- While **zidovudine (AZT)** can cause **bone marrow suppression** leading to **anemia** and requiring hemoglobin monitoring, this is a known side effect of zidovudine itself, not a specific precaution *after pancreatitis resolves* that was induced by didanosine.
- Checking hemoglobin would be part of routine monitoring for patients on zidovudine, but not the primary intervention for pancreatitis resolution in this context.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 4: A 43-year-old man with HIV infection comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of progressive diarrhea and a 3-kg (6.6-lb) weight loss. During this period, he has had 3–4 episodes of watery stools daily, with multiple instances of blood in the stool. He is currently receiving antiretroviral therapy with zidovudine, lamivudine, and dolutegravir. Physical examination shows pallor and dry mucous membranes. A colonoscopy shows multiple linear ulcers. Polymerase chain reaction of a stool sample is positive for cytomegalovirus. Treatment with valganciclovir is begun. Adding this drug to his current medication regimen puts this patient at greatest risk for which of the following adverse effects?
- A. Hepatic steatosis
- B. Abnormal dreams
- C. Pancytopenia (Correct Answer)
- D. Orthostatic dysregulation
- E. Hyperglycemia
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***Pancytopenia***
- **Valganciclovir** is a known cause of **bone marrow suppression**, leading to **pancytopenia** (low red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets).
- The patient is also on **zidovudine**, an antiretroviral that can cause **myelosuppression**, thus the combined use significantly increases the risk of pancytopenia.
*Hepatic steatosis*
- **Hepatic steatosis** (fatty liver) is a rare but known adverse effect of some nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), particularly older ones.
- While lamivudine is an NRTI, **valganciclovir** is not primarily associated with hepatic steatosis, and the combination does not specifically heighten this risk more than other options.
*Abnormal dreams*
- **Abnormal dreams** are a common side effect associated with certain antiretroviral drugs, particularly the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor **efavirenz**.
- This patient is on dolutegravir (an integrase inhibitor), zidovudine, and lamivudine, none of which are primarily known for causing abnormal dreams as a prominent side effect, and valganciclovir does not contribute to this.
*Orthostatic dysregulation*
- **Orthostatic dysregulation** (orthostatic hypotension) can be a side effect of various medications, but it is not a prominent adverse effect of either **valganciclovir** or the patient's current antiretroviral regimen.
- While dehydration from diarrhea can cause it, the medication itself does not directly increase this risk in particular.
*Hyperglycemia*
- **Hyperglycemia** can be a side effect of certain antiretroviral drugs, particularly some **protease inhibitors** and older NRTIs.
- However, the patient's current regimen (zidovudine, lamivudine, dolutegravir) and **valganciclovir** are not strongly associated with hyperglycemia as a primary adverse effect compared to other options.
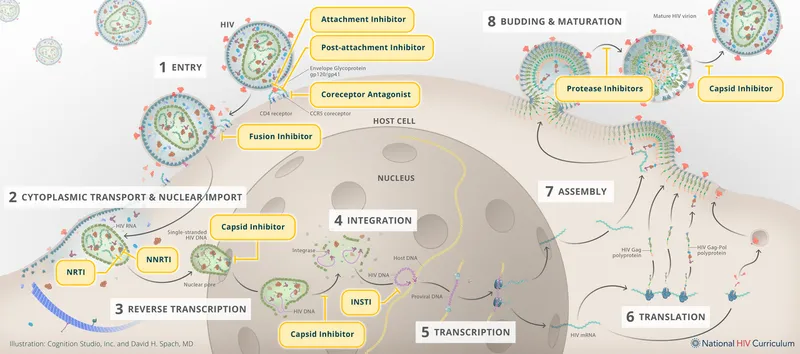
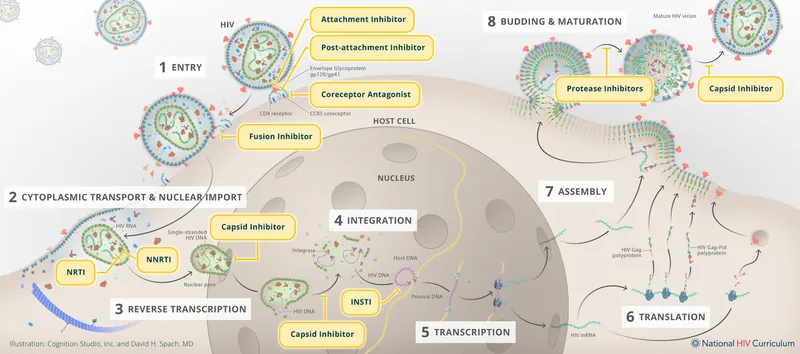
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 5: An investigator is studying the mechanism of HIV infection in cells obtained from a human donor. The effect of a drug that impairs viral fusion and entry is being evaluated. This drug acts on a protein that is cleaved off of a larger glycosylated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum of the host cell. The protein that is affected by the drug is most likely encoded by which of the following genes?
- A. gag
- B. env (Correct Answer)
- C. tat
- D. pol
- E. rev
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***env***
- The **env (envelope) gene** of HIV encodes for the precursor protein **gp160**, which is then cleaved by host cellular proteases into **gp120** and **gp41** within the endoplasmic reticulum.
- **gp120** and **gp41** together form the viral envelope glycoproteins responsible for viral binding to host cells and **fusion/entry**, making them the target of drugs that impair these processes.
*gag*
- The **gag (group-specific antigen) gene** encodes for structural proteins of the viral core, such as **p24 (capsid protein)**, p17 (matrix protein), and p7 (nucleocapsid protein).
- These proteins are primarily involved in the assembly of new virions and do not directly mediate viral fusion and entry.
*tat*
- The **tat (trans-activator of transcription) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that significantly enhances the transcription of viral genes.
- It plays a crucial role in the viral life cycle by increasing the efficiency of HIV gene expression, but it is not directly involved in viral fusion or entry.
*pol*
- The **pol (polymerase) gene** encodes for essential viral enzymes, including **reverse transcriptase**, integrase, and protease.
- These enzymes are critical for converting viral RNA into DNA, integrating viral DNA into the host genome, and cleaving viral polyproteins, respectively, but they are not involved in mediating viral entry.
*rev*
- The **rev (regulator of virion expression) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that facilitates the transport of unspliced and partially spliced viral RNAs from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- This transport is crucial for the synthesis of structural and enzymatic proteins and for packaging viral RNA into new virions, but it does not directly participate in viral fusion and entry.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 6: A 35-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of fatigue and increased sweating at night. He says that he feels “constantly tired” and needs more rest than usual although he sleeps well. In the morning, his sheets are often wet and his skin is clammy. He has not had any sore throat, runny nose, or cough recently. He has not traveled anywhere. Over the past 4 months, he has had a 6.8-kg (15-lb) weight loss, despite having a normal appetite. He does not drink or urinate more than usual. He is 181 cm (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 72 kg (159 lb); BMI is 22 kg/m2. His temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 65/min, and blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. An HIV screening test and confirmatory test are both positive. The CD4 count is 600 cells/μl and the viral load is 104 copies/mL. Treatment with lamivudine, zidovudine, and indinavir is begun. The patient is at greatest risk for which of the following adverse effects?
- A. Urolithiasis (Correct Answer)
- B. Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- C. Hypersensitivity reaction
- D. Chronic kidney disease
- E. Pancreatitis
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***Urolithiasis***
- The patient is receiving **indinavir**, a protease inhibitor known to cause **nephrolithiasis** (kidney stones) due to the drug's poor solubility.
- Patients on indinavir should be well-hydrated to reduce the risk of stone formation.
*Stevens-Johnson syndrome*
- This severe skin reaction is more commonly associated with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) like **nevirapine** and **efavirenz**, or with sulfonamide antibiotics, rather than indinavir.
- While possible with many drugs, it is not the *greatest risk* among the options for this specific regimen.
*Hypersensitivity reaction*
- While hypersensitivity can occur with many drugs, particularly abacavir (an NRTI not included in this regimen), it is not the most prominent or specific adverse effect for the given combination, especially indinavir.
- Symptoms usually include fever, rash, and multi-organ involvement, which can be acute.
*Chronic kidney disease*
- While some antiretrovirals, particularly **tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)**, can cause renal tubular dysfunction and lead to chronic kidney disease, TDF is not part of this patient's regimen.
- Indinavir's primary renal complication is acute stone formation, not typically chronic kidney disease in the absence of pre-existing conditions or other nephrotoxic drugs.
*Pancreatitis*
- Pancreatitis is a known adverse effect of some NRTIs, particularly **didanosine** and **stavudine**, neither of which are in this patient's treatment plan.
- Lamivudine and zidovudine have a lower risk of pancreatitis compared to other NRTIs.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 7: A 46-year-old woman comes to the physician for a 6-month history of worsening bronchial asthma control. Before this issue began, she only used her salbutamol inhaler once a day. Now, she has to use it multiple times daily and also reports frequent nighttime awakening. Seven months ago, she moved to an apartment that is damp and has mold on some of the walls. The physician injects 0.1 mL of Candida albicans extract on the mid-volar surface of the right arm intradermally. After 48 hours there is a palpable induration of 17 mm. This reaction is most likely a result of release of which of the following substances?
- A. Interleukin-10
- B. Superoxide anion
- C. Tryptase
- D. Interferon-γ (Correct Answer)
- E. Lysozyme
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***Interferon-γ***
- The patient's worsened asthma, fungal exposure, and positive delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) skin test to *Candida albicans* suggest a **Th1-mediated immune response**.
- **Interferon-γ (IFN-γ)** is a key cytokine produced by Th1 cells, crucial for activating macrophages and cell-mediated immunity, which drives the induration observed in DTH reactions.
*Interleukin-10*
- **Interleukin-10 (IL-10)** is primarily an **anti-inflammatory cytokine** that suppresses immune responses, particularly Th1 and Th2 activity.
- Its release is associated with downregulating, rather than mediating, the robust inflammatory reaction seen in a positive DTH test.
*Superoxide anion*
- **Superoxide anion** is a reactive oxygen species produced by phagocytes (e.g., neutrophils, macrophages) as part of the **respiratory burst** to kill ingested pathogens.
- While important for host defense, it is not the primary mediator responsible for the induration and cellular infiltration characteristic of a *Candida* DTH skin test.
*Tryptase*
- **Tryptase** is an enzyme released by **mast cells** upon activation, typically during **immediate hypersensitivity reactions (Type I)**.
- Its presence is indicative of allergic reactions mediated by IgE, which manifest as wheal and flare, not the delayed induration seen in this case.
*Lysozyme*
- **Lysozyme** is an enzyme found in secretions (e.g., tears, saliva) and phagocytes, which degrades bacterial cell walls.
- It plays a role in innate immunity against bacteria but is not directly involved in the mediation of a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to fungal antigens.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 8: A 39-year-old man presents with a 4-week history of painless, non-discharging lesions on his penis and scrotum. He was diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukemia two years ago and treated with imatinib. He currently takes no medications. He has a 20-pack-year smoking history and drinks 1-2 beers on weekends. He reports unprotected intercourse with a woman while traveling abroad 4 months ago. His temperature is 37°C, pulse is 85/min, and blood pressure is 128/82 mm Hg. Examination reveals three non-tender lesions, each approximately 1 cm in size, on his genitalia. There is no inguinal lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
- A. Haemophilus ducreyi
- B. Chlamydia trachomatis
- C. Treponema pallidum (Correct Answer)
- D. Herpes simplex virus
- E. Klebsiella granulomatis
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***Treponema pallidum***
- The presentation of **painless, non-discharging genital lesions** (chancre) after unprotected intercourse 4 months prior is highly characteristic of **primary syphilis**, caused by *Treponema pallidum*.
- The absence of **inguinal lymphadenopathy** is not uncommon in early primary syphilis, and the patient's history of travel and unprotected sex increases the risk.
*Haemophilus ducreyi*
- This bacterium causes **chancroid**, which typically presents as **painful genital ulcers** with irregular borders and often significant **inguinal lymphadenopathy** (buboes).
- The patient's lesions are described as painless, ruling out chancroid.
*Chlamydia trachomatis*
- While certain serovars of *Chlamydia trachomatis* cause **lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)**, initial lesions are usually small, transient, and often go unnoticed, followed by prominent and often painful **inguinal lymphadenopathy**.
- Other serovars cause nongonococcal urethritis or cervicitis, which do not typically present with the described painless ulcers.
*Herpes simplex virus*
- **Herpes simplex virus (HSV)** infection usually causes **painful, vesicular lesions** that can ulcerate and crust, often accompanied by prodromal symptoms like itching or tingling.
- The lesions in this case are described as painless and non-vesicular.
*Klebsiella granulomatis*
- This organism causes **granuloma inguinale (donovanosis)**, which is characterized by **painless, beefy-red, friable ulcers** that can be extensive and bleed easily.
- While painless, the description of "non-discharging lesions" and the typical appearance of syphilis differ from the classic "beefy red" appearance of donovanosis.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 9: A 5-year-old African American female has experienced recurrent respiratory infections. To determine how well her cell-mediated immunity is performing, a Candida skin injection is administered. After 48 hours, there is no evidence of induration at the injection site. Of the following cell types, which one would normally mediate this type of immune reaction?
- A. Plasma cells
- B. Fibroblasts
- C. T-cells (Correct Answer)
- D. Mast cells
- E. Basophils
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***T-cells***
- The **Candida skin injection** tests for **delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH)**, also known as **Type IV hypersensitivity**, which is a classic example of **cell-mediated immunity**.
- **CD4+ Th1 helper T-cells** are the primary mediators of DTH responses. Upon re-exposure to Candida antigens, these memory T-cells release **IFN-γ and other cytokines** that recruit and activate **macrophages**, causing **induration** at the injection site within **48-72 hours**.
- The absence of induration in this patient suggests **impaired cell-mediated immunity**, which explains her recurrent infections.
*Plasma cells*
- **Plasma cells** are responsible for producing and secreting **antibodies**, which are part of the **humoral immune response** (Type II and III hypersensitivity), not cell-mediated immunity.
- While antibodies can play a role in fighting infections, they do not mediate the DTH reaction observed in a skin test.
*Fibroblasts*
- **Fibroblasts** are connective tissue cells involved in wound healing and structural support in tissues, producing **collagen** and other extracellular matrix components.
- They do not directly participate in the initiation or mediation of immune responses like cell-mediated hypersensitivity.
*Mast cells*
- **Mast cells** are primarily involved in **allergic reactions** and defense against parasites through the release of **histamine** and other inflammatory mediators.
- They mediate **immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions (Type I)**, which occur within minutes, not the delayed-type hypersensitivity response tested by a Candida skin injection that peaks at 48-72 hours.
*Basophils*
- **Basophils** are granulocytes that release **histamine** and other mediators, similar to mast cells, and are involved in **allergic reactions** and **parasitic infections**.
- Like mast cells, they primarily contribute to **Type I immediate hypersensitivity**, not the cell-mediated response of DTH.
Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG Question 10: Four scientists were trying to measure the effect of a new inhibitor X on the expression levels of transcription factor, HNF4alpha. They measured the inhibition levels by using RT-qPCR. In short they converted the total mRNA of the cells to cDNA (RT part), and used PCR to amplify the cDNA quantifying the amplification with a dsDNA binding dye (qPCR part). Which of the following group characteristics contains a virus(es) that has the enzyme necessary to convert the mRNA to cDNA used in the above scenario?
- A. Enveloped, dimeric (+) ssRNA (Correct Answer)
- B. Enveloped, circular (-) ssRNA
- C. Nonenveloped, (+) ssRNA
- D. Nonenveloped, ssDNA
- E. Nonenveloped, circular dsDNA
Antiretroviral therapy principles Explanation: ***Enveloped, dimeric (+) ssRNA***
- This group describes **retroviruses**, which possess the enzyme **reverse transcriptase**.
- **Reverse transcriptase** is essential for converting their **RNA genome** into **cDNA**, a process analogous to the RT step in RT-qPCR.
- Examples include **HIV**, which is tagged to this topic.
*Enveloped, circular (-) ssRNA*
- This description does not accurately represent a major viral family.
- Most enveloped negative-sense RNA viruses have **linear or segmented genomes** (e.g., **Orthomyxoviruses**, **Bunyaviruses**), not circular.
- These viruses replicate using an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase** to synthesize mRNA from their negative-sense RNA genome.
- They do not inherently carry or require **reverse transcriptase** for their life cycle.
*Nonenveloped, (+) ssRNA*
- These viruses, like **Picornaviruses**, directly use their positive-sense RNA as mRNA and replicate via an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase**.
- They do not possess **reverse transcriptase** for cDNA synthesis.
*Nonenveloped, ssDNA*
- Viruses with a **single-stranded DNA genome**, such as **Parvoviruses**, replicate by first synthesizing a double-stranded DNA intermediate.
- Their replication machinery does not involve **reverse transcriptase** to convert RNA to DNA.
*Nonenveloped, circular dsDNA*
- Viruses in this group, like **Papillomaviruses** and **Polyomaviruses**, have a circular double-stranded DNA genome and replicate within the host nucleus using the host's DNA polymerase.
- They do not utilize or encode **reverse transcriptase** for their replication cycle.
More Antiretroviral therapy principles US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.