Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Environmental sources and prevention. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He was diagnosed with HIV infection 2 weeks ago. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 162/mm3 (N ≥ 500). An interferon-gamma release assay is negative. Prophylactic treatment against which of the following pathogens is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Cytomegalovirus
- B. Toxoplasma gondii
- C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- D. Aspergillus fumigatus
- E. Pneumocystis jirovecii (Correct Answer)
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Pneumocystis jirovecii***
- This patient's **CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of 162/mm3** is below the threshold of 200/mm3, indicating a significant risk for **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**, an opportunistic infection in HIV.
- Prophylaxis with **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is highly effective and recommended for HIV patients with CD4 counts less than 200/mm3.
*Cytomegalovirus*
- **CMV prophylaxis** is generally not recommended for all HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is evidence of active disease or extremely low CD4 counts (e.g., <50/mm3) with high viral loads.
- While CMV can cause end-organ disease in advanced HIV, routine primary prophylaxis is not standard for this CD4 level.
*Toxoplasma gondii*
- **Toxoplasma prophylaxis** is indicated for HIV patients with **CD4 counts less than 100/mm3** who are also seropositive for *Toxoplasma gondii*.
- The patient's CD4 count is 162/mm3, and there's no mention of *Toxoplasma* serostatus, making it less appropriate than PCP prophylaxis.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
- The patient's **interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) is negative**, which suggests no **latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)**, thus making primary prophylaxis unnecessary at this time.
- While HIV patients are at high risk for TB, prophylaxis is typically given for LTBI or as secondary prophylaxis for those who have completed treatment for active TB.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- **Aspergillus infections** are typically seen in patients with severe **neutropenia** or those receiving high-dose corticosteroids, not primarily in HIV patients based solely on CD4 count.
- Routine prophylaxis for Aspergillus is not recommended for HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is a specific risk factor.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 2: A 33-year-old HIV-positive male is seen in clinic for follow-up care. When asked if he has been adhering to his HIV medications, the patient exclaims that he has been depressed, thus causing him to not take his medication for six months. His CD4+ count is now 33 cells/mm3. What medication(s) should he take in addition to his anti-retroviral therapy?
- A. Azithromycin and fluconazole
- B. Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole
- C. Dapsone
- D. Fluconazole
- E. Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Correct Answer)
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole***
- With a **CD4+ count of 33 cells/mm3**, this patient is at high risk for **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)** and **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis**, for which **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is the prophylaxis of choice.
- He is also at very high risk for **Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection**, for which **azithromycin** is the recommended preventative treatment when the CD4 count is below 50 cells/mm3.
*Azithromycin and fluconazole*
- While **azithromycin** is indicated for MAC prophylaxis, **fluconazole** is typically used for **cryptococcal meningitis** or **candidiasis**, which are not the primary, immediate prophylactic concerns at this specific CD4 count unless there's evidence of these infections.
- The most critical opportunistic infections to prevent at a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3 are PJP, Toxoplasmosis, and MAC.
*Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole*
- **Dapsone** can be used as an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** if TMP-SMX is contraindicated, but it is not the first-line choice and does not cover toxoplasmosis as effectively as TMP-SMX alone.
- **Fluconazole** again is not a primary prophylactic agent at this CD4 count in the absence of specific indications.
*Dapsone*
- **Dapsone** is an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** and can also prevent **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis** when combined with pyrimethamine, but it is not the first-line recommendation.
- It does not provide coverage against **MAC infection**, which is a significant risk at this CD4 count.
*Fluconazole*
- **Fluconazole** is primarily used for **fungal infections** like **candidiasis** or **cryptococcosis**.
- It does not prevent **PJP, Toxoplasmosis, or MAC**, which are the most critical prophylactic concerns for a patient with a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 3: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-day history of a productive cough, shortness of breath, and low-grade fever. He works as a farmer in southern Arizona. Physical examination shows multiple skin lesions with a dark blue center, pale intermediate zone, and red peripheral rim on the upper and lower extremities. There are diffuse crackles on the left side of the chest. An x-ray of the chest shows left basilar consolidation and left hilar lymphadenopathy. A photomicrograph of tissue obtained from a biopsy of the lung is shown. Which of the following is the most likely causal pathogen?
- A. Coccidioides immitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
- C. Candida albicans
- D. Blastomyces dermatitidis
- E. Aspergillus fumigatus
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Coccidioides immitis***
- The patient's presentation with **respiratory symptoms**, **skin lesions** (erythema multiforme-like), and **hilar lymphadenopathy** in a farmer from **southern Arizona** is highly characteristic of coccidioidomycosis. The image shows **spherules** containing **endospores**, which are diagnostic of *Coccidioides*.
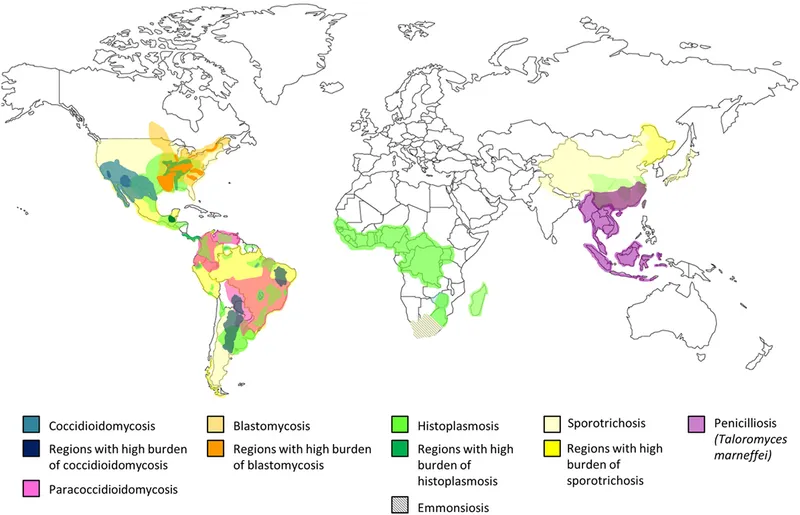
- *Coccidioides immitis* is a **dimorphic fungus** endemic to the **Southwestern United States** (including Arizona) and parts of Mexico and Central/South America, commonly causing **valley fever**.
*Paracoccidioides brasiliensis*
- This fungus is associated with **Paracoccidioidomycosis**, which is primarily found in **Latin America** (excluding the US Southwest).
- Microscopically, it presents as a **captain's wheel** appearance with multiple buds, which is not seen here.
*Candida albicans*
- *Candida albicans* is a **yeast** that typically causes **mucocutaneous infections** (e.g., thrush, vaginitis) and can cause systemic candidiasis in immunocompromised individuals.
- It forms **pseudohyphae and budding yeasts** microscopically, which are distinct from the spherules seen in the image.
*Blastomyces dermatitidis*
- **Blastomycosis** is endemic to the **Great Lakes region and Ohio/Mississippi River valleys** and usually presents with pneumonia and skin lesions.
- Microscopic examination reveals **broad-based budding yeasts**, which are different from the features shown in the image.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- *Aspergillus fumigatus* causes various conditions, including allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), aspergilloma, and invasive aspergillosis, particularly in **immunocompromised patients**.
- Microscopically, it is characterized by **acute-angle branching septate hyphae**, which is not consistent with the image provided.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator is studying growth patterns of various fungal pathogens. Incubation of an isolated fungus at 25°C shows branching hyphae with rosettes of conidia under light microscopy. After incubation at 37°C, microscopic examination of the same organism instead shows smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells. Infection with the investigated pathogen is most likely to cause which of the following conditions?
- A. Pityriasis versicolor
- B. Candidiasis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Sporotrichosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Coccidioidomycosis
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Sporotrichosis***
- The description of a fungal pathogen exhibiting **thermal dimorphism** (different forms at 25°C and 37°C) is characteristic of **Sporothrix schenckii**.
- At 25°C, it typically grows as **mold with branching hyphae and conidia in rosettes**, and at 37°C, it grows as **yeast-like cells (cigar-shaped bodies in tissue)**, which can appear rounded and elongated.
*Pityriasis versicolor*
- Caused by **Malassezia globosa**, which is a **lipophilic yeast** and does not exhibit thermal dimorphism described here.
- Characterized by **hypo- or hyperpigmented skin patches**, not deep tissue infection with dimorphic growth.
*Candidiasis*
- Caused by **Candida species**, which are **opportunistic yeasts** that can form pseudohyphae and true hyphae but do not display the specific dimorphism with rosettes of conidia at 25°C.
- Infections range from superficial mucocutaneous to systemic, but the fungal morphology described does not fit.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Caused by **Cryptococcus neoformans** or **Cryptococcus gattii**, which are **encapsulated yeasts** and do not exhibit dimorphism (mold at 25°C, yeast at 37°C).
- Primarily causes **meningoencephalitis** or pulmonary disease, and is identified by its capsule and yeast form.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- Caused by **Coccidioides immitis** or **Coccidioides posadasii**, which are **thermally dimorphic fungi**, but their morphology differs from the description.
- At 25°C, they grow as molds with **arthroconidia**, and at 37°C, they form **spherules containing endospores** in tissue, not smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 5: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, cough, and chest pain. Physical examination shows diffuse inspiratory crackles over the left lung field. An x-ray of the chest shows hilar lymphadenopathy and well-defined nodules with central calcifications. Urine studies show the presence of a polysaccharide antigen. A biopsy specimen of the lung shows cells with basophilic, crescent-shaped nuclei and pericellular halos located within macrophages. This patient's history is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Visit to Arizona desert
- B. Recent trip to Brazil
- C. Previous mycobacterial infection
- D. Exposure to bat droppings (Correct Answer)
- E. Treatment with inhaled glucocorticoids
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Exposure to bat droppings***
- The clinical presentation, including fever, cough, chest pain, **hilar lymphadenopathy**, **nodules with central calcifications**, and **intracellular encapsulated yeasts** in macrophages, is classic for **histoplasmosis**.
- **Histoplasma capsulatum** is endemic to the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and is transmitted through inhalation of spores from soil contaminated with **bat or bird droppings**.
*Visit to Arizona desert*
- Exposure in the **Arizona desert** is associated with **coccidioidomycosis** (Valley Fever), which presents with similar pulmonary symptoms but is caused by Coccidioides immitis/posadasii, characterized by **spherules** containing endospores.
- While it can cause hilar lymphadenopathy and nodules, the characteristic intracellular budding yeasts within macrophages and the polysaccharide antigen in urine point away from coccidioidomycosis.
*Recent trip to Brazil*
- A trip to **Brazil** might suggest diseases like **Paracoccidioidomycosis**, which presents with chronic mucocutaneous or disseminated lesions, or various tropical infections, but is not typically characterized by the specific pulmonary and microscopic findings described here.
- The histopathological findings of **intracellular yeasts with pericellular halos** (consistent with Histoplasma) would not be the primary finding for paracoccidioidomycosis, which generally shows characteristic **"pilot wheel"** or multiple budding yeasts.
*Previous mycobacterial infection*
- A previous **mycobacterial infection** would lead to tuberculosis, characterized by **acid-fast bacilli** and granulomas with **caseating necrosis**, which is different from the described intracellular yeasts and polysaccharide antigen.
- While tuberculosis can cause hilar lymphadenopathy and pulmonary nodules, the given microscopic description of cells with basophilic nuclei and pericellular halos within macrophages does not fit Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
*Treatment with inhaled glucocorticoids*
- Inhaled glucocorticoids are used to treat conditions like asthma or COPD and, while prolonged use can rarely predispose to **opportunistic fungal infections** (e.g., aspergillosis, candidiasis), they are not a cause of this specific clinical presentation or the microbiological findings of histoplasmosis.
- The use of inhaled steroids would not explain the geographic exposure, hilar lymphadenopathy, or the specific appearance of the fungal elements within macrophages described.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 6: A 40-year-old farmer from Ohio seeks evaluation at a clinic with complaints of a chronic cough, fevers, and anorexia of several months duration. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy with hepatosplenomegaly. A chest radiograph reveals local infiltrates and patchy opacities involving all lung fields. Fine needle aspiration of an enlarged lymph node shows the presence of intracellular yeast. A fungal culture shows the presence of smooth, thin-walled microconidia and tuberculate macroconidia. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Blastomycosis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Histoplasmosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Sporotrichosis
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Histoplasmosis***
- **Histoplasmosis** is characterized by the presence of **intracellular yeast** in tissue samples and **tuberculate macroconidia** in fungal cultures, which are key diagnostic findings in this case.
- The patient's presentation with chronic cough, fevers, anorexia, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and lung infiltrates, along with geographic exposure in **Ohio** (part of the Ohio River Valley endemic area), is highly consistent with disseminated histoplasmosis.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- While coccidioidomycosis can cause lung infiltrates, it is typically endemic to the **southwestern United States** and Mexico, not Ohio.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules** containing endospores, not intracellular yeast with tuberculate macroconidia.
*Blastomycosis*
- Blastomycosis is also endemic to the Ohio River Valley, but it is characterized by **broad-based budding yeast** in tissue, and its cultures typically do not show tuberculate macroconidia.
- While it causes pulmonary and disseminated disease, the specific microscopic and culture findings differentiate it from histoplasmosis.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Cryptococcosis primarily affects immunocompromised individuals and is characterized by encapsulated yeast, which would be visible with India ink stain.
- It typically presents as **meningitis** or pneumonia, and its culture morphology does not include tuberculate macroconidia.
*Sporotrichosis*
- Sporotrichosis is commonly associated with **cutaneous lesions** following traumatic inoculation of spores from soil or vegetation, and it rarely causes disseminated disease with extensive systemic symptoms like those described.
- The yeast forms in tissue are typically smaller and cigar-shaped, and the culture morphology differs significantly from what is described.
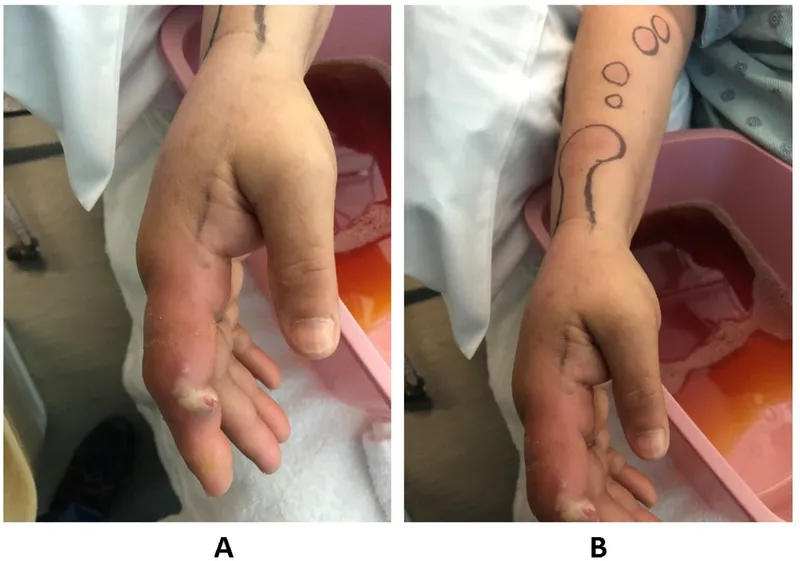
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 7: A 54-year-old gardener with diabetes mellitus from the Northeast Jilin Province in China acquired a small scratch from a thorn while working in his flower garden. After 3 weeks, he noticed a small pink, painless bump at the site of a scratch. He was not concerned by the bump; however, additional linearly-distributed bumps that resembled boils began to appear 1 week later that were quite painful. When the changes took on the appearance of open sores that drained clear fluid without any evidence of healing (as shown on the image), he finally visited his physician. The physician referred to the gardener for a skin biopsy to confirm his working diagnosis and to start treatment as soon as possible. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Cat scratch disease
- B. Leishmaniasis
- C. Sporotrichosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Paracoccidioidomycosis
- E. Blastomycosis
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Sporotrichosis***
- The patient's history of a **thorn scratch** in a garden, followed by a **painless pink bump** that progressed to **linearly-distributed painful nodules** resembling boils and eventually **non-healing ulcers** with clear fluid drainage, is highly characteristic of **sporotrichosis** (also known as "rose gardener's disease"). This pattern is called **lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis**.
- **Sporotrichosis** is caused by the fungus *Sporothrix schenckii*, which is commonly found in soil and on plants, explaining the gardener's exposure.
*Cat scratch disease*
- This disease is caused by *Bartonella henselae* and is typically transmitted by the scratch or bite of a cat, not a thorn.
- It usually presents with a papule or pustule at the inoculum site followed by **lymphadenopathy** in the regional lymph nodes, which is distinct from the linear spread observed here.
*Leishmaniasis*
- Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease transmitted by the bite of infected **sandflies**.
- While it can cause skin lesions ranging from papules to ulcers, the mode of transmission and the characteristic linear spread of nodules following a thorn injury do not fit this diagnosis.
*Paracoccidioidomycosis*
- This is a systemic fungal infection endemic to Central and South America, not typically seen in China's Jillin Province.
- It primarily affects the lungs, skin, and mucous membranes, with skin lesions often appearing as chronic, progressive ulcers but without the specific linear nodular pattern described.
*Blastomycosis*
- **Blastomycosis** is a fungal infection typically acquired by inhaling spores, primarily affecting the lungs, but it can disseminate to the skin, bones, and other organs.
- Cutaneous lesions are usually sharply demarcated, crusted plaques or verrucous lesions, but they do not typically present with the linear, nodular, and ulcerative progression seen in this case.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 8: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his host parents for evaluation of a progressively pruritic rash over his shoulders and buttocks for the past 6 months. He recently came to the United States from Nigeria to attend a year of high school. He reports that it has been increasingly difficult for him to read the whiteboard during classes. Physical examination shows symmetrically distributed papules 4–8 mm in diameter, excoriation marks, and patchy hyperpigmentation over his shoulders, waist, and buttocks. There is nontender inguinal lymphadenopathy and several firm, nontender subcutaneous nodules along the right iliac crest. Six skin snip biopsies are taken from the pelvic girdle, buttocks, and thigh, and are then incubated in saline. After 24 hours, microscopic examination shows motile microfilariae. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Cysticercosis
- B. Onchocerciasis (Correct Answer)
- C. Lymphatic filariasis
- D. Cutaneous larva migrans
- E. Trichuriasis
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Onchocerciasis***
- The presentation of **pruritic rash with papules**, **subcutaneous nodules** (onchocercomas), and **visual difficulties** (river blindness) in an individual from an endemic area (Nigeria) is classic for **onchocerciasis**.
- The presence of **motile microfilariae in skin snips** after saline incubation is a diagnostic hallmark of this condition, caused by *Onchocerca volvulus*.
*Cysticercosis*
- This condition is caused by the larval stage of *Taenia solium* and typically presents with **calcified lesions** in the muscle and brain (neurocysticercosis), which can lead to seizures.
- It does not typically cause the generalized pruritic rash, subcutaneous nodules, or ocular symptoms described, nor would **motile microfilariae** be found in skin snips.
*Lymphatic filariasis*
- Caused by *Wuchereria bancrofti* or *Brugia malayi*, this disease is characterized by **lymphedema** and **hydrocele**, eventually leading to **elephantiasis**.
- While it involves filarial worms and can cause lymphadenopathy, it does not typically manifest with the described rash, vision problems, or **subcutaneous nodules** (onchocercomas).
*Cutaneous larva migrans*
- This condition, caused by hookworm larvae (e.g., *Ancylostoma braziliense*), presents as a **serpiginous, intensely pruritic eruption** where the larvae migrate under the skin.
- It does not cause subcutaneous nodules, generalized papular rash, or ocular involvement, and skin snips would not show **microfilariae**.
*Trichuriasis*
- Caused by the **whipworm** (*Trichuris trichiura*), this is an intestinal nematode infection that can lead to **abdominal pain**, **diarrhea**, **rectal prolapse**, and **anemia**.
- It does not present with skin lesions, subcutaneous nodules, or visual impairment, and diagnosis is typically made by finding **ova in stool samples**, not microfilariae in skin snips.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 9: A 30-year-old woman who is 24-weeks pregnant presents to the emergency department with fever, painful urination, and headache. The patient's blood pressure is 111/67 mm Hg, the pulse is 95/min, the respiratory rate is 16/min, and the temperature is 38.3°C (101.1°F). Physical examination reveals bilateral tender inguinal lymphadenopathy and painful genital lesions. On closer inspection, the patient’s genital lesions contain clear fluid and measure 5–6 mm in diameter. What is the appropriate description of these lesions?
- A. Pustule
- B. Ulcer
- C. Papule
- D. Bulla
- E. Vesicle (Correct Answer)
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Vesicle***
- A **vesicle** is defined as a **circumscribed, elevated lesion** (macule/papule) containing **clear fluid** and measuring less than 1 cm in diameter.
- The patient's lesions, which are 5-6 mm in diameter and contain clear fluid, perfectly fit the description of vesicles, characteristic of **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** infection.
*Pustule*
- A **pustule** is a small, elevated lesion similar to a vesicle but filled with **pus**, not clear fluid.
- Examples include acne or folliculitis, which are typically opaque and yellowish, unlike the described lesions.
*Ulcer*
- An **ulcer** is a defect or excavation of the skin past the **epidermis**, resulting in the loss of tissue.
- The patient's lesions are described as fluid-filled and elevated, not as an open wound with tissue loss.
*Papule*
- A **papule** is a **solid, elevated lesion** measuring less than 1 cm in diameter.
- While elevated and small, a papule does **not contain fluid**, which is a key characteristic of the described lesions.
*Bulla*
- A **bulla** is a **fluid-filled lesion** that is **larger than 1 cm** in diameter.
- The lesions described are 5-6 mm, making them smaller than the definition of a bulla.
Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG Question 10: A 29-year-old internal medicine resident presents to the emergency department with complaints of fevers, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and skin rash for 2 days. He feels fatigued and has lost his appetite. On further questioning, he says that he returned from his missionary trip to Brazil last week. He is excited as he talks about his trip. Besides a worthy clinical experience, he also enjoyed local outdoor activities, like swimming and rafting. His past medical history is insignificant. The blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, the pulse is 100/min, and the temperature is 38.3°C (100.9°F). On examination, there is a rash on the legs. The rest of the examination is normal. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient’s condition?
- A. Schistosoma mansoni (Correct Answer)
- B. Schistosoma haematobium
- C. Vibrio cholerae
- D. Onchocerca volvulus
- E. Schistosoma japonicum
Environmental sources and prevention Explanation: ***Schistosoma mansoni***
- The patient's symptoms (fevers, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, fatigue) after swimming and rafting in Brazil are classic for **acute schistosomiasis (Katayama fever)**, and *Schistosoma mansoni* is endemic to South America, including Brazil, affecting the **gastrointestinal tract**.
- The rash on the legs is consistent with the entry points of **cercariae** through the skin, and the systemic symptoms develop as the adult worms mature and lay eggs.
*Schistosoma haematobium*
- This species primarily causes **urinary schistosomiasis**, with symptoms like **hematuria**, dysuria, and bladder wall calcification.
- It is prevalent in Africa and the Middle East, not typically associated with Brazil.
*Vibrio cholerae*
- *Vibrio cholerae* causes severe, watery **diarrhea** (rice-water stools) and rapid **dehydration**, usually without a prominent rash or prolonged systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever as the primary presentation.
- While diarrhea is present, the array of other symptoms and the exposure history do not align with cholera.
*Onchocerca volvulus*
- This parasite causes **onchocerciasis (river blindness)**, transmitted by blackflies, and primarily manifests as **dermatitis**, subcutaneous nodules, and significant eye disease leading to blindness.
- It does not typically cause acute febrile illness with prominent gastrointestinal symptoms like those described.
*Schistosoma japonicum*
- *Schistosoma japonicum* is found in East Asia (e.g., China, Philippines), not South America, and primarily affects the **gastrointestinal tract** and liver, similar to *S. mansoni*.
- The geographical exposure to Brazil makes *S. mansoni* the most likely cause, despite similar clinical features to *S. japonicum*.
More Environmental sources and prevention US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.