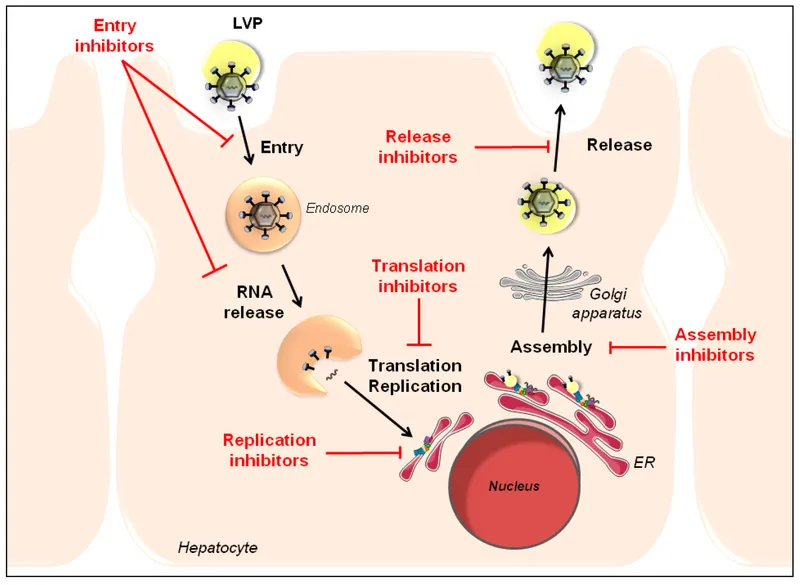
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Direct-acting antivirals for HCV. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 1: A 25-year-old sexually active male presents to an internal medicine physician for a routine health check up after having several unprotected sexual encounters. After appropriate testing the physician discusses with the patient that he is HIV+ and must be started on anti-retroviral treatment. Which of the following medications prescribed acts on the gp41 subunit of the HIV envelope glycoprotein?
- A. Zidovudine
- B. Saquinavir
- C. Enfuvirtide (Correct Answer)
- D. Amantadine
- E. Rimantadine
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Enfuvirtide***
- **Enfuvirtide** is a **fusion inhibitor** that binds specifically to the **gp41 subunit** of the HIV envelope glycoprotein.
- By binding to gp41, Enfuvirtide prevents the **fusion of the viral and host cell membranes**, thereby blocking viral entry and replication.
*Zidovudine*
- **Zidovudine** is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)**.
- It works by inhibiting the enzyme **reverse transcriptase**, which is responsible for converting viral RNA into DNA.
*Saquinavir*
- **Saquinavir** is a **protease inhibitor (PI)**.
- This drug works by inhibiting the **HIV protease enzyme**, which is crucial for cleaving viral polyproteins into functional proteins required for viral assembly and maturation.
*Amantadine*
- **Amantadine** is an **antiviral agent** primarily used to treat **influenza A**.
- It works by interfering with the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, thus inhibiting viral uncoating.
*Rimantadine*
- **Rimantadine** is another **antiviral agent** used for **influenza A treatment and prophylaxis**.
- Similar to amantadine, it targets the **M2 proton channel** of the influenza A virus, preventing the uncoating step necessary for viral replication.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 2: A 30-year-old woman presents with generalized fatigue, joint pain, and decreased appetite. She says that symptoms onset a year ago and have not improved. The patient’s husband says he has recently noticed that her eyes and skin are yellowish. The patient denies any history of smoking or alcohol use, but she admits to using different kinds of intravenous illicit drugs during her college years. The patient is afebrile and vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination is unremarkable, except for moderate scleral icterus. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of a blood sample is positive for a viral infection that reveals a positive-sense RNA virus, that is small, enveloped, and single-stranded. The patient is started on a drug that resembles a purine RNA nucleotide. She agrees not to get pregnant before or during the use of this medication. Which of the following is the drug that was most likely given to this patient?
- A. Sofosbuvir
- B. Cidofovir
- C. Ribavirin (Correct Answer)
- D. Simeprevir
- E. Interferon-alpha
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Ribavirin***
- The patient's history of **intravenous drug use**, fatigue, joint pain, decreased appetite, and **scleral icterus** are highly suggestive of **chronic Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection**. The description of the virus as a **small, enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus** confirms HCV. The patient is started on a drug that resembles a **purine RNA nucleotide** and is instructed not to get pregnant, which is characteristic of Ribavirin.
- **Ribavirin** is a **guanosine analog** that interferes with viral RNA synthesis and is known to be **teratogenic**, necessitating strict contraception during and after treatment.
*Sofosbuvir*
- While **Sofosbuvir** is used to treat Hepatitis C and is a **nucleotide analog** (specifically a uridine analog), it is a **prodrug** that mimics a uridine nucleotide, not a purine, and it is **not associated with the severe teratogenicity** that requires a two-contraception rule like Ribavirin.
- Sofosbuvir is a **direct-acting antiviral (DAA)** that inhibits the HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, but the description of a purine RNA nucleotide points away from this drug.
*Cidofovir*
- **Cidofovir** is a **cytosine nucleotide analog** primarily used to treat **cytomegalovirus (CMV)** retinitis in HIV/AIDS patients.
- It works by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase, and it is **not used for Hepatitis C infection**.
*Simeprevir*
- **Simeprevir** is an **HCV protease inhibitor**, not a nucleotide analog. It specifically targets the **NS3/4A protease** of the Hepatitis C virus.
- Although it is an effective DAA for HCV, its mechanism of action and class are different from the described "purine RNA nucleotide."
*Interferon-alpha*
- **Interferon-alpha** was historically used to treat Hepatitis C, but it is a **cytokine** that modulates the immune response, not a nucleoside/nucleotide analog.
- Its use has largely been replaced by more effective and better-tolerated direct-acting antivirals due to significant side effects and lower efficacy.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of fatigue and myalgia. Over the past month, she has had intermittent episodes of nausea. She has a history of intravenous drug use, but she has not used illicit drugs for the past five years. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 14 years and drinks one alcoholic beverage daily. She takes no medications. Her last visit to a physician was 4 years ago. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Physical examination shows jaundice and hepatosplenomegaly. There are also blisters and erosions on the dorsum of both hands. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8,300/mm3
Platelet count 250,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 170 mg/dL
Albumin 3.0 g/dL
Total bilirubin 2.2 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 80 U/L
AST 92 U/L
ALT 76 U/L
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Hepatitis B surface antibody positive
Hepatitis B core antibody positive
Hepatitis C antibody positive
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. PCR for viral DNA
- B. Western blot for HIV
- C. Serology for anti-HAV IgM
- D. PCR for viral RNA (Correct Answer)
- E. Liver biopsy
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Correct: PCR for viral RNA***
- The patient has high suspicion for **chronic hepatitis C infection** due to a history of intravenous drug use, the presence of **fatigue**, **myalgia**, **jaundice**, hepatosplenomegaly, and **elevated liver enzymes (AST and ALT)**
- The **blisters and erosions on the dorsum of both hands** are highly suggestive of **porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)**, a well-established complication of chronic hepatitis C caused by hepatic uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase deficiency
- The positive **Hepatitis C antibody** indicates exposure to HCV, but does not distinguish between acute, chronic, or resolved infection
- **PCR for viral RNA (HCV RNA)** is required to confirm **active viral replication** and diagnose current hepatitis C infection, which is crucial for treatment decisions
- The elevated glucose (170 mg/dL) may also represent hepatogenous diabetes related to chronic liver disease
*Incorrect: PCR for viral DNA*
- This test is primarily used for diagnosing active infections caused by **DNA viruses**, such as **hepatitis B** (HBV DNA) or cytomegalovirus
- The patient's hepatitis B serology indicates **past infection with immunity** (HBsAg negative, HBsAb positive, HBcAb positive), so HBV DNA testing is not indicated
- The clinical picture points toward HCV (an RNA virus), not a DNA virus
*Incorrect: Western blot for HIV*
- While the patient has a history of intravenous drug use (a risk factor for HIV), initial HIV screening is done with a **fourth-generation antigen/antibody combination assay**, not Western blot
- **Western blot** is a confirmatory test used only when initial HIV screening tests are reactive
- HIV testing may be appropriate given her risk factors, but it does not address the most pressing concern of active hepatitis C infection with complications (PCT)
*Incorrect: Serology for anti-HAV IgM*
- **Anti-HAV IgM** indicates **acute hepatitis A infection**, typically transmitted via the fecal-oral route
- The patient's symptoms, risk factors (IV drug use), positive HCV antibody, and characteristic skin findings (PCT) are not consistent with hepatitis A as the primary diagnosis
- Hepatitis A would not explain the chronic nature of symptoms or the skin manifestations
*Incorrect: Liver biopsy*
- **Liver biopsy** is an invasive procedure used to assess the **extent of liver damage**, inflammation, and fibrosis/cirrhosis after diagnosis of liver disease has been established
- It is not the most appropriate initial step to confirm **active viral replication**; PCR for HCV RNA should be performed first to establish that there is ongoing infection
- Once active HCV is confirmed, non-invasive methods (e.g., FibroScan, serum markers) are often preferred over biopsy for staging liver fibrosis
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old woman comes to the physician because of abdominal discomfort, anorexia, and mild fatigue. She has systemic lupus erythematosus and takes hydroxychloroquine. She does not drink alcohol or use illicit drugs. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Alanine aminotransferase 455 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase 205 U/L
Hepatitis B surface antigen positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody negative
Hepatitis B envelope antigen positive
Hepatitis B core antigen IgG antibody positive
Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
- A. Acyclovir
- B. Tenofovir (Correct Answer)
- C. Pegylated interferon-alpha
- D. Dolutegravir
- E. Sofosbuvir
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Tenofovir***
- This patient has **chronic active hepatitis B infection**, as indicated by **positive HBsAg**, **HBeAg**, and elevated liver enzymes. Antiviral therapy with **tenofovir** is highly effective and appropriate to suppress viral replication.
- The coexistence of **Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)** and **hydroxychloroquine** use increases the importance of managing HBV, as immunosuppression can lead to viral reactivation; tenofovir effectively targets the virus without significant interactions.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat infections caused by **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** and **varicella-zoster virus (VZV)**.
- It has **no efficacy** against hepatitis B virus (HBV) and therefore would not be appropriate for this patient's condition.
*Pegylated interferon-alpha*
- **Pegylated interferon-alpha** is an immunomodulatory agent used to treat chronic hepatitis B and C; however, it has a **less favorable side effect profile** and is often reserved for patients who cannot tolerate or respond to nucleoside/nucleotide analogs.
- The patient's underlying **SLE** could be **exacerbated by interferon**, making tenofovir a safer and more appropriate first-line choice given its better tolerability and potent antiviral effect.
*Dolutegravir*
- **Dolutegravir** is an **integrase inhibitor** used in the treatment of **HIV infection**.
- It has **no antiviral activity** against the hepatitis B virus and is therefore not indicated for this patient's condition.
*Sofosbuvir*
- **Sofosbuvir** is a direct-acting antiviral agent primarily used to treat **chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection**.
- It is **not effective** against hepatitis B virus (HBV) and would not be the correct treatment for this patient.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 5: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 6: A 45-year-old man presents for follow-up to monitor his chronic hepatitis C treatment. The patient was infected with hepatitis C genotype 1, one year ago. He has been managed on a combination of pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin, but a sustained viral response has not been achieved. Past medical history is significant for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease for the last 5 years. Which of the following, if added to the patient’s current treatment regimen, would most likely benefit this patient?
- A. Emtricitabine
- B. Entecavir
- C. Simeprevir (Correct Answer)
- D. Tenofovir
- E. Telbivudine
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Simeprevir***
- Simeprevir is a **first-generation direct-acting antiviral (DAA)**, specifically a **protease inhibitor (NS3/4A inhibitor)**, highly effective against **HCV genotype 1**.
- Adding simeprevir to a regimen of **pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin** significantly increases the likelihood of achieving a **sustained virologic response** for patients who previously failed interferon-based therapy.
- **Note:** While this triple therapy approach was standard practice historically, current guidelines (as of 2024-2025) favor **interferon-free DAA combination regimens** (such as sofosbuvir/ledipasvir or glecaprevir/pibrentasvir) as first-line treatment for HCV genotype 1. However, among the options provided, simeprevir remains the only appropriate HCV-specific antiviral agent.
*Emtricitabine*
- This is a **nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)** primarily used in the treatment of **HIV infection** and sometimes for hepatitis B.
- It has **no significant role** in the treatment of **hepatitis C viral infection**.
*Entecavir*
- Entecavir is an **antiviral agent** specifically used for the treatment of **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It has **no established efficacy** against the **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
*Tenofovir*
- Tenofovir is a **nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor** primarily used for treating **HIV infection** and **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It is **not effective** against **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
*Telbivudine*
- Telbivudine is an **oral antiviral agent** indicated specifically for the treatment of **chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection.
- It does **not have antiviral activity** against the **hepatitis C virus (HCV)**.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 7: A 57-year-old man comes to the physician because of generalized malaise, yellowish discoloration of the eyes, and pruritus on the back of his hands that worsens when exposed to sunlight for the past several months. He has not seen a physician in 15 years. Physical examination shows scleral icterus and mild jaundice. There is a purpuric rash with several small vesicles and hyperpigmented lesions on the dorsum of both hands. The causal pathogen of this patient's underlying condition was most likely acquired in which of the following ways?
- A. Ingestion of raw shellfish
- B. Inhalation of spores
- C. Needlestick injury (Correct Answer)
- D. Bathing in freshwater
- E. Sexual contact
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Needlestick injury***
- The jaundice, scleral icterus, pruritus, and **purpuric rash worsened by sunlight** (suggesting **Porphyria Cutanea Tarda**) are highly indicative of **chronic Hepatitis C virus infection**.
- **Hepatitis C** is primarily transmitted through **blood-to-blood contact**, with **needlestick injuries** and intravenous drug use being the most common routes.
*Ingestion of raw shellfish*
- **Hepatitis A virus** and **Vibrio vulnificus** can be acquired this way, but they typically cause acute, self-limiting illness or severe sepsis, respectively, not chronic liver disease with porphyria.
- **Hepatitis A** does not lead to chronic hepatitis or the dermatological manifestations described.
*Inhalation of spores*
- **Inhalation of spores** is associated with fungal infections like **histoplasmosis** or **coccidioidomycosis**, which do not typically cause chronic hepatitis, jaundice, pruritus, or porphyria cutanea tarda.
- These infections primarily affect the lungs, though disseminated forms can occur, they do not match the presented symptoms.
*Bathing in freshwater*
- **Bathing in freshwater** can transmit pathogens like **Leptospira** or **Schistosoma**, causing leptospirosis or schistosomiasis, respectively.
- These infections present with different clinical pictures and are not associated with chronic hepatitis, jaundice, or porphyria cutanea tarda.
*Sexual contact*
- While **Hepatitis C** can be transmitted sexually, this route is significantly **less efficient** than blood-to-blood contact.
- **Hepatitis B** is more commonly associated with sexual transmission and can also cause chronic liver disease, but the presence of **Porphyria Cutanea Tarda** is a characteristic extrahepatic manifestation strongly associated with **chronic Hepatitis C infection**.
- Given the clinical presentation, **needlestick injury or intravenous drug use** (blood-borne transmission) is the most likely route of HCV acquisition.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 8: A 6-year-old female from a rural village in Afghanistan presents with her mother to a local health center complaining of leg weakness. Her mother also reports that the patient had a fever, fatigue, and headache a week prior that resolved. The patient has not received any immunizations since being born. Her temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination reveals 1/5 strength in right hip and knee actions and 0/5 strength in left hip and knee actions. Tone is notably decreased in both lower extremities. Sensation to touch, temperature, and vibration is intact. Patellar and Achilles reflexes are absent bilaterally. The most likely cause of this patient’s condition has which of the following characteristics?
- A. Non-enveloped (+) ssRNA virus (Correct Answer)
- B. Enveloped (-) ssRNA virus
- C. Enveloped (+) ssRNA virus
- D. dsRNA virus
- E. Non-enveloped (-) ssRNA virus
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Non-enveloped (+) ssRNA virus***
- This describes **Poliovirus**, the causative agent of polio, which is characterized by **acute flaccid paralysis** and absent reflexes due to damage to **anterior horn cells**.
- The patient's presentation with **unvaccinated status**, **acute onset of asymmetric flaccid paralysis** following a febrile illness, and **areflexia** is highly suggestive of poliomyelitis.
*Enveloped (-) ssRNA virus*
- This describes viruses such as **Measles**, **Mumps**, or **Rabies**, which cause different clinical syndromes and are not typically associated with acute flaccid paralysis.
- While these can cause neurological symptoms, they manifest differently (e.g., encephalitis, specific rashes) and are not the primary cause of the described motor deficits.
*Enveloped (+) ssRNA virus*
- This describes viruses like **Dengue**, **Zika**, or **Coronaviruses (SARS-CoV-2)**, which are associated with various fever syndromes, rashes, or respiratory illness, but not typically the specific flaccid paralysis seen here.
- While some can cause neurological complications (e.g., Guillain-Barré syndrome with Zika), the direct neuronal damage leading to areflexic flaccid paralysis as seen in polio is not characteristic.
*dsRNA virus*
- This describes viruses like **Rotavirus**, which primarily cause **gastroenteritis** (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), or **Reoviruses**.
- They are not known to cause acute flaccid paralysis or the specific neurological findings described in the patient.
*Non-enveloped (-) ssRNA virus*
- This type of virus is less common, but the description does not fit the typical etiologies for acute flaccid paralysis. Most common medically relevant (-) ssRNA viruses are enveloped.
- This classification does not align with any known human pathogen that presents with the classic symptoms of poliomyelitis.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 9: A group of researchers conducted various studies on hepatitis C incidence and prevalence. They noticed that there is a high prevalence of hepatitis C in third-world countries, where it has a significant impact on the quality of life of the infected individual. The research group made several attempts to produce a vaccine that prevents hepatitis C infection but all attempts failed. Which of the following would most likely be the reason for the failure to produce a vaccine?
- A. Non-DNA genome
- B. Tolerance
- C. Antigenic mimicry
- D. Polysaccharide envelope
- E. Antigenic variation (Correct Answer)
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Antigenic variation***
- The **hepatitis C virus (HCV)** undergoes rapid **antigenic variation**, particularly in its envelope glycoproteins, which allows it to evade the host immune system.
- This high mutation rate presents a significant challenge for vaccine development, as a vaccine designed against one viral strain may not be effective against others.
*Non-DNA genome*
- While HCV is an **RNA virus** (non-DNA genome), this characteristic alone does not inherently prevent vaccine development; many effective RNA virus vaccines exist (e.g., measles, mumps).
- The type of genome is less critical than its stability and the virus's ability to mutate rapidly.
*Tolerance*
- **Immune tolerance** occurs when the immune system fails to respond to an antigen, often due to chronic exposure. While relevant in chronic HCV infection, it's not the primary reason for vaccine failure.
- The goal of a vaccine is to induce an effective immune response before tolerance can set in.
*Antigenic mimicry*
- **Antigenic mimicry** involves a pathogen's antigens resembling host antigens, potentially leading to autoimmune responses or immune evasion.
- While it can be a factor in some chronic infections, the rapid, diverse changes in HCV's surface antigens are a more prominent obstacle to vaccine design.
*Polysaccharide envelope*
- HCV is an **enveloped virus**, but its envelope is composed of **lipoproteins** with viral glycoproteins, not a polysaccharide capsule.
- Polysaccharide capsules are a feature of some bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae) and fungi, and while they can pose vaccine challenges, they are not relevant to HCV.
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG Question 10: A 13-year-old boy presents to the pediatrician with yellow discoloration of the sclerae since yesterday, and dark-colored urine for 2 days. A detailed history is taken and reveals that he had a cough, cold, and fever the week before the onset of the current symptoms, and was treated with over-the-counter medications. He reports an improvement in his upper respiratory symptoms but has been experiencing fatigue, nausea, and poor appetite since then. There is no past history of recurrent nausea, vomiting, jaundice or abdominal pain, and he has not received any blood transfusion. In addition, he frequently eats at a roadside restaurant near his school. His growth and development are normal for his age and sex. The temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 96/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and the respiratory rate is 22/min. The physical examination shows icterus. The examination of the abdomen reveals tender hepatomegaly with the liver having a firm, sharp, and smooth edge. The laboratory test results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 14.2 g/dL
WBC (white blood cell) 10,500/mm3
Differential leukocyte count
Segmented neutrophils 56%
Bands 4%
Lymphocytes 35%
Eosinophils 2%
Basophils 0%
Monocytes 3%
Platelet count 270,000/mm3
Serum total bilirubin 8.4 mg/dL
Serum direct bilirubin 7.8 mg/dL
Serum alanine aminotransferase 350 U/L
Serum alkaline phosphatase 95 U/L
Prothrombin time 20 seconds
Which of the following laboratory tests is most likely used to diagnose the condition of this patient?
- A. Plasma tyrosine and methionine
- B. Serum anti-HAV IgM antibody (Correct Answer)
- C. Quantitative assay for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity
- D. Urine for reducing substances
- E. Percutaneous liver biopsy
Direct-acting antivirals for HCV Explanation: ***Serum anti-HAV IgM antibody***
- The patient's symptoms (jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, nausea, tender hepatomegaly) following an upper respiratory illness, especially with a history of eating at a roadside restaurant, are highly suggestive of **acute hepatitis A infection**.
- **IgM antibodies** to hepatitis A virus (HAV) are detectable early in the course of infection and indicate **acute or recent infection**, making it the most appropriate diagnostic test.
*Plasma tyrosine and methionine*
- These tests are used in the diagnosis of **tyrosinemia**, a rare inherited metabolic disorder that can cause liver failure.
- The patient's acute presentation and history of potential exposure to HAV make tyrosinemia less likely, and **elevated transaminases** are not specific to tyrosinemia.
*Quantitative assay for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity*
- This assay is used to diagnose **G6PD deficiency**, an inherited condition that can cause hemolytic anemia, particularly after exposure to certain drugs or foods, which might lead to jaundice from unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- However, the patient's presentation with **tender hepatomegaly**, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia (direct bilirubin significantly elevated), and elevated transaminases is more consistent with **hepatocellular injury** rather than hemolysis.
*Urine for reducing substances*
- This test is used to screen for **galactosemia** or other disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in infants and young children, where undigested sugars appear in the urine.
- It is not indicated for the diagnosis of acute hepatitis in an adolescent with the presented clinical picture.
*Percutaneous liver biopsy*
- While a liver biopsy can provide definitive information about liver pathology, it is an **invasive procedure** and is generally not the initial diagnostic test for acute viral hepatitis due to its risks.
- **Serological markers** for viral hepatitis are less invasive and usually sufficient for diagnosing acute hepatitis A.
More Direct-acting antivirals for HCV US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.