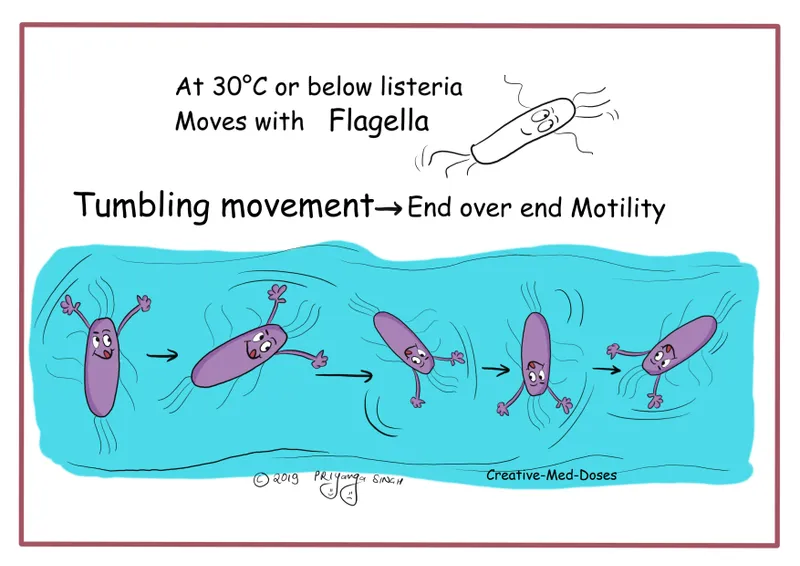
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Listeria monocytogenes. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 1: An 18-month-old boy presents to the emergency department for malaise. The boy’s parents report worsening fatigue for 3 days with associated irritability and anorexia. The patient’s newborn screening revealed a point mutation in the beta-globin gene but the patient has otherwise been healthy since birth. On physical exam, his temperature is 102.4°F (39.1°C), blood pressure is 78/42 mmHg, pulse is 124/min, and respirations are 32/min. The child is tired-appearing and difficult to soothe. Laboratory testing is performed and reveals the following:
Serum:
Na+: 137 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 4.4 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 16 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL
Glucose: 96 mg/dL
Leukocyte count: 19,300/mm^3 with normal differential
Hemoglobin: 7.8 g/dL
Hematocrit: 21%
Mean corpuscular volume: 82 um^3
Platelet count: 324,000/mm^3
Reticulocyte index: 3.6%
Which of the following is the most likely causative organism for this patient's presentation?
- A. Streptococcus pneumoniae (Correct Answer)
- B. Listeria monocytogenes
- C. Haemophilus influenzae
- D. Neisseria meningitidis
- E. Salmonella
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Streptococcus pneumoniae***
- Patients with **sickle cell disease** (indicated by the beta-globin gene mutation) are functionally **asplenic** and highly susceptible to encapsulated bacteria, with *S. pneumoniae* being the most common cause of **sepsis** in this population.
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **hypotension**, **tachycardia**, and **leukocytosis** is consistent with **sepsis**, and the elevated reticulocyte index suggests a hemolytic process or bone marrow response, common in sickle cell crises exacerbated by infection.
*Listeria monocytogenes*
- This pathogen primarily affects **neonates**, **immunocompromised individuals**, and **elderly** patients, often presenting as meningitis or sepsis.
- While it can cause sepsis, it is a less common cause of severe infection in a non-neonatal toddler with sickle cell disease compared to *S. pneumoniae*.
*Haemophilus influenzae*
- Although *H. influenzae* is an encapsulated bacterium that can cause severe infections in functionally asplenic patients, routine childhood vaccinations have significantly reduced its incidence.
- While possible, it is less likely than *S. pneumoniae* in an 18-month-old, especially if vaccinated, and *S. pneumoniae* remains the leading cause of sepsis in sickle cell patients.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- *N. meningitidis* is another encapsulated bacterium that can cause serious infections, including **meningitis** and **sepsis**, particularly in immunocompromised individuals like those with sickle cell disease.
- However, the incidence of **meningococcal disease** is generally lower than **pneumococcal disease** in this age group, and the absence of classic meningeal signs or petechial rash makes it a less probable primary suspect compared to *S. pneumoniae*.
*Salmonella*
- *Salmonella* species can cause **osteomyelitis** and **sepsis** in patients with sickle cell disease, often presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms.
- While a known pathogen in this population, the clinical picture of **rapidly progressive sepsis** without clear GI focus makes *S. pneumoniae* a more immediate and common concern.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 2: A neonate born at 33 weeks is transferred to the NICU after a complicated pregnancy and C-section. A week after being admitted, he developed a fever and became lethargic and minimally responsive to stimuli. A lumbar puncture is performed that reveals the following:
Appearance Cloudy
Protein 64 mg/dL
Glucose 22 mg/dL
Pressure 330 mm H20
Cells 295 cells/mm³ (> 90% PMN)
A specimen is sent to microbiology and reveals gram-negative rods. Which of the following is the next appropriate step in management?
- A. MRI scan of the head
- B. Start the patient on IV ceftriaxone
- C. Provide supportive measures only
- D. Start the patient on IV cefotaxime (Correct Answer)
- E. Start the patient on oral rifampin
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Start the patient on IV cefotaxime***
- The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis with **cloudy appearance, elevated protein, low glucose, high pressure, and predominant PMNs**, coupled with **gram-negative rods** on microscopy, is highly suggestive of **bacterial meningitis** in a neonate.
- **Cefotaxime** is a third-generation cephalosporin commonly used for neonatal meningitis caused by gram-negative organisms due to its excellent CSF penetration and broad-spectrum activity, particularly against common neonatal pathogens like *E. coli* which can present as gram-negative rods.
*MRI scan of the head*
- An MRI would be considered **after initiating appropriate antibiotic treatment** to assess for complications like abscess formation or ventriculitis, not as the immediate next step in an acute, life-threatening infection.
- Delaying antibiotic treatment for imaging in acute bacterial meningitis can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
*Start the patient on IV ceftriaxone*
- While ceftriaxone is a third-generation cephalosporin, it is **generally avoided in neonates** due to the risk of **biliary sludging** and **kernicterus**.
- Ceftriaxone competes with bilirubin for albumin binding sites, which is particularly risky in neonates who are already prone to hyperbilirubinemia.
*Provide supportive measures only*
- Given the strong evidence of **bacterial meningitis**, providing only supportive measures without specific antibiotic treatment would be inadequate and would lead to rapid deterioration and potentially fatal outcomes.
- Bacterial meningitis requires prompt and aggressive antimicrobial therapy.
*Start the patient on oral rifampin*
- **Rifampin is never used as monotherapy for bacterial meningitis** due to rapid resistance development and its primary role is in specific infections like tuberculosis or as part of combination therapy for certain resistant bacteria.
- Oral administration is also not ideal for acutely ill neonates with meningitis needing rapid, high-concentration antibiotics in the CSF.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 3: A previously healthy 10-day-old infant is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of episodes of weakness and spasms for the past 12 hours. His mother states that he has also had difficulty feeding and a weak suck. He has not had fever, cough, diarrhea, or vomiting. He was born at 39 weeks' gestation via uncomplicated vaginal delivery at home. Pregnancy was uncomplicated. The mother refused antenatal vaccines out of concern they would cause side effects. She is worried his symptoms may be from some raw honey his older sister maybe inadvertently fed him 5 days ago. He appears irritable. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F). Examination shows generalized muscle stiffness and twitches. His fontanelles are soft and flat. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Listeria monocytogenes
- B. Neisseria meningitidis
- C. Escherichia coli
- D. Clostridium botulinum (Correct Answer)
- E. Clostridium tetani
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Clostridium botulinum***
- The symptoms of **weakness, spasms, difficulty feeding, weak suck**, and history of possible **raw honey ingestion** are highly suggestive of **infant botulism**.
- **Infant botulism** occurs when *Clostridium botulinum* spores are ingested and colonize the immature gut, producing **neurotoxins** that cause **descending flaccid paralysis**.
- The "muscle stiffness" noted can represent early hypotonia and the **loss of head control** typical of botulism, rather than true spastic rigidity.
- **Honey exposure** in infants under 12 months is a classic risk factor due to spore contamination.
*Listeria monocytogenes*
- This pathogen typically causes **meningitis** or **sepsis** in neonates, with symptoms such as **fever, lethargy**, and **poor feeding**, which differ from the presented neuromuscular symptoms.
- While *Listeria* can be transmitted transplacentally or during birth, it would not be directly associated with the ingestion of **honey**.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- *N. meningitidis* is a common cause of **bacterial meningitis** and **meningococcemia**, presenting with **fever, rash, irritability**, and **meningeal signs**, which are not the primary symptoms described.
- While it can affect infants, it does not typically cause the specific **neuromuscular symptoms** seen in this patient nor is it linked to honey ingestion.
*Escherichia coli*
- **E. coli** is a frequent cause of **neonatal sepsis** and **meningitis**, often presenting with **fever, poor feeding, lethargy, and vomiting**.
- The clinical picture of **weakness, difficulty feeding**, and **neuromuscular symptoms** without significant fever or systemic signs points away from typical *E. coli* infections.
*Clostridium tetani*
- **Clostridium tetani** causes **tetanus**, characterized by **muscle spasms, rigidity, and lockjaw** (trismus), which represents **spastic paralysis**.
- However, the history of **raw honey ingestion** is a classic risk factor for **botulism**, not tetanus.
- **Neonatal tetanus** is associated with unhygienic umbilical cord practices, and while **rigidity** is prominent in tetanus, the **flaccid paralysis, weakness**, and **weak suck** are characteristic of **botulism**, not tetanus.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 4: A 13-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of worsening fever, headache, photophobia, and nausea for 2 days. One week ago, she returned from summer camp. She has received all age-appropriate immunizations. Her temperature is 39.1°C (102.3°F). She is oriented to person, place, and time. Physical examination shows a maculopapular rash. There is rigidity of the neck; forced flexion of the neck results in involuntary flexion of the knees and hips. Cerebrospinal fluid studies show:
Opening pressure 120 mm H2O
Appearance Clear
Protein 47 mg/dL
Glucose 68 mg/dL
White cell count 280/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 15%
Lymphocytes 85%
Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Echovirus (Correct Answer)
- B. Listeria monocytogenes
- C. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- D. Herpes simplex virus
- E. Neisseria meningitidis
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Echovirus***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, headache, photophobia, maculopapular rash, neck rigidity) along with CSF findings of **lymphocytic pleocytosis**, **normal glucose**, and **moderately elevated protein** are highly suggestive of **aseptic meningitis**.
- **Enteroviruses**, such as Echovirus, are the most common cause of **viral (aseptic) meningitis**, especially in children and during summer months, fitting the patient's age and recent summer camp attendance.
*Listeria monocytogenes*
- This organism typically causes meningitis in **neonates, elderly, or immunocompromised individuals**, which does not fit this healthy 13-year-old girl.
- While it can cause lymphocytic pleocytosis, it is less likely given the patient's age and presentation.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- This is a common cause of **bacterial meningitis**, characterized by **PMN predominance (neutrophilic pleocytosis)**, **low CSF glucose**, and **markedly elevated CSF protein**, which are not seen in this case.
- The patient is also described as having received all age-appropriate immunizations, likely including the pneumococcal vaccine.
*Herpes simplex virus*
- HSV can cause aseptic meningitis or encephalitis, but it often presents with **focal neurological deficits** or **seizures** in cases of encephalitis, which are absent here.
- While it can cause lymphocytic pleocytosis, the maculopapular rash is less typical for HSV meningitis compared to enteroviruses.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- This typically causes **bacterial meningitis** with characteristic CSF findings of **neutrophilic pleocytosis**, **low glucose**, and **high protein**.
- Although it can cause a rash (petechial or purpuric), the CSF profile and absence of petechiae make bacterial meningitis less likely.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 5: A 25-day-old male infant presents to the emergency department because his mother states that he has been acting irritable for the past 2 days and has now developed a fever. On exam, the infant appears uncomfortable and has a temperature of 39.1 C. IV access is immediately obtained and a complete blood count and blood cultures are drawn. Lumbar puncture demonstrates an elevated opening pressure, elevated polymorphonuclear neutrophil, elevated protein, and decreased glucose. Ampicillin and cefotaxime are immediately initiated and CSF culture eventually demonstrates infection with a Gram-negative rod. Which of the following properties of this organism was necessary for the infection of this infant?
- A. K capsule (Correct Answer)
- B. M protein
- C. Fimbriae
- D. IgA protease
- E. LPS endotoxin
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***K capsule***
- The K capsule (specifically **K1 antigen**) is a specific virulence factor found in **E. coli** strains, which are a common cause of neonatal meningitis.
- This capsule is **antiphagocytic** and helps the bacteria evade the immune system, allowing it to cross the **blood-brain barrier** and cause meningitis in neonates.
*M protein*
- **M protein** is a major virulence factor associated with **Streptococcus pyogenes** (Group A Strep), playing a role in attachment and immune evasion.
- While *S. pyogenes* can cause infections, it is not typically the Gram-negative rod responsible for **neonatal meningitis** and its M protein is not relevant here.
*Fimbriae*
- **Fimbriae** (pili) are important for bacterial **adhesion** to host cells, often in the initial stages of infection, particularly in urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- While gram-negative rods possess fimbriae, the specific virulence factor critical for **meningitis** caused by *E. coli* in neonates is the K1 capsule, not fimbriae which are more for initial colonization.
*IgA protease*
- **IgA protease** is an enzyme produced by some bacteria (e.g., *N. meningitidis, H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae*) that cleaves **IgA antibodies**, helping them colonize mucous membranes.
- This enzyme is not a primary virulence factor for the **Gram-negative rod** causing neonatal meningitis, where capsule formation is more critical for invasion.
*LPS endotoxin*
- **Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) endotoxin** is a component of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and is responsible for many symptoms of sepsis and **systemic inflammation**.
- While LPS contributes to the overall disease severity, it primarily mediates **inflammation and fever**, and is not the specific factor necessary for **invasion and survival within the central nervous system**, which is facilitated by the K capsule.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 6: Antigen presentation of extracellular pathogens by antigen presenting cells requires endocytosis of the antigen, followed by the degradation in the acidic environment of the formed phagolysosome. Should the phagolysosome become unable to lower its pH, what is the most likely consequence?
- A. Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD4 T-cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Deficient cell extravasation
- C. Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD8 T-cells
- D. Deficient NK cell activation
- E. Deficient expression of B7
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD4 T-cells***
- The acidic environment of the **phagolysosome** is crucial for optimal **antigen degradation** and processing into peptides that can bind to **MHC class II molecules**.
- Without proper acidification, peptide loading onto **MHC class II** is impaired, leading to deficient presentation of extracellular pathogens to **CD4 T-cells**.
*Deficient cell extravasation*
- **Cell extravasation** involves events like rolling, adhesion, and transendothelial migration, which are primarily regulated by **adhesion molecules** and **chemokines**, not phagolysosomal pH.
- A defect in phagolysosomal pH would not directly impede the ability of cells to exit the vasculature.
*Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD8 T-cells*
- **CD8 T-cell** activation primarily involves the presentation of **intracellular antigens** via **MHC class I molecules**, which typically occurs through degradation in the **cytosol** via proteasomes.
- While some cross-presentation pathways exist, the primary mechanism of CD8 T-cell antigen presentation is not dependent on the acidification of phagolysosomes for extracellular pathogens.
*Deficient NK cell activation*
- **Natural Killer (NK) cells** recognize and kill target cells based on the presence or absence of **MHC class I molecules** and activating ligands, not on the processing of extracellular antigens within phagolysosomes.
- Their activation depends on cytokine environments and surface receptor interactions, not directly on phagolysosomal pH.
*Deficient expression of B7*
- **B7 molecules (CD80/CD86)** are **co-stimulatory molecules** expressed by antigen-presenting cells that are crucial for full T-cell activation. While antigen processing can influence APC activation, a specific defect in phagolysosomal pH would primarily affect the *presentation* of peptides, not the *expression* of co-stimulatory molecules.
- The expression of B7 is more broadly regulated by inflammatory signals and toll-like receptor (TLR) engagement, rather than being solely dependent on proper phagolysosomal acidification.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 7: A 10-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain. Four days ago, she visited a petting zoo with her family. Her temperature is 39.4°C (102.9°F). Abdominal examination shows tenderness to palpation of the right lower quadrant. Stool cultures at 42°C grow colonies that turn black after adding phenylenediamine. Which of the following best describes the most likely causal organism?
- A. Gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that form spores
- B. Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that produce catalase
- C. Gram-negative, non-flagellated bacteria that do not ferment lactose
- D. Gram-negative, flagellated bacteria that do not ferment lactose (Correct Answer)
- E. Gram-negative, non-flagellated bacteria that ferment lactose
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Gram-negative, flagellated bacteria that do not ferment lactose***
- The clinical presentation of **bloody diarrhea**, **abdominal pain**, and fever, along with a history of **petting zoo exposure**, strongly suggests a *Campylobacter* infection, which is a **gram-negative, flagellated, curved rod** that does not ferment lactose.
- The growth at **42°C (thermophilic)** and a **positive oxidase test** (indicated by colonies turning black after adding phenylenediamine, an oxidase reagent) are characteristic features of *Campylobacter spp*.
*Gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that form spores*
- This description typically refers to organisms like *Clostridium difficile* or *Clostridium perfringens*, which can cause diarrhea.
- However, they are **anaerobic** and would not grow well in typical stool culture conditions without specific anaerobic techniques, nor would they produce a positive oxidase test.
*Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that produce catalase*
- This describes organisms like *Listeria monocytogenes* or *Bacillus cereus*.
- While *Listeria* can cause gastrointestinal symptoms, it's less commonly associated with the acute, bloody diarrhea and petting zoo exposure seen here, and *Bacillus cereus* typically causes food poisoning with vomiting.
*Gram-negative, non-flagellated bacteria that do not ferment lactose*
- This description commonly applies to *Shigella spp.*
- While *Shigella* causes **bloody diarrhea** and **abdominal pain**, it is typically **non-motile** (non-flagellated), whereas *Campylobacter* is motile due to its flagella.
*Gram-negative, non-flagellated bacteria that ferment lactose*
- This description would fit organisms like enteropathogenic *E. coli* (EPEC) or enterotoxigenic *E. coli* (ETEC).
- However, the specific growth conditions (thermophilic) and positive oxidase test pointed to by phenylenediamine reactivity are not characteristic of these organisms.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 8: A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department from a senior-care facility after he was found with a decreased level of consciousness and fever. His personal history is relevant for colorectal cancer that was managed with surgical excision of the tumor. Upon admission, he is found to have a blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg, a pulse of 102/min, a respiratory rate of 20/min, and a body temperature 38.8°C (101.8°F). There is no rash on physical examination; he is found to have neck rigidity, confusion, and photophobia. There are no focal neurological deficits. A head CT is normal without mass or hydrocephalus. A lumbar puncture was performed and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is sent to analysis while ceftriaxone and vancomycin are started. Which of the following additional antimicrobials should be added in the management of this patient?
- A. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)
- B. Ampicillin (Correct Answer)
- C. Amphotericin
- D. Meropenem
- E. Clindamycin
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Ampicillin***
- This patient is a 62-year-old, indicating an increased risk for **Listeria monocytogenes** meningitis, which is typically susceptible to ampicillin.
- Given his age and presentation with **meningeal signs** and fever, empirical coverage for Listeria with ampicillin is crucial, especially before CSF culture results are known.
*Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)*
- While TMP-SMX can cover Listeria, it is generally considered a **second-line agent** for severe infections like meningitis due to slower bactericidal activity and potential for higher rates of treatment failure compared to ampicillin.
- Ampicillin is the **preferred first-line treatment** for Listeria meningitis unless there is a specific contraindication.
*Amphotericin*
- Amphotericin is an **antifungal agent** used for fungal meningitis.
- Although fungemia can occur in immunocompromised individuals or those with indwelling catheters, the initial presentation with bacterial meningitis symptoms and absence of specific risk factors for fungal infection do not support its empirical use.
*Meropenem*
- Meropenem is a **carbapenem** with a broad spectrum of activity, including many gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, and some anaerobes.
- While it has good CNS penetration and could cover some organisms like penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae or gram-negative rods, it is not the primary empirical choice specifically for **Listeria monocytogenes**, and there's no indication for its broad-spectrum coverage over standard empirical therapy currently.
*Clindamycin*
- Clindamycin is primarily active against **gram-positive bacteria**, especially anaerobes and some staphylococci and streptococci.
- It has **poor penetration into the CNS** and is therefore not effective for meningitis treatment, especially for common bacterial pathogens or Listeria.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 9: An 8-day-old male infant presents to the pediatrician with a high-grade fever and poor feeding pattern with regurgitation of milk after each feeding. On examination the infant showed abnormal movements, hypertonia, and exaggerated DTRs. The mother explains that during her pregnancy, she has tried to eat only unprocessed foods and unpasteurized dairy so that her baby would not be exposed to any preservatives or unhealthy chemicals. Which of the following characteristics describes the causative agent that caused this illness in the infant?
- A. Gram-positive, facultative intracellular, motile bacilli (Correct Answer)
- B. Gram-negative, maltose fermenting diplococci
- C. Gram-positive, catalase-negative, alpha hemolytic, optochin sensitive cocci
- D. Gram-positive, catalase-negative, beta hemolytic, bacitracin resistant cocci
- E. Gram-negative, lactose-fermenting, facultative anaerobic bacilli
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***Gram-positive, facultative intracellular, motile bacilli***
- The infant's symptoms (fever, poor feeding, regurgitation, abnormal movements, hypertonia, exaggerated DTRs) are highly suggestive of **meningitis** or **meningoencephalitis** in a neonate.
- The mother's consumption of **unpasteurized dairy** is a significant risk factor for **Listeria monocytogenes infection**, which is a **gram-positive, facultative intracellular, motile bacillus** that can cause neonatal sepsis and meningitis.
*Gram-negative, maltose fermenting diplococci*
- This description refers to **Neisseria meningitidis**, which is a common cause of meningitis but typically affects older infants, children, and young adults.
- While Neisseria can cause neonatal infection, it is less commonly associated with unpasteurized dairy consumption.
*Gram-positive, catalase-negative, alpha hemolytic, optochin sensitive cocci*
- This describes **Streptococcus pneumoniae**, a common cause of bacterial meningitis, otitis media, and pneumonia.
- S. pneumoniae is generally **catalase-negative** and **alpha-hemolytic**, but it is not typically associated with unpasteurized dairy transmission in neonates.
*Gram-positive, catalase-negative, beta hemolytic, bacitracin resistant cocci*
- This description points to **Group B Streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae)**, a leading cause of early-onset neonatal sepsis and meningitis.
- While GBS is a common neonatal pathogen, it is transmitted vertically from the mother's birth canal and not primarily through unpasteurized dairy products.
*Gram-negative, lactose-fermenting, facultative anaerobic bacilli*
- This describes organisms like **Escherichia coli**, a common cause of neonatal meningitis, especially in premature or low-birth-weight infants.
- While E. coli can be transmitted via fecal-oral routes, the specific history of unpasteurized dairy strongly points away from E. coli as the *most likely* causative agent in this scenario.
Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG Question 10: A 34-year-old woman presents with confusion, drowsiness, and headache. The patient’s husband says her symptoms began 2 days ago and have progressively worsened with an acute deterioration of her mental status 2 hours ago. The patient describes the headaches as severe, localized to the frontal and periorbital regions, and worse in the morning. Review of symptoms is significant for a mild, low-grade fever, fatigue, and nausea for the past week. Past medical history is significant for HIV infection for which she is not currently receiving therapy. Her CD4+ T cell count last month was 250/mm3. The blood pressure is 140/85 mm Hg, the pulse rate is 90/min, and the temperature is 37.7°C (100.0°F). On physical examination, the patient is conscious but drowsy. Papilledema is present. No pain is elicited with extension of the leg at the knee joint. The remainder of the physical examination is negative. Laboratory findings, including panculture, are ordered. A noncontrast CT scan of the head is negative and is followed by a lumbar puncture. CSF analysis is significant for:
Opening pressure 250 mm H2O (70-180 mm H2O)
Glucose 30 mg/dL (40-70 mg/dL)
Protein 100 mg/dL (<40 mg/dL)
Cell count 20/mm3 (0-5/mm3)
Which of the following additional findings would most likely be found in this patient?
- A. Gram-positive diplococci are present on microscopy
- B. CSF shows a positive acid-fast bacillus stain
- C. Multiple ring-enhancing lesions are seen on a CT scan
- D. CSF shows gram negative diplococci
- E. CSF India ink stain shows encapsulated yeast cells (Correct Answer)
Listeria monocytogenes Explanation: ***CSF India ink stain shows encapsulated yeast cells***
- The patient's presentation with **subacute meningitis symptoms** (headache, confusion, low-grade fever) in the setting of **untreated HIV infection** with a low CD4+ count (250/mm3) strongly suggests an opportunistic infection.
- The CSF findings of **elevated opening pressure**, **low glucose**, **high protein**, and **moderate pleocytosis** are classic for **cryptococcal meningitis**, for which the India ink stain is diagnostic for encapsulated yeast cells.
*Gram-positive diplococci are present on microscopy*
- This finding suggests **bacterial meningitis**, specifically caused by organisms like *Streptococcus pneumoniae*.
- While bacterial meningitis presents acutely with severe symptoms, the **subacute course** and moderate pleocytosis are less typical, and the patient's immune status points towards an opportunistic infection.
*CSF shows a positive acid-fast bacillus stain*
- A positive **acid-fast bacillus (AFB) stain** in CSF would indicate **tuberculous meningitis**.
- While tuberculous meningitis can present subacutely with similar CSF findings in HIV patients, it typically involves a more significant lymphocytic pleocytosis and a more pronounced chronic course than suggested by the acute worsening.
*Multiple ring-enhancing lesions are seen on a CT scan*
- **Multiple ring-enhancing lesions** on CT or MRI are characteristic of **Toxoplasma encephalopathy** or **CNS lymphoma** in HIV-positive patients.
- While these are common HIV-related CNS complications, the patient's primary presentation points to **meningitis** (inflammation of meninges with CSF abnormalities) rather than focal brain lesions without meningeal involvement.
*CSF shows gram negative diplococci*
- **Gram-negative diplococci** in CSF suggest **meningococcal meningitis** (*Neisseria meningitidis*).
- This typically presents as an **acute, severe bacterial meningitis** with rapid deterioration, usually in immunocompetent individuals or specific outbreaks, which doesn't align with the subacute onset and specific CSF profile for cryptococcus.
More Listeria monocytogenes US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.