Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
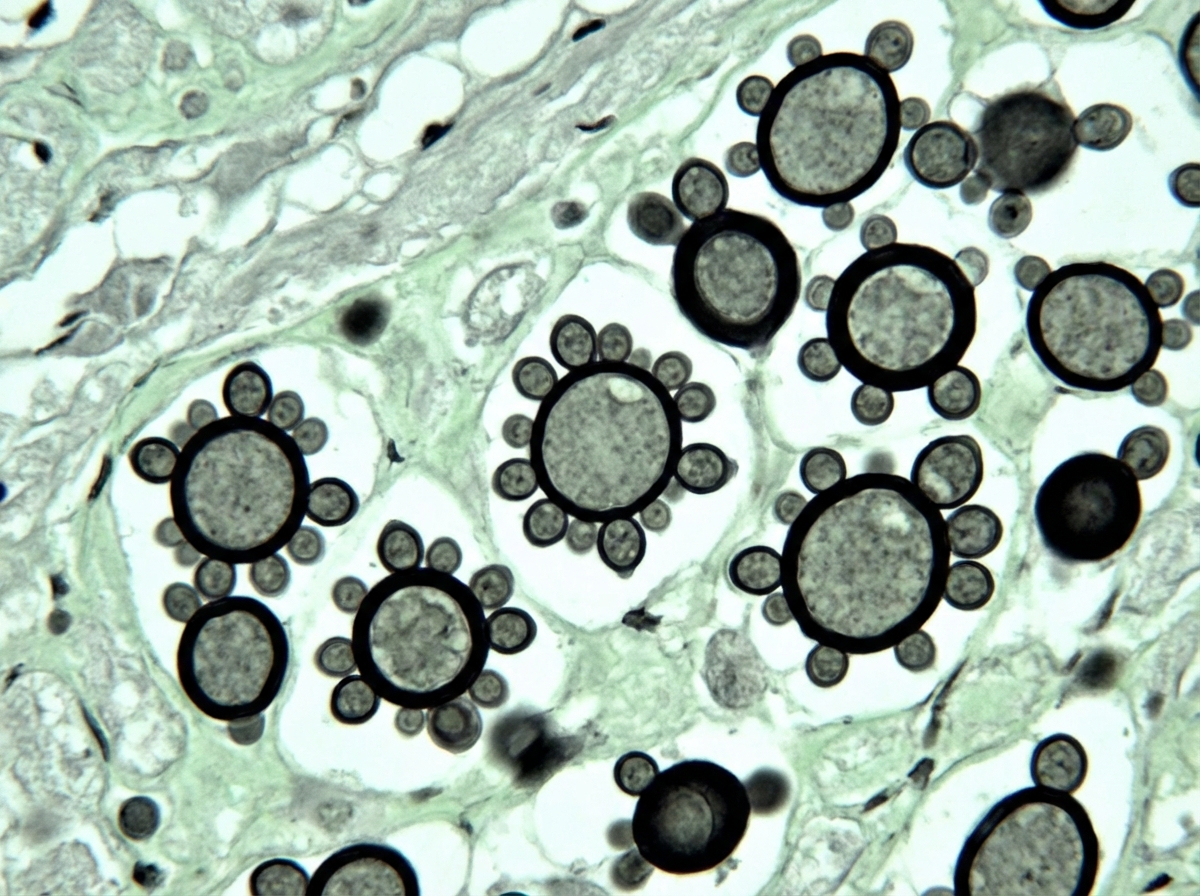
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of fever, weakness, diffuse abdominal pain, and multiple lumps on his body. He has recently returned to the USA from a 3-month agricultural internship in South America. Physical examination shows enlarged superficial cervical and inguinal lymph nodes. There is tender hepatomegaly. A photomicrograph of a liver biopsy sample after methenamine silver staining is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Aspergillosis
- B. Paracoccidioidomycosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Blastomycosis
- D. Malaria
- E. Histoplasmosis
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: **Paracoccidioidomycosis**
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **weakness**, **abdominal pain**, **multiple body lumps**, **diffuse lymphadenopathy**, and **hepatomegaly** after returning from **South America** is highly suggestive of a systemic fungal infection.
- The liver biopsy showing **yeast forms** with **multiple budding cells** (often described as a **"mariner's wheel"** or **"Mickey Mouse ears"** appearance on methenamine silver stain) is characteristic of *Paracoccidioides brasiliensis*, the causative agent of paracoccidioidomycosis.
*Aspergillosis*
- Generally presents with **pulmonary infections** (e.g., aspergilloma, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, invasive aspergillosis) or disseminated disease in immunocompromised individuals.
- Microscopic findings would show **hyphae with acute-angle branching septate forms**, not budding yeast.
*Blastomycosis*
- Typically found in the **Mississippi and Ohio River basins** and Great Lakes region of North America.
- Microscopic examination reveals **broad-based budding yeast** cells, often larger than *Paracoccidioides*, without the characteristic multiple budding pattern.
*Malaria*
- Caused by a **parasite** (*Plasmodium*) transmitted by mosquitos, and would present with cyclical fevers, chills, anemia, and splenomegaly.
- A definitive diagnosis is made by **blood smear** showing parasites within red blood cells, not fungal elements in a tissue biopsy.
*Histoplasmosis*
- Endemic in the **Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys** and parts of Central and South America.
- Microscopic findings would show **small, oval yeast cells** within macrophages, often much smaller than *Paracoccidioides* and without multiple budding, making disseminated disease a possibility, but less likely given the specific biopsy findings.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old woman visits a physician because of fever, chills, dry cough, and a few enlarging masses on her cheeks and neck. Wart-like lesions are present on the nose as shown in the photograph. She reports that she visited the Mississippi area a few months before on a business trip. Her temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F), the pulse is 80/min, and the blood pressure is 121/78 mm Hg. A fine needle aspirate of the lymph node is sent for pathological investigation. Culture growth shows white colonies on Sabouraud glucose agar (SGA). Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Histoplasma capsulatum
- B. Malassezia furfur
- C. Blastomyces dermatitidis (Correct Answer)
- D. Coccidioides immitis
- E. Aspergillus fumigatus
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Blastomyces dermatitidis***
- The patient's symptoms, including **fever, chills, dry cough, enlarging masses on cheeks and neck, and wart-like lesions on the nose**, along with a history of travel to the **Mississippi area**, are highly characteristic of **blastomycosis**.
- **_Blastomyces dermatitidis_** is a dimorphic fungus endemic to the **Ohio and Mississippi River valleys** and the Great Lakes region, often causing pulmonary disease that can disseminate to the skin, bones, and other organs, producing lesions such as those described.
*Histoplasma capsulatum*
- This fungus is also endemic to the **Ohio and Mississippi River valleys** but typically causes **histoplasmosis**, which often presents with asymptomatic lung infection, or in severe cases, disseminated disease with **hepatosplenomegaly** and **oral ulcers**, rather than aggressive cutaneous **wart-like lesions**.
- While it can cause pulmonary symptoms, the prominent **skin lesions** and masses described are less typical for disseminated histoplasmosis compared to **blastomycosis**.
*Malassezia furfur*
- **_Malassezia furfur_** is associated with superficial fungal infections like **tinea versicolor** (pityriasis versicolor), which presents as hypopigmented or hyperpigmented patches on the skin, mainly on the trunk and upper extremities.
- It does not typically cause **deep-seated infections** with systemic symptoms (fever, chills, cough) or **wart-like lesions** on the nose and neck masses.
*Coccidioides immitis*
- **_Coccidioides immitis_** is endemic to the **southwestern United States** (e.g., California, Arizona) and is the causative agent of **Coccidioidomycosis** (Valley Fever).
- While it can cause pulmonary symptoms and disseminate, the classic dermatological manifestations are often **erythema nodosum** or **erythema multiforme**, not the wart-like, verrucous lesions described in this case, and its endemic region does not fit the patient's travel history to Mississippi.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- **_Aspergillus fumigatus_** is an opportunistic mold that primarily causes allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), aspergilloma (fungus ball in pre-existing lung cavities), or invasive aspergillosis in **immunocompromised individuals**.
- It is not typically associated with cutaneous **wart-like lesions** or the specific endemic pattern and systemic symptoms described in an otherwise seemingly immunocompetent individual in the Mississippi region.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is studying growth patterns of various fungal pathogens. Incubation of an isolated fungus at 25°C shows branching hyphae with rosettes of conidia under light microscopy. After incubation at 37°C, microscopic examination of the same organism instead shows smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells. Infection with the investigated pathogen is most likely to cause which of the following conditions?
- A. Pityriasis versicolor
- B. Candidiasis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Sporotrichosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Coccidioidomycosis
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Sporotrichosis***
- The description of a fungal pathogen exhibiting **thermal dimorphism** (different forms at 25°C and 37°C) is characteristic of **Sporothrix schenckii**.
- At 25°C, it typically grows as **mold with branching hyphae and conidia in rosettes**, and at 37°C, it grows as **yeast-like cells (cigar-shaped bodies in tissue)**, which can appear rounded and elongated.
*Pityriasis versicolor*
- Caused by **Malassezia globosa**, which is a **lipophilic yeast** and does not exhibit thermal dimorphism described here.
- Characterized by **hypo- or hyperpigmented skin patches**, not deep tissue infection with dimorphic growth.
*Candidiasis*
- Caused by **Candida species**, which are **opportunistic yeasts** that can form pseudohyphae and true hyphae but do not display the specific dimorphism with rosettes of conidia at 25°C.
- Infections range from superficial mucocutaneous to systemic, but the fungal morphology described does not fit.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Caused by **Cryptococcus neoformans** or **Cryptococcus gattii**, which are **encapsulated yeasts** and do not exhibit dimorphism (mold at 25°C, yeast at 37°C).
- Primarily causes **meningoencephalitis** or pulmonary disease, and is identified by its capsule and yeast form.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- Caused by **Coccidioides immitis** or **Coccidioides posadasii**, which are **thermally dimorphic fungi**, but their morphology differs from the description.
- At 25°C, they grow as molds with **arthroconidia**, and at 37°C, they form **spherules containing endospores** in tissue, not smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 4: A 67-year-old male presents to his primary care physician for evaluation of fever and an unintended weight loss of 25 pounds over the last 4 months. He also has decreased appetite and complains of abdominal pain located in the right upper quadrant. The patient has not noticed any changes in stool or urine. He emigrated from Malaysia to the United States one year prior. Social history reveals that he smokes half a pack per day and has 5-7 drinks of alcohol per day. The patient is up to date on all of his vaccinations. Physical exam findings include mild jaundice as well as an enlarged liver edge that is tender to palpation. Based on clinical suspicion, biomarker labs are sent and show polycythemia and an elevated alpha fetoprotein level but a normal CA 19-9 level. Surface antigen for hepatitis B is negative. Ultrasound reveals a normal sized gallbladder. Given this presentation, which of the following organisms was most likely associated with the development of disease in this patient?
- A. Naked DNA virus
- B. Enveloped DNA virus
- C. Curved gram-negative bacteria
- D. Acute angle branching fungus
- E. Trematode from undercooked fish (Correct Answer)
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Trematode from undercooked fish***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, RUQ pain, weight loss, jaundice, hepatomegaly, elevated **AFP**, and normal CA 19-9) point strongly towards **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**.
- The history of emigration from Malaysia and the elevated **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)** despite negative hepatitis B antigen, suggest a parasitic infection, specifically a liver fluke (trematode), as a risk factor for HCC. **Clonorchis sinensis** and **Opisthorchis viverrini** are trematodes acquired from undercooked freshwater fish, endemic to Southeast Asia, and are known to cause cholangiocarcinoma and, less commonly, HCC.
*Naked DNA virus*
- This typically refers to viruses like **human papillomavirus (HPV)** or **adenovirus**, which are not primary causes of the described liver pathology or HCC with this specific presentation.
- While some naked DNA viruses can cause human disease, they are not typically linked to the patient's specific symptoms and lab findings (elevated AFP) in the context of liver cancer from a Southeast Asian background.
*Enveloped DNA virus*
- This category includes viruses like **Herpesviruses** and **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)**. While HBV is a major cause of HCC, the patient's hepatitis B surface antigen is negative, ruling out active or chronic HBV infection as the direct cause in this case.
- Other enveloped DNA viruses do not commonly cause this specific cluster of symptoms and risk factors for HCC.
*Curved gram-negative bacteria*
- This description often refers to bacteria like **Campylobacter** or **Helicobacter pylori**. These can cause gastrointestinal issues but are not typically associated with liver masses, jaundice, and elevated AFP in the context of HCC.
- They do not explain the patient's risk factors or presentation that strongly suggests chronic liver inflammation leading to cancer.
*Acute angle branching fungus*
- This refers to fungi like **Aspergillus**, which can cause invasive infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
- While Aspergillus can cause pulmonary infections and, less commonly, disseminate to other organs including the liver, it does not typically present with the described risk factors (Southeast Asian origin, undercooked fish consumption) or lab findings (elevated AFP) for HCC, nor does it fit the general clinical picture.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 5: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of fever, fatigue, dry cough, headache, and myalgia over the past week. Two days ago, he developed several painful oral lesions and difficulty swallowing. He underwent kidney transplantation 3 years ago. His temperature is 38.2°C (100.7°F). Physical examination shows bilateral rales, hepatosplenomegaly, and multiple 1–2 cm ulcerative lesions with raised borders in the oral mucosa. A photomicrograph of a liver biopsy specimen is shown. Which of the following is the most likely causal pathogen?
- A. Aspergillus fumigatus
- B. Blastomyces dermatitidis
- C. Coccidioides immitis
- D. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
- E. Histoplasma capsulatum (Correct Answer)
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Histoplasma capsulatum***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, fatigue, dry cough, headache, myalgia, respiratory symptoms (bilateral rales), hepatosplenomegaly**, and **painful oral ulcerative lesions** in an **immunocompromised individual (kidney transplant recipient)** is highly suggestive of **disseminated histoplasmosis**.
- The photomicrograph shows numerous **small, intracellular yeast forms within macrophages**, which is the pathognomonic finding for *Histoplasma capsulatum*.
- *Histoplasma* is endemic to the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and commonly causes disseminated disease in immunocompromised patients.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- *Aspergillus* typically causes invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients, presenting with **fever and cough**, but generally does not cause **oral ulcerative lesions** or **hepatosplenomegaly** in this disseminated pattern.
- Microscopically, *Aspergillus* appears as **septate hyphae with acute-angle branching (45°)**, which is inconsistent with the intracellular yeasts in the image provided.
*Blastomyces dermatitidis*
- *Blastomyces* can cause pulmonary disease and disseminate to the **skin and bones**, but **oral lesions** and **hepatosplenomegaly** are less common presenting features.
- The yeast forms of *Blastomyces* are characteristically **large (8-15 μm), broad-based budding yeasts**, which are much larger than the small organisms seen in the photomicrograph.
*Coccidioides immitis*
- *Coccidioidomycosis* is endemic to the southwestern U.S. and can cause pulmonary symptoms, but disseminated disease typically involves the **skin, bones, joints, and meninges**, with **oral lesions and hepatosplenomegaly** being less frequent manifestations.
- Microscopically, *Coccidioides* is characterized by **large spherules (20-80 μm) containing endospores**, which are not seen in the provided image showing small intracellular organisms.
*Paracoccidioides brasiliensis*
- This fungus is endemic to Central and South America and can cause oral lesions that are typically **mulberry-like** or **verrucous** in appearance, with disseminated disease often affecting the lungs, lymph nodes, and mucosal surfaces.
- Microscopic examination reveals **multiple budding yeasts** with a characteristic **"ship's wheel" or "pilot's wheel" appearance**, which differs significantly from the small intracellular yeasts within macrophages shown in the image.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old woman presents to the clinic with severe pain in her left knee of 1-day duration. Physical examination reveals a red, swollen, warm, and tender left knee with a decreased range of motion. The patient affirms that she has been sexually active with several partners over the last year and that 1 of her partners has complained of dysuria and yellow urethral discharge. An arthrocentesis was performed and showed a WBC count of 60,000/µL, with 90% polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Visualization of the patient's synovial fluid is provided in the image. Which of the following is a characteristic feature of the organism causing this condition?
- A. It causes the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction when treated with penicillin
- B. It produces a heat-labile toxin that prevents protein synthesis
- C. It selectively grows on Thayer-Martin medium (Correct Answer)
- D. It is a gram-positive diplococcus
- E. It ferments maltose
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***It selectively grows on Thayer-Martin medium***
- The patient's presentation with **septic arthritis**, a history of multiple sexual partners, and a partner with symptoms of **urethritis** suggests **gonococcal arthritis** caused by *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*.
- *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* is a fastidious organism that requires an enriched selective medium like **Thayer-Martin agar** for optimal growth, which contains antimicrobial agents to inhibit commensal flora.
*It causes the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction when treated with penicillin*
- The **Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction** is typically associated with treatment of **spirochetal diseases** like **syphilis** (caused by *Treponema pallidum)* or **Lyme disease** (caused by *Borrelia burgdorferi*) with penicillin.
- This reaction results from the rapid lysis of spirochetes and the release of endotoxins, which is not characteristic of gonococcal infection or its treatment.
*It produces a heat-labile toxin that prevents protein synthesis*
- This description is characteristic of toxins produced by organisms like **diphtheria toxin** (*Corynebacterium diphtheriae*) or **Shiga toxin** (*Shigella dysenteriae* and enterohemorrhagic *E. coli*), which inhibit protein synthesis but are not associated with *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*.
- *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* possesses virulence factors like pili, Opa proteins, and LOS, but its primary pathogenicity mechanism does not involve a heat-labile toxin that prevents protein synthesis.
*It is a gram-positive diplococcus*
- The image clearly shows **gram-negative diplococci** within phagocytes (neutrophils), which is a classic microscopic finding for *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*.
- *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* is specifically a **Gram-negative organism**, not Gram-positive.
*It ferments maltose*
- *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* metabolizes **glucose only** and does not ferment maltose, which helps differentiate it from *Neisseria meningitidis* (which ferments both glucose and maltose).
- This metabolic characteristic is a key biochemical test used in the laboratory for the identification of *Neisseria* species.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 7: A 44-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of productive cough, fever, and lethargy. He also has several skin lesions over his body. His symptoms began 3 weeks after he returned from a camping trip in Kentucky. Three years ago, he underwent kidney transplantation for polycystic kidney disease. Current medications include sirolimus and prednisone. His temperature is 38°C (100.4°F). Diffuse crackles are heard over the lung fields. There are 4 white, verrucous skin patches over his chest and upper limbs. A photomicrograph of a skin biopsy specimen from one of the lesions is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Mucormycosis
- C. Blastomycosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Cryptococcosis
- E. Histoplasmosis
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Blastomycosis***
- The patient's history of **camping in Kentucky**, along with the presence of **pulmonary symptoms** (productive cough, fever, crackles) and **verrucous skin lesions**, are classic for blastomycosis.
- The photomicrograph showing **broad-based budding yeast** is pathognomonic for *Blastomyces dermatitidis*.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- This is typical in the **Southwestern United States and parts of Mexico**, not Kentucky.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules containing endospores**, which are not seen in the provided image.
*Mucormycosis*
- This infection is characterized by **irregular, broad, non-septate hyphae** with **wide-angle branching**, often invading blood vessels, leading to tissue necrosis.
- It primarily affects immunocompromised patients but typically presents as **rhinocerebral** or **pulmonary infection**, less commonly with verrucous skin lesions of this type.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Primarily affects the **lungs and central nervous system**, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Microscopy typically shows **encapsulated yeast** cells, which would be visible with India ink stain, and are not represented by the broad-based budding in the image.
*Histoplasmosis*
- Prevalent in the **Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys**, which includes Kentucky, and is often associated with **bird or bat droppings**.
- On microscopy, it presents as **small intracellular yeast** within macrophages, which is morphologically distinct from the large, broad-based budding yeast shown.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 8: A 48-year-old man with HIV comes to the physician because of skin lesions over his face and neck for 2 weeks. They are not itchy or painful. He does not have fever or a sore throat. He was treated for candidal esophagitis 3 months ago. He is sexually active with his wife, who knows of his condition, and uses condoms consistently. He is currently receiving triple antiretroviral therapy with lamivudine, abacavir, and efavirenz. He is 175 cm (5 ft 9 in) tall and weighs 58 kg (128 lb); BMI is 18.8 kg/m2. Examination shows multiple skin colored papules over his face and neck with a dimpled center. Cervical lymphadenopathy is present. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. His hemoglobin concentration is 12.1 g/dL, leukocyte count is 4,900/mm3, and platelet count is 143,000/mm3; serum studies and urinalysis show no abnormalities. CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 312/mm3 (normal ≥ 500). Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
- A. Poxvirus (Correct Answer)
- B. A herpesvirus
- C. Papillomavirus
- D. Coccidioides
- E. Bartonella
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Poxvirus***
- The description of **skin-colored papules with a dimpled (umbilicated) center** is highly characteristic of **molluscum contagiosum**, which is caused by a poxvirus. This condition is common in immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV.
- The patient's **HIV-positive status** and **CD4+ count of 312/mm³** indicate immunocompromise, making him susceptible to severe or widespread molluscum contagiosum, often seen on the face and neck.
*A herpesvirus*
- Herpes simplex virus typically causes **painful, clustered vesicles** on an erythematous base, often with recurrent outbreaks; this presentation does not match the described painless, umbilicated papules.
- Varicella-zoster virus (another herpesvirus) causes chickenpox or shingles, presenting as **vesicles and crusts in a dermatomal pattern** (shingles) or diffuse rash (chickenpox), which is inconsistent with this patient's lesions.
*Papillomavirus*
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) causes **warts**, which are typically rough, hyperkeratotic papules or nodules, lacking the characteristic central umbilication seen in this patient.
- While common in immunocompromised individuals, HPV lesions usually present differently and are not described as skin-colored with a dimpled center.
*Coccidioides*
- **Coccidioidomycosis** is a fungal infection that can cause various skin manifestations, including **erythema nodosum**, **erythema multiforme**, or subcutaneous nodules, but not the distinct umbilicated papules characteristic of molluscum contagiosum.
- Systemic symptoms like fever, cough, and fatigue are common in disseminated coccidioidomycosis, and while skin lesions can occur, they do not typically present as solitary or multiple umbilicated papules.
*Bartonella*
- *Bartonella* infections, particularly *Bartonella henselae* (cat scratch disease) or *Bartonella quintana* (bacillary angiomatosis), typically present as **reddish-purple vascular lesions** (angiomatous papules or nodules) or localized lymphadenopathy.
- The lesions described are skin-colored and umbilicated, not vascular, making *Bartonella* an unlikely cause.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 9: A study is designed to assess the functions of immune components. The investigator obtains a lymph node biopsy from a healthy subject and observes it under a microscope. A photomicrograph of the cross-section of this lymph node is shown. Which of the following immunologic processes most likely occurs in the region labeled with an arrow?
- A. Isotype switching (Correct Answer)
- B. V(D)J recombination
- C. Macrophage activation
- D. T cell activation
- E. Negative selection
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Isotype switching***
- The arrow points to a **germinal center**, a specialized microenvironment within lymph nodes where B cells undergo **affinity maturation** and **isotype switching**.
- Isotype switching (or class switching) is the process by which B cells change the type of **antibody** they produce, e.g., from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE, to mediate different effector functions while retaining antigen specificity.
*V(D)J recombination*
- **V(D)J recombination** is the genetic mechanism by which the diverse repertoires of T cell receptors (TCRs) and immunoglobulins (antibodies) are generated, primarily in the **bone marrow** (for B cells) and **thymus** (for T cells) during their development.
- This process occurs much earlier in lymphocyte development and is largely completed before B cells migrate to secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and form germinal centers.
*Macrophage activation*
- **Macrophage activation** is a process where macrophages acquire enhanced phagocytic and microbicidal activity, often in response to cytokines like **IFN-γ** produced by T helper cells.
- While macrophages are present in lymph nodes and play a role in antigen presentation and immune responses, their primary activation does not specifically occur within germinal centers; the germinal center is mainly a site for B cell maturation.
*T cell activation*
- **T cell activation** primarily occurs in the **T cell zones** (paracortex) of lymph nodes, where **naïve T cells** encounter antigen-presenting cells (APCs) presenting their specific antigen.
- While T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, a type of T cell, are crucial for sustaining germinal center reactions, the germinal center itself is not the primary site for the initial activation of most T cells.
*Negative selection*
- **Negative selection** is a critical process in lymphocyte development, occurring in the **thymus** for T cells and **bone marrow** for B cells, where self-reactive lymphocytes are eliminated.
- This process ensures central tolerance and occurs long before mature lymphocytes populate secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes.
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG Question 10: A 3-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of progressive difficulty breathing and a dry cough. Five weeks ago, she was diagnosed with diffuse hemangiomas involving the intrathoracic cavity and started treatment with prednisolone. She appears uncomfortable and in moderate respiratory distress. Her temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), pulse is 150/min, respirations are 50/min, and blood pressure is 88/50 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 87%. Oral examination shows a white plaque covering the tongue that bleeds when scraped. Chest examination shows subcostal and intercostal retractions. Scattered fine crackles and rhonchi are heard throughout both lung fields. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 21,000/mm3 and an increased serum beta-D-glucan concentration. An x-ray of the chest shows symmetrical, diffuse interstitial infiltrates. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Tuberculin skin test
- B. Urine antigen test
- C. CT scan of the chest
- D. Bronchoalveolar lavage (Correct Answer)
- E. DNA test for CFTR mutation
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei Explanation: ***Bronchoalveolar lavage***
- The patient, an infant on **prednisolone** (immunosuppression) with **diffuse interstitial infiltrates**, **uncomfortable appearance**, **respiratory distress**, and **oral thrush (white plaque that bleeds when scraped)**, points to **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**.
- **Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)** is the gold standard for diagnosing PCP by identifying **Pneumocystis jirovecii cysts** or **trophozoites** using special stains (e.g., Giemsa, methenamine silver).
*Tuberculin skin test*
- The **tuberculin skin test** is used to diagnose **tuberculosis**, which typically presents with **granulomas** and **cavitary lesions** on chest X-ray, not diffuse interstitial infiltrates.
- While tuberculosis can cause respiratory symptoms, the presence of oral thrush and immunosuppression suggests an opportunistic fungal infection like PCP rather than TB.
*Urine antigen test*
- A **urine antigen test** is commonly used for diagnosing **Legionnaires' disease** or **pneumococcal pneumonia** in adults, and is not applicable for PCP.
- It does not detect *Pneumocystis jirovecii*, which is the suspected pathogen in this immunosuppressed infant.
*CT scan of the chest*
- A **CT scan of the chest** would show **diffuse ground-glass opacities** characteristic of PCP but is a **radiological finding**, not a definitive diagnostic test for the pathogen itself.
- While it can further characterize the pulmonary findings, it cannot identify the causative organism, which is crucial for targeted treatment.
*DNA test for CFTR mutation*
- A **DNA test for CFTR mutation** is used to diagnose **cystic fibrosis**, a genetic disorder affecting mucus production, and is not relevant in this acute presentation of respiratory distress and immunosuppression.
- Cystic fibrosis typically presents with recurrent respiratory infections, pancreatic insufficiency, and failure to thrive, not primarily with opportunistic infections like PCP.
More Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.