HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for HCC screening in viral hepatitis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 1: A 65-year-old man comes to the clinic complaining of abdominal pain for the past 2 months. He describes the pain as a dull, aching, 6/10 pain that is diffuse but worse in the right upper quadrant (RUQ). His past medical history is significant for diabetes controlled with metformin and a cholecystectomy 10 years ago. He reports fatigue and a 10-lb weight loss over the past month that he attributes to poor appetite; he denies fever, nausea/vomiting, palpitations, chest pain, or bowel changes. Physical examination is significant for mild scleral icterus and tenderness at the RUQ. Further workup reveals a high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm of the liver. What relevant detail would you expect to find in this patient’s history?
- A. Chronic alcohol abuse
- B. Heavy ingestion of acetaminophen
- C. Infection with the hepatitis B virus
- D. Obesity
- E. Prior occupation in a chemical plastics manufacturing facility (Correct Answer)
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***Prior occupation in a chemical plastics manufacturing facility***
- This history suggests exposure to **vinyl chloride**, a known carcinogen associated with hepatic angiosarcoma, a rare but aggressive **vascular neoplasm of the liver**.
- **Hepatic angiosarcoma** often presents with vague symptoms like abdominal pain, weight loss, and fatigue, as seen in this patient, and can lead to liver failure and jaundice [1].
*Chronic alcohol abuse*
- While chronic alcohol abuse can lead to various liver diseases, including **alcoholic hepatitis**, **cirrhosis**, and **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, it is not typically associated with angiosarcomas.
- The patient's symptoms are more consistent with a rapidly progressing malignancy, and HCC typically presents in patients with underlying cirrhosis or hepatitis.
*Heavy ingestion of acetaminophen*
- Acute or chronic overdose of **acetaminophen** primarily causes **centrilobular necrosis** and liver failure, but it is not linked to the development of hepatic vascular neoplasms like angiosarcoma.
- The patient's presentation of a high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm points away from drug-induced liver injury as the primary cause.
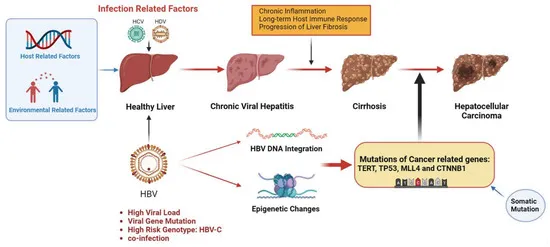
*Infection with the hepatitis B virus*
- **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection is a major risk factor for **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, a common primary liver cancer, but not for hepatic angiosarcoma.
- The patient's clinical picture of a "high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm" is less typical for HCC, which originates from hepatocytes, not vascular endothelial cells.
*Obesity*
- Obesity is a risk factor for **non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)**, which can progress to **non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)**, cirrhosis, and **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)** [2].
- However, obesity is not directly linked to the development of primary hepatic vascular neoplasms like angiosarcoma.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 2: A 60-year-old rock musician presents to the office because he has been feeling increasingly tired for the past 6 months. He has a history of intravenous drug use and alcohol abuse. He states that he feels quite tired, but he otherwise has no complaints. Physical examination is noncontributory. His laboratory values are normal other than moderately elevated liver enzymes. Which of the following additional tests should you order first?
- A. Hepatitis C virus antibodies (Correct Answer)
- B. Hepatitis B surface antigen
- C. Hepatitis E virus-specific IgM antibodies
- D. Hepatitis D virus-specific IgG antibody
- E. Hepatitis A virus-specific IgM antibodies
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***Hepatitis C virus antibodies***
- The patient's history of **intravenous drug use** and **chronic fatigue** with **elevated liver enzymes** strongly suggests chronic viral hepatitis, with hepatitis C being the most common blood-borne infection in persons with IVDU history.
- **Hepatitis C** is the **most prevalent chronic viral hepatitis** in the United States among persons with history of injection drug use, with transmission efficiency via needle sharing being very high.
- Hepatitis C often has a **long asymptomatic phase** (decades) before symptoms like fatigue and liver damage become apparent, making antibody testing the appropriate initial screen.
- While both HBV and HCV should ultimately be screened in this patient, **HCV prevalence is significantly higher** in the IVDU population, making it the priority initial test.
*Hepatitis B surface antigen*
- While **hepatitis B** can also be transmitted via intravenous drug use and cause chronic liver disease, **hepatitis C is more prevalent** in persons with IVDU history in the United States.
- **HBsAg** is used to detect active hepatitis B infection and should also be ordered, but given resource constraints and the clinical context, **anti-HCV is the higher-yield initial test**.
- Many IVDU patients have been vaccinated against HBV, further reducing its likelihood compared to HCV (for which no vaccine exists).
*Hepatitis E virus-specific IgM antibodies*
- **Hepatitis E** is typically transmitted via the **fecal-oral route** (contaminated water) and usually causes **acute, self-limiting hepatitis**, not chronic insidious fatigue and liver enzyme elevation in a Western patient.
- **IgM antibodies** would indicate an acute infection, which is less likely given the 6-month duration of symptoms.
- HEV rarely causes chronic infection except in immunocompromised patients.
*Hepatitis D virus-specific IgG antibody*
- **Hepatitis D** requires an existing **hepatitis B infection** to replicate (it's a satellite virus), meaning you would first need to confirm chronic hepatitis B before testing for HDV.
- While HDV can cause severe liver disease and is transmitted via blood exposure, it's not the initial test to pursue without evidence of HBV co-infection.
*Hepatitis A virus-specific IgM antibodies*
- **Hepatitis A** is transmitted via the **fecal-oral route** and causes an **acute, self-limiting infection** with complete resolution, rarely leading to chronic liver disease or persistent fatigue over 6 months.
- **IgM antibodies** are indicative of acute infection, which contradicts the chronic nature of the patient's symptoms.
- HAV does not cause chronic hepatitis.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 3: A 56-year-old African American presents to the emergency department due to abdominal pain, fatigue, and weight loss over the past 3 months. He has a long-standing history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection complicated by cirrhosis. On examination, he has jaundice, leg edema, and a palpable mass in the right upper abdominal quadrant. Abdominal ultrasound shows a 3-cm liver mass with poorly defined margins and coarse, irregular internal echoes. Blood investigations are shown:
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 90 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 50 U/L
Total bilirubin 2 mg/dL
Albumin 3 g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 100 U/L
Alpha fetoprotein 600 micrograms/L
Which of the following targeted agents is approved for advanced-stage hepatoma?
- A. Ustekinumab
- B. Daclizumab
- C. Sorafenib (Correct Answer)
- D. Abciximab
- E. Palivizumab
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***Sorafenib***
- This patient's presentation with chronic hepatitis B, cirrhosis, a liver mass, and an **elevated alpha-fetoprotein** is highly suggestive of **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, also known as hepatoma.
- **Sorafenib** is a **multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor** that inhibits tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis by targeting VEGFR, PDGFR, Raf kinases, and other kinases involved in tumor progression.
- It was the **first systemic therapy approved for advanced-stage HCC** and remains an important first-line treatment option for patients with advanced disease who are not candidates for surgical or locoregional therapies.
*Ustekinumab*
- **Ustekinumab** is a monoclonal antibody that targets the **p40 subunit of IL-12 and IL-23**, primarily used in the treatment of **psoriasis** and psoriatic arthritis, not HCC.
- It works by blocking inflammatory pathways involved in autoimmune conditions.
*Daclizumab*
- **Daclizumab** is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the **CD25 subunit of the IL-2 receptor**; it was previously used for treating **multiple sclerosis** but has been largely discontinued due to safety concerns.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of any form of cancer.
*Abciximab*
- **Abciximab** is a monoclonal antibody that targets the **glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor** on platelets, used as an **antiplatelet agent** in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.
- Its mechanism of action is related to inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombosis, not cancer therapy.
*Palivizumab*
- **Palivizumab** is a monoclonal antibody used for the **prevention of serious lower respiratory tract disease** caused by **respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)** in high-risk infants.
- It provides passive immunity against RSV and has no role in cancer treatment.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain that started while she was at the gym. The patient competes as a power lifter and states that her pain started after one of her heavier lifts. The patient has no significant past medical history and is currently taking a multivitamin and oral contraceptive pills. She smokes cigarettes and drinks alcohol regularly and is currently sexually active with multiple partners. Her temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 85/55 mmHg, pulse is 125/min, respirations are 18/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical exam is notable for right upper quadrant abdominal tenderness, acne, and muscle hypertrophy. Right upper quadrant ultrasound demonstrates a solitary heterogeneous mass. Which of the following other findings is most likely to be found in this patient?
- A. Elevated viral core antigen
- B. Elevated alpha fetoprotein
- C. Increased pigmentation in flexural areas
- D. Prolonged PT and PTT
- E. Increased LDL and decreased HDL (Correct Answer)
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***Increased LDL and decreased HDL***
- This patient's presentation is most consistent with **hepatic adenoma rupture** related to **anabolic steroid use** (suggested by powerlifting, muscle hypertrophy, and acne) combined with oral contraceptive use.
- **Anabolic steroids have well-documented effects on lipid metabolism**, characteristically causing **decreased HDL cholesterol** and **increased LDL cholesterol**, which significantly increases cardiovascular risk.
- This lipid pattern is one of the most consistent and clinically significant metabolic effects of anabolic steroid abuse and would be expected in this patient.
*Elevated alpha fetoprotein*
- **Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)** is a tumor marker for **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, not hepatic adenoma.
- While anabolic steroids can cause hepatic adenomas and rarely HCC, this acute presentation with hemodynamic instability in a young woman on oral contraceptives is classic for **ruptured hepatic adenoma**, which does **not** elevate AFP.
- AFP elevation would not be expected in this clinical scenario.
*Elevated viral core antigen*
- Elevated viral core antigen would indicate active **hepatitis B infection**, a risk factor for chronic liver disease and HCC.
- There is no evidence in this vignette to suggest viral hepatitis, and this would not be related to the acute presentation or anabolic steroid use.
*Increased pigmentation in flexural areas*
- **Acanthosis nigricans** (hyperpigmentation in flexural areas) is associated with insulin resistance and certain malignancies.
- While anabolic steroids can affect glucose metabolism, acanthosis nigricans is not a characteristic finding of steroid use or hepatic adenoma.
*Prolonged PT and PTT*
- While severe liver dysfunction can cause coagulopathy with prolonged PT and PTT, this is not the most characteristic finding in hepatic adenoma.
- The acute presentation is more likely due to hemorrhage from adenoma rupture rather than chronic liver failure with synthetic dysfunction.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 5: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man presents to urgent care for weakness and weight loss. He states for the past several months he has felt progressively weaker and has lost 25 pounds. The patient also endorses intermittent abdominal pain. The patient has not seen a physician in 30 years and recalls being current on most of his vaccinations. He says that a few years ago, he went to the emergency department due to abdominal pain and was found to have increased liver enzymes due to excessive alcohol use and incidental gallstones. The patient has a 50 pack-year smoking history. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 161/108 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. Physical exam reveals an emaciated man. The patient has a negative Murphy's sign and his abdomen is non-tender. Cardiopulmonary exam is within normal limits. Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. CT scan of the abdomen (Correct Answer)
- B. CT scan of the liver
- C. Right upper quadrant ultrasound
- D. HIDA scan
- E. Smoking cessation advice and primary care follow up
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***CT scan of the abdomen***
- The patient presents with **constitutional symptoms** (weakness, significant weight loss), **intermittent abdominal pain**, and a **50 pack-year smoking history**, which are red flags for potential **malignancy**.
- A CT scan of the abdomen is the most appropriate initial imaging study to **evaluate for masses, metastases, or other pathologies** that would explain these symptoms comprehensively.
*CT scan of the liver*
- While the patient has a history of elevated liver enzymes and gallstones, focusing solely on the liver might **miss other abdominal pathologies** that could explain his symptoms.
- A CT of the liver is a more targeted scan, usually performed after a broader abdominal assessment suggests a primary liver issue.
*Right upper quadrant ultrasound*
- An ultrasound of the right upper quadrant is excellent for evaluating the **gallbladder, bile ducts, and liver parenchyma** for stones, cholecystitis, or focal lesions.
- However, it has **limited ability to visualize the retroperitoneum, pancreas, or other bowel structures** which could be the source of the patient's symptoms.
*HIDA scan*
- A HIDA scan is used to assess **gallbladder function** and is primarily indicated for suspected **acute cholecystitis** when ultrasound findings are equivocal, or for chronic gallbladder dysfunction.
- The patient's presentation of generalized weakness, significant weight loss, and non-tender abdomen does not acutely point towards biliary obstruction or acute cholecystitis.
*Smoking cessation advice and primary care follow up*
- While **smoking cessation** is crucial for long-term health, and **primary care follow-up** is necessary, these steps are not the *next best step in management* for a patient presenting with alarming symptoms of weakness, significant weight loss, and abdominal pain.
- These are important secondary measures, but the immediate concern is to **investigate the cause of his current severe symptoms**.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 7: A 52-year-old female presents to her primary care physician for medical evaluation prior to an elective hip replacement surgery. She has hypertension and diabetes, both of which are well controlled on oral medications. She also admits to occasional use of recreational injection drugs so a panel of serologies are obtained. Based on the results, the patient is found to have had a previous infection with hepatitis B from which she has fully recovered. Which of the following is a characteristic of the immunoglobulin subtype that most likely binds to hepatitis B core antigen in this patient?
- A. It exists as a dimer
- B. It is only activated by multivalent immunogens
- C. It exists as a pentamer
- D. It activates mast cells
- E. It exists as a monomer (Correct Answer)
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***It exists as a monomer***
- In a recovered hepatitis B infection, **anti-HBc IgG** antibodies are prominent, indicating past exposure and immunity.
- **IgG** is the most abundant immunoglobulin in serum and exists primarily as a **monomer**, providing long-term immunity.
*It exists as a dimer*
- This characteristic primarily describes **secretory IgA**, which is found in mucosal secretions like tears, saliva, and breast milk.
- While IgA can be involved in host defense, it's not the primary antibody subtype associated with sustained immunity after hepatitis B recovery, nor does it typically target the **core antigen** in this context.
*It is only activated by multivalent immunogens*
- This statement is more characteristic of **IgM**, which often requires multiple binding sites to activate complement efficiently due to its pentameric structure.
- **IgG** can bind to both univalent and multivalent antigens and is effective in neutralizing pathogens and activating other immune responses.
*It exists as a pentamer*
- This describes **IgM**, which is typically the first antibody produced during a primary immune response and is found on the surface of B cells.
- In a recovered infection, IgM would have largely subsided, replaced by **IgG**.
*It activates mast cells*
- This is a hallmark function of **IgE**, which binds to receptors on mast cells and basophils, triggering the release of histamine and other mediators in allergic reactions.
- **IgG** has different effector functions, such as opsonization, neutralization, and complement activation.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 8: A 52-year-old male patient with chronic alcoholism presents to an ambulatory medical clinic, where the hepatologist elects to perform comprehensive hepatitis B screening, in addition to several other screening and preventative measures. Given the following choices, which serologic marker, if positive, would indicate the patient’s immunity to the hepatitis B virus?
- A. HBeAb
- B. HBeAg
- C. HBsAb (Correct Answer)
- D. HBsAg
- E. HBcAb
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***HBsAb***
- A positive **HBsAb** (Hepatitis B surface antibody) indicates immunity to hepatitis B virus, either from successful **vaccination** or **recovery from past infection**.
- This antibody provides **protective immunity** against future HBV infection and is the definitive marker of immunity.
*HBeAb*
- **HBeAb** (Hepatitis B e antibody) indicates **seroconversion** from HBeAg during chronic HBV infection, suggesting lower viral replication.
- It does **not confer immunity** against the virus itself and only reflects a phase of chronic infection.
*HBeAg*
- **HBeAg** (Hepatitis B e antigen) indicates **active viral replication** with high infectivity during ongoing hepatitis B infection.
- Its presence signifies a **replicative phase** of infection and increased risk of transmission to others.
*HBsAg*
- **HBsAg** (Hepatitis B surface antigen) indicates **active hepatitis B infection**, whether acute or chronic.
- This antigen is the **first serologic marker** to appear following exposure and confirms presence of the virus.
*HBcAb*
- **HBcAb** (Hepatitis B core antibody) indicates **previous or current exposure** to hepatitis B virus.
- It does **not differentiate** between acute, chronic, or resolved infection and does not confer protective immunity.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 9: A 3255-g (7-lb) female newborn is delivered at term. Pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated. On the day of her birth, she is given a routine childhood vaccine that contains a noninfectious glycoprotein. This vaccine will most likely help prevent infection by which of the following pathogens?
- A. Bordetella pertussis
- B. Rotavirus
- C. Poliovirus
- D. Haemophilus influenzae type b
- E. Hepatitis B virus (Correct Answer)
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***Hepatitis B virus***
- The **Hepatitis B vaccine** is routinely given at birth and contains a **noninfectious glycoprotein** (HBsAg) that elicits an immune response.
- This vaccine is crucial for preventing mother-to-child transmission and provides long-term protection against **Hepatitis B infection**.
*Bordetella pertussis*
- The vaccine for **Bordetella pertussis** (whooping cough) is part of the DTaP vaccine and is typically given at 2 months of age, not at birth.
- The DTaP vaccine usually contains **inactivated toxins** or acellular components, not solely a glycoprotein.
*Rotavirus*
- The **Rotavirus vaccine** is an **oral live-attenuated vaccine** administered in two or three doses, with the first dose typically given at 2 months of age.
- It does not contain a noninfectious glycoprotein.
*Poliovirus*
- The **Poliovirus vaccine** (IPV) is an **inactivated vaccine** given at 2 months of age, and the **oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV)** is a live-attenuated vaccine.
- Neither is routinely given at birth, nor described as a noninfectious glycoprotein.
*Haemophilus influenzae type b*
- The **Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine** is a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine, first administered at 2 months of age.
- While it contains a protein component, it is not typically given at birth.
HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG Question 10: A scientist is studying the replication sequences of a number of different viruses. He observes that one particular virus he is studying creates a single stranded DNA from an RNA template during its replication sequence. Which of the following viruses is he most likely observing?
- A. Hepatitis C virus
- B. Norovirus
- C. Hepatitis B virus (Correct Answer)
- D. HSV-1
- E. Hepatitis A virus
HCC screening in viral hepatitis Explanation: ***Hepatitis B virus***
- This virus is a **DNA virus** that replicates via an **RNA intermediate**, using a **reverse transcriptase** enzyme to synthesize DNA from an RNA template.
- Its replication cycle involves creating a pre-genomic RNA from its DNA genome, which is then reverse-transcribed into **partially double-stranded DNA** for packaging into new virions.
*Hepatitis C virus*
- This is an **RNA virus** that replicates entirely within the cytoplasm and does not utilize a DNA intermediate or reverse transcriptase.
- Its replication involves the synthesis of a **negative-sense RNA strand** from the positive-sense genomic RNA, which then serves as a template for new positive-sense RNA genomes.
*Norovirus*
- This is a **positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus** that replicates in the cytoplasm of host cells.
- It uses an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase** to synthesize new RNA genomes directly from an RNA template, without a DNA intermediate.
*HSV-1*
- **Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1)** is a **double-stranded DNA virus** that replicates in the nucleus of infected cells.
- Its replication pathway involves **DNA-dependent DNA polymerase** to replicate its genome and does not involve an RNA to DNA transcription step.
*Hepatitis A virus*
- This is a **positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus** that belongs to the **Picornaviridae family**.
- Like other RNA viruses, it replicates its genome via an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, directly creating new RNA copies from an RNA template without a reverse transcription step.
More HCC screening in viral hepatitis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.