Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Natural history of HCV infection. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 1: A 60-year-old rock musician presents to the office because he has been feeling increasingly tired for the past 6 months. He has a history of intravenous drug use and alcohol abuse. He states that he feels quite tired, but he otherwise has no complaints. Physical examination is noncontributory. His laboratory values are normal other than moderately elevated liver enzymes. Which of the following additional tests should you order first?
- A. Hepatitis C virus antibodies (Correct Answer)
- B. Hepatitis B surface antigen
- C. Hepatitis E virus-specific IgM antibodies
- D. Hepatitis D virus-specific IgG antibody
- E. Hepatitis A virus-specific IgM antibodies
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Hepatitis C virus antibodies***
- The patient's history of **intravenous drug use** and **chronic fatigue** with **elevated liver enzymes** strongly suggests chronic viral hepatitis, with hepatitis C being the most common blood-borne infection in persons with IVDU history.
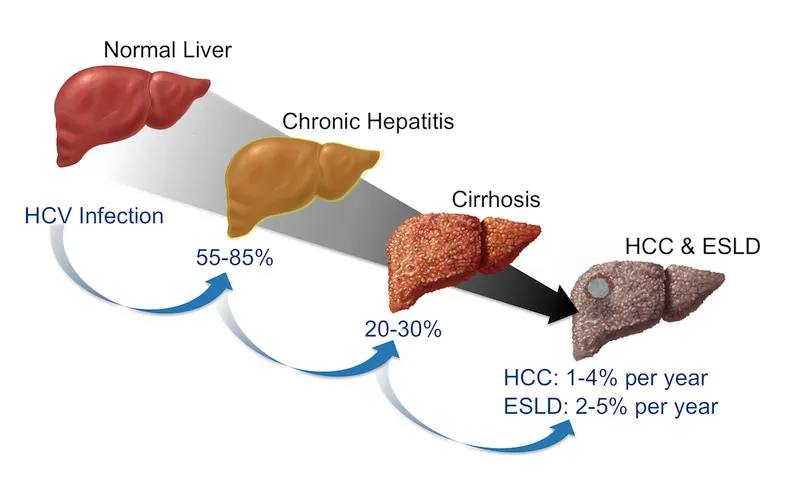
- **Hepatitis C** is the **most prevalent chronic viral hepatitis** in the United States among persons with history of injection drug use, with transmission efficiency via needle sharing being very high.
- Hepatitis C often has a **long asymptomatic phase** (decades) before symptoms like fatigue and liver damage become apparent, making antibody testing the appropriate initial screen.
- While both HBV and HCV should ultimately be screened in this patient, **HCV prevalence is significantly higher** in the IVDU population, making it the priority initial test.
*Hepatitis B surface antigen*
- While **hepatitis B** can also be transmitted via intravenous drug use and cause chronic liver disease, **hepatitis C is more prevalent** in persons with IVDU history in the United States.
- **HBsAg** is used to detect active hepatitis B infection and should also be ordered, but given resource constraints and the clinical context, **anti-HCV is the higher-yield initial test**.
- Many IVDU patients have been vaccinated against HBV, further reducing its likelihood compared to HCV (for which no vaccine exists).
*Hepatitis E virus-specific IgM antibodies*
- **Hepatitis E** is typically transmitted via the **fecal-oral route** (contaminated water) and usually causes **acute, self-limiting hepatitis**, not chronic insidious fatigue and liver enzyme elevation in a Western patient.
- **IgM antibodies** would indicate an acute infection, which is less likely given the 6-month duration of symptoms.
- HEV rarely causes chronic infection except in immunocompromised patients.
*Hepatitis D virus-specific IgG antibody*
- **Hepatitis D** requires an existing **hepatitis B infection** to replicate (it's a satellite virus), meaning you would first need to confirm chronic hepatitis B before testing for HDV.
- While HDV can cause severe liver disease and is transmitted via blood exposure, it's not the initial test to pursue without evidence of HBV co-infection.
*Hepatitis A virus-specific IgM antibodies*
- **Hepatitis A** is transmitted via the **fecal-oral route** and causes an **acute, self-limiting infection** with complete resolution, rarely leading to chronic liver disease or persistent fatigue over 6 months.
- **IgM antibodies** are indicative of acute infection, which contradicts the chronic nature of the patient's symptoms.
- HAV does not cause chronic hepatitis.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 2: A previously healthy 25-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a one-week history of diffuse abdominal pain. Her temperature is 39.1°C (102.3°F). Physical examination shows numerous scars and excoriations along both arms, scleral icterus, and tender hepatomegaly. Serum studies show:
Alanine aminotransferase 927 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase 796 U/L
Hepatitis B surface antigen positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody negative
Anti-hepatitis B core antibody positive
Hepatitis C antibody negative
Which of the following is the most likely outcome of this patient's infection?
- A. Fulminant hepatitis
- B. Asymptomatic carrier state
- C. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- D. Liver cirrhosis
- E. Transient infection (Correct Answer)
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Transient infection***
- The patient has classic signs of **acute hepatitis B viral infection** (**icterus**, **tender hepatomegaly**, very high **ALT/AST**), and the serology (HBsAg+, anti-HBc+, HBsAb-) confirms an acute infection.
- The majority of immunocompetent adults (95%) with acute HBV infection will have a **transient infection** that resolves completely, leading to seroconversion (HBsAb+ and HBsAg- later).
*Fulminant hepatitis*
- While possible in acute HBV, **fulminant hepatitis** is rare (less than 1%) and characterized by rapid liver failure with **hepatic encephalopathy** and coagulopathy, which are not described.
- The patient's symptoms, though severe, do not meet the criteria for fulminant liver failure.
*Asymptomatic carrier state*
- An **asymptomatic carrier state** usually occurs when the immune system fails to clear the virus, leading to chronic infection with persistent HBsAg.
- While this is a possibility for some individuals, the patient's severe symptoms and high transaminase levels indicate an active, acute infection, not an asymptomatic carrier status.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma*
- **Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)** is a long-term complication of **chronic hepatitis B infection**,
- It does not develop during the acute phase of the disease.
*Liver cirrhosis*
- **Liver cirrhosis** is a consequence of **chronic liver injury**, typically evolving over many years due to chronic hepatitis B.
- It is not an outcome of acute HBV infection.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 3: A 50-year-old man comes to the physician for the evaluation of recurrent episodes of chest pain, difficulty breathing, and rapid heart beating over the past two months. During this period, he has had a 4-kg (8.8-lb) weight loss, malaise, pain in both knees, and diffuse muscle pain. Five years ago, he was diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B infection and was started on tenofovir. His temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities except for tachycardia. There are several ulcerations around the ankle and calves bilaterally. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11 g/dL
Leukocyte count 14,000/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 80 mm/h
Serum
Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen positive
Urine
Protein +2
RBC 6-7/hpf
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- B. Giant cell arteritis
- C. Thromboangiitis obliterans
- D. Polyarteritis nodosa (Correct Answer)
- E. Takayasu arteritis
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)***
- This patient presents with **fever**, **weight loss**, **myalgia**, and **arthralgia** along with **skin ulcerations** and **renal involvement** (proteinuria, hematuria), signs of systemic inflammation, and **medium-sized vessel vasculitis**. The history of **chronic Hepatitis B infection** is strongly associated with PAN.
- The elevated **ESR** and **leukocytosis** indicate ongoing inflammation, and the chest pain/rapid heart beating could be signs of cardiac involvement, which is common in PAN. The negative p-ANCA also helps rule out other vasculitides.
*Granulomatosis with polyangiitis*
- This condition is typically associated with **upper and lower respiratory tract involvement**, **glomerulonephritis**, and **c-ANCA positivity** (anti-PR3 antibodies).
- The patient's symptoms do not primarily involve sinusitis, pulmonary nodules, or other upper/lower airway disease, and p-ANCA is negative, rather than c-ANCA positive.
*Giant cell arteritis*
- This is a vasculitis affecting primarily **large-sized arteries**, especially the carotid artery branches, and typically occurs in patients **older than 50 years** (though this patient is 50, other symptoms rule it out).
- Key symptoms include **new-onset headache**, **jaw claudication**, **scalp tenderness**, and potential vision loss, none of which are reported here.
*Thromboangiitis obliterans*
- This condition is strongly linked to **heavy tobacco use** and results in **segmental thrombosis and inflammation of small and medium-sized arteries and veins** in the extremities.
- It primarily causes **ischemia of the digits** (fingers and toes), leading to pain, ulcerations, and gangrene, which is not fully consistent with the patient's widespread systemic symptoms and organ involvement.
*Takayasu arteritis*
- This is a **large-vessel vasculitis** primarily affecting the **aorta and its major branches**, typically seen in **younger women**.
- Symptoms often include **claudication**, **absent or diminished pulses**, and **discrepancies in blood pressure between limbs**, which are not described in this patient.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 4: A 37-year-old man presents to an urgent care clinic with complaints of speech problems and yellowing of his eyes for a week. He admits to using illicit intravenous drugs. His vital signs include: blood pressure 110/60 mm Hg, pulse rate 78/min, and respiratory rate 22/min. On examination, the patient appears jaundiced, and his speech is slurred. His liver enzymes and viral markers are as follows:
Aspartate aminotransferase 6,700 IU/L
Alanine aminotransferase 5,000 IU/L
HBsAg Negative
Anti-HBs Negative
Anti-HCV Ab Positive
HCV RNA Positive
If this patient develops chronic hepatitis C infection, he is at risk of developing a secondary dermatological condition. A biopsy of this skin condition would most likely show which of the following findings?
- A. Intraepithelial cleavage with acantholysis
- B. Noncaseating granulomas
- C. Microabscesses with fibrin and neutrophils
- D. Crypt abscesses containing neutrophils
- E. Lymphocytic infiltrate at the dermal-epidermal junction (Correct Answer)
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Lymphocytic infiltrate at the dermal-epidermal junction***
- Chronic hepatitis C infection is strongly associated with **lichen planus**, a dermatological condition characterized histologically by a **lymphocytic infiltrate along the dermal-epidermal junction**, often described as a "sawtooth" pattern.
- The history of IV drug use, jaundiced eyes, elevated liver enzymes, and positive HCV RNA confirm a diagnosis of **acute hepatitis C**, which can progress to chronic infection and lead to extrahepatic manifestations like lichen planus.
*Intraepithelial cleavage with acantholysis*
- This finding is characteristic of **pemphigus vulgaris**, an autoimmune blistering disorder where antibodies target desmoglein 3, leading to loss of cohesion between keratinocytes.
- Pemphigus vulgaris is not typically associated with chronic hepatitis C infection.
*Noncaseating granulomas*
- **Noncaseating granulomas** are the hallmark histological feature of **sarcoidosis** and Crohn's disease.
- While sarcoidosis can have cutaneous manifestations, it is not directly linked to chronic hepatitis C in the way lichen planus is.
*Microabscesses with fibrin and neutrophils*
- This description aligns with findings in conditions such as **dermatitis herpetiformis** (neutrophilic infiltrates in dermal papillae) or acute neutrophilic dermatoses, but it is not the characteristic feature of skin conditions directly associated with chronic hepatitis C.
- Skin conditions like vasculitis can also show neutrophilic infiltrates, but the primary association with HCV and the provided options points away from this.
*Crypt abscesses containing neutrophils*
- **Crypt abscesses** are histological features typically found in the intestinal lining in conditions like **ulcerative colitis**, an inflammatory bowel disease.
- This finding is not relevant to dermatological conditions associated with chronic hepatitis C.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 5: A 52-year-old man presents to his physician after his routine screening revealed that he has elevated liver enzymes. He complains of occasional headaches during the past year, but otherwise feels well. The patient reports that he was involved in a serious car accident in the 1980s. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. He has no history of illicit intravenous drug use. He does not currently take any medications and has no known allergies. His father had a history of alcoholism and died of liver cancer. The patient appears thin. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. The physical examination reveals no abnormalities. The laboratory test results show the following:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin 14 g/dL
Leukocyte count 10,000/mm3
Platelet count 146,000/mm3
Comprehensive metabolic profile
Glucose 150 mg/dL
Albumin 3.2 g/dL
Total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 75 IU/L
AST 95 IU/L
ALT 73 IU/L
Other lab tests
HIV negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Hepatitis C antibody positive
HCV RNA positive
HCV genotype 1
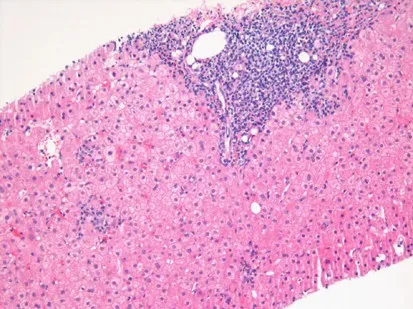
A liver biopsy is performed and shows mononuclear infiltrates localized to portal tracts that reveal periportal hepatocyte necrosis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Peginterferon alpha therapy
- B. Interferon and ribavirin therapy
- C. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir therapy (Correct Answer)
- D. Tenofovir and entecavir therapy
- E. Tenofovir and velpatasvir therapy
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir therapy***
- This patient has chronic **Hepatitis C (HCV) infection** (HCV antibody positive, HCV RNA positive). **Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir** is an effective **direct-acting antiviral (DAA)** regimen for **genotype 1 HCV**, which is indicated for treatment-naïve patients without cirrhosis.
- The liver biopsy findings of **mononuclear infiltrates** and **periportal necrosis** confirm active hepatitis and the need for antiviral treatment to prevent progression to cirrhosis.
*Peginterferon alpha therapy*
- **Peginterferon alpha** was historically used for HCV, but its use has largely been replaced by **DAAs** due to significant side effects and lower efficacy.
- This therapy is associated with numerous adverse effects, including **flu-like symptoms**, **depression**, and **bone marrow suppression**.
*Interferon and ribavirin therapy*
- This combination was a standard treatment for HCV before the advent of DAAs, but it is associated with a high burden of **side effects** like **hemolytic anemia** (from ribavirin) and **flu-like symptoms** (from interferon).
- Given the availability of highly effective and well-tolerated DAAs, this regimen is no longer considered first-line for chronic HCV.
*Tenofovir and entecavir therapy*
- **Tenofovir** and **entecavir** are antiviral medications primarily used for the treatment of **chronic Hepatitis B (HBV) infection**.
- This patient's **Hepatitis B surface antigen is negative**, ruling out chronic HBV infection as the primary issue requiring these specific drugs.
*Tenofovir and velpatasvir therapy*
- While **velpatasvir** is a DAA used for HCV, its combination with **tenofovir** is not a standard HCV treatment for genotype 1.
- **Tenofovir** is primarily an anti-HBV drug; for HCV, velpatasvir is typically combined with **sofosbuvir** (as in Epclusa) for pan-genotypic coverage.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 6: A 25-year-old construction worker presents to the office due to a yellowish discoloration of his skin and eyes for the past 2 weeks. He also complains of nausea and loss of appetite for the same duration. The past medical history is insignificant. He is a smoker, but recently has grown a distaste for smoking. The vital signs include: heart rate 83/min, respiratory rate 13/min, temperature 36.5°C (97.7°F), and blood pressure 111/74 mm Hg. On physical examination, there is mild hepatomegaly. The results of the hepatitis viral panel are as follows:
Anti-HAV IgM positive
HBsAg negative
IgM anti-HBc negative
Anti-HCV negative
HCV-RNA negative
Anti-HDV negative
Anti-HEV negative
What is the most common mode of transmission for this patient’s diagnosis?
- A. Breast milk
- B. Perinatal
- C. Fecal-oral (Correct Answer)
- D. Blood transfusion
- E. Sexual contact
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Fecal-oral***
- This patient's symptoms (jaundice, nausea, anorexia) and labs (**positive Anti-HAV IgM**) indicate acute **Hepatitis A virus (HAV)** infection
- **HAV** is predominantly transmitted via the **fecal-oral route**, often through contaminated food or water
- This is the **most common mode** of transmission, particularly in areas with poor sanitation or through contaminated food handlers
*Breast milk*
- While some viruses can be transmitted via breast milk, it is **not a common mode** of transmission for acute **Hepatitis A**
- **HAV** primarily spreads through contaminated ingestion via the fecal-oral route
*Perinatal*
- **Perinatal transmission** refers to infection from mother to child during pregnancy or childbirth, which is common for viruses like **HBV or HIV**
- **HAV** is not typically transmitted **perinatally** and is not a concern during pregnancy in the same way bloodborne viruses are
*Blood transfusion*
- **Bloodborne pathogens** like **Hepatitis B, C, or HIV** are transmissible through blood transfusions
- **Hepatitis A** is an **enteric virus** and is rarely transmitted via blood transfusions, especially with modern screening practices
- Viremia in HAV is transient and brief compared to chronic bloodborne hepatitis viruses
*Sexual contact*
- Although **HAV** can be transmitted through close person-to-person contact, including sexual contact (particularly among men who have sex with men), it is **not its most common mode of transmission** overall
- The primary route remains **fecal-oral**, especially in settings with contaminated food or water
- Sexual transmission typically involves fecal-oral exposure during sexual practices
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 7: A 30-year-old woman presents to the clinic because of fever, joint pain, and a rash on her lower extremities. She admits to intravenous drug use. Physical examination reveals palpable petechiae and purpura on her lower extremities. Laboratory results reveal a negative antinuclear antibody, positive rheumatoid factor, and positive serum cryoglobulins. Which of the following underlying conditions in this patient is responsible for these findings?
- A. Dermatomyositis
- B. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- C. Hepatitis C infection (Correct Answer)
- D. HIV infection
- E. Hepatitis B infection
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Hepatitis C infection***
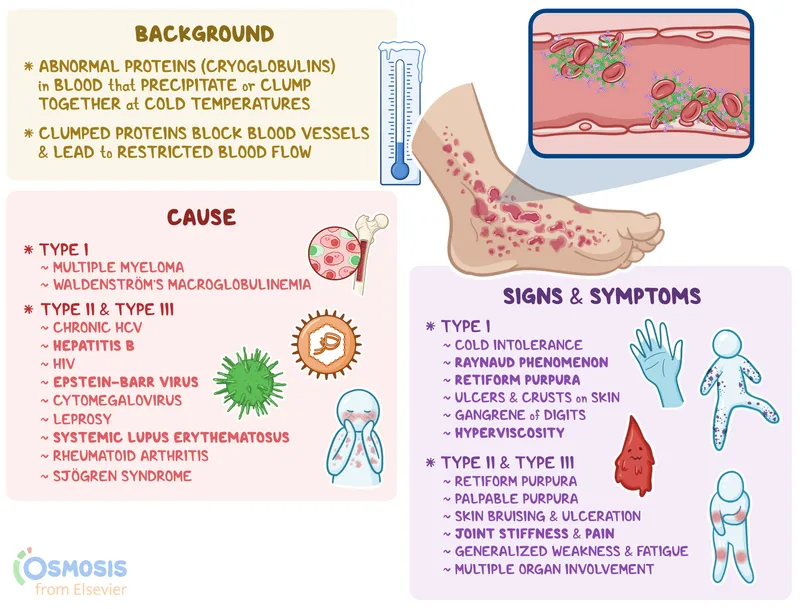
- The combination of **intravenous drug use**, **fever**, **joint pain**, **palpable purpura**, **positive rheumatoid factor**, and **positive serum cryoglobulins** is highly suggestive of **mixed cryoglobulinemia**, which is most commonly associated with chronic **Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection**.
- **Cryoglobulinemia** is a systemic vasculitis caused by immune complex deposition, a common extrahepatic manifestation of HCV.
*Dermatomyositis*
- Characterized by **proximal muscle weakness** and characteristic skin rashes (e.g., **Gottron's papules**, **heliotrope rash**), which are not described here.
- While dermatomyositis can be associated with inflammatory markers, it typically does not present with palpable purpura or positive cryoglobulins.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)*
- While SLE can cause **fever**, **arthralgia**, and a **rash**, the patient's **negative antinuclear antibody (ANA)** makes SLE highly unlikely.
- **Cryoglobulinemia** is rare in SLE, and the specific finding of palpable purpura points away from typical SLE rashes.
*HIV infection*
- HIV can cause a variety of skin lesions and arthralgias, but **palpable purpura** and **mixed cryoglobulinemia** are not its primary or most common manifestations.
- While **rheumatoid factor** can be positive in HIV, the overall clinical picture strongly favors HCV-associated cryoglobulinemia.
*Hepatitis B infection*
- Hepatitis B can be associated with **vasculitis** (e.g., **polyarteritis nodosa**) and immune complex-mediated disease.
- However, **mixed cryoglobulinemia**, characterized by the specific combination of symptoms and laboratory findings presented, is overwhelmingly more associated with **Hepatitis C** than Hepatitis B.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 8: A 42-year-old male with a history significant for IV drug use comes to the emergency department complaining of persistent fatigue and malaise for the past three weeks. On physical exam, you observe a lethargic male with icteric sclera and hepatomegaly. AST and ALT are elevated at 600 and 750, respectively. HCV RNA is positive. Albumin is 3.8 g/dL and PT is 12. A liver biopsy shows significant inflammation with bridging fibrosis. What is the current first-line treatment?
- A. Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Correct Answer)
- B. Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir
- C. Sofosbuvir/Ledipasvir
- D. Ribavirin monotherapy
- E. Interferon monotherapy
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir***
- This is a **pan-genotypic direct-acting antiviral (DAA)** combination that is highly effective for all HCV genotypes and is recommended as a **first-line regimen** by AASLD/IDSA guidelines.
- It is particularly appropriate for patients with **significant fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis**, as seen in this patient with bridging fibrosis on biopsy.
- The standard treatment duration is **12 weeks** for treatment-naive patients, with high sustained virologic response (SVR) rates exceeding 95%.
- It has a favorable safety profile and is effective regardless of baseline viral load or HCV genotype.
*Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir*
- While this is also an excellent **pan-genotypic DAA** combination with high efficacy, it requires longer treatment duration (12-16 weeks) in patients with **significant fibrosis (F3)** or cirrhosis.
- It is **contraindicated in decompensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh B/C)**, making sofosbuvir-based regimens more universally applicable for patients with advanced liver disease.
- The often-cited 8-week treatment advantage applies primarily to patients **without cirrhosis**, not to this patient with bridging fibrosis.
*Sofosbuvir/Ledipasvir*
- This combination is primarily effective for **HCV genotypes 1, 4, 5, and 6** but is not truly pan-genotypic like sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
- It is an acceptable alternative for genotype 1 infection but has been largely superseded by newer pan-genotypic regimens that don't require genotype testing.
- Treatment duration is typically **12 weeks** for treatment-naive patients without cirrhosis.
*Ribavirin monotherapy*
- **Ribavirin** is a nucleoside analog with **minimal antiviral activity** against HCV when used as monotherapy.
- It is only used as an **adjunctive agent** in combination with DAAs in specific circumstances (e.g., treatment-experienced patients with cirrhosis).
- Major side effect is **hemolytic anemia**, requiring close monitoring.
*Interferon monotherapy*
- **Interferon-alpha** monotherapy has very **poor efficacy** for chronic HCV, with sustained virologic response (SVR) rates of only 10-20%.
- It is associated with significant side effects including flu-like symptoms, depression, and cytopenias, making it **poorly tolerated**.
- This regimen is now **obsolete** and has been replaced by highly effective and well-tolerated DAA combinations.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 9: A 45-year-old man presents to an urgent care clinic because he coughed up blood this morning. Although he had a persistent cough for the past 3 weeks, he had never coughed up blood until now. His voice is hoarse and admits that it has been like that for the past few months. Both his past medical history and family history are insignificant. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes a day since the age of 20 and drinks wine every night before bed. His vitals are: heart rate of 78/min, respiratory rate of 14/min, temperature of 36.5°C (97.8°F), blood pressure of 140/88 mm Hg. An indirect laryngoscopy reveals a rough vegetating lesion on the free border of the right vocal cord. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Acute laryngitis
- B. Polypoid corditis
- C. Leukoplakia
- D. Laryngeal carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Vocal cord nodule
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Laryngeal carcinoma***
- The patient's long history of **smoking**, chronic **hoarseness** (lasting months), and especially the new onset of **hemoptysis** (coughing up blood) are highly suspicious for laryngeal carcinoma. The **rough vegetating lesion** on the vocal cord seen on laryngoscopy further supports this diagnosis.
- Alcohol consumption, in addition to smoking, significantly increases the risk of head and neck cancers, including **laryngeal carcinoma**. The duration of symptoms and the nature of the lesion point towards a malignant process rather than a benign or acute condition.
*Acute laryngitis*
- This is typically an **acute inflammatory condition** of the larynx, often viral in origin, lasting a few days to a couple of weeks, and usually resolves spontaneously.
- The patient's symptoms have been present for **months**, and the finding of a distinct **vegetating lesion** is not characteristic of acute laryngitis.
*Polypoid corditis*
- Also known as **Reinke's edema**, this condition is characterized by **edematous degeneration** of the vocal cords, primarily due to chronic irritation from smoking.
- While it causes hoarseness, it rarely presents with **hemoptysis** and the lesion described as "rough vegetating" is more suggestive of malignancy than the smooth, baggy appearance of Reinke's edema.
*Leukoplakia*
- **Leukoplakia** refers to white patches on mucous membranes that cannot be scraped off and are often **premalignant**. They can be caused by chronic irritation, such as smoking.
- Although leukoplakia can progress to carcinoma, the presence of **hemoptysis** and a "vegetating lesion" indicates a more advanced, likely malignant process rather than just a benign or premalignant white patch.
*Vocal cord nodule*
- **Vocal cord nodules** are benign growths, often bilateral, resulting from vocal abuse or misuse, and typically cause hoarseness and vocal fatigue.
- Nodules are usually **smooth** and rarely cause **hemoptysis** or appear as a "vegetating lesion." The patient's smoking history and hemoptysis point away from simple vocal cord nodules.
Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG Question 10: A 57-year-old man comes to the physician because of generalized malaise, yellowish discoloration of the eyes, and pruritus on the back of his hands that worsens when exposed to sunlight for the past several months. He has not seen a physician in 15 years. Physical examination shows scleral icterus and mild jaundice. There is a purpuric rash with several small vesicles and hyperpigmented lesions on the dorsum of both hands. The causal pathogen of this patient's underlying condition was most likely acquired in which of the following ways?
- A. Ingestion of raw shellfish
- B. Inhalation of spores
- C. Needlestick injury (Correct Answer)
- D. Bathing in freshwater
- E. Sexual contact
Natural history of HCV infection Explanation: ***Needlestick injury***
- The jaundice, scleral icterus, pruritus, and **purpuric rash worsened by sunlight** (suggesting **Porphyria Cutanea Tarda**) are highly indicative of **chronic Hepatitis C virus infection**.
- **Hepatitis C** is primarily transmitted through **blood-to-blood contact**, with **needlestick injuries** and intravenous drug use being the most common routes.
*Ingestion of raw shellfish*
- **Hepatitis A virus** and **Vibrio vulnificus** can be acquired this way, but they typically cause acute, self-limiting illness or severe sepsis, respectively, not chronic liver disease with porphyria.
- **Hepatitis A** does not lead to chronic hepatitis or the dermatological manifestations described.
*Inhalation of spores*
- **Inhalation of spores** is associated with fungal infections like **histoplasmosis** or **coccidioidomycosis**, which do not typically cause chronic hepatitis, jaundice, pruritus, or porphyria cutanea tarda.
- These infections primarily affect the lungs, though disseminated forms can occur, they do not match the presented symptoms.
*Bathing in freshwater*
- **Bathing in freshwater** can transmit pathogens like **Leptospira** or **Schistosoma**, causing leptospirosis or schistosomiasis, respectively.
- These infections present with different clinical pictures and are not associated with chronic hepatitis, jaundice, or porphyria cutanea tarda.
*Sexual contact*
- While **Hepatitis C** can be transmitted sexually, this route is significantly **less efficient** than blood-to-blood contact.
- **Hepatitis B** is more commonly associated with sexual transmission and can also cause chronic liver disease, but the presence of **Porphyria Cutanea Tarda** is a characteristic extrahepatic manifestation strongly associated with **chronic Hepatitis C infection**.
- Given the clinical presentation, **needlestick injury or intravenous drug use** (blood-borne transmission) is the most likely route of HCV acquisition.
More Natural history of HCV infection US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.