HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for HBV vaccination and prevention. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 1: A 35-year-old male anesthesiologist presents to the occupational health clinic after a needlestick exposure while obtaining an arterial line in a patient with cirrhosis. In addition to a standard bloodborne pathogen laboratory panel sent for all needlestick exposures at his hospital, additional hepatitis panels are ordered upon the patient's request. The patient's results are shown below:
HIV 4th generation Ag/Ab: Negative/Negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): Negative
Hepatitis C antibody: Negative
Anti-hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb): Positive
Anti-hepatitis B core IgM antibody (HBc IgM): Negative
Anti-hepatitis B core IgG antibody (HBc IgG): Positive
What is the most likely explanation of the results above?
- A. Window period
- B. Chronic infection
- C. Acute infection
- D. Immune due to infection (Correct Answer)
- E. Immune due to vaccination
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***Immune due to infection***
- The presence of **anti-HBc IgG** along with **anti-HBsAb** in the absence of **HBsAg** indicates past resolution of HBV infection.
- This combination confers **natural immunity** following a prior exposure, distinguishing it from vaccine-induced immunity (which would lack anti-HBc IgG).
*Window period*
- This period is characterized by the absence of **HBsAg** and **anti-HBsAb**, with the only positive marker being **anti-HBc IgM**.
- The patient's results show positive **anti-HBsAb** and **anti-HBc IgG**, which rule out a window period.
*Chronic infection*
- Chronic infection is defined by the persistence of **HBsAg** for more than six months.
- The patient's **HBsAg is negative**, therefore excluding chronic infection.
*Acute infection*
- Acute infection would be evidenced by the presence of **HBsAg** and often **anti-HBc IgM**.
- Both **HBsAg** and **anti-HBc IgM** are negative in this patient, ruling out acute infection.
*Immune due to vaccination*
- Vaccination leads to the development of **anti-HBsAb** but does not produce **anti-HBc antibodies**.
- The presence of **anti-HBc IgG** in this patient indicates exposure to the complete virus, not just vaccination.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 2: A 52-year-old male patient with chronic alcoholism presents to an ambulatory medical clinic, where the hepatologist elects to perform comprehensive hepatitis B screening, in addition to several other screening and preventative measures. Given the following choices, which serologic marker, if positive, would indicate the patient’s immunity to the hepatitis B virus?
- A. HBeAb
- B. HBeAg
- C. HBsAb (Correct Answer)
- D. HBsAg
- E. HBcAb
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***HBsAb***
- A positive **HBsAb** (Hepatitis B surface antibody) indicates immunity to hepatitis B virus, either from successful **vaccination** or **recovery from past infection**.
- This antibody provides **protective immunity** against future HBV infection and is the definitive marker of immunity.
*HBeAb*
- **HBeAb** (Hepatitis B e antibody) indicates **seroconversion** from HBeAg during chronic HBV infection, suggesting lower viral replication.
- It does **not confer immunity** against the virus itself and only reflects a phase of chronic infection.
*HBeAg*
- **HBeAg** (Hepatitis B e antigen) indicates **active viral replication** with high infectivity during ongoing hepatitis B infection.
- Its presence signifies a **replicative phase** of infection and increased risk of transmission to others.
*HBsAg*
- **HBsAg** (Hepatitis B surface antigen) indicates **active hepatitis B infection**, whether acute or chronic.
- This antigen is the **first serologic marker** to appear following exposure and confirms presence of the virus.
*HBcAb*
- **HBcAb** (Hepatitis B core antibody) indicates **previous or current exposure** to hepatitis B virus.
- It does **not differentiate** between acute, chronic, or resolved infection and does not confer protective immunity.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 3: A 28-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for a 1-week history of jaundice and nausea. She recalls eating some seafood last weekend at a cookout. She lives at home with her 2-year-old son who attends a daycare center. The child's immunizations are up-to-date, and his last hepatitis A vaccine was administered 6 weeks ago. The woman's temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 82/min, and blood pressure is 134/84 mm Hg. Examination shows scleral icterus. The liver is palpated 2-cm below the right costal margin and is tender. Her serum studies show:
Total bilirubin 3.4 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 89 U/L
AST 185 U/L
ALT 723 U/L
Hepatitis A IgM antibody positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody positive
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Hepatitis B core IgM antibody negative
Hepatitis C antibody negative
Which of the following health maintenance recommendations is most appropriate for the child at this time?
- A. Isolate the child
- B. Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin and hepatitis B vaccine
- C. No additional steps are needed (Correct Answer)
- D. Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin only
- E. Administer hepatitis A vaccine and hepatitis A immunoglobulin
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***No additional steps are needed***
- The child received his **last hepatitis A vaccine 6 weeks ago**, which provides adequate protection against hepatitis A infection.
- According to **CDC/ACIP guidelines**, children who have received **at least one dose** of hepatitis A vaccine do **not require post-exposure prophylaxis** (neither additional vaccine nor immunoglobulin) after exposure to hepatitis A.
- One dose of hepatitis A vaccine provides protection within **2-4 weeks**, and since 6 weeks have elapsed, the child is already immune.
- The child's **immunizations are up-to-date**, confirming he is on the appropriate hepatitis A vaccination schedule (2-dose series).
*Administer hepatitis A vaccine and hepatitis A immunoglobulin*
- This would be appropriate for **previously unvaccinated** individuals exposed to hepatitis A, immunocompromised patients, or infants under 12 months.
- However, this child has **already been vaccinated** 6 weeks ago and therefore has adequate protection.
- Administering both vaccine and immunoglobulin is **unnecessary** and not indicated per current guidelines when prior vaccination has occurred.
*Isolate the child*
- Isolation is not the primary recommendation for hepatitis A post-exposure management in household contacts.
- The focus should be on **prevention through immunization**, but this child is already protected by prior vaccination.
- Standard hygiene measures (handwashing) are recommended but formal isolation is not necessary.
*Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin and hepatitis B vaccine*
- The mother's serology shows **HBsAg negative** and **HBsAb positive**, indicating she is **immune to hepatitis B** (likely from prior vaccination) and not currently infected.
- There is **no risk of hepatitis B transmission** from the mother to the child.
- This intervention addresses the wrong infection entirely.
*Administer hepatitis B immunoglobulin only*
- This is inappropriate because the mother does **not have active hepatitis B infection** (HBsAg negative).
- This option does not address the **hepatitis A exposure**, which is the relevant concern in this scenario.
- Hepatitis B immunoglobulin is indicated only for exposure to hepatitis B, not hepatitis A.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 4: A 28-year-old woman gives birth to a 2.2 kg child while on vacation. The mother's medical records are faxed to the hospital and demonstrate the following on hepatitis panel: hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) positive, anti-hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbcAg) positive, hepatitis C RNA is detected, hepatitis C antibody is reactive. Which of the following should be administered to the patient's newborn child?
- A. Hepatitis B vaccine, ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
- B. Hepatitis B IVIG and vaccine (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatitis B IVIG, hepatitis B vaccine and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
- D. Hepatitis B IVIG now, hepatitis B vaccine in one month
- E. Hepatitis B vaccine
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***Hepatitis B IVIG and vaccine***
- The mother is **HBsAg positive** and **anti-HBcAg positive**, indicating a **chronic hepatitis B infection**. To prevent vertical transmission, the neonate must receive both **Hepatitis B Immune Globulin (HBIG)** and the **Hepatitis B vaccine** within 12 hours of birth.
- While the mother also has **Hepatitis C (HCV) RNA detected** and **HCV antibody reactive**, there is currently no preventative measure for HCV transmission to the newborn at birth, as antiviral medications like ledipasvir/sofosbuvir are not administered to neonates for this purpose.
*Hepatitis B vaccine, ledipisvir/sofosbuvir*
- Administering ledipasvir/sofosbuvir to the newborn is **not indicated** for preventing vertical transmission of Hepatitis C; these antivirals are used for treating HCV infection in adults and older children.
- While the Hepatitis B vaccine is necessary, it is **insufficient alone** for preventing perinatal HBV transmission in infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers.
*Hepatitis B IVIG, hepatitis B vaccine and ledipisvir/sofosbuvir*
- **Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir** is not a recommended prophylactic or treatment measure for newborns to prevent hepatitis C infection.
- While HBIG and the vaccine are correct for Hepatitis B, the addition of HCV antivirals for the neonate is **inappropriate**.
*Hepatitis B IVIG now, hepatitis B vaccine in one month*
- Both **HBIG** and the **first dose of the Hepatitis B vaccine** must be given **within 12 hours of birth** to be maximally effective in preventing perinatal HBV transmission. Delaying the vaccine dose significantly reduces its protective efficacy.
- This regimen would leave the newborn **unprotected** for a crucial period during which HBV transmission is most likely.
*Hepatitis B vaccine*
- Giving only the **Hepatitis B vaccine** is **insufficient** for an infant born to an HBsAg-positive mother.
- In such cases, **HBIG** is also required to provide immediate passive immunity and maximize protection against perinatal HBV infection, which has a high risk of chronicity.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 5: A 3255-g (7-lb) female newborn is delivered at term. Pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated. On the day of her birth, she is given a routine childhood vaccine that contains a noninfectious glycoprotein. This vaccine will most likely help prevent infection by which of the following pathogens?
- A. Bordetella pertussis
- B. Rotavirus
- C. Poliovirus
- D. Haemophilus influenzae type b
- E. Hepatitis B virus (Correct Answer)
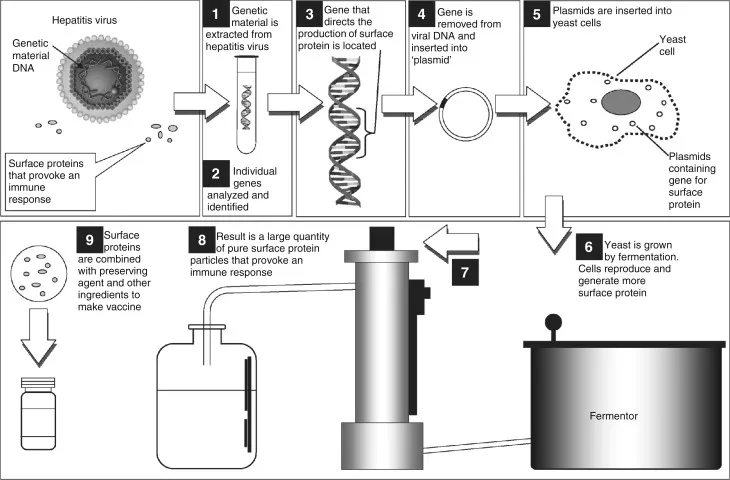
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***Hepatitis B virus***
- The **Hepatitis B vaccine** is routinely given at birth and contains a **noninfectious glycoprotein** (HBsAg) that elicits an immune response.
- This vaccine is crucial for preventing mother-to-child transmission and provides long-term protection against **Hepatitis B infection**.
*Bordetella pertussis*
- The vaccine for **Bordetella pertussis** (whooping cough) is part of the DTaP vaccine and is typically given at 2 months of age, not at birth.
- The DTaP vaccine usually contains **inactivated toxins** or acellular components, not solely a glycoprotein.
*Rotavirus*
- The **Rotavirus vaccine** is an **oral live-attenuated vaccine** administered in two or three doses, with the first dose typically given at 2 months of age.
- It does not contain a noninfectious glycoprotein.
*Poliovirus*
- The **Poliovirus vaccine** (IPV) is an **inactivated vaccine** given at 2 months of age, and the **oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV)** is a live-attenuated vaccine.
- Neither is routinely given at birth, nor described as a noninfectious glycoprotein.
*Haemophilus influenzae type b*
- The **Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine** is a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine, first administered at 2 months of age.
- While it contains a protein component, it is not typically given at birth.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 6: A 35-year-old man with no known past medical history presents to his physician because he is applying for a job as a healthcare worker, which requires screening for the hepatitis B virus (HBV). The patient states that he is in good health and denies any symptoms. His vital signs and physical exam are unremarkable. Labs are drawn, and the patient's HBV serology shows the following:
HBsAg: positive
anti-HBsAg antibody: negative
anti-HBcAg IgM: negative
anti-HBcAg IgG: positive
HBeAg: negative
anti-HBeAg antibody: positive
Which of the following best describes this patient's results?
- A. Immune due to previous infection
- B. Chronically infected, low infectivity (Correct Answer)
- C. Immune due to previous vaccination
- D. Acutely infected
- E. Chronically infected, high infectivity
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***Chronically infected, low infectivity***
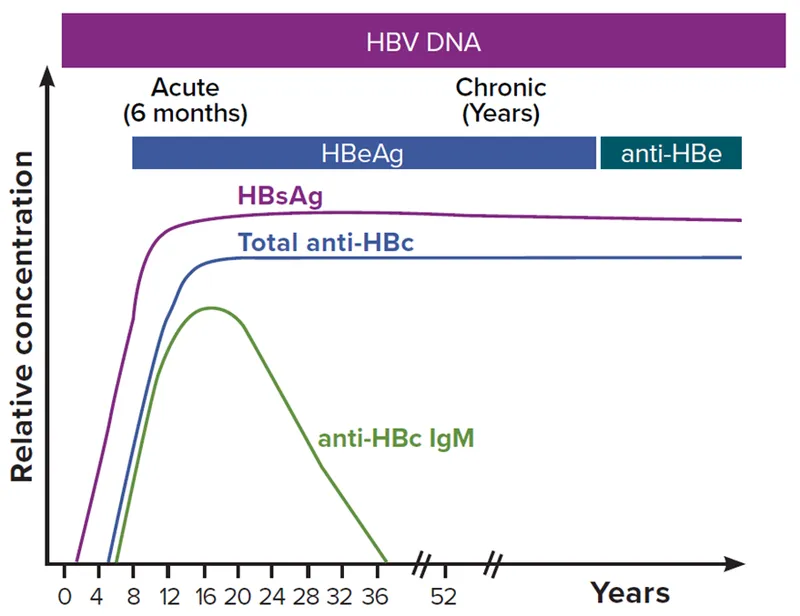
- The presence of **HBsAg positive** for more than 6 months indicates **chronic HBV infection**. The presence of **anti-HBeAg antibody** and **negative HBeAg** suggests **low viral replication activity** and thus low infectivity.
- **HBeAg negativity** along with positivity for **HBV DNA** (if tested, though not provided here) would further differentiate this state as **"HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B,"** which typically implies lower, but still present, infectivity compared to HBeAg-positive chronic infection.
*Immune due to previous infection*
- Immunity due to previous infection is characterized by **negative HBsAg** and **positive anti-HBsAg antibody**, along with **positive anti-HBcAg IgG**.
- This patient, however, is **HBsAg positive** and **anti-HBsAg antibody negative**, ruling out resolved infection.
*Immune due to previous vaccination*
- Immunity due to vaccination is characterized by **negative HBsAg**, **positive anti-HBsAg antibody**, and **negative anti-HBcAg antibody** (both IgM and IgG).
- This patient has **positive HBsAg** and **positive anti-HBcAg IgG**, indicating either current or past infection, not vaccination-induced immunity.
*Acutely infected*
- **Acute infection** is characterized by **positive HBsAg**, **negative anti-HBsAg antibody**, and typically **positive anti-HBcAg IgM**.
- This patient has **negative anti-HBcAg IgM**, which makes acute infection unlikely, as IgM antibodies are present early in acute infection.
*Chronically infected, high infectivity*
- **High infectivity** in chronic HBV infection is typically indicated by **positive HBsAg** and **positive HBeAg**, often with high levels of HBV DNA.
- This patient is **HBeAg negative** and **anti-HBeAg antibody positive**, indicating a lower level of viral replication and thus lower infectivity.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician because of several days of fever, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. She drank water from a stream 1 week ago while she was hiking in the woods. Abdominal examination shows increased bowel sounds. Stool analysis for ova and parasites shows flagellated multinucleated trophozoites. Further evaluation shows the presence of antibodies directed against the pathogen. Secretion of these antibodies most likely requires binding of which of the following?
- A. CD28 to B7 protein
- B. CD80/86 to CTLA-4
- C. gp120 to CD4
- D. CD8 to MHC I
- E. CD40 to CD40 ligand (Correct Answer)
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***CD40 to CD40 ligand***
- The interaction between **CD40 on B cells** and **CD40 ligand (CD40L) on activated T helper cells** is crucial for **T cell-dependent B cell activation** and antibody class switching.
- This binding leads to the maturation of the immune response, including the secretion of **high-affinity antibodies** like IgA, which is especially important for mucosal immunity against pathogens like *Giardia lamblia* (the likely cause of the patient's symptoms).
*CD28 to B7 protein*
- The binding of **CD28 on T cells** to **B7 protein (CD80/86) on antigen-presenting cells (APCs)** provides the **second co-stimulatory signal** required for T cell activation.
- While essential for T cell activation, this interaction primarily supports T cell proliferation and differentiation, rather than directly mediating antibody secretion by B cells.
*CD80/86 to CTLA-4*
- **CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4)** is a receptor on T cells that binds to **CD80/86 (B7)** on APCs with higher affinity than CD28.
- This interaction provides an **inhibitory signal** that downregulates T cell activation, serving as a negative feedback mechanism, and does not promote antibody secretion.
*gp120 to CD4*
- The **gp120 glycoprotein** on the surface of **HIV** binds to the **CD4 receptor** on T helper cells, initiating the entry of the virus into the cell.
- This interaction is specific to HIV infection and is not involved in the normal process of antibody secretion in response to other pathogens.
*CD8 to MHC I*
- **CD8** is a co-receptor expressed on **cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs)** that binds to **MHC class I molecules** on target cells.
- This interaction is essential for the recognition of virally infected or cancerous cells by CTLs, leading to their destruction, but it is not directly involved in antibody production.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 8: A group of researchers conducted various studies on hepatitis C incidence and prevalence. They noticed that there is a high prevalence of hepatitis C in third-world countries, where it has a significant impact on the quality of life of the infected individual. The research group made several attempts to produce a vaccine that prevents hepatitis C infection but all attempts failed. Which of the following would most likely be the reason for the failure to produce a vaccine?
- A. Non-DNA genome
- B. Tolerance
- C. Antigenic mimicry
- D. Polysaccharide envelope
- E. Antigenic variation (Correct Answer)
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***Antigenic variation***
- The **hepatitis C virus (HCV)** undergoes rapid **antigenic variation**, particularly in its envelope glycoproteins, which allows it to evade the host immune system.
- This high mutation rate presents a significant challenge for vaccine development, as a vaccine designed against one viral strain may not be effective against others.
*Non-DNA genome*
- While HCV is an **RNA virus** (non-DNA genome), this characteristic alone does not inherently prevent vaccine development; many effective RNA virus vaccines exist (e.g., measles, mumps).
- The type of genome is less critical than its stability and the virus's ability to mutate rapidly.
*Tolerance*
- **Immune tolerance** occurs when the immune system fails to respond to an antigen, often due to chronic exposure. While relevant in chronic HCV infection, it's not the primary reason for vaccine failure.
- The goal of a vaccine is to induce an effective immune response before tolerance can set in.
*Antigenic mimicry*
- **Antigenic mimicry** involves a pathogen's antigens resembling host antigens, potentially leading to autoimmune responses or immune evasion.
- While it can be a factor in some chronic infections, the rapid, diverse changes in HCV's surface antigens are a more prominent obstacle to vaccine design.
*Polysaccharide envelope*
- HCV is an **enveloped virus**, but its envelope is composed of **lipoproteins** with viral glycoproteins, not a polysaccharide capsule.
- Polysaccharide capsules are a feature of some bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae) and fungi, and while they can pose vaccine challenges, they are not relevant to HCV.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 9: A 13-year-old boy presents to the pediatrician with yellow discoloration of the sclerae since yesterday, and dark-colored urine for 2 days. A detailed history is taken and reveals that he had a cough, cold, and fever the week before the onset of the current symptoms, and was treated with over-the-counter medications. He reports an improvement in his upper respiratory symptoms but has been experiencing fatigue, nausea, and poor appetite since then. There is no past history of recurrent nausea, vomiting, jaundice or abdominal pain, and he has not received any blood transfusion. In addition, he frequently eats at a roadside restaurant near his school. His growth and development are normal for his age and sex. The temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 96/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and the respiratory rate is 22/min. The physical examination shows icterus. The examination of the abdomen reveals tender hepatomegaly with the liver having a firm, sharp, and smooth edge. The laboratory test results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 14.2 g/dL
WBC (white blood cell) 10,500/mm3
Differential leukocyte count
Segmented neutrophils 56%
Bands 4%
Lymphocytes 35%
Eosinophils 2%
Basophils 0%
Monocytes 3%
Platelet count 270,000/mm3
Serum total bilirubin 8.4 mg/dL
Serum direct bilirubin 7.8 mg/dL
Serum alanine aminotransferase 350 U/L
Serum alkaline phosphatase 95 U/L
Prothrombin time 20 seconds
Which of the following laboratory tests is most likely used to diagnose the condition of this patient?
- A. Plasma tyrosine and methionine
- B. Serum anti-HAV IgM antibody (Correct Answer)
- C. Quantitative assay for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity
- D. Urine for reducing substances
- E. Percutaneous liver biopsy
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***Serum anti-HAV IgM antibody***
- The patient's symptoms (jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, nausea, tender hepatomegaly) following an upper respiratory illness, especially with a history of eating at a roadside restaurant, are highly suggestive of **acute hepatitis A infection**.
- **IgM antibodies** to hepatitis A virus (HAV) are detectable early in the course of infection and indicate **acute or recent infection**, making it the most appropriate diagnostic test.
*Plasma tyrosine and methionine*
- These tests are used in the diagnosis of **tyrosinemia**, a rare inherited metabolic disorder that can cause liver failure.
- The patient's acute presentation and history of potential exposure to HAV make tyrosinemia less likely, and **elevated transaminases** are not specific to tyrosinemia.
*Quantitative assay for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity*
- This assay is used to diagnose **G6PD deficiency**, an inherited condition that can cause hemolytic anemia, particularly after exposure to certain drugs or foods, which might lead to jaundice from unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- However, the patient's presentation with **tender hepatomegaly**, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia (direct bilirubin significantly elevated), and elevated transaminases is more consistent with **hepatocellular injury** rather than hemolysis.
*Urine for reducing substances*
- This test is used to screen for **galactosemia** or other disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in infants and young children, where undigested sugars appear in the urine.
- It is not indicated for the diagnosis of acute hepatitis in an adolescent with the presented clinical picture.
*Percutaneous liver biopsy*
- While a liver biopsy can provide definitive information about liver pathology, it is an **invasive procedure** and is generally not the initial diagnostic test for acute viral hepatitis due to its risks.
- **Serological markers** for viral hepatitis are less invasive and usually sufficient for diagnosing acute hepatitis A.
HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG Question 10: A scientist is studying the replication sequences of a number of different viruses. He observes that one particular virus he is studying creates a single stranded DNA from an RNA template during its replication sequence. Which of the following viruses is he most likely observing?
- A. Hepatitis C virus
- B. Norovirus
- C. Hepatitis B virus (Correct Answer)
- D. HSV-1
- E. Hepatitis A virus
HBV vaccination and prevention Explanation: ***Hepatitis B virus***
- This virus is a **DNA virus** that replicates via an **RNA intermediate**, using a **reverse transcriptase** enzyme to synthesize DNA from an RNA template.
- Its replication cycle involves creating a pre-genomic RNA from its DNA genome, which is then reverse-transcribed into **partially double-stranded DNA** for packaging into new virions.
*Hepatitis C virus*
- This is an **RNA virus** that replicates entirely within the cytoplasm and does not utilize a DNA intermediate or reverse transcriptase.
- Its replication involves the synthesis of a **negative-sense RNA strand** from the positive-sense genomic RNA, which then serves as a template for new positive-sense RNA genomes.
*Norovirus*
- This is a **positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus** that replicates in the cytoplasm of host cells.
- It uses an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase** to synthesize new RNA genomes directly from an RNA template, without a DNA intermediate.
*HSV-1*
- **Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1)** is a **double-stranded DNA virus** that replicates in the nucleus of infected cells.
- Its replication pathway involves **DNA-dependent DNA polymerase** to replicate its genome and does not involve an RNA to DNA transcription step.
*Hepatitis A virus*
- This is a **positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus** that belongs to the **Picornaviridae family**.
- Like other RNA viruses, it replicates its genome via an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, directly creating new RNA copies from an RNA template without a reverse transcription step.
More HBV vaccination and prevention US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.