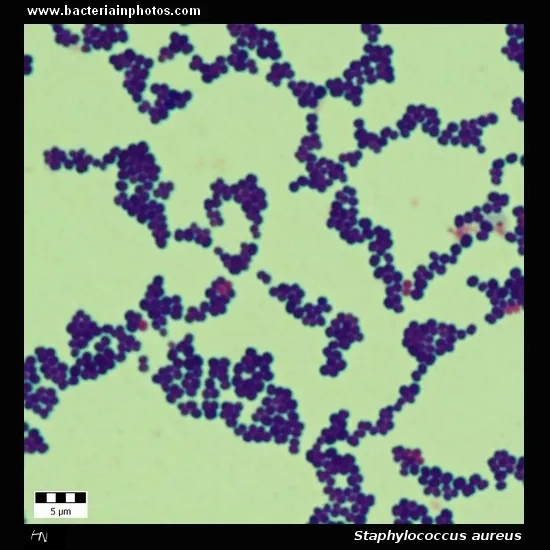
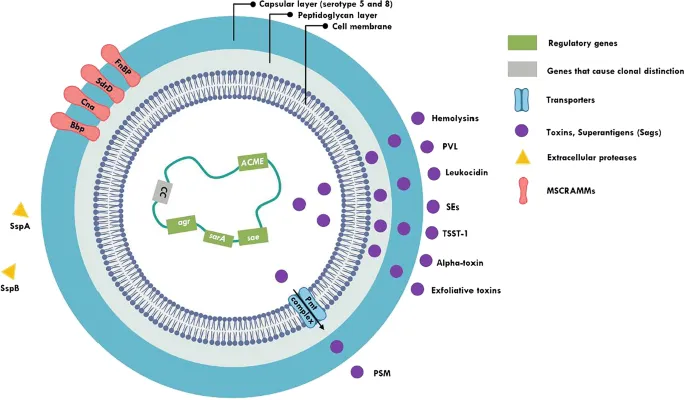
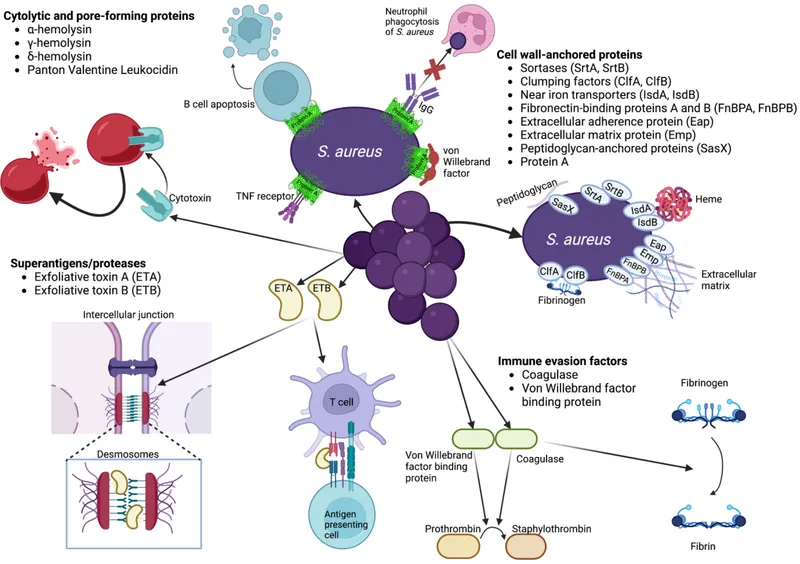
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Staphylococcus aureus. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 1: A 62-year-old woman presents to the emergency department for evaluation of a spreading skin infection that began from an ulcer on her foot. The patient has type 2 diabetes mellitus that is poorly controlled. On examination, there is redness and erythema to the lower limb with skin breakdown along an extensive portion of the leg. The patient’s tissues separate readily from the fascial plane, prompting a diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. What is the exotoxin most likely associated with this patient’s presentation?
- A. Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin A
- B. TSST-1
- C. Diphtheria toxin
- D. Exfoliative toxin
- E. Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin B (Correct Answer)
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin B***
- **Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin B** is a **cysteine protease** that directly degrades tissue, including collagen and fibronectin, leading to the rapid tissue destruction characteristic of **necrotizing fasciitis**.
- This exotoxin is frequently associated with **Group A Streptococcus (GAS)** infections, a common cause of severe soft tissue infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals like diabetics.
*Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin A*
- This exotoxin acts as a **superantigen**, primarily causing symptoms of **streptococcal toxic shock syndrome** (STSS), characterized by fever, rash, and organ failure.
- While GAS can cause necrotizing fasciitis, Exotoxin A is more closely linked to toxic shock phenomena rather than direct tissue destruction.
*TSST-1*
- **Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1)** is produced by **Staphylococcus aureus** and is a classic cause of **staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome**.
- It acts as a **superantigen** but is not directly responsible for the extensive tissue necrosis seen in necrotizing fasciitis caused by streptococci.
*Diphtheria toxin*
- **Diphtheria toxin**, produced by *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*, inhibits **protein synthesis** by inactivating elongation factor-2 (EF-2), leading to cell death.
- It causes diphtheria, characterized by a **pseudomembrane** in the throat and myocarditis, not necrotizing fasciitis.
*Exfoliative toxin*
- **Exfoliative toxins A and B** are produced by **Staphylococcus aureus** and are responsible for **Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)**.
- These toxins cause cleavage of desmoglein-1 in the epidermis, leading to widespread blistering and desquamation, not deep tissue necrosis.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 2: A 4-year-old boy is presented to the clinic by his mother due to a peeling erythematous rash on his face, back, and buttocks which started this morning. Two days ago, the patient’s mother says his skin was extremely tender and within 24 hours progressed to desquamation. She also says that, for the past few weeks, he was very irritable and cried more than usual during diaper changes. The patient is up to date on his vaccinations and has been meeting all developmental milestones. No significant family history. On physical examination, the temperature is 38.4°C (101.1°F) and the pulse is 70/min. The epidermis separates from the dermis by gentle lateral stroking of the skin. Systemic antibiotics are prescribed, and adequate fluid replacement is provided. Which of the following microorganisms most likely caused this patient’s condition?
- A. Clostridium sp.
- B. Staphylococcus aureus (Correct Answer)
- C. Neisseria meningitidis
- D. Bacillus anthracis
- E. Streptococcus sp.
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Staphylococcus aureus***
- The presentation of a **peeling erythematous rash** that started this morning following a period of **extremely tender skin** and **progression to desquamation (Nikolsky's sign)** is highly characteristic of **Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)**.
- **Staphylococcus aureus** produces **exfoliative toxins A and B** that cleave desmoglein-1 in the stratum granulosum, leading to intraepidermal cleavage and superficial skin peeling.
*Clostridium sp.*
- Clostridium species are primarily known for causing diseases like **gas gangrene** and **tetanus**, which involve deep tissue infections and neurological symptoms, not superficial skin peeling.
- They are often associated with **severe wound infections** or **food poisoning**, with different clinical manifestations.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- Neisseria meningitidis is a common cause of **meningitis** and **meningococcemia**, which typically presents with a **petechial or purpuric rash** that does not involve peeling or desquamation.
- Symptoms would primarily include fever, headache, stiff neck, and rapid clinical deterioration.
*Bacillus anthracis*
- Bacillus anthracis causes **anthrax**, with cutaneous anthrax presenting as a **papule progressing to a painless ulcer with a black eschar** (black, necrotic center), without generalized peeling or tenderness.
- This is clearly distinct from the diffuse erythematous and peeling rash described.
*Streptococcus sp.*
- While Streptococcus pyogenes can cause **scarlet fever** with a diffuse erythematous rash and subsequent desquamation, the rash in scarlet fever is typically **sandpaper-like** and the desquamation occurs later, usually in sheets on hands and feet.
- **Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)** due to Streptococcus pyogenes can cause a diffuse rash and desquamation, but typically presents with more severe systemic illness and hypotension, and the characteristic tenderness and rapid progression to widespread peeling as seen in SSSS are less typical for Streptococcus.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 3: A 69-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her husband because of a 1-day history of fever, shortness of breath, dizziness, and cough productive of purulent sputum. Six days ago, she developed malaise, headache, sore throat, and myalgias that improved initially. Her temperature is 39.3°C (102.7°F) and blood pressure is 84/56 mm Hg. Examination shows an erythematous, desquamating rash of the distal extremities. A sputum culture grows gram-positive, coagulase-positive cocci in clusters. The most likely causal organism of this patient's current symptoms produces a virulence factor with which of the following functions?
- A. Binding of Fc domain of immunoglobulin G (Correct Answer)
- B. Inactivation of elongation factor 2
- C. Overstimulation of guanylate cyclase
- D. Destruction of immunoglobulin A
- E. Degradation of membranous phospholipids
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Binding of Fc domain of immunoglobulin G***
- The clinical presentation, including the biphasic illness (initial viral-like symptoms followed by severe respiratory distress with purulent sputum, fever, and hypotension) and the **desquamating rash**, strongly suggests **secondary bacterial pneumonia** with **toxic shock syndrome**, likely caused by *Staphylococcus aureus* following an influenza infection.
- *Staphylococcus aureus* produces **Protein A**, a virulence factor that **binds to the Fc region of IgG**, preventing phagocytosis and complement activation, thus interfering with the immune response.
*Inactivation of elongation factor 2*
- This function is characteristic of **diphtheria toxin**, produced by *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*, which causes diphtheria—a disease typically presenting with pseudomembranes in the throat and myocarditis, not acute pneumonia and toxic shock.
- It works by **ADP-ribosylating elongation factor 2**, inhibiting protein synthesis in host cells.
*Overstimulation of guanylate cyclase*
- **Heat-stable enterotoxin (ST)**, produced by **enterotoxigenic *E. coli*** (ETEC), activates guanylate cyclase, leading to increased cGMP and fluid secretion, causing watery diarrhea.
- This mechanism is not associated with the respiratory and systemic symptoms seen in the patient.
*Destruction of immunoglobulin A*
- **IgA proteases**, produced by bacteria such as *Neisseria meningitidis*, *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*, and *Haemophilus influenzae*, cleave **IgA** at its hinge region, facilitating mucosal colonization.
- While an important virulence factor for these pathogens, it doesn't align with the *Staphylococcus aureus* infection indicated by the clinical picture and sputum culture.
*Degradation of membranous phospholipids*
- This function is characteristic of **phospholipases** (e.g., **alpha-toxin** of *Clostridium perfringens* or **hemolysins** of other bacteria), which degrade host cell membranes.
- While *S. aureus* produces hemolysins, the question specifically points to a function tied to the systemic inflammatory response and immune evasion, making Protein A a more fitting answer for the described clinical syndrome.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 4: A patient is hospitalized for pneumonia. Gram-positive cocci in clusters are seen on sputum gram stain. Which of the following clinical scenarios is most commonly associated with this form of pneumonia?
- A. Elderly patient who has trouble swallowing and poor dentition
- B. An alcoholic with evidence of empyema and "currant jelly sputum"
- C. An otherwise healthy young adult with a week of mild fatigue, chills, and cough
- D. Hospitalized adult with development of pneumonia symptoms 2 weeks following a viral illness (Correct Answer)
- E. HIV positive adult with a CD4 count less than 150 and an impaired diffusion capacity
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Hospitalized adult with development of pneumonia symptoms 2 weeks following a viral illness***
- Gram-positive cocci in clusters suggests **Staphylococcus aureus**, which is a common cause of secondary bacterial pneumonia, often following **viral illnesses** (e.g., influenza).
- This scenario represents a classic presentation of **secondary bacterial pneumonia**, where the initial viral infection compromises the respiratory defenses, allowing bacterial superinfection.
*Elderly patient who has trouble swallowing and poor dentition*
- This scenario points towards **aspiration pneumonia**, often caused by a **polymicrobial infection** that includes oral anaerobes, not typically dominated by Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
- While *S. aureus* can cause aspiration pneumonia, the primary concern in this context would be **anaerobic bacteria**, given the aspiration risk factors.
*An alcoholic with evidence of empyema and \"currant jelly sputum\"*
- This description is highly suggestive of **Klebsiella pneumoniae** infection, which typically presents with thick, gelatinous, and often **blood-tinged sputum**.
- **Klebsiella** is a Gram-negative rod, not Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
*An otherwise healthy young adult with a week of mild fatigue, chills, and cough*
- This presentation is more consistent with **atypical pneumonia** caused by organisms like **Mycoplasma pneumoniae** or **Chlamydophila pneumoniae**, which would not show Gram-positive cocci in clusters on sputum stain.
- **Streptococcus pneumoniae** (Gram-positive cocci in chains) can also cause community-acquired pneumonia in otherwise healthy individuals, but the "clusters" indicate **Staphylococcus aureus**.
*HIV positive adult with a CD4 count less than 150 and an impaired diffusion capacity*
- This clinical picture strongly suggests **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)**, which is common in severely immunocompromised HIV patients.
- *P. jirovecii* is a fungus and would not be seen as Gram-positive cocci in clusters on a routine Gram stain.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old man with aortic valve disease is admitted to the hospital for a 3-week history of progressively worsening fatigue, fever, and night sweats. He does not smoke, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs. Temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F). Physical examination shows a systolic murmur and tender, erythematous nodules on the finger pads. Blood cultures show alpha-hemolytic, gram-positive cocci that are catalase-negative and optochin-resistant. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- B. Staphylococcus epidermidis
- C. Viridans streptococci (Correct Answer)
- D. Streptococcus pyogenes
- E. Streptococcus gallolyticus
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Viridans streptococci***
- The patient's presentation with **subacute onset** of fever, fatigue, cardiac murmur, and **Osler nodes** (tender finger nodules) points to **infective endocarditis**. The micro-organism is described as **alpha-hemolytic**, **catalase-negative**, and **optochin-resistant**, which are characteristic features of **Viridans streptococci**.
- **Viridans streptococci** are a common cause of **subacute bacterial endocarditis**, especially in patients with pre-existing valvular disease like the **aortic valve disease** mentioned.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- While **Streptococcus pneumoniae** is also **alpha-hemolytic** and **catalase-negative**, it is typically **optochin-sensitive** and a common cause of **pneumonia** and **meningitis**, not usually subacute endocarditis from oral flora.
- Endocarditis caused by *S. pneumoniae* is rare and usually associated with a more fulminant course.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- **Staphylococcus epidermidis** is a **coagulase-negative staphylococcus** that is a common cause of **prosthetic valve endocarditis** and is **catalase-positive**, unlike the organism described here.
- It is not typically alpha-hemolytic.
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
- **Streptococcus pyogenes** is **beta-hemolytic** and **catalase-negative**, and typically causes **pharyngitis** and **skin infections**, or sometimes **acute endocarditis**.
- It does not fit the description of an **alpha-hemolytic**, **optochin-resistant** organism.
*Streptococcus gallolyticus*
- **Streptococcus gallolyticus** (formerly *Streptococcus bovis*) is associated with **bacteremia** and **endocarditis**, particularly in patients with **gastrointestinal malignancies**.
- While it is **alpha-hemolytic** and **catalase-negative**, it is typically differentiated by its growth in **bile esculin** and is not primarily defined by optochin resistance characteristic of Viridans group.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 6: A group of medical students is studying bacteria and their pathogenesis. They have identified that a substantial number of bacteria cause human disease by producing exotoxins. Exotoxins are typically proteins, but they have different mechanisms of action and act at different sites. The following is a list of exotoxins together with mechanisms of action. Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
- A. Tetanospasmin - binds 60S ribosome subunit and inhibits protein synthesis
- B. Cholera toxin - ADP-ribosylates Gs, keeping adenylate cyclase active and ↑ [cAMP] (Correct Answer)
- C. Diphtheria toxin - cleaves synaptobrevin, blocking vesicle formation and the release of acetylcholine
- D. Botulinum toxin - cleaves synaptobrevin, blocking vesicle formation and the release of the inhibitory neurotransmitters GABA and glycine
- E. Anthrax toxin - ADP-ribosylates elongation factor - 2 (EF-2) and inhibits protein synthesis
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Cholera toxin - ADP-ribosylates Gs, keeping adenylate cyclase active and ↑ [cAMP]***
- **Cholera toxin** works by irrevocably activating **adenylate cyclase** via **ADP-ribosylation** of the **alpha subunit of Gs protein**.
- This leads to a persistent increase in intracellular **cyclic AMP (cAMP)**, resulting in excessive secretion of water and electrolytes into the intestinal lumen, causing characteristic **rice-water diarrhea**.
*Tetanospasmin - binds 60S ribosome subunit and inhibits protein synthesis*
- **Tetanospasmin (tetanus toxin)** acts by cleaving **synaptobrevin**, a SNARE protein, which inhibits the release of **inhibitory neurotransmitters (GABA and glycine)** from Renhaw cells in the spinal cord.
- This blockade of inhibitory signals leads to uncontrolled muscle contractions and **spastic paralysis**.
*Diphtheria toxin - cleaves synaptobrevin, blocking vesicle formation and the release of acetylcholine*
- **Diphtheria toxin** works by **ADP-ribosylating elongation factor-2 (EF-2)**, which is crucial for protein synthesis.
- The inactivation of **EF-2** leads to the arrest of protein synthesis and ultimately **cell death**.
*Botulinum toxin - cleaves synaptobrevin, blocking vesicle formation and the release of the inhibitory neurotransmitters GABA and glycine*
- **Botulinum toxin** cleaves **SNARE proteins** (including synaptobrevin) at the **neuromuscular junction**, specifically blocking the release of **acetylcholine**.
- This inhibition of neurotransmitter release at the presynaptic terminal leads to **flaccid paralysis**.
*Anthrax toxin - ADP-ribosylates elongation factor - 2 (EF-2) and inhibits protein synthesis*
- **Anthrax toxin** consists of three proteins: Protective Antigen (PA), Edema Factor (EF), and Lethal Factor (LF). The **Edema Factor (EF)** is a **calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase** that increases intracellular **cAMP**, and the **Lethal Factor (LF)** is a **metalloprotease** that targets MAPK pathways.
- **Anthrax toxin** does not work by ADP-ribosylating EF-2; that mechanism is characteristic of **diphtheria toxin**.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 7: A 54-year-old man comes to the physician because of persistent right knee pain and swelling for 2 weeks. Six months ago, he had a total knee replacement because of osteoarthritis. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 139/84 mm Hg. Examination shows warmth and erythema of the right knee; range of motion is limited by pain. His leukocyte count is 14,500/mm3, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 50 mm/hr. Blood cultures grow gram-positive, catalase-positive cocci. These bacteria grow on mannitol salt agar without color change. Production of which of the following is most important for the organism's virulence?
- A. Vi capsule
- B. Exotoxin A
- C. Cord factor
- D. Exopolysaccharides (Correct Answer)
- E. Protein A
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Exopolysaccharides***
- The patient presents with **fever**, **joint pain and swelling**, elevated **leukocyte count** and **ESR**, and a history of **total knee replacement**, all indicative of a **prosthetic joint infection**.
- The pathogen is described as **gram-positive**, **catalase-positive cocci** that grow on mannitol salt agar without a color change, suggesting **Staphylococcus epidermidis** or a similar coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species. These pathogens are known for forming **biofilms (exopolysaccharides)** on foreign bodies, making treatment difficult.
*Vi capsule*
- The **Vi capsule** is a virulence factor primarily associated with **Salmonella typhi**, which causes typhoid fever.
- The clinical presentation and microbiological findings (gram-positive cocci) do not match **Salmonella typhi** infection.
*Exotoxin A*
- **Exotoxin A** is a potent virulence factor produced by **Pseudomonas aeruginosa**, a gram-negative rod.
- The bacterial description in the stem (gram-positive, catalase-positive cocci) is inconsistent with **Pseudomonas aeruginosa**.
*Cord factor*
- **Cord factor** is a mycolic acid-containing glycolipid found in the cell wall of **Mycobacterium tuberculosis** and other mycobacteria.
- The pathogen in this case is described as **gram-positive cocci**, which rules out a mycobacterial infection.
*Protein A*
- **Protein A** is a cell wall component of **Staphylococcus aureus** that binds to the Fc region of IgG, inhibiting opsonization and phagocytosis.
- While *Staphylococcus aureus* is a gram-positive, catalase-positive cocci, its typical growth on mannitol salt agar involves **yellowing (fermentation of mannitol)** due to acid production, which is not described here ("without color change").
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 8: A 64-year-old female with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of painful red swelling on her left thigh. Examination shows a 3- x 4-cm, tender, fluctuant mass. Incision and drainage of the abscess are performed. Culture of the abscess fluid grows gram-positive, coagulase-positive cocci that are resistant to oxacillin. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of resistance of the causal organism to oxacillin?
- A. Degradation of the antibiotic
- B. Decreased uptake of the antibiotic
- C. Decreased activation of the antibiotic
- D. Altered target of the antibiotic (Correct Answer)
- E. Acetylation of the antibiotic
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Altered target of the antibiotic***
- The organism described (gram-positive, coagulase-positive cocci, oxacillin-resistant) is **methicillin-resistant *Staphylococcus aureus* (MRSA)**.
- MRSA achieves oxacillin (and other beta-lactam) resistance by acquiring the ***mecA* gene**, which encodes for a **modified penicillin-binding protein (PBP2a)** with reduced affinity for beta-lactam antibiotics.
*Degradation of the antibiotic*
- This mechanism, primarily through the production of **beta-lactamase enzymes**, can degrade beta-lactam antibiotics.
- While *Staphylococcus aureus* can produce beta-lactamases, oxacillin (a **penicillinase-resistant penicillin**) is specifically engineered to be stable against these enzymes.
*Decreased uptake of the antibiotic*
- Reduced permeability of the bacterial cell wall can lead to decreased uptake, a mechanism more commonly associated with **gram-negative bacteria** due to their outer membrane.
- This is not the primary mechanism of resistance for MRSA to oxacillin.
*Decreased activation of the antibiotic*
- Some antibiotics are prodrugs that require activation by bacterial enzymes, and resistance can arise from mutations affecting this activation.
- Oxacillin is active in its administered form and does not require bacterial activation.
*Acetylation of the antibiotic*
- **Enzymatic modification**, such as acetylation, adenylylation, or phosphorylation, is a common mechanism of resistance, particularly against **aminoglycoside antibiotics**.
- This specific mechanism is not responsible for oxacillin resistance in MRSA.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 9: A 7-year-old girl comes in to the emergency department with her mother for swelling of her left periorbital region. Yesterday morning she woke up with a painful, warm, soft lump on her left eyelid. Eye movement does not worsen the pain. Physical examination shows redness and swelling of the upper left eyelid, involving the hair follicles. Upon palpation, the swelling drains purulent fluid. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Xanthelasma
- B. Chalazion
- C. Dacryocystitis
- D. Blepharitis
- E. Hordeolum (Correct Answer)
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Hordeolum***
- A hordeolum (stye) is an **acute bacterial infection** of the sebaceous glands of the eyelid, often involving a hair follicle, presenting as a **painful, warm, soft lump with purulent drainage**.
- The swelling of the eyelid **involving hair follicles** and the presence of **purulent fluid** are classic signs of a hordeolum.
*Xanthelasma*
- **Xanthelasma** consists of **yellowish plaques** on the eyelids, typically caused by cholesterol deposits, and is painless and not inflammatory.
- It is a **chronic condition** and does not present with acute pain, warmth, or purulent discharge.
*Chalazion*
- A **chalazion** is a **painless, firm, non-tender nodule** resulting from a blocked meibomian gland, which is usually not painful or associated with acute inflammation and purulence.
- Unlike a hordeolum, it is a **granulomatous reaction** and typically presents as a non-infectious, chronic lesion.
*Dacryocystitis*
- **Dacryocystitis** is an infection of the **lacrimal sac**, located at the inner corner of the eye, presenting with swelling, redness, and pain in that specific area.
- This condition would not typically involve the eyelid's hair follicles or present with general eyelid purulence.
*Blepharitis*
- **Blepharitis** is a **chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins**, characterized by redness, flaking, and crusting of the eyelashes, often with itching or burning.
- It causes **generalized eyelid discomfort and irritation**, but not a localized warm, painful, purulent lump like described in the scenario.
Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old man presents with low-grade fever and malaise for the last 4 months. He also says he has lost 9 kg (20 lb) during this period and suffers from extreme fatigue. Past medical history is significant for a mitral valve replacement 5 years ago. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F), respirations are 22/min, pulse is 102/min, and blood pressure is 138/78 mm Hg. On physical examination, there is a new onset 2/6 holosystolic murmur loudest in the apical area of the precordium. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
- A. Enterococcus (Correct Answer)
- B. Candida albicans
- C. Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp.
- D. Escherichia coli
- E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staphylococcus aureus Explanation: ***Enterococcus***
- This patient has **late prosthetic valve endocarditis (PVE)**, occurring **5 years after mitral valve replacement**.
- Late PVE (>1 year post-surgery) is most commonly caused by **viridans streptococci** and ***Staphylococcus aureus***, followed by **Enterococcus species**.
- Among the given options, ***Enterococcus*** is the most common cause, particularly in **elderly patients**.
- The **subacute presentation** with **4 months of low-grade fever, malaise, weight loss**, and **new-onset murmur** is consistent with enterococcal endocarditis.
- Enterococcus is a common cause of healthcare-associated endocarditis and has increased prevalence in patients with prosthetic valves.
*Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp.*
- Coagulase-negative staphylococci (e.g., *S. epidermidis*) are the **most common cause of early PVE** (within the first year after surgery).
- At **5 years post-surgery**, this represents **late PVE**, where coagulase-negative staph is much less common than streptococci, *S. aureus*, and enterococci.
- While it can occur in late PVE, it is not the most likely organism in this timeframe.
*Escherichia coli*
- *E. coli* is an uncommon cause of endocarditis, typically associated with underlying gastrointestinal or urinary tract sources.
- It generally presents **acutely** rather than with the subacute 4-month course seen here.
- Not a typical cause of prosthetic valve endocarditis.
*Candida albicans*
- Fungal endocarditis is rare and typically seen in **immunocompromised patients, IV drug users**, or those with **prolonged ICU stays** with indwelling catheters.
- While *Candida* can cause PVE, it is much less common than bacterial causes in this clinical context.
*Pseudomonas aeruginosa*
- *Pseudomonas* endocarditis typically occurs in **IV drug users** and commonly affects the **tricuspid valve** (right-sided).
- Usually presents as an **acute infection** rather than the subacute presentation here.
- Not a common cause of late prosthetic valve endocarditis in non-IVDU patients.
More Staphylococcus aureus US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.