Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
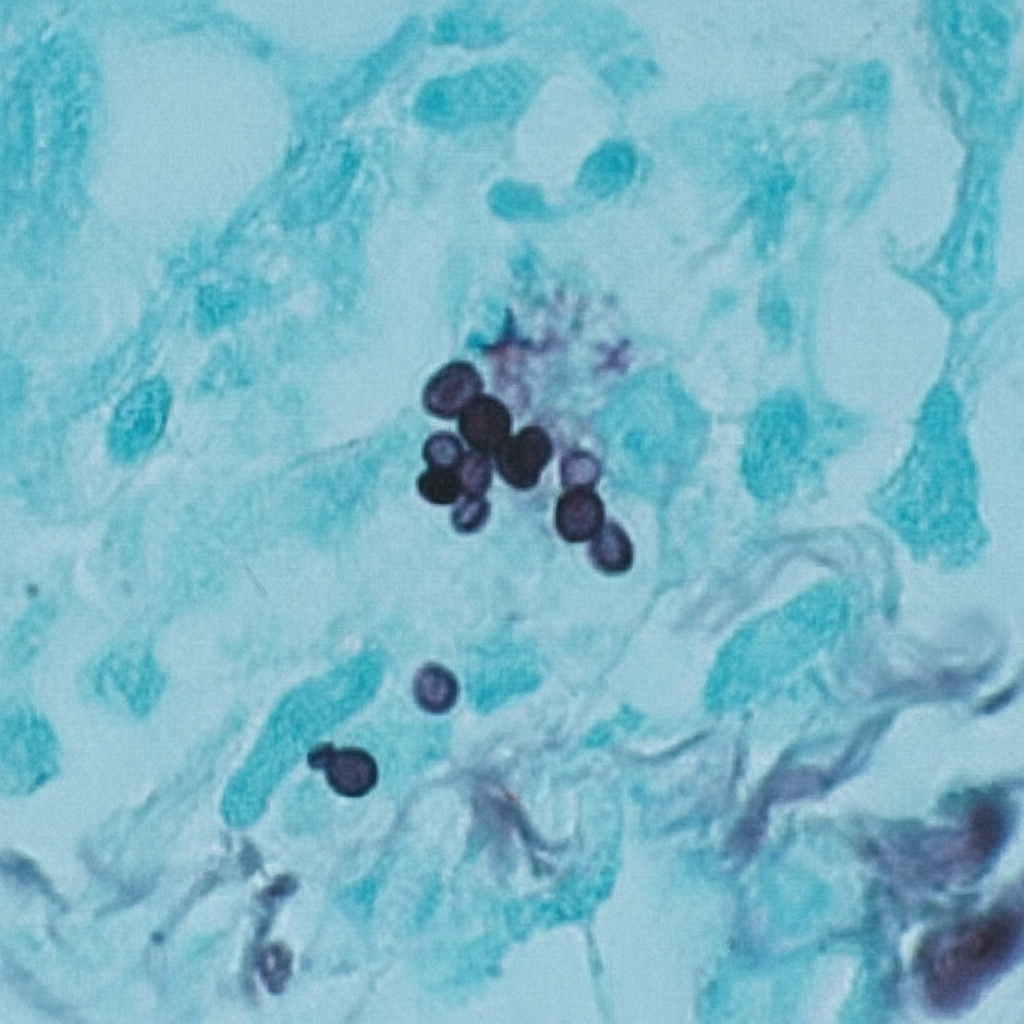
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 1: A 44-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of productive cough, fever, and lethargy. He also has several skin lesions over his body. His symptoms began 3 weeks after he returned from a camping trip in Kentucky. Three years ago, he underwent kidney transplantation for polycystic kidney disease. Current medications include sirolimus and prednisone. His temperature is 38°C (100.4°F). Diffuse crackles are heard over the lung fields. There are 4 white, verrucous skin patches over his chest and upper limbs. A photomicrograph of a skin biopsy specimen from one of the lesions is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Mucormycosis
- C. Blastomycosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Cryptococcosis
- E. Histoplasmosis
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Blastomycosis***
- The patient's history of **camping in Kentucky**, along with the presence of **pulmonary symptoms** (productive cough, fever, crackles) and **verrucous skin lesions**, are classic for blastomycosis.
- The photomicrograph showing **broad-based budding yeast** is pathognomonic for *Blastomyces dermatitidis*.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- This is typical in the **Southwestern United States and parts of Mexico**, not Kentucky.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules containing endospores**, which are not seen in the provided image.
*Mucormycosis*
- This infection is characterized by **irregular, broad, non-septate hyphae** with **wide-angle branching**, often invading blood vessels, leading to tissue necrosis.
- It primarily affects immunocompromised patients but typically presents as **rhinocerebral** or **pulmonary infection**, less commonly with verrucous skin lesions of this type.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Primarily affects the **lungs and central nervous system**, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Microscopy typically shows **encapsulated yeast** cells, which would be visible with India ink stain, and are not represented by the broad-based budding in the image.
*Histoplasmosis*
- Prevalent in the **Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys**, which includes Kentucky, and is often associated with **bird or bat droppings**.
- On microscopy, it presents as **small intracellular yeast** within macrophages, which is morphologically distinct from the large, broad-based budding yeast shown.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 2: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-day history of a productive cough, shortness of breath, and low-grade fever. He works as a farmer in southern Arizona. Physical examination shows multiple skin lesions with a dark blue center, pale intermediate zone, and red peripheral rim on the upper and lower extremities. There are diffuse crackles on the left side of the chest. An x-ray of the chest shows left basilar consolidation and left hilar lymphadenopathy. A photomicrograph of tissue obtained from a biopsy of the lung is shown. Which of the following is the most likely causal pathogen?
- A. Coccidioides immitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
- C. Candida albicans
- D. Blastomyces dermatitidis
- E. Aspergillus fumigatus
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Coccidioides immitis***
- The patient's presentation with **respiratory symptoms**, **skin lesions** (erythema multiforme-like), and **hilar lymphadenopathy** in a farmer from **southern Arizona** is highly characteristic of coccidioidomycosis. The image shows **spherules** containing **endospores**, which are diagnostic of *Coccidioides*.
- *Coccidioides immitis* is a **dimorphic fungus** endemic to the **Southwestern United States** (including Arizona) and parts of Mexico and Central/South America, commonly causing **valley fever**.
*Paracoccidioides brasiliensis*
- This fungus is associated with **Paracoccidioidomycosis**, which is primarily found in **Latin America** (excluding the US Southwest).
- Microscopically, it presents as a **captain's wheel** appearance with multiple buds, which is not seen here.
*Candida albicans*
- *Candida albicans* is a **yeast** that typically causes **mucocutaneous infections** (e.g., thrush, vaginitis) and can cause systemic candidiasis in immunocompromised individuals.
- It forms **pseudohyphae and budding yeasts** microscopically, which are distinct from the spherules seen in the image.
*Blastomyces dermatitidis*
- **Blastomycosis** is endemic to the **Great Lakes region and Ohio/Mississippi River valleys** and usually presents with pneumonia and skin lesions.
- Microscopic examination reveals **broad-based budding yeasts**, which are different from the features shown in the image.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- *Aspergillus fumigatus* causes various conditions, including allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), aspergilloma, and invasive aspergillosis, particularly in **immunocompromised patients**.
- Microscopically, it is characterized by **acute-angle branching septate hyphae**, which is not consistent with the image provided.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is studying growth patterns of various fungal pathogens. Incubation of an isolated fungus at 25°C shows branching hyphae with rosettes of conidia under light microscopy. After incubation at 37°C, microscopic examination of the same organism instead shows smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells. Infection with the investigated pathogen is most likely to cause which of the following conditions?
- A. Pityriasis versicolor
- B. Candidiasis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Sporotrichosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Coccidioidomycosis
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Sporotrichosis***
- The description of a fungal pathogen exhibiting **thermal dimorphism** (different forms at 25°C and 37°C) is characteristic of **Sporothrix schenckii**.
- At 25°C, it typically grows as **mold with branching hyphae and conidia in rosettes**, and at 37°C, it grows as **yeast-like cells (cigar-shaped bodies in tissue)**, which can appear rounded and elongated.
*Pityriasis versicolor*
- Caused by **Malassezia globosa**, which is a **lipophilic yeast** and does not exhibit thermal dimorphism described here.
- Characterized by **hypo- or hyperpigmented skin patches**, not deep tissue infection with dimorphic growth.
*Candidiasis*
- Caused by **Candida species**, which are **opportunistic yeasts** that can form pseudohyphae and true hyphae but do not display the specific dimorphism with rosettes of conidia at 25°C.
- Infections range from superficial mucocutaneous to systemic, but the fungal morphology described does not fit.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Caused by **Cryptococcus neoformans** or **Cryptococcus gattii**, which are **encapsulated yeasts** and do not exhibit dimorphism (mold at 25°C, yeast at 37°C).
- Primarily causes **meningoencephalitis** or pulmonary disease, and is identified by its capsule and yeast form.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- Caused by **Coccidioides immitis** or **Coccidioides posadasii**, which are **thermally dimorphic fungi**, but their morphology differs from the description.
- At 25°C, they grow as molds with **arthroconidia**, and at 37°C, they form **spherules containing endospores** in tissue, not smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 4: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, cough, and chest pain. Physical examination shows diffuse inspiratory crackles over the left lung field. An x-ray of the chest shows hilar lymphadenopathy and well-defined nodules with central calcifications. Urine studies show the presence of a polysaccharide antigen. A biopsy specimen of the lung shows cells with basophilic, crescent-shaped nuclei and pericellular halos located within macrophages. This patient's history is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Visit to Arizona desert
- B. Recent trip to Brazil
- C. Previous mycobacterial infection
- D. Exposure to bat droppings (Correct Answer)
- E. Treatment with inhaled glucocorticoids
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Exposure to bat droppings***
- The clinical presentation, including fever, cough, chest pain, **hilar lymphadenopathy**, **nodules with central calcifications**, and **intracellular encapsulated yeasts** in macrophages, is classic for **histoplasmosis**.
- **Histoplasma capsulatum** is endemic to the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and is transmitted through inhalation of spores from soil contaminated with **bat or bird droppings**.
*Visit to Arizona desert*
- Exposure in the **Arizona desert** is associated with **coccidioidomycosis** (Valley Fever), which presents with similar pulmonary symptoms but is caused by Coccidioides immitis/posadasii, characterized by **spherules** containing endospores.
- While it can cause hilar lymphadenopathy and nodules, the characteristic intracellular budding yeasts within macrophages and the polysaccharide antigen in urine point away from coccidioidomycosis.
*Recent trip to Brazil*
- A trip to **Brazil** might suggest diseases like **Paracoccidioidomycosis**, which presents with chronic mucocutaneous or disseminated lesions, or various tropical infections, but is not typically characterized by the specific pulmonary and microscopic findings described here.
- The histopathological findings of **intracellular yeasts with pericellular halos** (consistent with Histoplasma) would not be the primary finding for paracoccidioidomycosis, which generally shows characteristic **"pilot wheel"** or multiple budding yeasts.
*Previous mycobacterial infection*
- A previous **mycobacterial infection** would lead to tuberculosis, characterized by **acid-fast bacilli** and granulomas with **caseating necrosis**, which is different from the described intracellular yeasts and polysaccharide antigen.
- While tuberculosis can cause hilar lymphadenopathy and pulmonary nodules, the given microscopic description of cells with basophilic nuclei and pericellular halos within macrophages does not fit Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
*Treatment with inhaled glucocorticoids*
- Inhaled glucocorticoids are used to treat conditions like asthma or COPD and, while prolonged use can rarely predispose to **opportunistic fungal infections** (e.g., aspergillosis, candidiasis), they are not a cause of this specific clinical presentation or the microbiological findings of histoplasmosis.
- The use of inhaled steroids would not explain the geographic exposure, hilar lymphadenopathy, or the specific appearance of the fungal elements within macrophages described.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 5: A 43-year-old type 1 diabetic woman who is poorly compliant with her diabetes medications presented to the emergency department with hemorrhage from her nose. On exam, you observe the findings shown in figure A. What is the most likely explanation for these findings?
- A. Cryptococcal infection
- B. Sporotrichosis
- C. Gram negative bacterial infection
- D. Candida infection
- E. Rhizopus infection (Correct Answer)
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Rhizopus infection***
- The image likely depicts findings consistent with **mucormycosis**, an aggressive fungal infection caused by organisms like *Rhizopus*, characterized by **black necrotic eschars** and rapid tissue destruction.
- **Type 1 diabetes mellitus** with poor compliance (leading to **diabetic ketoacidosis**) is a major risk factor for mucormycosis due to impaired immune function and acidic environment.
*Cryptococcal infection*
- Primarily causes **meningitis** or **pulmonary disease**, especially in immunocompromised individuals, and less commonly presents as rhinocerebral mucormycosis-like lesions.
- Skin lesions can occur but are usually **papules**, **nodules**, or **ulcers**, not typically widespread necrotizing eschars of the nasal region.
*Sporothricosis*
- Typically presents as **subcutaneous nodules** that slowly enlarge and may ulcerate, often following trauma with contaminated plant material.
- It does not usually cause the rapid, aggressive, and necrotizing sinonasal infection seen in the context of uncontrolled diabetes.
*Gram negative bacterial infection*
- While gram-negative bacteria can cause severe infections, they typically present with **purulent discharge**, **cellulitis**, or **abscess formation**, rather than the characteristic black necrotic eschar of mucormycosis.
- Although immunosuppression increases risk, the specific clinical findings point away from a primary gram-negative bacterial infection.
*Candida infection*
- Commonly causes **oral thrush**, **esophagitis**, or **vaginitis**, or disseminated candidiasis in severely immunocompromised patients.
- While it can cause invasive sinusitis, it rarely produces the aggressive **necrotic eschar** seen in mucormycosis, and is generally less common in this specific presentation.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 6: A 54-year-old gardener with diabetes mellitus from the Northeast Jilin Province in China acquired a small scratch from a thorn while working in his flower garden. After 3 weeks, he noticed a small pink, painless bump at the site of a scratch. He was not concerned by the bump; however, additional linearly-distributed bumps that resembled boils began to appear 1 week later that were quite painful. When the changes took on the appearance of open sores that drained clear fluid without any evidence of healing (as shown on the image), he finally visited his physician. The physician referred to the gardener for a skin biopsy to confirm his working diagnosis and to start treatment as soon as possible. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Cat scratch disease
- B. Leishmaniasis
- C. Sporotrichosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Paracoccidioidomycosis
- E. Blastomycosis
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Sporotrichosis***
- The patient's history of a **thorn scratch** in a garden, followed by a **painless pink bump** that progressed to **linearly-distributed painful nodules** resembling boils and eventually **non-healing ulcers** with clear fluid drainage, is highly characteristic of **sporotrichosis** (also known as "rose gardener's disease"). This pattern is called **lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis**.
- **Sporotrichosis** is caused by the fungus *Sporothrix schenckii*, which is commonly found in soil and on plants, explaining the gardener's exposure.
*Cat scratch disease*
- This disease is caused by *Bartonella henselae* and is typically transmitted by the scratch or bite of a cat, not a thorn.
- It usually presents with a papule or pustule at the inoculum site followed by **lymphadenopathy** in the regional lymph nodes, which is distinct from the linear spread observed here.
*Leishmaniasis*
- Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease transmitted by the bite of infected **sandflies**.
- While it can cause skin lesions ranging from papules to ulcers, the mode of transmission and the characteristic linear spread of nodules following a thorn injury do not fit this diagnosis.
*Paracoccidioidomycosis*
- This is a systemic fungal infection endemic to Central and South America, not typically seen in China's Jillin Province.
- It primarily affects the lungs, skin, and mucous membranes, with skin lesions often appearing as chronic, progressive ulcers but without the specific linear nodular pattern described.
*Blastomycosis*
- **Blastomycosis** is a fungal infection typically acquired by inhaling spores, primarily affecting the lungs, but it can disseminate to the skin, bones, and other organs.
- Cutaneous lesions are usually sharply demarcated, crusted plaques or verrucous lesions, but they do not typically present with the linear, nodular, and ulcerative progression seen in this case.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 7: A 40-year-old farmer from Ohio seeks evaluation at a clinic with complaints of a chronic cough, fevers, and anorexia of several months duration. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy with hepatosplenomegaly. A chest radiograph reveals local infiltrates and patchy opacities involving all lung fields. Fine needle aspiration of an enlarged lymph node shows the presence of intracellular yeast. A fungal culture shows the presence of smooth, thin-walled microconidia and tuberculate macroconidia. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Blastomycosis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Histoplasmosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Sporotrichosis
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Histoplasmosis***
- **Histoplasmosis** is characterized by the presence of **intracellular yeast** in tissue samples and **tuberculate macroconidia** in fungal cultures, which are key diagnostic findings in this case.
- The patient's presentation with chronic cough, fevers, anorexia, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and lung infiltrates, along with geographic exposure in **Ohio** (part of the Ohio River Valley endemic area), is highly consistent with disseminated histoplasmosis.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- While coccidioidomycosis can cause lung infiltrates, it is typically endemic to the **southwestern United States** and Mexico, not Ohio.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules** containing endospores, not intracellular yeast with tuberculate macroconidia.
*Blastomycosis*
- Blastomycosis is also endemic to the Ohio River Valley, but it is characterized by **broad-based budding yeast** in tissue, and its cultures typically do not show tuberculate macroconidia.
- While it causes pulmonary and disseminated disease, the specific microscopic and culture findings differentiate it from histoplasmosis.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Cryptococcosis primarily affects immunocompromised individuals and is characterized by encapsulated yeast, which would be visible with India ink stain.
- It typically presents as **meningitis** or pneumonia, and its culture morphology does not include tuberculate macroconidia.
*Sporotrichosis*
- Sporotrichosis is commonly associated with **cutaneous lesions** following traumatic inoculation of spores from soil or vegetation, and it rarely causes disseminated disease with extensive systemic symptoms like those described.
- The yeast forms in tissue are typically smaller and cigar-shaped, and the culture morphology differs significantly from what is described.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 8: A 58-year-old man presents with a high-grade fever, throbbing left-sided headache, vision loss, and left orbital pain. He says that his symptoms started acutely 2 days ago with painful left-sided mid-facial swelling and a rash, which progressively worsened. Today, he woke up with complete vision loss in his left eye. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, diagnosed 5 years ago. He was started on an oral hypoglycemic agent which he discontinued after a year. His temperature is 38.9°C (102.0°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. On examination, there is purulent discharge from the left eye and swelling of the left half of his face including the orbit. Oral examination reveals extensive necrosis of the palate with a black necrotic eschar and purulent discharge. Ophthalmic examination is significant for left-sided ptosis, proptosis, and an absence of the pupillary light reflex. Laboratory findings are significant for a blood glucose level of 388 mg/dL and a white blood cell count of 19,000 cells/mm³. Urinary ketone bodies are positive. Fungal elements are found on a KOH mount of the discharge. Which of the following statements best describes the organism responsible for this patient’s condition?
- A. It appears as a narrow-based budding yeast with a thick capsule
- B. Histopathological examination shows non-septate branching hyphae (Correct Answer)
- C. It produces conidiospores
- D. It has budding and filamentous forms
- E. Histopathological examination shows acute angle branching hyphae
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Histopathological examination shows non-septate branching hyphae***
- The patient's presentation with **diabetic ketoacidosis**, orbital pain, vision loss, facial swelling, necrotic palatal eschar, and high fever strongly suggests **mucormycosis**, a severe fungal infection.
- Mucormycosis is caused by fungi belonging to **Mucorales order** (e.g., *Rhizopus*, *Mucor*, *Lichtheimia*), which are characterized by **broad, ribbon-like, non-septate hyphae with irregular, wide-angle branching**.
*It appears as a narrow-based budding yeast with a thick capsule*
- This description is characteristic of **Cryptococcus neoformans**, which causes cryptococcosis, often presenting with meningoencephalitis and lung involvement.
- The clinical picture and *KOH mount* findings in this patient are inconsistent with cryptococcosis.
*It produces conidiospores*
- **Conidiospores are asexual spores** produced by many fungi, including *Aspergillus* and *Penicillium*, but this is a general characteristic and not specific enough to definitively identify the pathogen responsible for mucormycosis.
- The *histopathological features* (non-septate hyphae) are the key identifier in mucormycosis.
*It has budding and filamentous forms*
- This description generally refers to **dimorphic fungi** (e.g., *Histoplasma*, *Blastomyces*, *Coccidioides*), which exhibit yeast forms in tissue and mold forms in culture.
- Mucorales are typically **molds** in both environments and are not considered dimorphic, nor do they commonly present with budding forms.
*Histopathological examination shows acute angle branching hyphae*
- This morphological description is characteristic of **Aspergillus species**, which cause aspergillosis, another opportunistic fungal infection.
- *Aspergillus* hyphae are typically **septate** and branch at acute angles (around 45 degrees), unlike the broad, non-septate, wide-angle branching hyphae of Mucorales.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old woman comes to the military physician because of a 2-day history of fever, joint pain, dry cough, chest pain, and a painful red rash on her lower legs. Two weeks ago, she returned from military training in Southern California. She appears ill. Her temperature is 39°C (102.1°F). Physical examination shows diffuse inspiratory crackles over all lung fields and multiple tender erythematous nodules over the anterior aspect of both legs. A biopsy specimen of this patient's lungs is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Septate hyphae with acute-angle branching
- B. Spherules filled with endospores (Correct Answer)
- C. Broad-based budding yeast
- D. Encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding
- E. Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: **Spherules filled with endospores**
- The patient's symptoms (fever, joint pain, dry cough, chest pain, erythema nodosum on legs) combined with her travel history to **Southern California** are highly suggestive of **Coccidioidomycosis** ("Valley Fever").
- A biopsy of affected lung tissue in coccidioidomycosis typically reveals **spherules** (thick-walled structures) containing numerous **endospores**, which are characteristic of the tissue phase of *Coccidioides immitis/posadasii*.
*Septate hyphae with acute-angle branching*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Aspergillus** species, which can cause opportunistic infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- While it can cause lung infections, the clinical presentation and geographic exposure do not point towards aspergillosis as the most likely diagnosis.
*Broad-based budding yeast*
- This describes the characteristic morphology of *Blastomyces dermatitidis*, the causative agent of **Blastomycosis**.
- **Blastomycosis** is typically found in the Great Lakes region, Ohio, Mississippi River valleys, and southeastern United States, not Southern California.
*Encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding*
- This describes **Cryptococcus neoformans**, which appears as an encapsulated yeast with narrow-based budding in tissue.
- While it can cause pulmonary disease, the classic presentation (erythema nodosum, acute illness after Southern California exposure) is not consistent with **cryptococcosis**, which typically presents subacutely in immunocompromised patients.
*Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae*
- This morphology is characteristic of *Candida albicans*, which commonly causes mucocutaneous infections and can cause systemic candidiasis, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
- The clinical picture of a healthy young woman with exposure in Southern California does not fit with a typical **Candida** infection.
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 10: A 3-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of progressive difficulty breathing and a dry cough. Five weeks ago, she was diagnosed with diffuse hemangiomas involving the intrathoracic cavity and started treatment with prednisolone. She appears uncomfortable and in moderate respiratory distress. Her temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), pulse is 150/min, respirations are 50/min, and blood pressure is 88/50 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 87%. Oral examination shows a white plaque covering the tongue that bleeds when scraped. Chest examination shows subcostal and intercostal retractions. Scattered fine crackles and rhonchi are heard throughout both lung fields. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 21,000/mm3 and an increased serum beta-D-glucan concentration. An x-ray of the chest shows symmetrical, diffuse interstitial infiltrates. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Tuberculin skin test
- B. Urine antigen test
- C. CT scan of the chest
- D. Bronchoalveolar lavage (Correct Answer)
- E. DNA test for CFTR mutation
Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections Explanation: ***Bronchoalveolar lavage***
- The patient, an infant on **prednisolone** (immunosuppression) with **diffuse interstitial infiltrates**, **uncomfortable appearance**, **respiratory distress**, and **oral thrush (white plaque that bleeds when scraped)**, points to **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**.
- **Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)** is the gold standard for diagnosing PCP by identifying **Pneumocystis jirovecii cysts** or **trophozoites** using special stains (e.g., Giemsa, methenamine silver).
*Tuberculin skin test*
- The **tuberculin skin test** is used to diagnose **tuberculosis**, which typically presents with **granulomas** and **cavitary lesions** on chest X-ray, not diffuse interstitial infiltrates.
- While tuberculosis can cause respiratory symptoms, the presence of oral thrush and immunosuppression suggests an opportunistic fungal infection like PCP rather than TB.
*Urine antigen test*
- A **urine antigen test** is commonly used for diagnosing **Legionnaires' disease** or **pneumococcal pneumonia** in adults, and is not applicable for PCP.
- It does not detect *Pneumocystis jirovecii*, which is the suspected pathogen in this immunosuppressed infant.
*CT scan of the chest*
- A **CT scan of the chest** would show **diffuse ground-glass opacities** characteristic of PCP but is a **radiological finding**, not a definitive diagnostic test for the pathogen itself.
- While it can further characterize the pulmonary findings, it cannot identify the causative organism, which is crucial for targeted treatment.
*DNA test for CFTR mutation*
- A **DNA test for CFTR mutation** is used to diagnose **cystic fibrosis**, a genetic disorder affecting mucus production, and is not relevant in this acute presentation of respiratory distress and immunosuppression.
- Cystic fibrosis typically presents with recurrent respiratory infections, pancreatic insufficiency, and failure to thrive, not primarily with opportunistic infections like PCP.
More Clinical presentations of dimorphic fungal infections US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.