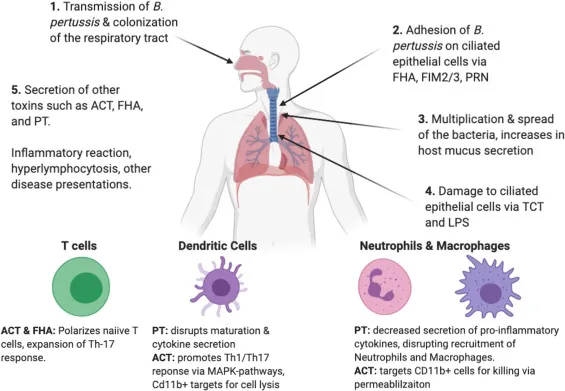
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bordetella pertussis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old pregnant woman, G4 P3, visits your office at week 30 of gestation. She is very excited about her pregnancy and wants to be the healthiest she can be in preparation for labor and for her baby. What vaccination should she receive at this visit?
- A. Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
- B. Varicella vaccine
- C. Herpes zoster vaccine
- D. Live attenuated influenza vaccine
- E. Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) (Correct Answer)
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap)***
- The Tdap vaccine is recommended during each pregnancy, preferably between **27 and 36 weeks of gestation**, to maximize maternal antibody response and passive antibody transfer to the fetus.
- This provides critical protection against **pertussis (whooping cough)** for the newborn, who is too young to be vaccinated.
*Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)*
- The **MMR vaccine is a live vaccine** and is **contraindicated during pregnancy** due to the theoretical risk of congenital rubella syndrome, although no cases have been reported.
- It should be administered **postpartum** if the mother is not immune to rubella.
*Varicella vaccine*
- The **varicella vaccine is a live vaccine** and is **contraindicated during pregnancy** due to the theoretical risk of congenital varicella syndrome.
- Like MMR, it should be offered in the **postpartum period** if the woman is not immune.
*Herpes zoster vaccine*
- The herpes zoster vaccine is typically recommended for **older adults** (50 years and older) for shingles prevention.
- It is **not routinely recommended during pregnancy**, and its safety and efficacy in this population have not been sufficiently established.
*Live attenuated influenza vaccine*
- The **live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV)** is **contraindicated during pregnancy** due to its live virus content.
- Pregnant women should receive the **inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV)**, which is safe and recommended during any trimester.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 2: An 11-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician by his parents for the routine Tdap immunization booster dose that is given during adolescence. Upon reviewing the patient’s medical records, the pediatrician notes that he was immunized according to CDC recommendations, with the exception that he received a catch-up Tdap immunization at the age of 8 years. When the pediatrician asks the boy’s parents about this delay, they inform the doctor that they immigrated to this country 3 years ago from Southeast Asia, where the child had not been immunized against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. Therefore, he received a catch-up series at 8 years of age, which included the first dose of the Tdap vaccine. Which of the following options should the pediatrician choose to continue the boy’s immunization schedule?
- A. A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age
- B. A single dose of Td vaccine now
- C. No further vaccination needed
- D. A single dose of Tdap vaccine now
- E. A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age (Correct Answer)
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age***
- The CDC recommends a **minimum interval of 5 years** between Tdap doses when Tdap is given as part of a catch-up series.
- Since this patient received his first Tdap at age 8, the earliest he should receive the adolescent booster is at **age 13** (5 years later).
- This timing ensures adequate spacing while still providing the recommended adolescent booster for **pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria** protection.
- The 5-year interval prevents excessive antigen exposure and optimizes immune response.
*A single dose of Tdap vaccine now*
- Giving Tdap now would result in only a **3-year interval** from the previous Tdap dose at age 8.
- This violates the CDC recommendation of a **minimum 5-year interval** between Tdap doses.
- Shorter intervals may increase local reactogenicity without improving protection.
*A single dose of Td vaccine now*
- While this would provide tetanus and diphtheria protection, it would **not protect against pertussis**, which is a critical component of adolescent vaccination.
- The Tdap vaccine is specifically recommended for adolescents to boost waning pertussis immunity.
- Additionally, giving it now would still be earlier than the recommended 5-year interval from the previous pertussis-containing vaccine.
*A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age*
- This option would result in a **10-year gap** from the last pertussis-containing vaccine, leaving the adolescent vulnerable during high-risk years.
- The adolescent Tdap booster is specifically timed for ages 11-13 to protect during peak transmission periods in middle and high school.
- Waiting until 18 would miss the critical window for pertussis protection.
*No further vaccination needed*
- While the patient completed a catch-up series, the CDC still recommends an **adolescent Tdap booster** even for those who received Tdap in a catch-up series.
- The adolescent booster is important to maintain immunity against pertussis, which wanes significantly over time.
- The booster should be given at age 13 to maintain the 5-year minimum interval.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old woman presents to the ED with symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease despite being previously treated with azithromycin for chlamydial infection. Based on your clinical understanding about the epidemiology of PID, you decide to obtain a gram stain which shows a gram-negative diplococci. What is the next step in order to confirm the identity of the organism described?
- A. Perform an RT-PCR
- B. Culture in TCBS agar
- C. Culture in Thayer-Martin media (Correct Answer)
- D. Obtain an acid fast stain
- E. Culture in Bordet-Gengou agar
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Culture in Thayer-Martin media***
- The presence of **gram-negative diplococci** in a patient with PID symptoms strongly suggests *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*.
- **Thayer-Martin media** is a selective **agar** specifically designed for the isolation and identification of *Neisseria* species, including *N. gonorrhoeae*, by inhibiting the growth of most commensal bacteria and fungi.
*Perform an RT-PCR*
- While **RT-PCR** can detect *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* nucleic acids, it is primarily used for **molecular diagnosis** and not directly for confirming the identity of a cultured organism visualized on gram stain.
- **RT-PCR** is generally used for direct detection from clinical samples and is particularly useful in situations where culture is difficult or unavailable.
*Culture in TCBS agar*
- **TCBS (Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Salts Sucrose) agar** is a selective medium primarily used for the isolation of *Vibrio* species, which are not typically associated with pelvic inflammatory disease or characterized as gram-negative diplococci.
- This medium is designed to differentiate between different *Vibrio* species based on sucrose fermentation.
*Obtain an acid fast stain*
- An **acid-fast stain** (e.g., Ziehl-Neelsen stain) is used to identify bacteria with a **waxy cell wall**, such as *Mycobacterium* species (e.g., *Mycobacterium tuberculosis*).
- *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* is not acid-fast, and this stain would not be appropriate for its identification.
*Culture in Bordet-Gengou agar*
- **Bordet-Gengou agar** is a specialized culture medium used for the isolation of *Bordetella pertussis*, the causative agent of whooping cough.
- This medium is not suitable for the isolation of *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 4: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 7-day history of a progressively worsening cough. The cough occurs in spells and consists of around 5–10 coughs in succession. After each spell he takes a deep, noisy breath. He has vomited occasionally following a bout of coughing. He had a runny nose for a week before the cough started. His immunization records are unavailable. He lives in an apartment with his father, mother, and his 2-week-old sister. The mother was given a Tdap vaccination 11 years ago. The father's vaccination records are unavailable. His temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F). Examination shows no abnormalities. His leukocyte count is 42,000/mm3. Throat swab culture and PCR results are pending. Which of the following are the most appropriate recommendations for this family?
- A. Administer oral azithromycin to the baby and father and Tdap vaccination to the father
- B. Administer oral azithromycin to all family members and Tdap vaccination to the father and mother (Correct Answer)
- C. Administer oral azithromycin to all family members and Tdap vaccination to the father
- D. Administer oral erythromycin to all family members and Tdap vaccination to the father
- E. Administer oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole to the father and baby and Tdap vaccination to the father
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Administer oral azithromycin to all family members and Tdap vaccination to the father and mother***
- The 8-year-old boy presents with classic symptoms of **pertussis** (whooping cough), including **paroxysmal cough**, post-tussive emesis, and a preceding catarrhal phase (runny nose). The high **leukocyte count** further supports this diagnosis. Given his exposure, the 2-week-old sister is at high risk of severe sequelae.
- **Prophylactic antibiotics** (e.g., azithromycin) are indicated for all close contacts, especially infants and pregnant women, to prevent the spread of *Bordetella pertussis*. Tdap vaccination is recommended for the father (whose vaccination status is unknown) and the mother, as her last Tdap was 11 years ago, and there is a high-risk infant in the household.
*Administer oral azithromycin to the baby and father and Tdap vaccination to the father*
- This option misses administering **prophylactic antibiotics** to the mother and **Tdap vaccination** to the mother, both of whom are close contacts and have a high-risk infant in the household.
- The mother's Tdap vaccination from 11 years ago may no longer provide sufficient protection, especially with a neonate in the home.
*Administer oral azithromycin to all family members and Tdap vaccination to the father*
- While this option correctly suggests prophylactic antibiotics for all family members, it incorrectly omits **Tdap vaccination for the mother**, whose last vaccination was 11 years ago.
- Updating the mother's Tdap vaccination status is crucial, especially in a household with a 2-week-old infant.
*Administer oral erythromycin to all family members and Tdap vaccination to the father*
- **Erythromycin** is an alternative macrolide for pertussis treatment/prophylaxis, but **azithromycin** is preferred due to a shorter course and better tolerability, especially in infants.
- This option also incorrectly omits **Tdap vaccination for the mother**.
*Administer oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole to the father and baby and Tdap vaccination to the father*
- **Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole** is a less preferred antibiotic for pertussis prophylaxis/treatment and is generally reserved for patients who cannot tolerate macrolides.
- This option incorrectly limits antibiotic prophylaxis to only the father and baby, excluding the mother and the 8-year-old boy, and also omits **Tdap vaccination for the mother**.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 5: A 9-year-old girl presents with a 3-week history of cough. Her mother reports that initially, she had a runny nose and was tired, with a slight cough, but as the runny nose resolved, the cough seemed to get worse. She further states that the cough is dry sounding and occurs during the day and night. She describes having coughing spasms that occasionally end in vomiting, but between episodes of coughing she is fine. She reports that during a coughing spasm, her daughter will gasp for air and sometimes make a “whooping” noise. A nasopharyngeal swab confirms a diagnosis of Bordetella pertussis. Which of the following statements apply to this patient?
- A. She should be started on azithromycin for more rapid resolution of cough.
- B. Her classmates should be treated with clarithromycin as prophylaxis.
- C. She will have lifelong natural immunity against Bordetella pertussis.
- D. Her 3-month-old brother should be treated with azithromycin as prophylaxis. (Correct Answer)
- E. Her classmates should receive a Tdap booster regardless of their vaccination status.
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Her 3-month-old brother should be treated with azithromycin as prophylaxis.***
- The patient's 3-month-old brother is at a very high risk of severe pertussis due to his age and direct exposure, making **post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)** crucial.
- **Azithromycin** is the recommended antibiotic for PEP in infants due to its efficacy and safety profile.
*She should be started on azithromycin for more rapid resolution of cough.*
- While **azithromycin** is the recommended treatment for pertussis, it is primarily effective in reducing the transmission of *Bordetella pertussis* if started early in the **catarrhal stage**.
- Once the patient is in the **paroxysmal (whooping cough) stage**, as described by the 3-week cough and "whooping" noises, antibiotics **do not significantly shorten the duration or severity of the cough**.
*Her classmates should be treated with clarithromycin as prophylaxis.*
- **Classmates** are generally considered at lower risk for severe disease compared to household contacts, and routine prophylaxis for an entire classroom is not typically recommended unless there is a specific outbreak investigation or direct close contact.
- If prophylaxis were considered for close contacts, **azithromycin** is generally preferred over clarithromycin in children due to fewer drug interactions and a more convenient dosing schedule.
*She will have lifelong natural immunity against Bordetella pertussis.*
- **Natural immunity** following a pertussis infection is not lifelong; it wanes over time, typically within a few years.
- This is why **booster vaccinations (Tdap)** are recommended for adolescents and adults to maintain protection.
*Her classmates should receive a Tdap booster regardless of their vaccination status.*
- **Tdap boosters** are recommended for adolescents and adults, but giving a booster *regardless of vaccination status* to all classmates is not the standard immediate public health response for isolated pertussis cases.
- Public health guidance often focuses on identifying and vaccinating **unvaccinated** or **under-vaccinated close contacts**, rather than providing universal boosters for an entire class.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 6: A 1-year-old girl is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. She has no history of serious illness. She receives a vaccine in which a polysaccharide is conjugated to a carrier protein. Which of the following pathogens is the most likely target of this vaccine?
- A. Hepatitis A virus
- B. Varicella zoster virus
- C. Streptococcus pneumoniae (Correct Answer)
- D. Bordetella pertussis
- E. Clostridium tetani
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Streptococcus pneumoniae***
- This pathogen is a common cause of **pneumonia**, **otitis media**, and **meningitis** in young children. The **pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV)** targets *Streptococcus pneumoniae*'s polysaccharide capsule by conjugating it to a carrier protein.
- Conjugating the polysaccharide to a protein carrier allows for a **T-cell-dependent immune response**, which is crucial for eliciting a robust and long-lasting antibody response in infants and young children, whose immune systems are not yet mature enough to respond effectively to unconjugated polysaccharide antigens.
*Hepatitis A virus*
- The vaccine for **Hepatitis A virus** is an **inactivated vaccine** containing whole killed virus particles, not a polysaccharide conjugated to a carrier protein.
- It is typically given to children to prevent **Hepatitis A infection**, which causes liver inflammation.
*Varicella zoster virus*
- The **varicella vaccine** for **Varicella zoster virus** is a **live, attenuated vaccine**, meaning it contains a weakened form of the live virus.
- This vaccine aims to prevent **chickenpox** and is not a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine.
*Bordetella pertussis*
- The vaccine for **Bordetella pertussis** (whooping cough) is part of the **DTaP vaccine** and is an **acellular vaccine**, containing purified components of the bacterium.
- These components are primarily **toxoids** (inactivated toxins) or other bacterial proteins, not polysaccharides.
*Clostridium tetani*
- The vaccine for **Clostridium tetani** is a **toxoid vaccine**, meaning it contains an inactivated form of the **tetanus toxin**.
- This is part of the **DTaP vaccine** and works by stimulating an immune response against the toxin, not bacterial polysaccharides.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 7: A 23-year-old man presents to student health for a cough. The patient states he has paroxysms of coughing followed by gasping for air. The patient is up to date on his vaccinations and is generally healthy. He states he has felt more stressed lately secondary to exams. His temperature is 101.0°F (38.3°C), blood pressure is 125/65 mmHg, pulse is 105/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Laboratory values are notable for the findings below.
Hemoglobin: 12 g/dL
Hematocrit: 36%
Leukocyte count: 13,500/mm^3 with a lymphocytosis
Platelet count: 197,000/mm^3
Physical exam is notable for clear breath sounds bilaterally. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Azithromycin (Correct Answer)
- B. PCR for Bordetella pertussis
- C. Chest radiograph
- D. Culture
- E. Penicillin
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Azithromycin***
- This patient's symptoms (paroxysmal cough followed by gasping), fever, and **lymphocytosis**, despite being vaccinated, are highly suggestive of **pertussis** (whooping cough).
- **Macrolide antibiotics** like azithromycin are the recommended treatment for pertussis, as they can reduce the duration and severity of symptoms and prevent transmission, especially when given early in the disease course.
*PCR for Bordetella pertussis*
- While a **PCR test** would confirm the diagnosis, the prompt asks for the **best next step in management**, implying treatment rather than diagnosis given the clear clinical picture.
- Due to the highly contagious nature of pertussis, treatment should ideally be initiated promptly based on clinical suspicion, especially within the **catarrhal** or early **paroxysmal stage**, without waiting for PCR results.
*Chest radiograph*
- A chest radiograph is generally **not indicated** for uncomplicated pertussis, as clear breath sounds are noted and it is usually a clinical diagnosis.
- It would be more relevant to rule out complications like **pneumonia**, which is not immediately suggested by the given information.
*Culture*
- **Bacterial culture** for *Bordetella pertussis* from a nasopharyngeal swab is a diagnostic tool, but it is **less sensitive** and **takes longer** to yield results compared to PCR.
- Given the urgency for treatment to reduce transmission and symptoms, culture is not the most appropriate *next step in management*.
*Penicillin*
- Penicillin is **not effective** against *Bordetella pertussis* as *B. pertussis* is **a** Gram-negative bacterium that is inherently resistant to penicillins.
- **Macrolide antibiotics** are the drug class of choice for pertussis due to their efficacy against this organism.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 8: A 34-year-old poultry worker presents to his physician with a sore throat and a non-productive cough for 2 weeks. His cough is associated with fever. The vital signs include: blood pressure 120/80 mm Hg, heart rate 67/min, respiratory rate 18/min, and temperature 37.6°C (98.0°F). Physical examination shows oropharyngeal erythema and scattered, moist rales on lung auscultation. The patient's X-ray demonstrates patchy reticular opacities in the perihilar regions of both lungs. After some additional tests, he is diagnosed with community-acquired pneumonia and is initially treated with cephalexin with no significant improvement. Which of the following best describes the immune response elicited by the pathogen that is causing this patient's condition?
- A. Antibody-mediated immunity plays the leading role in the elimination of this pathogen.
- B. It primarily induces the Th1-cell response. (Correct Answer)
- C. Peptidoglycan is its major antigen that induces an immune response.
- D. This pathogen evades the immune response by encapsulation.
- E. It activates TLR5 on the surface of macrophages.
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***It primarily induces the Th1-cell response.***
- The patient's symptoms (poultry worker, sore throat, non-productive cough, fever, patchy reticular opacities, modest improvement with cephalexin) are highly suggestive of **Chlamydophila psittaci** pneumonia (**psittacosis**).
- As an **obligate intracellular bacterium**, Chlamydophila psittaci primarily elicits a **cell-mediated immune response**, specifically a **Th1-cell response**, which is crucial for clearing intracellular pathogens.
*Antibody-mediated immunity plays the leading role in the elimination of this pathogen.*
- While antibodies play a role, **humoral immunity** is generally less effective against **intracellular pathogens** like Chlamydophila psittaci because antibodies cannot access the pathogen within host cells.
- The primary defense against intracellular bacteria relies on **cell-mediated immunity** to destroy infected cells or activate macrophages.
*Peptidoglycan is its major antigen that induces an immune response.*
- **Chlamydophila psittaci** lacks a conventional **peptidoglycan layer** in its cell wall, distinguishing it from most other bacteria.
- Therefore, **peptidoglycan** is not a major antigen that induces an immune response against this pathogen.
*This pathogen evades the immune response by encapsulation.*
- **Chlamydia** species, including Chlamydophila psittaci, do **not possess a capsule** as a primary mechanism of immune evasion.
- Their main evasion strategy is their **intracellular lifestyle**, which protects them from humoral immune responses.
*It activates TLR5 on the surface of macrophages.*
- **TLR5** specifically recognizes **flagellin**, a protein component of bacterial flagella.
- **Chlamydophila psittaci** is a **non-motile bacterium** and does not possess flagella, so it would not activate TLR5.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 9: An 81-year-old man comes to the emergency department with severe left ear pain and drainage for 3 days. He has a history of poorly-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. He appears uncomfortable. Physical examination of the ear shows marked periauricular erythema, exquisite tenderness on palpation, and granulation tissue in the external auditory canal. The most likely causal pathogen produces an exotoxin that acts by a mechanism most similar to a toxin produced by which of the following organisms?
- A. Corynebacterium diphtheriae (Correct Answer)
- B. Bacillus anthracis
- C. Staphylococcus aureus
- D. Bordetella pertussis
- E. Shigella dysenteriae
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Corynebacterium diphtheriae***
- The clinical picture describes **malignant otitis externa** (MOE), likely caused by *Pseudomonas aeruginosa*, particularly in an elderly diabetic patient. Both *Pseudomonas aeruginosa* exotoxin A and *Corynebacterium diphtheriae* diphtheria toxin **inhibit protein synthesis by ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor-2 (EF-2)**.
- This shared mechanism of action makes *Corynebacterium diphtheriae* the most appropriate comparative organism based on the question's premise of exotoxin mechanism.
*Bacillus anthracis*
- Produces **anthrax toxin**, which consists of Protective Antigen (PA), Edema Factor (EF), and Lethal Factor (LF). LF is a **zinc-dependent metalloprotease** that cleaves mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK) family proteins.
- This mechanism is distinct from the ADP-ribosylation of EF-2.
*Staphylococcus aureus*
- Produces several toxins, including **toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1)** and **exfoliatin**, which act as **superantigens** or **proteases** respectively.
- These mechanisms differ from the ADP-ribosylation of EF-2.
*Bordetella pertussis*
- Produces **pertussis toxin**, which **ADP-ribosylates Gi proteins**, leading to increased cAMP levels by disinhibiting adenylate cyclase.
- This is a different target and mechanism compared to the ADP-ribosylation of EF-2.
*Shigella dysenteriae*
- Produces **Shiga toxin**, which is an **N-glycosidase** that cleaves the adenine residue from the 28S rRNA of the 60S ribosomal subunit, thereby **inhibiting protein synthesis**.
- While it inhibits protein synthesis, the specific mechanism is different from ADP-ribosylation of EF-2.
Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG Question 10: Blood cultures are sent to the laboratory and empiric treatment with intravenous vancomycin is started. Blood cultures grow gram-negative bacilli identified as Cardiobacterium hominis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Switch to intravenous gentamicin
- B. Switch to intravenous ampicillin
- C. Switch to intravenous ceftriaxone (Correct Answer)
- D. Switch to intravenous cefazolin
- E. Add intravenous rifampin
Bordetella pertussis Explanation: ***Switch to intravenous ceftriaxone***
- **Cardiobacterium hominis** is part of the **HACEK group** of bacteria, which are known for causing **endocarditis**.
- These organisms are typically susceptible to **beta-lactam antibiotics**, with **third-generation cephalosporins** like ceftriaxone being the drug of choice due to their excellent activity and good penetration.
*Switch to intravenous gentamicin*
- While **aminoglycosides** like gentamicin can be used in combination regimens for serious infections, they are generally **not monotherapy** for HACEK endocarditis and are associated with **nephrotoxicity** and **ototoxicity**.
- The primary treatment for HACEK endocarditis is a **beta-lactam antibiotic**, not an aminoglycoside alone.
*Switch to intravenous ampicillin*
- **Ampicillin** is a beta-lactam, but it may not consistently provide optimal coverage for all HACEK organisms, and some strains may have reduced susceptibility.
- **Third-generation cephalosporins** are preferred due to their broader and more consistent activity against this group.
*Switch to intravenous cefazolin*
- **Cefazolin** is a first-generation cephalosporin and typically has **limited activity** against gram-negative bacilli, especially those like Cardiobacterium hominis which require broader-spectrum beta-lactams.
- Its spectrum of activity is primarily against **gram-positive bacteria** and some **gram-negative cocci**.
*Add intravenous rifampin*
- **Rifampin** is primarily used for **mycobacterial infections** and in combination regimens for specific bacterial infections (e.g., bone and joint infections, prosthetic device infections) often due to resistant staphylococci.
- It is **not a first-line agent** for Cardiobacterium hominis infections and there's no indication for its use here with an organism susceptible to ceftriaxone.
More Bordetella pertussis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.