Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 1: A 34-year-old woman presents with multiple round, scaly patches on her chest and back. The lesions are hypopigmented and slightly pruritic. KOH preparation of skin scrapings shows short, angular hyphae. Which of the following best describes the causative organism's morphology in culture?
- A. Branching, septate hyphae with characteristic 'spaghetti and meatballs' appearance (Correct Answer)
- B. Non-septate hyphae with sporangiospores
- C. Branching, septate hyphae with tear-drop microconidia
- D. Pseudohyphae with blastoconidia
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Branching, septate hyphae with characteristic 'spaghetti and meatballs' appearance***
- The clinical presentation of **hypopigmented, scaly patches** on the trunk, especially with mild pruritus, is highly suggestive of **tinea versicolor**.
- A **KOH preparation** showing **short, angular hyphae** is characteristic of *Malassezia furfur*, which when cultured, displays both **mycelial elements (spaghetti)** and **yeast forms (meatballs)**.
*Non-septate hyphae with sporangiospores*
- This morphology is characteristic of **zygomycetes** (e.g., *Rhizopus*, *Mucor*), which cause diseases like mucormycosis, a much more severe and rapidly progressive infection, not tinea versicolor.
- **Zygomycetes** are typically associated with invasive infections in immunocompromised individuals.
*Branching, septate hyphae with tear-drop microconidia*
- This describes the typical dermatophyte, *Trichophyton rubrum*, which causes conditions like tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis, usually presenting with **erythematous, annular lesions** with active borders, different from tinea versicolor.
- While it also has septate hyphae, the distinct microconidia morphology differentiates it from *Malassezia*.
*Pseudohyphae with blastoconidia*
- This morphology is typical of **Candida species**, which cause conditions like candidiasis (e.g., thrush, diaper rash, vulvovaginitis).
- Though *Candida* can cause skin infections, the hypopigmentation and characteristic KOH findings of short, angular hyphae are inconsistent with *Malassezia*.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 2: A 29-year-old woman comes to the military physician because of a 2-day history of fever, joint pain, dry cough, chest pain, and a painful red rash on her lower legs. Two weeks ago, she returned from military training in Southern California. She appears ill. Her temperature is 39°C (102.1°F). Physical examination shows diffuse inspiratory crackles over all lung fields and multiple tender erythematous nodules over the anterior aspect of both legs. A biopsy specimen of this patient's lungs is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Septate hyphae with acute-angle branching
- B. Spherules filled with endospores (Correct Answer)
- C. Broad-based budding yeast
- D. Encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding
- E. Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: **Spherules filled with endospores**
- The patient's symptoms (fever, joint pain, dry cough, chest pain, erythema nodosum on legs) combined with her travel history to **Southern California** are highly suggestive of **Coccidioidomycosis** ("Valley Fever").
- A biopsy of affected lung tissue in coccidioidomycosis typically reveals **spherules** (thick-walled structures) containing numerous **endospores**, which are characteristic of the tissue phase of *Coccidioides immitis/posadasii*.
*Septate hyphae with acute-angle branching*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Aspergillus** species, which can cause opportunistic infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- While it can cause lung infections, the clinical presentation and geographic exposure do not point towards aspergillosis as the most likely diagnosis.
*Broad-based budding yeast*
- This describes the characteristic morphology of *Blastomyces dermatitidis*, the causative agent of **Blastomycosis**.
- **Blastomycosis** is typically found in the Great Lakes region, Ohio, Mississippi River valleys, and southeastern United States, not Southern California.
*Encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding*
- This describes **Cryptococcus neoformans**, which appears as an encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding in tissue.
- While it can cause pulmonary disease, the classic presentation (erythema nodosum, acute illness after Southern California exposure) is not consistent with **cryptococcosis**, which typically presents subacutely in immunocompromised patients.
*Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae*
- This morphology is characteristic of *Candida albicans*, which commonly causes mucocutaneous infections and can cause systemic candidiasis, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
- The clinical picture of a healthy young woman with exposure in Southern California does not fit with a typical **Candida** infection.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 3: A 73-year-old man presents to the office, complaining of “weird blisters” on his right hand, which appeared 2 weeks ago. The patient says that he initially had a rash, which progressed to blisters. He denies any trauma or known contact with sick people. He is worried because he hasn’t been able to garden since the rash appeared, and he was planning on entering his roses into an annual competition this month. His vital signs are stable. On physical exam, the patient has multiple bullae accompanied by red, papular lesions on his right hand, which progress to his forearm. The right axillary lymph nodes are swollen and tender. What is the treatment for the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
- A. Itraconazole (Correct Answer)
- B. Azithromycin
- C. Topical corticosteroids
- D. Doxycycline
- E. Potassium iodide solution
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Itraconazole***
- This patient likely has **sporotrichosis**, a subcutaneous fungal infection, given the history of **gardening** (exposure to soil/plants), **papular lesions progressing to blisters**, and **lymphatic spread** (swollen axillary lymph nodes).
- **Itraconazole** is the **first-line treatment** for cutaneous and lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis.
*Azithromycin*
- **Azithromycin** is an **antibiotic** used to treat bacterial infections, not fungal infections like sporotrichosis.
- It is often used for respiratory tract infections, sexually transmitted infections, and some skin infections.
*Topical corticosteroids*
- **Topical corticosteroids** are anti-inflammatory agents that would likely worsen a fungal infection by suppressing the immune response.
- They are used for inflammatory dermatoses like eczema or psoriasis and would not be effective against sporotrichosis.
*Doxycycline*
- **Doxycycline** is a broad-spectrum **antibiotic**, effective against a variety of bacterial infections, including some atypical pathogens.
- It has no antifungal activity and would not be an appropriate treatment for sporotrichosis.
*Potassium iodide solution*
- While traditionally used for sporotrichosis, **potassium iodide (KI) solution** is now considered a **second-line treatment** due to its side effects and the availability of more effective and safer antifungals like itraconazole.
- It is used only in cases where itraconazole is contraindicated or ineffective.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 4: A 74-year-old man is admitted to the medical ward after he developed a fungal infection. He has aplastic anemia. The most recent absolute neutrophil count was 450/µL. An anti-fungal agent is administered that inhibits the fungal enzyme, (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase, and thereby disrupts the integrity of the fungal cell wall. He responds well to the treatment. Although amphotericin B is more efficacious for his condition, it was not used because of the side effect profile. What was the most likely infection?
- A. Invasive aspergillosis
- B. Mucormycosis
- C. Histoplasmosis
- D. Paracoccidioidomycosis
- E. Candidemia (Correct Answer)
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Candidemia***
- The patient's **neutropenia** (absolute neutrophil count of 450/µL) due to aplastic anemia is a major risk factor for invasive candidiasis, including candidemia.
- The antifungal agent's mechanism of action, targeting **(1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase**, is characteristic of **echinocandins**, which are first-line agents for candidemia, especially in critically ill or neutropenic patients, and often preferred over amphotericin B due to a better side effect profile.
*Invasive aspergillosis*
- While neutropenia is a significant risk factor for invasive aspergillosis, the primary antifungal drugs for this condition are typically **voriconazole** or **isavuconazole**, although echinocandins may be used as salvage therapy or in combination.
- The description of the drug's mechanism specifically targeting **(1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase** does not make aspergillosis the *most likely* infection, as some Aspergillus species may have less β-D-glucan in their cell walls compared to *Candida*.
*Mucormycosis*
- This aggressive fungal infection is often seen in immunocompromised patients, particularly those with **diabetes** or profound neutropenia, but the primary treatment is usually **amphotericin B**.
- Mucorales fungi typically **lack ergosterol** and their cell walls do not contain **(1→3)-β-D-glucan**, making echinocandins ineffective.
*Histoplasmosis*
- This is a dimorphic fungal infection endemic to certain geographic regions, primarily affecting the lungs and disseminating in immunocompromised individuals.
- The drug of choice for severe or disseminated histoplasmosis is **amphotericin B**, followed by azoles; echinocandins are generally not active against *Histoplasma*.
*Paracoccidioidomycosis*
- This is a chronic systemic mycosis found in Latin America, primarily affecting the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes.
- Treatment for severe forms typically involves **amphotericin B**, followed by sulfonamides or azoles for maintenance; echinocandins are not effective against *Paracoccidioides*.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old female presents to her primary care physician because she is concerned about lighter colored patches on her skin. She recently went sunbathing and noticed that these areas also did not tan. Her doctor explains that she has a fungal infection of the skin that damages melanocytes by producing acids. She is prescribed selenium sulfide and told to follow-up in one month. Which of the following describes the appearance of the most likely infectious organism under microscopy?
- A. Broad based budding yeast
- B. "Captain's wheel" yeast
- C. Germ tube forming fungus
- D. Branching septate hyphae
- E. "Spaghetti and meatballs" fungus (Correct Answer)
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***"Spaghetti and meatballs" fungus***
- The "spaghetti and meatballs" appearance on microscopy, referring to a mixture of short, septate hyphae and spherical yeast forms, is characteristic of **Malassezia globosa** or other *Malassezia* species, which cause **tinea versicolor**.
- **Tinea versicolor** presents as hypopigmented patches, especially after sun exposure, because the fungus produces **azelaic acid** that inhibits melanin synthesis.
*Broad based budding yeast*
- This description is characteristic of **Blastomyces dermatitidis**, which causes **blastomycosis**, a deep fungal infection.
- Blastomycosis typically manifests as pulmonary disease or disseminated lesions, not superficial hypopigmented skin patches.
*"Captain's wheel" yeast*
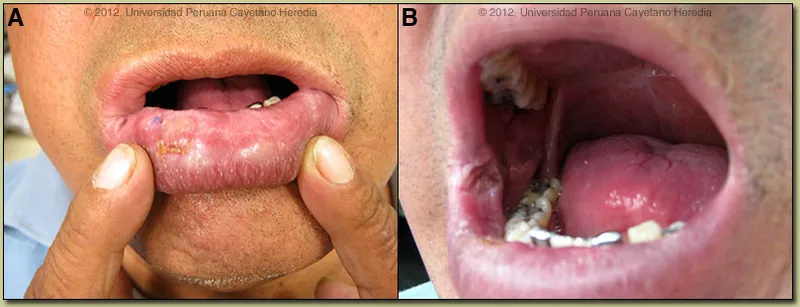
- The "captain's wheel" or multi-budding yeast appearance is characteristic of **Paracoccidioides brasiliensis**, the causative agent of **paracoccidioidomycosis**.
- This is a systemic mycosis primarily affecting the lungs and mucocutaneous areas, not a superficial skin infection like tinea versicolor.
*Germ tube forming fungus*
- The formation of **germ tubes** when incubated in serum at 37°C is a characteristic feature used to identify **Candida albicans**.
- *Candida* most commonly causes mucocutaneous candidiasis (e.g., thrush, vaginitis) or invasive infections, not hypopigmented skin patches that fail to tan.
*Branching septate hyphae*
- **Branching septate hyphae** are a general microscopic feature seen in many filamentous fungi, including dermatophytes like *Trichophyton* and *Microsporum*, which cause **tinea corporis** or **tinea pedis**.
- While dermatophytes cause skin infections, they typically result in erythematous, scaly, and often pruritic lesions and do not usually present as hypopigmented patches that fail to tan due to melanin inhibition, as seen in tinea versicolor.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 6: A 35-year-old woman with type 1 diabetes mellitus comes to the emergency department for evaluation of a 1-month history of fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, and a 3.6-kg (8-lb) weight loss. She has also had a cough for the last 2 months. She reports recent loss of pubic hair. The patient immigrated from the Philippines 7 weeks ago. Her mother has systemic lupus erythematosus. She has never smoked and does not drink alcohol. Her only medication is insulin, but she sometimes misses doses. She is 165 cm (5 ft 5 in) tall and weighs 49 kg (108 lb); BMI is 18 kg/m2. She appears lethargic. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), pulse is 58/min, and blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. Examination shows decreased sensation to touch and vibration over both feet. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Serum studies show:
Na+ 122 mEq/L
Cl- 100 mEq/L
K+ 5.8 mEq/L
Glucose 172 mg/dL
Albumin 2.8 g/dL
Cortisol 2.5 μg/dL
ACTH 531.2 pg/mL (N=5–27 pg/mL)
CT scan of the abdomen with contrast shows bilateral adrenal enlargement. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Infection with acid-fast bacilli (Correct Answer)
- B. Adrenal infarction
- C. Pituitary tumor
- D. Autoimmune adrenalitis
- E. Adrenal hemorrhage
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Infection with acid-fast bacilli***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, weight loss, cough, fatigue, low blood pressure, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, low cortisol, elevated ACTH, and **bilateral adrenal enlargement**) are highly suggestive of **primary adrenal insufficiency** with an infectious etiology.
- Given her recent immigration from the **Philippines** (an endemic area for tuberculosis), the prolonged cough (2 months), and **bilateral adrenal enlargement**, **adrenal tuberculosis caused by acid-fast bacilli** is the most likely diagnosis.
- Adrenal TB is the most common cause of adrenal insufficiency in developing countries and causes adrenal enlargement (unlike autoimmune causes which cause atrophy).
*Adrenal infarction*
- Adrenal infarction typically presents with **acute, severe flank pain** and rapid onset of adrenal insufficiency, which does not match the patient's **subacute presentation over 1-2 months**.
- While it can cause bilateral adrenal damage, it is not associated with a prolonged cough, fever, or history from a TB-endemic area.
*Pituitary tumor*
- A pituitary tumor causing adrenal insufficiency (secondary adrenal insufficiency) would lead to **low ACTH levels**, whereas this patient has markedly **elevated ACTH (531.2 pg/mL)**, indicating a primary adrenal problem.
- A pituitary tumor would not explain the bilateral adrenal enlargement or the constitutional symptoms like cough, fever, and weight loss.
*Autoimmune adrenalitis*
- While autoimmune adrenalitis is the most common cause of **primary adrenal insufficiency** in developed countries, it typically causes **adrenal atrophy rather than enlargement**.
- The patient's country of origin, prolonged cough, fever, and **adrenal enlargement** point more strongly towards an infectious cause like tuberculosis.
*Adrenal hemorrhage*
- Adrenal hemorrhage usually presents as an **acute, life-threatening event** with sudden onset of severe abdominal or flank pain and rapid hemodynamic collapse.
- It often occurs in settings of **sepsis, anticoagulant use, trauma, or stress**, none of which are described in this patient's subacute presentation over months.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 7: A 40-year-old farmer from Ohio seeks evaluation at a clinic with complaints of a chronic cough, fevers, and anorexia of several months duration. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy with hepatosplenomegaly. A chest radiograph reveals local infiltrates and patchy opacities involving all lung fields. Fine needle aspiration of an enlarged lymph node shows the presence of intracellular yeast. A fungal culture shows the presence of smooth, thin-walled microconidia and tuberculate macroconidia. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Blastomycosis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Histoplasmosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Sporotrichosis
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Histoplasmosis***
- **Histoplasmosis** is characterized by the presence of **intracellular yeast** in tissue samples and **tuberculate macroconidia** in fungal cultures, which are key diagnostic findings in this case.
- The patient's presentation with chronic cough, fevers, anorexia, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and lung infiltrates, along with geographic exposure in **Ohio** (part of the Ohio River Valley endemic area), is highly consistent with disseminated histoplasmosis.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- While coccidioidomycosis can cause lung infiltrates, it is typically endemic to the **southwestern United States** and Mexico, not Ohio.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules** containing endospores, not intracellular yeast with tuberculate macroconidia.
*Blastomycosis*
- Blastomycosis is also endemic to the Ohio River Valley, but it is characterized by **broad-based budding yeast** in tissue, and its cultures typically do not show tuberculate macroconidia.
- While it causes pulmonary and disseminated disease, the specific microscopic and culture findings differentiate it from histoplasmosis.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Cryptococcosis primarily affects immunocompromised individuals and is characterized by encapsulated yeast, which would be visible with India ink stain.
- It typically presents as **meningitis** or pneumonia, and its culture morphology does not include tuberculate macroconidia.
*Sporotrichosis*
- Sporotrichosis is commonly associated with **cutaneous lesions** following traumatic inoculation of spores from soil or vegetation, and it rarely causes disseminated disease with extensive systemic symptoms like those described.
- The yeast forms in tissue are typically smaller and cigar-shaped, and the culture morphology differs significantly from what is described.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old woman who is 24-weeks pregnant presents to the emergency department with fever, painful urination, and headache. The patient's blood pressure is 111/67 mm Hg, the pulse is 95/min, the respiratory rate is 16/min, and the temperature is 38.3°C (101.1°F). Physical examination reveals bilateral tender inguinal lymphadenopathy and painful genital lesions. On closer inspection, the patient’s genital lesions contain clear fluid and measure 5–6 mm in diameter. What is the appropriate description of these lesions?
- A. Pustule
- B. Ulcer
- C. Papule
- D. Bulla
- E. Vesicle (Correct Answer)
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Vesicle***
- A **vesicle** is defined as a **circumscribed, elevated lesion** (macule/papule) containing **clear fluid** and measuring less than 1 cm in diameter.
- The patient's lesions, which are 5-6 mm in diameter and contain clear fluid, perfectly fit the description of vesicles, characteristic of **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** infection.
*Pustule*
- A **pustule** is a small, elevated lesion similar to a vesicle but filled with **pus**, not clear fluid.
- Examples include acne or folliculitis, which are typically opaque and yellowish, unlike the described lesions.
*Ulcer*
- An **ulcer** is a defect or excavation of the skin past the **epidermis**, resulting in the loss of tissue.
- The patient's lesions are described as fluid-filled and elevated, not as an open wound with tissue loss.
*Papule*
- A **papule** is a **solid, elevated lesion** measuring less than 1 cm in diameter.
- While elevated and small, a papule does **not contain fluid**, which is a key characteristic of the described lesions.
*Bulla*
- A **bulla** is a **fluid-filled lesion** that is **larger than 1 cm** in diameter.
- The lesions described are 5-6 mm, making them smaller than the definition of a bulla.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of progressive difficulty breathing and a dry cough. Five weeks ago, she was diagnosed with diffuse hemangiomas involving the intrathoracic cavity and started treatment with prednisolone. She appears uncomfortable and in moderate respiratory distress. Her temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), pulse is 150/min, respirations are 50/min, and blood pressure is 88/50 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 87%. Oral examination shows a white plaque covering the tongue that bleeds when scraped. Chest examination shows subcostal and intercostal retractions. Scattered fine crackles and rhonchi are heard throughout both lung fields. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 21,000/mm3 and an increased serum beta-D-glucan concentration. An x-ray of the chest shows symmetrical, diffuse interstitial infiltrates. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Tuberculin skin test
- B. Urine antigen test
- C. CT scan of the chest
- D. Bronchoalveolar lavage (Correct Answer)
- E. DNA test for CFTR mutation
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Bronchoalveolar lavage***
- The patient, an infant on **prednisolone** (immunosuppression) with **diffuse interstitial infiltrates**, **uncomfortable appearance**, **respiratory distress**, and **oral thrush (white plaque that bleeds when scraped)**, points to **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**.
- **Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)** is the gold standard for diagnosing PCP by identifying **Pneumocystis jirovecii cysts** or **trophozoites** using special stains (e.g., Giemsa, methenamine silver).
*Tuberculin skin test*
- The **tuberculin skin test** is used to diagnose **tuberculosis**, which typically presents with **granulomas** and **cavitary lesions** on chest X-ray, not diffuse interstitial infiltrates.
- While tuberculosis can cause respiratory symptoms, the presence of oral thrush and immunosuppression suggests an opportunistic fungal infection like PCP rather than TB.
*Urine antigen test*
- A **urine antigen test** is commonly used for diagnosing **Legionnaires' disease** or **pneumococcal pneumonia** in adults, and is not applicable for PCP.
- It does not detect *Pneumocystis jirovecii*, which is the suspected pathogen in this immunosuppressed infant.
*CT scan of the chest*
- A **CT scan of the chest** would show **diffuse ground-glass opacities** characteristic of PCP but is a **radiological finding**, not a definitive diagnostic test for the pathogen itself.
- While it can further characterize the pulmonary findings, it cannot identify the causative organism, which is crucial for targeted treatment.
*DNA test for CFTR mutation*
- A **DNA test for CFTR mutation** is used to diagnose **cystic fibrosis**, a genetic disorder affecting mucus production, and is not relevant in this acute presentation of respiratory distress and immunosuppression.
- Cystic fibrosis typically presents with recurrent respiratory infections, pancreatic insufficiency, and failure to thrive, not primarily with opportunistic infections like PCP.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG Question 10: A 4-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his father because of a progressively worsening rash on his buttocks for the last week. He cries during diaper changes and is more fussy than usual. Physical examination of the boy shows erythematous papules and plaques in the bilateral inguinal creases, on the scrotum, and in the gluteal cleft. Small areas of maceration are also present. A diagnosis is made, and treatment with topical clotrimazole is initiated. Microscopic examination of skin scrapings from this patient's rash is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Round yeast surrounded by budding yeast cells
- B. Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae (Correct Answer)
- C. Broad-based budding yeast
- D. Fruiting bodies with septate, acute-angle hyphae
- E. Narrow budding, encapsulated yeast
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Explanation: ***Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae***
- This morphology is characteristic of *Candida albicans*, which commonly causes **diaper rash** due to the warm, moist environment in the diaper area.
- The rash described, with **erythematous papules and plaques** in the inguinal creases, scrotum, and gluteal cleft, along with **maceration**, is typical of candidal diaper dermatitis.
*Round yeast surrounded by budding yeast cells*
- This description ("wagon wheel" appearance) is characteristic of *Malasseella globosa*, the causative agent of **tinea versicolor**.
- Tinea versicolor typically presents with hypo- or hyperpigmented patches, not the erythematous, macerated rash seen in this infant.
*Broad-based budding yeast*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Blastomycosis**, caused by *Blastomyces dermatitidis*.
- This infection typically causes **pulmonary disease** or **cutaneous lesions** that are often verrucous or ulcerative, not a diaper rash.
*Fruiting bodies with septate, acute-angle hyphae*
- This describes the microscopic appearance of *Aspergillus* species.
- *Aspergillus* typically causes **invasive pulmonary disease** in immunocompromised individuals or **allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis**, not diaper dermatitis.
*Narrow budding, encapsulated yeast*
- This is the characteristic microscopic appearance of *Cryptococcus neoformans*.
- *Cryptococcus* commonly causes **meningitis** or **pulmonary infections**, particularly in immunocompromised patients, and is not associated with diaper rash.
More Paracoccidioides brasiliensis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.