MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for MRSA and VRE. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 1: A 33-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of weakness and fatigue. He states that his symptoms have worsened over the past day. He has a past medical history of IV drug abuse and alcoholism and he currently smells of alcohol. His temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 111/68 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for focal tenderness over the lumbar spine. Initial lab values and blood cultures are drawn and are notable for leukocytosis and an elevated C-reactive protein (CRP). Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
- A. Nafcillin
- B. Ceftriaxone
- C. Piperacillin-tazobactam
- D. Vancomycin (Correct Answer)
- E. Ibuprofen and warm compresses
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Vancomycin***
- The patient's history of **IV drug abuse**, fever, leukocytosis, elevated CRP, and focal lumbar tenderness is highly suggestive of **vertebral osteomyelitis** or **discitis**, often caused by methicillin-resistant *Staphylococcus aureus* (MRSA).
- **Vancomycin** is the appropriate empiric treatment for suspected severe *S. aureus* infections in patients with risk factors for MRSA until culture and sensitivity results are available.
*Nafcillin*
- **Nafcillin** is effective against **methicillin-sensitive *Staphylococcus aureus* (MSSA)**.
- Given the patient's history of IV drug abuse, there's a high likelihood of MRSA, making nafcillin an inadequate empiric choice.
*Ceftriaxone*
- **Ceftriaxone** is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin effective against many gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria, but it has **poor coverage against *Staphylococcus aureus***, particularly MRSA.
- It would be ineffective as a monotherapy for the suspected staphylococcal infection.
*Piperacillin-tazobactam*
- This combination provides broad-spectrum coverage, including **Pseudomonas** and many gram-negative and anaerobic bacteria, but its coverage for **MRSA is limited**.
- It would not be the first-line empiric choice for a suspected MRSA infection in this setting.
*Ibuprofen and warm compresses*
- This treatment addresses pain and inflammation but does not treat the underlying **infectious process**.
- Overlooking the infection would lead to significant morbidity and potential mortality, making this an inappropriate primary treatment.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 2: A 42-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency department complaining of pain in his right knee and fever. The patient is having difficulty walking and looks visibly uncomfortable. On examination, he is disheveled but his behavior is not erratic. The patient’s right knee is erythematous, edematous, and warm, with evidence of a 3 cm wound that is weeping purulent fluid. The patient has a decreased range of motion secondary to pain and swelling. The wound is cultured and empiric antibiotic therapy is initiated. Four minutes into the patient’s antibiotic therapy, he develops a red, pruritic rash on his face and neck. What is the most likely antibiotic this patient is being treated with?
- A. Gentamicin
- B. Linezolid
- C. Penicillin G
- D. Erythromycin
- E. Vancomycin (Correct Answer)
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Vancomycin***
- The rapid development of a **red, pruritic rash** on the face and neck shortly after starting antibiotic therapy for a systemic infection (likely **septic arthritis** given the symptoms) is highly characteristic of **Red Man Syndrome**.
- **Red Man Syndrome** is a pseudoallergic reaction caused by rapid infusion of **vancomycin**, leading to **histamine release**.
*Gentamicin*
- **Gentamicin** is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used for gram-negative infections, but it is not typically associated with a rapid-onset facial rash.
- Its primary adverse effects include **ototoxicity** and **nephrotoxicity**, which develop with prolonged use rather than acute infusion.
*Linezolid*
- **Linezolid** is an oxazolidinone antibiotic primarily used for resistant gram-positive bacteria like MRSA.
- While it can cause side effects like **myelosuppression** and **serotonin syndrome** (if co-administered with serotonergic drugs), it does not typically cause a rapid, prominent facial rash.
*Penicillin G*
- **Penicillin G** is a beta-lactam antibiotic that can cause allergic reactions, but these are typically **IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions** (e.g., anaphylaxis, urticaria, angioedema) and less commonly present as a specific "red man" flush.
- The rash associated with penicillin allergy is usually a more widespread **maculopapular rash** or urticaria, not localized to the face and neck in this specific fashion minutes after administration.
*Erythromycin*
- **Erythromycin** is a macrolide antibiotic whose common side effects include **gastrointestinal upset** (e.g., nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain) and QT prolongation.
- It is not known to cause a rapid-onset, pruritic facial rash like the one described.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 3: A 77-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from her nursing home because she was found down overnight. On presentation she was found to be delirious and was unable to answer questions. Chart review shows that she is allergic to cephalosporins. Her temperature is 102.2°F (39°C), blood pressure is 105/52 mmHg, pulse is 94/min, and respirations are 23/min. Physical exam reveals a productive cough. A metabolic panel is obtained with the following results:
Serum:
Na+: 135 mEq/L
Cl-: 95 mEq/L
K+: 4 mEq/L
HCO3-: 19 mEq/L
BUN: 40 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.5 mg/dL
Glucose: 150 mg/dL
Based on these findings two different drugs are started empirically. Gram stain on a blood sample is performed showing the presence of gram-positive organisms on all samples. One of the drugs is subsequently stopped. The drug that was most likely stopped has which of the following characteristics?
- A. Resistance conveyed through acetylation
- B. Associated with red man syndrome
- C. Single-ringed ß-lactam structure (Correct Answer)
- D. Causes discolored teeth in children
- E. Accumulates inside bacteria via O2-dependent uptake
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Single-ringed ß-lactam structure***
- The patient presents with **sepsis** due to **pneumonia** likely caused by **gram-positive organisms**. Given a cephalosporin allergy, **aztreonam** (a monobactam) would be an initial empirical antibiotic choice to cover gram-negative bacteria, alongside a drug for gram-positive coverage (like vancomycin).
- Since the **blood cultures** confirmed **gram-positive organisms**, the drug covering gram-negative bacteria (aztreonam) would be stopped. Aztreonam is characterized by its **single-ringed β-lactam structure**.
*Resistance conveyed through acetylation*
- This mechanism of resistance is typical of **aminoglycosides** (e.g., gentamicin) and **chloramphenicol**.
- Aminoglycosides were unlikely to be one of the empirically started drugs, as they are often used in combination with β-lactams, and this patient has a cephalosporin allergy.
*Associated with red man syndrome*
- **Red man syndrome** is a common adverse effect associated with **vancomycin** administration, especially with rapid infusion.
- Vancomycin would likely be continued, as it effectively targets gram-positive organisms, including **MRSA**, and is a suitable alternative given the cephalosporin allergy.
*Causes discolored teeth in children*
- This is a characteristic side effect of **tetracyclines** (e.g., doxycycline), which are contraindicated in young children and pregnant women due to their effects on bone and teeth development.
- Tetracyclines are not typically first-line empiric therapy for severe pneumonia or sepsis, especially in an elderly patient.
*Accumulates inside bacteria via O2-dependent uptake*
- This describes the mechanism of uptake for **aminoglycosides**. Their entry into bacteria is an **energy-dependent process** requiring oxygen.
- As mentioned, aminoglycosides are less likely to be the initial drug stopped in this scenario, as they target gram-negative bacteria.
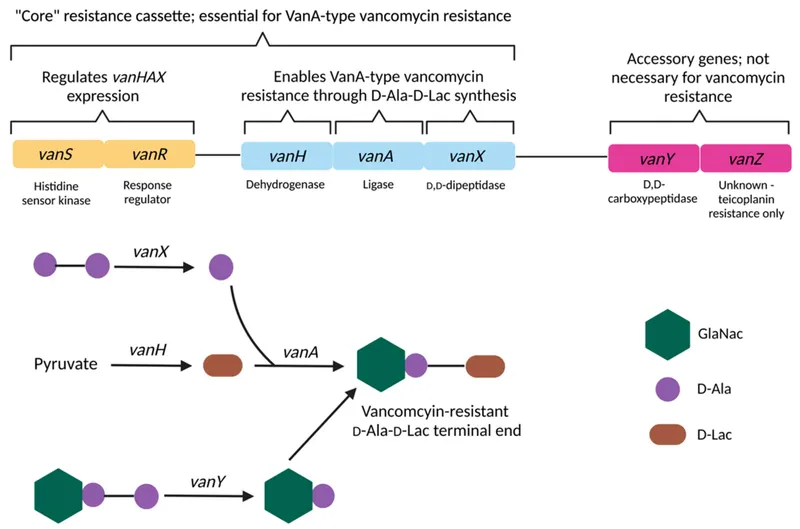
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old female with a bacterial infection is prescribed a drug that binds the dipeptide D-Ala-D-Ala. Which of the following drugs was this patient prescribed?
- A. Polymyxin B
- B. Nalidixic acid
- C. Chloramphenicol
- D. Vancomycin (Correct Answer)
- E. Penicillin
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Vancomycin***
- **Vancomycin** is a glycopeptide antibiotic that directly binds to the **D-Ala-D-Ala** terminus of peptidoglycan precursors.
- This binding prevents the **transpeptidation** and **transglycosylation** steps required for bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to cell lysis.
*Polymyxin B*
- **Polymyxins** are **cationic detergents** that disrupt the integrity of the bacterial **outer membrane** in Gram-negative bacteria.
- They bind to **lipopolysaccharide (LPS)**, causing increased permeability and leakage of intracellular components, but do not target D-Ala-D-Ala.
*Nalidixic acid*
- **Nalidixic acid** is a **quinolone antibiotic** that inhibits bacterial **DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II)** and **topoisomerase IV**.
- Its mechanism of action involves preventing DNA replication and transcription, not cell wall synthesis or D-Ala-D-Ala binding.
*Chloramphenicol*
- **Chloramphenicol** is an antibiotic that inhibits bacterial **protein synthesis** by binding to the **50S ribosomal subunit**.
- It prevents the formation of **peptide bonds** by inhibiting peptidyl transferase, an entirely different target from D-Ala-D-Ala in the cell wall.
*Penicillin*
- **Penicillin** is a beta-lactam antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to and inactivating **penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs)**.
- PBPs are **transpeptidases** involved in cross-linking peptidoglycan, but penicillin does not directly bind to the D-Ala-D-Ala substrate itself; instead, it prevents the enzymes from using it.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 5: A 64-year-old female with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of painful red swelling on her left thigh. Examination shows a 3- x 4-cm, tender, fluctuant mass. Incision and drainage of the abscess are performed. Culture of the abscess fluid grows gram-positive, coagulase-positive cocci that are resistant to oxacillin. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of resistance of the causal organism to oxacillin?
- A. Degradation of the antibiotic
- B. Decreased uptake of the antibiotic
- C. Decreased activation of the antibiotic
- D. Altered target of the antibiotic (Correct Answer)
- E. Acetylation of the antibiotic
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Altered target of the antibiotic***
- The organism described (gram-positive, coagulase-positive cocci, oxacillin-resistant) is **methicillin-resistant *Staphylococcus aureus* (MRSA)**.
- MRSA achieves oxacillin (and other beta-lactam) resistance by acquiring the ***mecA* gene**, which encodes for a **modified penicillin-binding protein (PBP2a)** with reduced affinity for beta-lactam antibiotics.
*Degradation of the antibiotic*
- This mechanism, primarily through the production of **beta-lactamase enzymes**, can degrade beta-lactam antibiotics.
- While *Staphylococcus aureus* can produce beta-lactamases, oxacillin (a **penicillinase-resistant penicillin**) is specifically engineered to be stable against these enzymes.
*Decreased uptake of the antibiotic*
- Reduced permeability of the bacterial cell wall can lead to decreased uptake, a mechanism more commonly associated with **gram-negative bacteria** due to their outer membrane.
- This is not the primary mechanism of resistance for MRSA to oxacillin.
*Decreased activation of the antibiotic*
- Some antibiotics are prodrugs that require activation by bacterial enzymes, and resistance can arise from mutations affecting this activation.
- Oxacillin is active in its administered form and does not require bacterial activation.
*Acetylation of the antibiotic*
- **Enzymatic modification**, such as acetylation, adenylylation, or phosphorylation, is a common mechanism of resistance, particularly against **aminoglycoside antibiotics**.
- This specific mechanism is not responsible for oxacillin resistance in MRSA.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 6: A scientist is studying the mechanisms by which bacteria become resistant to antibiotics. She begins by obtaining a culture of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and conducts replicate plating experiments. In these experiments, colonies are inoculated onto a membrane and smeared on 2 separate plates, 1 containing vancomycin and the other with no antibiotics. She finds that all of the bacterial colonies are vancomycin resistant because they grow on both plates. She then maintains the bacteria in liquid culture without vancomycin while she performs her other studies. Fifteen generations of bacteria later, she conducts replicate plating experiments again and finds that 20% of the colonies are now sensitive to vancomycin. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely explanation for why these colonies have become vancomycin sensitive?
- A. Point mutation
- B. Gain of function mutation
- C. Viral infection
- D. Plasmid loss (Correct Answer)
- E. Loss of function mutation
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Plasmid loss***
- The initial **vancomycin resistance** in *Enterococcus faecalis* is often mediated by genes located on **plasmids**, which are extrachromosomal DNA.
- In the absence of selective pressure (vancomycin), bacteria that lose the plasmid (and thus the resistance genes) have a **growth advantage** over those that retain the energetically costly plasmid, leading to an increase in sensitive colonies over generations.
*Point mutation*
- A **point mutation** typically involves a change in a single nucleotide and could lead to loss of resistance if it occurred in a gene conferring resistance.
- However, since there was no selective pressure for loss of resistance, it is less likely that 20% of the population would acquire such a specific point mutation to revert resistance.
*Gain of function mutation*
- A **gain of function mutation** would imply that the bacteria acquired a *new* advantageous trait, not the *loss* of resistance.
- This type of mutation would not explain why some colonies became sensitive to vancomycin after the drug was removed.
*Viral infection*
- **Viral infection** (bacteriophages) can transfer genes through transduction or cause bacterial lysis, but it's not the primary mechanism for a widespread reversion of resistance in the absence of antibiotic pressure.
- It would not explain the observed increase in vancomycin-sensitive colonies due to evolutionary pressure.
*Loss of function mutation*
- While a **loss of function mutation** in a gene conferring resistance could lead to sensitivity, it's generally less likely to explain a 20% shift without selective pressure than **plasmid loss**.
- Plasmids are often unstable and are easily lost in the absence of selection, whereas a specific gene mutation causing loss of function would need to arise and become prevalent in the population.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old man presents to the emergency department with weakness and a fever for the past week. The patient is homeless and has a past medical history of alcohol and IV drug abuse. His temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 107/68 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a tremulous patient with antecubital scars and a murmur over the left lower sternal border. Blood cultures are drawn and the patient is started on vancomycin and ceftriaxone and is admitted to the ICU. The patient's fever and symptoms do not improve despite antibiotic therapy for which the initial identified organism is susceptible. Cultures currently reveal MRSA as one of the infective organisms. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Transesophageal echocardiography (Correct Answer)
- B. Obtain new blood cultures
- C. CT scan of the chest
- D. Nafcillin and piperacillin-tazobactam
- E. Vancomycin and gentamicin
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Transesophageal echocardiography***
- The patient's history of **IV drug abuse**, **fever**, **new murmur**, and identification of **MRSA** strongly suggest **infective endocarditis**.
- A Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is the **most sensitive and specific imaging modality** to detect vegetations, abscesses, or valvular damage, which is crucial for guiding further management.
*Obtain new blood cultures*
- While repeating blood cultures can be useful to confirm eradication or identify new pathogens, the initial blood cultures already revealed MRSA, which is a common cause of **endocarditis in IV drug users**.
- The immediate priority given the lack of improvement and high suspicion of endocarditis is to visualize the heart valves for vegetations.
*CT scan of the chest*
- A CT scan of the chest would be useful to look for complications such as **septic emboli in the lungs** or other pulmonary pathologies.
- However, it would not provide the detailed visualization of heart valves necessary to diagnose or rule out valvular vegetations characteristic of endocarditis.
*Nafcillin and piperacillin-tazobactam*
- **Nafcillin** is active against **methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)**, but the patient's cultures already identified **MRSA**.
- **Piperacillin-tazobactam** is a broad-spectrum antibiotic but not a first-line treatment for MRSA infections and would not be appropriate given the identified pathogen.
*Vancomycin and gentamicin*
- The patient is already on **Vancomycin**, which is appropriate for MRSA, but adding **gentamicin** without clear indication would not be the best next step.
- While gentamicin is sometimes used as an adjunct in specific endocarditis regimens (e.g., enterococcal), the primary concern here is the lack of clinical improvement despite appropriate MRSA coverage, pointing towards a structural cardiac issue.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 8: A 46-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of headache, muscle pain, and recurrent fever spikes that occur without a noticeable rhythm. Two weeks ago, he returned from a 5-week-long world trip during which he climbed several mountains in India, Africa, and Appalachia. Chemoprophylaxis with chloroquine was initiated one week prior to the trip. Physical examination shows jaundice. The spleen is palpated 2 cm below the left costal margin. His hemoglobin concentration is 10 g/dL. A photomicrograph of a peripheral blood smear is shown. Which of the following agents is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
- A. Chikungunya virus
- B. Trypanosoma cruzi
- C. Leishmania donovani
- D. Plasmodium falciparum (Correct Answer)
- E. Trypanosoma brucei
MRSA and VRE Explanation: **Plasmodium falciparum**
- The image shows **multiple ring forms** and **applique forms** within red blood cells, which are characteristic of *Plasmodium falciparum* malaria. The clinical presentation of **headache, muscle pain, recurrent fever spikes without a noticeable rhythm, jaundice, splenomegaly, and anemia (Hb 10 g/dL)** in a traveler returning from India and Africa is highly consistent with malaria, especially given the chloroquine chemoprophylaxis which is often ineffective against chloroquine-resistant strains of *P. falciparum*.
- *P. falciparum* can cause severe disease, including **anemia** due to red blood cell destruction and **jaundice** due to hemolysis and liver involvement, and is notorious for its **irregular fever patterns** early in the infection cycle.
*Chikungunya virus*
- Chikungunya typically presents with **high fever, severe polyarthralgia**, and rash, but does not cause the parasitemia or specific red blood cell morphology seen in the image.
- While present in endemic regions like India and Africa, it does not lead to **anemia, splenomegaly, or jaundice** to the extent seen in this patient, nor does it appear on a blood smear as intracellular parasites.
*Trypanosoma cruzi*
- *Trypanosoma cruzi* causes **Chagas disease**, which is endemic to **Central and South America**, not India or Africa.
- While it can be found in blood smears during the acute phase (trypomastigotes), its morphology differs significantly from the ring forms seen, and the overall clinical picture of **fever, jaundice, and marked splenomegaly with characteristic RBC parasites** does not fit Chagas disease.
*Leishmania donovani*
- *Leishmania donovani* causes **visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar)**, characterized by **prolonged fever, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, pancytopenia**, and weight loss.
- While present in India and Africa, the parasites (**amastigotes**) are typically found within **macrophages** in bone marrow, spleen, or liver aspirates, not as ring forms within red blood cells on a peripheral blood smear.
*Trypanosoma brucei*
- *Trypanosoma brucei* causes **African sleeping sickness**, which involves **fever, headache, joint pain, neurological symptoms**, and lymphadenopathy (Winterbottom's sign).
- The parasites (trypomastigotes) are observed extracellularly in the blood, lymph, or CSF, and have a distinct **elongated, flagellated morphology** that is completely different from the intracellular ring forms seen in the provided image.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 9: An 11-year-old boy presents with a sore throat, fever, chills, and difficulty swallowing for the past 3 days. The patient’s mother says that last night he was short of breath and had a headache. Past medical history is unremarkable. The patient has not been vaccinated as his mother thinks it is "unnecessary". His temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respiratory rate is 18/min. On physical examination, the patient is ill-appearing and dehydrated. A grayish-white membrane and pharyngeal erythema are present in the oropharynx. Significant cervical lymphadenopathy is also present. A throat swab is taken and gram staining shows gram-positive club-shaped bacilli along with few neutrophils. Which of the following would most likely be the result of the bacterial culture of the throat swab in this patient?
- A. Hemolytic black colonies on blood agar
- B. Metallic green colonies on eosin-methylene blue agar
- C. Greyish-white colonies on Thayer-Martin agar
- D. Small black colonies on tellurite agar (Correct Answer)
- E. Creamy white colonies on Loeffler's serum
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Small black colonies on tellurite agar***
- The clinical presentation, including **sore throat**, **fever**, **grayish-white membrane** in the oropharynx, and **cervical lymphadenopathy** in an **unvaccinated child**, strongly suggests **diphtheria** caused by *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*.
- *Corynebacterium diphtheriae* produces **small gray-black colonies** on **potassium tellurite agar** (e.g., Blood Tellurite Agar or Tinsdale agar) due to the reduction of tellurite to elemental tellurium within the bacterial cells.
- This is the **definitive culture characteristic** used for laboratory diagnosis of diphtheria.
*Hemolytic black colonies on blood agar*
- **Hemolytic black colonies** are not characteristic of *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*.
- *C. diphtheriae* may show minimal or no hemolysis on blood agar, and does not produce black colonies on this medium.
- Black colonies with hemolysis might suggest other organisms but are not typical for diphtheria diagnosis.
*Metallic green colonies on eosin-methylene blue agar*
- **Metallic green colonies** on **eosin-methylene blue (EMB) agar** are characteristic of **lactose-fermenting bacteria**, particularly *Escherichia coli*.
- This finding is associated with **Gram-negative enteric bacteria**, not the Gram-positive club-shaped bacilli seen in this patient.
*Greyish-white colonies on Thayer-Martin agar*
- **Greyish-white colonies** on **Thayer-Martin agar** are typically seen with **fastidious Gram-negative diplococci**, such as *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* or *Neisseria meningitidis*.
- This medium is selective for *Neisseria* species and would not be used for isolating *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*, which is a Gram-positive rod.
*Creamy white colonies on Loeffler's serum*
- **Loeffler's serum medium** is indeed used to enhance the growth of *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*, and the organism produces **creamy white to grayish colonies** on this medium.
- However, Loeffler's medium is primarily used to demonstrate the characteristic **metachromatic granules** (Babes-Ernst bodies) on microscopy, not for definitive culture identification.
- **Tellurite agar**, not Loeffler's medium, is the **gold standard** for culture diagnosis because the black colony appearance is pathognomonic for *C. diphtheriae*.
MRSA and VRE US Medical PG Question 10: A 24-hour-old newborn presents to the emergency department after a home birth because of fever, irritability alternating with lethargy, and poor feeding. The patient’s mother says symptoms acutely onset 12 hours ago and have not improved. No significant past medical history. His mother did not receive any prenatal care, and she had rupture of membranes 20 hours prior to delivery. His vital signs include: heart rate 150/min, respiratory rate 65/min, temperature 39.0°C (102.2°F), and blood pressure 60/40 mm Hg. On physical examination, the patient has delayed capillary refill. Laboratory studies show a pleocytosis and a low glucose level in the patient’s cerebrospinal fluid. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism for this patient’s condition?
- A. Group A Streptococcus
- B. Enterovirus
- C. Group B Streptococcus (Correct Answer)
- D. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- E. Cryptococcus neoformans
MRSA and VRE Explanation: ***Group B Streptococcus***
- This newborn presents with **fever, irritability/lethargy, poor feeding**, and signs of **sepsis (tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotension, delayed capillary refill)**, along with **abnormal CSF (pleocytosis, low glucose)**, indicating **neonatal meningitis**.
- **Group B Streptococcus (GBS)** is the **most common cause of early-onset neonatal sepsis and meningitis**, especially with risk factors such as **lack of prenatal care** and **prolonged rupture of membranes (>18 hours)**, as seen in this case.
*Group A Streptococcus*
- While Group A Streptococcus can cause severe infections, it is an **uncommon cause of neonatal sepsis and meningitis** compared to GBS.
- More typically associated with **pharyngitis, impetigo, and necrotizing fasciitis** in older children and adults.
*Enterovirus*
- Enteroviruses are a common cause of **viral meningitis in neonates and infants**, but typically present with a **lymphocytic pleocytosis** and **normal CSF glucose**, in contrast to the features (pleocytosis, low glucose) seen here.
- While fever and irritability can be present, the CSF findings point more towards a bacterial infection.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- *Streptococcus pneumoniae* can cause bacterial meningitis but is **less common in the immediate neonatal period** (first 7 days of life) compared to GBS.
- Risk factors often include **preterm birth** or **underlying immune deficiencies**, which are not specified here.
*Cryptococcus neoformans*
- *Cryptococcus neoformans* is an **opportunistic fungal pathogen** that typically causes meningitis in **immunocompromised individuals**, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
- It is **extremely rare** in immunocompetent newborns and would not be the most likely cause in this clinical scenario.
More MRSA and VRE US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.