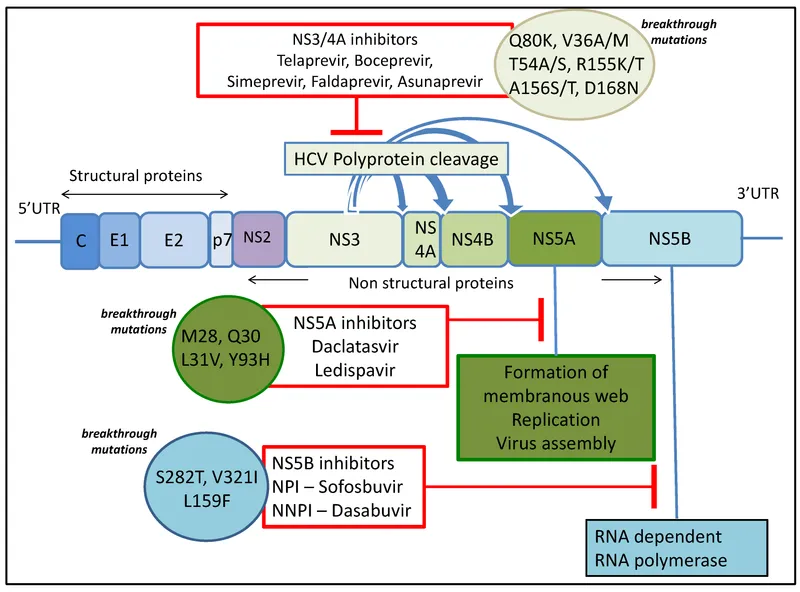
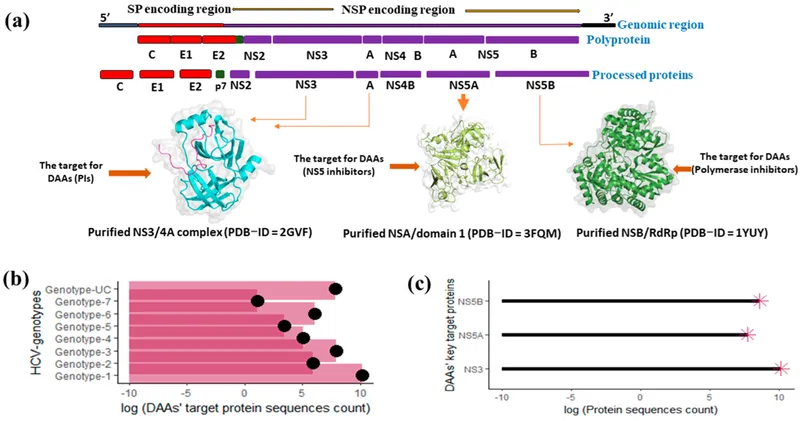
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for HCV resistance and treatment failure. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 1: A 23-year-old male with a homozygous CCR5 mutation is found to be immune to HIV infection. The patient’s CCR5 mutation interferes with the function of which viral protein?
- A. gp41
- B. Reverse transcriptase
- C. pp17
- D. gp120 (Correct Answer)
- E. p24
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***gp120***
- The **gp120 protein** on the HIV envelope is responsible for binding to the **CD4 receptor** and the **coreceptor CCR5** or CXCR4 on host cells, which is the initial step for viral entry.
- A homozygous **CCR5 mutation** (specifically the **CCR5-Δ32** deletion) prevents HIV from using this coreceptor, thereby blocking the binding of gp120 and subsequent viral entry.
*gp41*
- **gp41** is another envelope protein that, after gp120 binds to CD4 and a coreceptor, undergoes a conformational change to mediate **fusion** of the viral and host cell membranes.
- While essential for entry, gp41 acts downstream of gp120's primary binding to the coreceptor, so a CCR5 mutation primarily affects gp120's ability to engage with the cell.
*Reverse transcriptase*
- **Reverse transcriptase** is a viral enzyme responsible for **converting viral RNA into DNA** once the virus has already entered the host cell cytoplasm.
- A CCR5 mutation prevents viral entry, thus the activity of reverse transcriptase is not directly interfered with by the mutation itself but rather by the lack of cellular access.
*pp17*
- **pp17**, also known as **matrix protein**, is an internal structural protein that plays a role in the assembly of new virions and guiding the **reverse transcribed DNA** into the nucleus.
- This protein is involved in later stages of the viral life cycle *after* entry and integration, and its function is not directly blocked by a CCR5 mutation.
*p24*
- **p24** is the major **capsid protein** that forms the core of the HIV virus, enclosing the viral RNA and enzymes.
- It is critical for maintaining the structural integrity of the virus and is a key target for diagnostic tests, but it does not directly participate in the initial binding and entry process that is affected by a CCR5 mutation.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 2: A 52-year-old man presents to his physician after his routine screening revealed that he has elevated liver enzymes. He complains of occasional headaches during the past year, but otherwise feels well. The patient reports that he was involved in a serious car accident in the 1980s. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. He has no history of illicit intravenous drug use. He does not currently take any medications and has no known allergies. His father had a history of alcoholism and died of liver cancer. The patient appears thin. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. The physical examination reveals no abnormalities. The laboratory test results show the following:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin 14 g/dL
Leukocyte count 10,000/mm3
Platelet count 146,000/mm3
Comprehensive metabolic profile
Glucose 150 mg/dL
Albumin 3.2 g/dL
Total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 75 IU/L
AST 95 IU/L
ALT 73 IU/L
Other lab tests
HIV negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Hepatitis C antibody positive
HCV RNA positive
HCV genotype 1
A liver biopsy is performed and shows mononuclear infiltrates localized to portal tracts that reveal periportal hepatocyte necrosis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Peginterferon alpha therapy
- B. Interferon and ribavirin therapy
- C. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir therapy (Correct Answer)
- D. Tenofovir and entecavir therapy
- E. Tenofovir and velpatasvir therapy
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir therapy***
- This patient has chronic **Hepatitis C (HCV) infection** (HCV antibody positive, HCV RNA positive). **Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir** is an effective **direct-acting antiviral (DAA)** regimen for **genotype 1 HCV**, which is indicated for treatment-naïve patients without cirrhosis.
- The liver biopsy findings of **mononuclear infiltrates** and **periportal necrosis** confirm active hepatitis and the need for antiviral treatment to prevent progression to cirrhosis.
*Peginterferon alpha therapy*
- **Peginterferon alpha** was historically used for HCV, but its use has largely been replaced by **DAAs** due to significant side effects and lower efficacy.
- This therapy is associated with numerous adverse effects, including **flu-like symptoms**, **depression**, and **bone marrow suppression**.
*Interferon and ribavirin therapy*
- This combination was a standard treatment for HCV before the advent of DAAs, but it is associated with a high burden of **side effects** like **hemolytic anemia** (from ribavirin) and **flu-like symptoms** (from interferon).
- Given the availability of highly effective and well-tolerated DAAs, this regimen is no longer considered first-line for chronic HCV.
*Tenofovir and entecavir therapy*
- **Tenofovir** and **entecavir** are antiviral medications primarily used for the treatment of **chronic Hepatitis B (HBV) infection**.
- This patient's **Hepatitis B surface antigen is negative**, ruling out chronic HBV infection as the primary issue requiring these specific drugs.
*Tenofovir and velpatasvir therapy*
- While **velpatasvir** is a DAA used for HCV, its combination with **tenofovir** is not a standard HCV treatment for genotype 1.
- **Tenofovir** is primarily an anti-HBV drug; for HCV, velpatasvir is typically combined with **sofosbuvir** (as in Epclusa) for pan-genotypic coverage.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 3: A 45-year-old man presents for follow-up to monitor his chronic hepatitis C treatment. The patient was infected with hepatitis C genotype 1, one year ago. He has been managed on a combination of pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin, but a sustained viral response has not been achieved. Past medical history is significant for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease for the last 5 years. Which of the following, if added to the patient’s current treatment regimen, would most likely benefit this patient?
- A. Emtricitabine
- B. Entecavir
- C. Simeprevir (Correct Answer)
- D. Tenofovir
- E. Telbivudine
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Simeprevir***
- Simeprevir is a **first-generation direct-acting antiviral (DAA)**, specifically a **protease inhibitor (NS3/4A inhibitor)**, highly effective against **HCV genotype 1**.
- Adding simeprevir to a regimen of **pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin** significantly increases the likelihood of achieving a **sustained virologic response** for patients who previously failed interferon-based therapy.
- **Note:** While this triple therapy approach was standard practice historically, current guidelines (as of 2024-2025) favor **interferon-free DAA combination regimens** (such as sofosbuvir/ledipasvir or glecaprevir/pibrentasvir) as first-line treatment for HCV genotype 1. However, among the options provided, simeprevir remains the only appropriate HCV-specific antiviral agent.
*Emtricitabine*
- This is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)** primarily used in the treatment of **HIV infection** and sometimes for hepatitis B.
- It has **no significant role** in the treatment of **hepatitis C viral infection**.
*Entecavir*
- Entecavir is an **antiviral agent** specifically used for the treatment of **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It has **no established efficacy** against the **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
*Tenofovir*
- Tenofovir is a **nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor** primarily used for treating **HIV infection** and **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It is **not effective** against **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
*Telbivudine*
- Telbivudine is an **oral antiviral agent** indicated specifically for the treatment of **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It does **not have antiviral activity** against the **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old male with a history significant for IV drug use comes to the emergency department complaining of persistent fatigue and malaise for the past three weeks. On physical exam, you observe a lethargic male with icteric sclera and hepatomegaly. AST and ALT are elevated at 600 and 750, respectively. HCV RNA is positive. Albumin is 3.8 g/dL and PT is 12. A liver biopsy shows significant inflammation with bridging fibrosis. What is the current first-line treatment?
- A. Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir (Correct Answer)
- B. Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir
- C. Sofosbuvir/Ledipasvir
- D. Ribavirin monotherapy
- E. Interferon monotherapy
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir***
- This is a **pan-genotypic direct-acting antiviral (DAA)** combination that is highly effective for all HCV genotypes and is recommended as a **first-line regimen** by AASLD/IDSA guidelines.
- It is particularly appropriate for patients with **significant fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis**, as seen in this patient with bridging fibrosis on biopsy.
- The standard treatment duration is **12 weeks** for treatment-naive patients, with high sustained virologic response (SVR) rates exceeding 95%.
- It has a favorable safety profile and is effective regardless of baseline viral load or HCV genotype.
*Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir*
- While this is also an excellent **pan-genotypic DAA** combination with high efficacy, it requires longer treatment duration (12-16 weeks) in patients with **significant fibrosis (F3)** or cirrhosis.
- It is **contraindicated in decompensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh B/C)**, making sofosbuvir-based regimens more universally applicable for patients with advanced liver disease.
- The often-cited 8-week treatment advantage applies primarily to patients **without cirrhosis**, not to this patient with bridging fibrosis.
*Sofosbuvir/Ledipasvir*
- This combination is primarily effective for **HCV genotypes 1, 4, 5, and 6** but is not truly pan-genotypic like sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
- It is an acceptable alternative for genotype 1 infection but has been largely superseded by newer pan-genotypic regimens that don't require genotype testing.
- Treatment duration is typically **12 weeks** for treatment-naive patients without cirrhosis.
*Ribavirin monotherapy*
- **Ribavirin** is a nucleoside analog with **minimal antiviral activity** against HCV when used as monotherapy.
- It is only used as an **adjunctive agent** in combination with DAAs in specific circumstances (e.g., treatment-experienced patients with cirrhosis).
- Major side effect is **hemolytic anemia**, requiring close monitoring.
*Interferon monotherapy*
- **Interferon-alpha** monotherapy has very **poor efficacy** for chronic HCV, with sustained virologic response (SVR) rates of only 10-20%.
- It is associated with significant side effects including flu-like symptoms, depression, and cytopenias, making it **poorly tolerated**.
- This regimen is now **obsolete** and has been replaced by highly effective and well-tolerated DAA combinations.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 5: A 57-year-old man comes to the physician because of generalized malaise, yellowish discoloration of the eyes, and pruritus on the back of his hands that worsens when exposed to sunlight for the past several months. He has not seen a physician in 15 years. Physical examination shows scleral icterus and mild jaundice. There is a purpuric rash with several small vesicles and hyperpigmented lesions on the dorsum of both hands. The causal pathogen of this patient's underlying condition was most likely acquired in which of the following ways?
- A. Ingestion of raw shellfish
- B. Inhalation of spores
- C. Needlestick injury (Correct Answer)
- D. Bathing in freshwater
- E. Sexual contact
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Needlestick injury***
- The jaundice, scleral icterus, pruritus, and **purpuric rash worsened by sunlight** (suggesting **Porphyria Cutanea Tarda**) are highly indicative of **chronic Hepatitis C virus infection**.
- **Hepatitis C** is primarily transmitted through **blood-to-blood contact**, with **needlestick injuries** and intravenous drug use being the most common routes.
*Ingestion of raw shellfish*
- **Hepatitis A virus** and **Vibrio vulnificus** can be acquired this way, but they typically cause acute, self-limiting illness or severe sepsis, respectively, not chronic liver disease with porphyria.
- **Hepatitis A** does not lead to chronic hepatitis or the dermatological manifestations described.
*Inhalation of spores*
- **Inhalation of spores** is associated with fungal infections like **histoplasmosis** or **coccidioidomycosis**, which do not typically cause chronic hepatitis, jaundice, pruritus, or porphyria cutanea tarda.
- These infections primarily affect the lungs, though disseminated forms can occur, they do not match the presented symptoms.
*Bathing in freshwater*
- **Bathing in freshwater** can transmit pathogens like **Leptospira** or **Schistosoma**, causing leptospirosis or schistosomiasis, respectively.
- These infections present with different clinical pictures and are not associated with chronic hepatitis, jaundice, or porphyria cutanea tarda.
*Sexual contact*
- While **Hepatitis C** can be transmitted sexually, this route is significantly **less efficient** than blood-to-blood contact.
- **Hepatitis B** is more commonly associated with sexual transmission and can also cause chronic liver disease, but the presence of **Porphyria Cutanea Tarda** is a characteristic extrahepatic manifestation strongly associated with **chronic Hepatitis C infection**.
- Given the clinical presentation, **needlestick injury or intravenous drug use** (blood-borne transmission) is the most likely route of HCV acquisition.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 6: A 32-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with fever, dyspnea, and impaired consciousness. His wife reports that he has also had an episode of dark urine today. Two weeks ago, he returned from a trip to the Republic of Congo. His temperature is 39.4°C (103°F), pulse is 114/min, and blood pressure is 82/51 mm Hg. Physical examination shows scleral icterus. Decreased breath sounds and expiratory crackles are heard on auscultation of the lungs bilaterally. His hemoglobin concentration is 6.3 g/dL. A blood smear shows red blood cells with normal morphology and ring-shaped inclusions. Further laboratory testing shows normal rates of NADPH production. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
- A. Proguanil
- B. Dapsone
- C. Chloroquine
- D. Artesunate (Correct Answer)
- E. Atovaquone
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Artesunate***
- This patient presents with **severe malaria**, indicated by fever, impaired consciousness, hypotension, dyspnea, dark urine (hemoglobinuria), scleral icterus (hemolysis), and anemia, following travel to an endemic area (Republic of Congo). The blood smear finding of **ring-shaped inclusions** with normal red cell morphology is characteristic of **Plasmodium falciparum** infection.
- **Artesunate** is the drug of choice for **severe malaria** due to its rapid parasitic clearance and superior efficacy compared to other antimalarials, especially in regions with high chloroquine resistance, as is typical in the Republic of Congo for *P. falciparum*.
*Proguanil*
- Proguanil is primarily used in **malaria prophylaxis** or in combination with other drugs (e.g., atovaquone-proguanil) for uncomplicated malaria.
- It is not indicated as monotherapy for **severe *P. falciparum* malaria**, nor is it suitable for emergency treatment of life-threatening infections.
*Dapsone*
- Dapsone is an **antibiotic** primarily used in the treatment of **leprosy** and prevention of *Pneumocystis jirovecii* pneumonia or toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised patients.
- It has **no significant role** in the treatment of malaria, especially severe *P. falciparum* infection.
*Chloroquine*
- Chloroquine was historically a first-line treatment for malaria but is largely ineffective against **chloroquine-resistant *P. falciparum***, which is widely prevalent in the Republic of Congo and contributes to severe disease.
- Administering chloroquine in this context would likely lead to **treatment failure** and worsening of the patient's severe condition.
*Atovaquone*
- Atovaquone, usually combined with proguanil (Malarone), is effective for **uncomplicated malaria** and prophylaxis.
- However, it is **not the preferred agent for severe malaria** due to slower action and lack of intravenous formulation for initial critical management.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 7: Two viruses, X and Y, infect the same cell and begin to reproduce within the cell. As a result of the co-infection, some viruses are produced where the genome of Y is surrounded by the nucleocapsid of X and vice versa with the genome of X and nucleocapsid of Y. When the virus containing genome X surrounded by the nucleocapsid of Y infects another cell, what is the most likely outcome?
- A. Virions containing genome Y and nucleocapsid Y will be produced
- B. No virions will be produced
- C. Virions containing genome X and nucleocapsid Y will be produced
- D. Virions containing genome Y and nucleocapsid X will be produced
- E. Virions containing genome X and nucleocapsid X will be produced (Correct Answer)
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Virions containing genome X and nucleocapsid X will be produced***
- The virus containing **genome X** surrounded by **nucleocapsid Y** is a pseudotype. During the infection of a new cell, the **genome X** will direct the synthesis of new viral components, including **nucleocapsid X**.
- Since the genetic material (genome X) dictates the production of viral proteins, the new virions will be genetically identical to virus X, thus containing its own genome and nucleocapsid.
*Virions containing genome Y and nucleocapsid Y will be produced*
- This is incorrect because the infecting particle carried **genome X**, not genome Y.
- The genetic information encoded in the genome determines the type of progeny viruses produced.
*No virions will be produced*
- This is unlikely as the pseudotyped virus is capable of infection and delivery of a functional genome into the host cell.
- The cell is presumed to be permissive for virus replication.
*Virions containing genome X and nucleocapsid Y will be produced*
- This would only happen if the **nucleocapsid Y** was somehow replicated independently of its original genome, which is not how viral replication works.
- The progeny nucleocapsids are always encoded by the genome that is replicating within the cell.
*Virions containing genome Y and nucleocapsid X will be produced*
- This is incorrect. The infecting virus introduced **genome X** into the cell, not genome Y.
- The genetic material delivered determines the type of viral particles that will be synthesized.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 8: A group of researchers conducted various studies on hepatitis C incidence and prevalence. They noticed that there is a high prevalence of hepatitis C in third-world countries, where it has a significant impact on the quality of life of the infected individual. The research group made several attempts to produce a vaccine that prevents hepatitis C infection but all attempts failed. Which of the following would most likely be the reason for the failure to produce a vaccine?
- A. Non-DNA genome
- B. Tolerance
- C. Antigenic mimicry
- D. Polysaccharide envelope
- E. Antigenic variation (Correct Answer)
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Antigenic variation***
- The **hepatitis C virus (HCV)** undergoes rapid **antigenic variation**, particularly in its envelope glycoproteins, which allows it to evade the host immune system.
- This high mutation rate presents a significant challenge for vaccine development, as a vaccine designed against one viral strain may not be effective against others.
*Non-DNA genome*
- While HCV is an **RNA virus** (non-DNA genome), this characteristic alone does not inherently prevent vaccine development; many effective RNA virus vaccines exist (e.g., measles, mumps).
- The type of genome is less critical than its stability and the virus's ability to mutate rapidly.
*Tolerance*
- **Immune tolerance** occurs when the immune system fails to respond to an antigen, often due to chronic exposure. While relevant in chronic HCV infection, it's not the primary reason for vaccine failure.
- The goal of a vaccine is to induce an effective immune response before tolerance can set in.
*Antigenic mimicry*
- **Antigenic mimicry** involves a pathogen's antigens resembling host antigens, potentially leading to autoimmune responses or immune evasion.
- While it can be a factor in some chronic infections, the rapid, diverse changes in HCV's surface antigens are a more prominent obstacle to vaccine design.
*Polysaccharide envelope*
- HCV is an **enveloped virus**, but its envelope is composed of **lipoproteins** with viral glycoproteins, not a polysaccharide capsule.
- Polysaccharide capsules are a feature of some bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae) and fungi, and while they can pose vaccine challenges, they are not relevant to HCV.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 9: A 13-year-old boy presents to the pediatrician with yellow discoloration of the sclerae since yesterday, and dark-colored urine for 2 days. A detailed history is taken and reveals that he had a cough, cold, and fever the week before the onset of the current symptoms, and was treated with over-the-counter medications. He reports an improvement in his upper respiratory symptoms but has been experiencing fatigue, nausea, and poor appetite since then. There is no past history of recurrent nausea, vomiting, jaundice or abdominal pain, and he has not received any blood transfusion. In addition, he frequently eats at a roadside restaurant near his school. His growth and development are normal for his age and sex. The temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 96/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and the respiratory rate is 22/min. The physical examination shows icterus. The examination of the abdomen reveals tender hepatomegaly with the liver having a firm, sharp, and smooth edge. The laboratory test results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 14.2 g/dL
WBC (white blood cell) 10,500/mm3
Differential leukocyte count
Segmented neutrophils 56%
Bands 4%
Lymphocytes 35%
Eosinophils 2%
Basophils 0%
Monocytes 3%
Platelet count 270,000/mm3
Serum total bilirubin 8.4 mg/dL
Serum direct bilirubin 7.8 mg/dL
Serum alanine aminotransferase 350 U/L
Serum alkaline phosphatase 95 U/L
Prothrombin time 20 seconds
Which of the following laboratory tests is most likely used to diagnose the condition of this patient?
- A. Plasma tyrosine and methionine
- B. Serum anti-HAV IgM antibody (Correct Answer)
- C. Quantitative assay for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity
- D. Urine for reducing substances
- E. Percutaneous liver biopsy
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Serum anti-HAV IgM antibody***
- The patient's symptoms (jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, nausea, tender hepatomegaly) following an upper respiratory illness, especially with a history of eating at a roadside restaurant, are highly suggestive of **acute hepatitis A infection**.
- **IgM antibodies** to hepatitis A virus (HAV) are detectable early in the course of infection and indicate **acute or recent infection**, making it the most appropriate diagnostic test.
*Plasma tyrosine and methionine*
- These tests are used in the diagnosis of **tyrosinemia**, a rare inherited metabolic disorder that can cause liver failure.
- The patient's acute presentation and history of potential exposure to HAV make tyrosinemia less likely, and **elevated transaminases** are not specific to tyrosinemia.
*Quantitative assay for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity*
- This assay is used to diagnose **G6PD deficiency**, an inherited condition that can cause hemolytic anemia, particularly after exposure to certain drugs or foods, which might lead to jaundice from unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- However, the patient's presentation with **tender hepatomegaly**, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia (direct bilirubin significantly elevated), and elevated transaminases is more consistent with **hepatocellular injury** rather than hemolysis.
*Urine for reducing substances*
- This test is used to screen for **galactosemia** or other disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in infants and young children, where undigested sugars appear in the urine.
- It is not indicated for the diagnosis of acute hepatitis in an adolescent with the presented clinical picture.
*Percutaneous liver biopsy*
- While a liver biopsy can provide definitive information about liver pathology, it is an **invasive procedure** and is generally not the initial diagnostic test for acute viral hepatitis due to its risks.
- **Serological markers** for viral hepatitis are less invasive and usually sufficient for diagnosing acute hepatitis A.
HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG Question 10: A scientist is studying the replication sequences of a number of different viruses. He observes that one particular virus he is studying creates a single stranded DNA from an RNA template during its replication sequence. Which of the following viruses is he most likely observing?
- A. Hepatitis C virus
- B. Norovirus
- C. Hepatitis B virus (Correct Answer)
- D. HSV-1
- E. Hepatitis A virus
HCV resistance and treatment failure Explanation: ***Hepatitis B virus***
- This virus is a **DNA virus** that replicates via an **RNA intermediate**, using a **reverse transcriptase** enzyme to synthesize DNA from an RNA template.
- Its replication cycle involves creating a pre-genomic RNA from its DNA genome, which is then reverse-transcribed into **partially double-stranded DNA** for packaging into new virions.
*Hepatitis C virus*
- This is an **RNA virus** that replicates entirely within the cytoplasm and does not utilize a DNA intermediate or reverse transcriptase.
- Its replication involves the synthesis of a **negative-sense RNA strand** from the positive-sense genomic RNA, which then serves as a template for new positive-sense RNA genomes.
*Norovirus*
- This is a **positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus** that replicates in the cytoplasm of host cells.
- It uses an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase** to synthesize new RNA genomes directly from an RNA template, without a DNA intermediate.
*HSV-1*
- **Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1)** is a **double-stranded DNA virus** that replicates in the nucleus of infected cells.
- Its replication pathway involves **DNA-dependent DNA polymerase** to replicate its genome and does not involve an RNA to DNA transcription step.
*Hepatitis A virus*
- This is a **positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus** that belongs to the **Picornaviridae family**.
- Like other RNA viruses, it replicates its genome via an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, directly creating new RNA copies from an RNA template without a reverse transcription step.
More HCV resistance and treatment failure US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.