Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Dimorphic fungi characteristics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
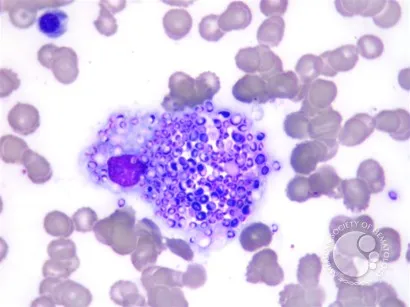
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 1: A 44-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of productive cough, fever, and lethargy. He also has several skin lesions over his body. His symptoms began 3 weeks after he returned from a camping trip in Kentucky. Three years ago, he underwent kidney transplantation for polycystic kidney disease. Current medications include sirolimus and prednisone. His temperature is 38°C (100.4°F). Diffuse crackles are heard over the lung fields. There are 4 white, verrucous skin patches over his chest and upper limbs. A photomicrograph of a skin biopsy specimen from one of the lesions is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Mucormycosis
- C. Blastomycosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Cryptococcosis
- E. Histoplasmosis
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Blastomycosis***
- The patient's history of **camping in Kentucky**, along with the presence of **pulmonary symptoms** (productive cough, fever, crackles) and **verrucous skin lesions**, are classic for blastomycosis.
- The photomicrograph showing **broad-based budding yeast** is pathognomonic for *Blastomyces dermatitidis*.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- This is typical in the **Southwestern United States and parts of Mexico**, not Kentucky.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules containing endospores**, which are not seen in the provided image.
*Mucormycosis*
- This infection is characterized by **irregular, broad, non-septate hyphae** with **wide-angle branching**, often invading blood vessels, leading to tissue necrosis.
- It primarily affects immunocompromised patients but typically presents as **rhinocerebral** or **pulmonary infection**, less commonly with verrucous skin lesions of this type.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Primarily affects the **lungs and central nervous system**, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Microscopy typically shows **encapsulated yeast** cells, which would be visible with India ink stain, and are not represented by the broad-based budding in the image.
*Histoplasmosis*
- Prevalent in the **Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys**, which includes Kentucky, and is often associated with **bird or bat droppings**.
- On microscopy, it presents as **small intracellular yeast** within macrophages, which is morphologically distinct from the large, broad-based budding yeast shown.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 2: An 18-year-old man presents to the office, complaining of an itchy patch on his torso that appeared one week ago. The patient is on the college wrestling team and is concerned he will not be able to compete if it gets infected. He has no significant medical history, and his vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, there is an erythematous, scaly plaque with central clearing at approximately the level of rib 6 on the left side of his torso. What diagnostic test would be most appropriate at this time?
- A. Eaton agar
- B. Wood’s lamp examination
- C. Thayer-Martin agar
- D. Sabouraud agar
- E. KOH preparation (Correct Answer)
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***KOH preparation***
- A **KOH (potassium hydroxide) preparation** is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test for suspected **dermatophytosis** (ringworm), a common fungal infection often seen in wrestlers due to skin-to-skin contact.
- The KOH dissolves keratin and cellular debris, allowing for easier visualization of **fungal hyphae** and **spores** under a microscope, confirming the diagnosis.
*Eaton agar*
- **Eaton agar** is a specialized culture medium used for isolating and growing **Mycoplasma pneumoniae**, a bacterium that causes respiratory infections.
- It is not used for diagnosing fungal skin infections.
*Wood’s lamp examination*
- A **Wood's lamp examination** uses ultraviolet light to detect certain dermatophytes (like *Microsporum canis*), which may fluoresce
- However, many common dermatophytes, such as *Trichophyton rubrum*, do not fluoresce, making KOH preparation a more universally effective initial diagnostic tool.
*Thayer-Martin agar*
- **Thayer-Martin agar** is a selective culture medium primarily used for isolating and growing **Neisseria gonorrhoeae** and **Neisseria meningitidis**, bacteria responsible for sexually transmitted infections and meningitis, respectively.
- It is not indicated for diagnosing fungal skin infections.
*Sabouraud agar*
- **Sabouraud agar** is a recognized culture medium specifically designed for the isolation and identification of **fungi**, including dermatophytes.
- While useful for confirmation and species identification, a **KOH preparation** is a quicker and more immediate diagnostic test to confirm the presence of fungal elements in the clinic.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is studying growth patterns of various fungal pathogens. Incubation of an isolated fungus at 25°C shows branching hyphae with rosettes of conidia under light microscopy. After incubation at 37°C, microscopic examination of the same organism instead shows smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells. Infection with the investigated pathogen is most likely to cause which of the following conditions?
- A. Pityriasis versicolor
- B. Candidiasis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Sporotrichosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Coccidioidomycosis
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Sporotrichosis***
- The description of a fungal pathogen exhibiting **thermal dimorphism** (different forms at 25°C and 37°C) is characteristic of **Sporothrix schenckii**.
- At 25°C, it typically grows as **mold with branching hyphae and conidia in rosettes**, and at 37°C, it grows as **yeast-like cells (cigar-shaped bodies in tissue)**, which can appear rounded and elongated.
*Pityriasis versicolor*
- Caused by **Malassezia globosa**, which is a **lipophilic yeast** and does not exhibit thermal dimorphism described here.
- Characterized by **hypo- or hyperpigmented skin patches**, not deep tissue infection with dimorphic growth.
*Candidiasis*
- Caused by **Candida species**, which are **opportunistic yeasts** that can form pseudohyphae and true hyphae but do not display the specific dimorphism with rosettes of conidia at 25°C.
- Infections range from superficial mucocutaneous to systemic, but the fungal morphology described does not fit.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Caused by **Cryptococcus neoformans** or **Cryptococcus gattii**, which are **encapsulated yeasts** and do not exhibit dimorphism (mold at 25°C, yeast at 37°C).
- Primarily causes **meningoencephalitis** or pulmonary disease, and is identified by its capsule and yeast form.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- Caused by **Coccidioides immitis** or **Coccidioides posadasii**, which are **thermally dimorphic fungi**, but their morphology differs from the description.
- At 25°C, they grow as molds with **arthroconidia**, and at 37°C, they form **spherules containing endospores** in tissue, not smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator is studying the growth of an organism in different media. The organism is inoculated on a petri dish that contains heated sheep blood, vancomycin, nystatin, trimethoprim, and colistin. The resulting growth medium is incubated at 37°C. Numerous small, white colonies are seen after incubation for 48 hours. This organism is most likely to cause which of the following conditions?
- A. Pontiac fever
- B. Pseudomembranous colitis
- C. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
- D. Oral thrush
- E. Gonorrhea (Correct Answer)
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Gonorrhea***
- The growth medium described is **Thayer-Martin agar**, a selective medium containing **heated sheep blood** (supplies NAD+), **vancomycin** (inhibits Gram-positives), **colistin** (inhibits Gram-negatives), **nystatin** (inhibits fungi), and **trimethoprim** (inhibits Proteus). This medium is specifically designed for the isolation of *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* from polymicrobial samples.
- *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* typically grows as **small, translucent-to-white colonies** on selective media like Thayer-Martin agar, and incubation at 37°C in CO2 (not explicitly mentioned but often required) for 24-48 hours yields visible growth, causing **gonorrhea**.
*Pontiac fever*
- Pontiac fever is a mild, self-limiting form of **legionellosis**, caused by *Legionella pneumophila*.
- *Legionella* requires a specialized medium such as **buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar** for growth, not Thayer-Martin agar.
*Pseudomembranous colitis*
- This condition is caused by **toxin-producing *Clostridioides difficile***, often after antibiotic use.
- *C. difficile* is an obligate anaerobe and requires **anaerobic conditions** and specific selective media (e.g., CCFA agar) for isolation, not Thayer-Martin agar under aerobic conditions.
*Hemolytic uremic syndrome*
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is often caused by **Shiga toxin-producing *Escherichia coli* (STEC)**, particularly O157:H7.
- STEC can be isolated on media like **sorbitol MacConkey agar (SMAC)**, where O157:H7 appears as non-sorbitol fermenting colonies, distinct from the growth seen on Thayer-Martin.
*Oral thrush*
- Oral thrush is caused by *Candida albicans*, a yeast.
- *Candida* would be inhibited by **nystatin** in the Thayer-Martin medium, which is an antifungal agent.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 5: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, cough, and chest pain. Physical examination shows diffuse inspiratory crackles over the left lung field. An x-ray of the chest shows hilar lymphadenopathy and well-defined nodules with central calcifications. Urine studies show the presence of a polysaccharide antigen. A biopsy specimen of the lung shows cells with basophilic, crescent-shaped nuclei and pericellular halos located within macrophages. This patient's history is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Visit to Arizona desert
- B. Recent trip to Brazil
- C. Previous mycobacterial infection
- D. Exposure to bat droppings (Correct Answer)
- E. Treatment with inhaled glucocorticoids
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Exposure to bat droppings***
- The clinical presentation, including fever, cough, chest pain, **hilar lymphadenopathy**, **nodules with central calcifications**, and **intracellular encapsulated yeasts** in macrophages, is classic for **histoplasmosis**.
- **Histoplasma capsulatum** is endemic to the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and is transmitted through inhalation of spores from soil contaminated with **bat or bird droppings**.
*Visit to Arizona desert*
- Exposure in the **Arizona desert** is associated with **coccidioidomycosis** (Valley Fever), which presents with similar pulmonary symptoms but is caused by Coccidioides immitis/posadasii, characterized by **spherules** containing endospores.
- While it can cause hilar lymphadenopathy and nodules, the characteristic intracellular budding yeasts within macrophages and the polysaccharide antigen in urine point away from coccidioidomycosis.
*Recent trip to Brazil*
- A trip to **Brazil** might suggest diseases like **Paracoccidioidomycosis**, which presents with chronic mucocutaneous or disseminated lesions, or various tropical infections, but is not typically characterized by the specific pulmonary and microscopic findings described here.
- The histopathological findings of **intracellular yeasts with pericellular halos** (consistent with Histoplasma) would not be the primary finding for paracoccidioidomycosis, which generally shows characteristic **"pilot wheel"** or multiple budding yeasts.
*Previous mycobacterial infection*
- A previous **mycobacterial infection** would lead to tuberculosis, characterized by **acid-fast bacilli** and granulomas with **caseating necrosis**, which is different from the described intracellular yeasts and polysaccharide antigen.
- While tuberculosis can cause hilar lymphadenopathy and pulmonary nodules, the given microscopic description of cells with basophilic nuclei and pericellular halos within macrophages does not fit Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
*Treatment with inhaled glucocorticoids*
- Inhaled glucocorticoids are used to treat conditions like asthma or COPD and, while prolonged use can rarely predispose to **opportunistic fungal infections** (e.g., aspergillosis, candidiasis), they are not a cause of this specific clinical presentation or the microbiological findings of histoplasmosis.
- The use of inhaled steroids would not explain the geographic exposure, hilar lymphadenopathy, or the specific appearance of the fungal elements within macrophages described.
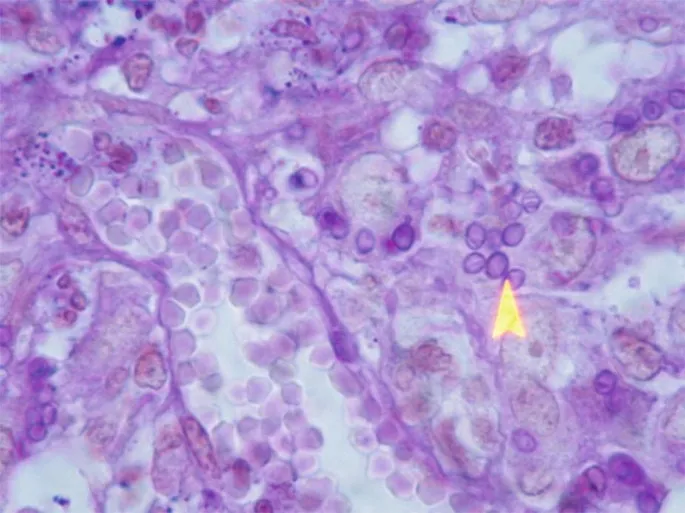
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of fever, fatigue, dry cough, headache, and myalgia over the past week. Two days ago, he developed several painful oral lesions and difficulty swallowing. He underwent kidney transplantation 3 years ago. His temperature is 38.2°C (100.7°F). Physical examination shows bilateral rales, hepatosplenomegaly, and multiple 1–2 cm ulcerative lesions with raised borders in the oral mucosa. A photomicrograph of a liver biopsy specimen is shown. Which of the following is the most likely causal pathogen?
- A. Aspergillus fumigatus
- B. Blastomyces dermatitidis
- C. Coccidioides immitis
- D. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
- E. Histoplasma capsulatum (Correct Answer)
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Histoplasma capsulatum***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, fatigue, dry cough, headache, myalgia, respiratory symptoms (bilateral rales), hepatosplenomegaly**, and **painful oral ulcerative lesions** in an **immunocompromised individual (kidney transplant recipient)** is highly suggestive of **disseminated histoplasmosis**.
- The photomicrograph shows numerous **small, intracellular yeast forms within macrophages**, which is the pathognomonic finding for *Histoplasma capsulatum*.
- *Histoplasma* is endemic to the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and commonly causes disseminated disease in immunocompromised patients.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- *Aspergillus* typically causes invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients, presenting with **fever and cough**, but generally does not cause **oral ulcerative lesions** or **hepatosplenomegaly** in this disseminated pattern.
- Microscopically, *Aspergillus* appears as **septate hyphae with acute-angle branching (45°)**, which is inconsistent with the intracellular yeasts in the image provided.
*Blastomyces dermatitidis*
- *Blastomyces* can cause pulmonary disease and disseminate to the **skin and bones**, but **oral lesions** and **hepatosplenomegaly** are less common presenting features.
- The yeast forms of *Blastomyces* are characteristically **large (8-15 μm), broad-based budding yeasts**, which are much larger than the small organisms seen in the photomicrograph.
*Coccidioides immitis*
- *Coccidioidomycosis* is endemic to the southwestern U.S. and can cause pulmonary symptoms, but disseminated disease typically involves the **skin, bones, joints, and meninges**, with **oral lesions and hepatosplenomegaly** being less frequent manifestations.
- Microscopically, *Coccidioides* is characterized by **large spherules (20-80 μm) containing endospores**, which are not seen in the provided image showing small intracellular organisms.
*Paracoccidioides brasiliensis*
- This fungus is endemic to Central and South America and can cause oral lesions that are typically **mulberry-like** or **verrucous** in appearance, with disseminated disease often affecting the lungs, lymph nodes, and mucosal surfaces.
- Microscopic examination reveals **multiple budding yeasts** with a characteristic **"ship's wheel" or "pilot's wheel" appearance**, which differs significantly from the small intracellular yeasts within macrophages shown in the image.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 7: A 16-year-old boy presents to his pediatrician because he has noticed white plaques forming on his tongue over the last 5 days. He recently returned from a boy scout trip where he traveled across the country and hiked through the woods. His past medical history is significant for asthma for which he uses an inhaler as needed. He says that during the trip he felt short of breath several times and had to use the inhaler. He also says that several of his friends appeared to get sick on the same trip and were coughing a lot. He has not experienced any other symptoms since returning from the trip. On presentation, he is found to have white plaques on the tongue that can be scraped off. Which of the following is a characteristic of the most likely cause of this patient's disease?
- A. Acute angle branching
- B. Spherules containing endospores
- C. Germ tube formation (Correct Answer)
- D. Latex agglutination
- E. Broad-based budding
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Germ tube formation***
- This patient presents with **oral thrush (candidiasis)**, characterized by **white plaques on the tongue that can be scraped off**. His history of **asthma and inhaler use** (likely corticosteroids) is a risk factor.
- **Germ tube formation** is a rapid diagnostic test for *Candida albicans*, the most common cause of oral thrush, where yeast cells produce filament-like extensions when incubated in serum.
*Acute angle branching*
- This is characteristic of **Aspergillus species**, which typically cause invasive mold infections in immunocompromised individuals, or allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, not oral thrush.
- *Aspergillus* infections are not typically associated with easily scraped-off oral plaques.
*Spherules containing endospores*
- **Spherules containing endospores** are the characteristic tissue form of **Coccidioides immitis/posadasii**, a dimorphic fungus causing coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever), typically presenting as a pulmonary infection.
- This feature is not associated with *Candida albicans* or oral thrush, though the patient's travel history could suggest dimorphic fungal exposure.
*Latex agglutination*
- **Latex agglutination** is a serological test primarily used for detecting **cryptococcal capsular antigen** in cerebrospinal fluid or serum, indicating cryptococcosis.
- It is not a characteristic feature or primary diagnostic method for *Candida* infections like oral thrush.
*Broad-based budding*
- **Broad-based budding** is a microscopic characteristic of **Blastomyces dermatitidis**, a dimorphic fungus causing blastomycosis, typically a pulmonary infection that can disseminate to skin, bone, or other organs.
- This feature is not associated with *Candida albicans* or oral thrush.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 8: A 40-year-old farmer from Ohio seeks evaluation at a clinic with complaints of a chronic cough, fevers, and anorexia of several months duration. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy with hepatosplenomegaly. A chest radiograph reveals local infiltrates and patchy opacities involving all lung fields. Fine needle aspiration of an enlarged lymph node shows the presence of intracellular yeast. A fungal culture shows the presence of smooth, thin-walled microconidia and tuberculate macroconidia. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Blastomycosis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Histoplasmosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Sporotrichosis
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Histoplasmosis***
- **Histoplasmosis** is characterized by the presence of **intracellular yeast** in tissue samples and **tuberculate macroconidia** in fungal cultures, which are key diagnostic findings in this case.
- The patient's presentation with chronic cough, fevers, anorexia, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and lung infiltrates, along with geographic exposure in **Ohio** (part of the Ohio River Valley endemic area), is highly consistent with disseminated histoplasmosis.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- While coccidioidomycosis can cause lung infiltrates, it is typically endemic to the **southwestern United States** and Mexico, not Ohio.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules** containing endospores, not intracellular yeast with tuberculate macroconidia.
*Blastomycosis*
- Blastomycosis is also endemic to the Ohio River Valley, but it is characterized by **broad-based budding yeast** in tissue, and its cultures typically do not show tuberculate macroconidia.
- While it causes pulmonary and disseminated disease, the specific microscopic and culture findings differentiate it from histoplasmosis.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Cryptococcosis primarily affects immunocompromised individuals and is characterized by encapsulated yeast, which would be visible with India ink stain.
- It typically presents as **meningitis** or pneumonia, and its culture morphology does not include tuberculate macroconidia.
*Sporotrichosis*
- Sporotrichosis is commonly associated with **cutaneous lesions** following traumatic inoculation of spores from soil or vegetation, and it rarely causes disseminated disease with extensive systemic symptoms like those described.
- The yeast forms in tissue are typically smaller and cigar-shaped, and the culture morphology differs significantly from what is described.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 9: A young woman from the Ohio River Valley in the United States currently on corticosteroid therapy for ulcerative colitis presented to a clinic complaining of fever, sweat, headache, nonproductive cough, malaise, and general weakness. A chest radiograph revealed patchy pneumonia in the lower lung fields, together with enlarged mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. Skin changes suggestive of erythema nodosum (i.e. an acute erythematous eruption) were noted. Because the patient was from a region endemic for fungal infections associated with her symptoms and the patient was in close contact with a person presenting similar symptoms, the attending physician suspected that systemic fungal infection might be responsible for this woman’s illness. Which of the following laboratory tests can the physician use to ensure early detection of the disease, and also effectively monitor the treatment response?
- A. Skin tests
- B. Fungal staining
- C. Antigen detection (Correct Answer)
- D. Culture method
- E. Antibody testing
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: ***Antigen detection***
- **Antigen detection assays** (e.g., *Histoplasma galactomannan antigen*) are highly sensitive for **disseminated histoplasmosis**, especially in immunosuppressed patients like this one on corticosteroids.
- They provide **early diagnosis** and are effective for **monitoring treatment response**, as antigen levels typically decrease with successful therapy.
*Skin tests*
- **Skin tests** (e.g., *histoplasmin skin test*) indicate **prior exposure** to the fungus and are not useful for diagnosing active, acute infection.
- A positive skin test does not differentiate between past exposure and current disease, making it unsuitable for early detection or monitoring.
*Fungal staining*
- **Fungal staining** of patient samples (e.g., sputum, biopsy) can reveal fungal elements but has **limited sensitivity** and may not identify the specific pathogen.
- It often requires **invasive procedures** to obtain suitable specimens and is not ideal for routine monitoring of treatment response due to variability.
*Culture method*
- **Fungal cultures** are a **definitive diagnostic method** but can take **several weeks** to yield results, which is too slow for early detection in an acutely ill patient.
- While useful for species identification and susceptibility testing, the **delayed turnaround time** makes it impractical for monitoring rapid treatment changes.
*Antibody testing*
- **Antibody tests** for fungal infections can be useful but may show **false negatives in immunocompromised patients** (like this patient on corticosteroids) due to a blunted immune response.
- Seroconversion or a significant rise in antibody titers can indicate infection, but antibodies may **persist long after resolution**, making them less reliable for monitoring acute treatment efficacy.
Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG Question 10: A 29-year-old woman comes to the military physician because of a 2-day history of fever, joint pain, dry cough, chest pain, and a painful red rash on her lower legs. Two weeks ago, she returned from military training in Southern California. She appears ill. Her temperature is 39°C (102.1°F). Physical examination shows diffuse inspiratory crackles over all lung fields and multiple tender erythematous nodules over the anterior aspect of both legs. A biopsy specimen of this patient's lungs is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Septate hyphae with acute-angle branching
- B. Spherules filled with endospores (Correct Answer)
- C. Broad-based budding yeast
- D. Encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding
- E. Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae
Dimorphic fungi characteristics Explanation: **Spherules filled with endospores**
- The patient's symptoms (fever, joint pain, dry cough, chest pain, erythema nodosum on legs) combined with her travel history to **Southern California** are highly suggestive of **Coccidioidomycosis** ("Valley Fever").
- A biopsy of affected lung tissue in coccidioidomycosis typically reveals **spherules** (thick-walled structures) containing numerous **endospores**, which are characteristic of the tissue phase of *Coccidioides immitis/posadasii*.
*Septate hyphae with acute-angle branching*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Aspergillus** species, which can cause opportunistic infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- While it can cause lung infections, the clinical presentation and geographic exposure do not point towards aspergillosis as the most likely diagnosis.
*Broad-based budding yeast*
- This describes the characteristic morphology of *Blastomyces dermatitidis*, the causative agent of **Blastomycosis**.
- **Blastomycosis** is typically found in the Great Lakes region, Ohio, Mississippi River valleys, and southeastern United States, not Southern California.
*Encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding*
- This describes **Cryptococcus neoformans**, which appears as an encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding in tissue.
- While it can cause pulmonary disease, the classic presentation (erythema nodosum, acute illness after Southern California exposure) is not consistent with **cryptococcosis**, which typically presents subacutely in immunocompromised patients.
*Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae*
- This morphology is characteristic of *Candida albicans*, which commonly causes mucocutaneous infections and can cause systemic candidiasis, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
- The clinical picture of a healthy young woman with exposure in Southern California does not fit with a typical **Candida** infection.
More Dimorphic fungi characteristics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.