Biofilms

On this page
🏗️ Biofilm Architecture: The Microbial Metropolis
Biofilms transform harmless bacteria into fortress communities up to 1,000 times more resistant to antibiotics, driving chronic infections from endocarditis to cystic fibrosis exacerbations. You'll discover how these microbial cities self-assemble through precise stages, deploy multiple defense mechanisms including persister cells and extracellular matrices, and why device-related infections remain so intractable. By mastering biofilm architecture, formation dynamics, and emerging disruption strategies, you'll gain the clinical framework to recognize, anticipate, and combat these sophisticated structures that account for over 65% of human bacterial infections.
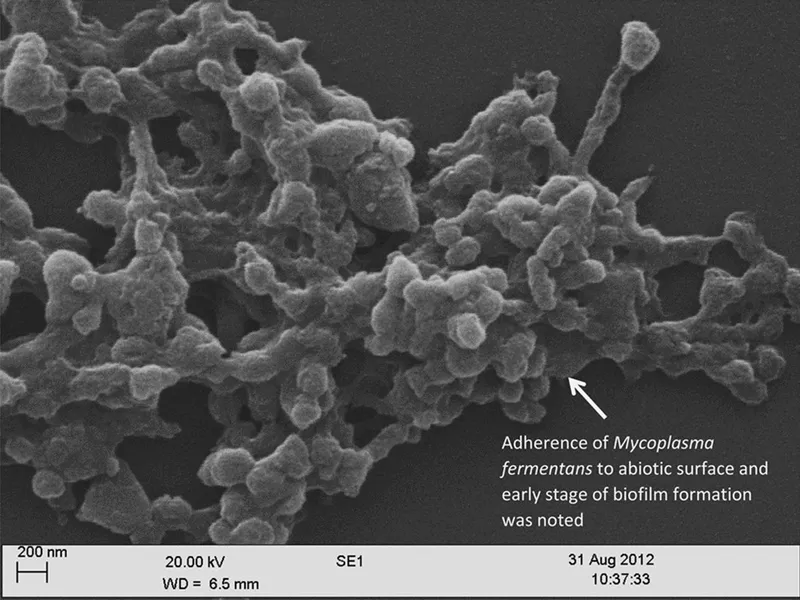

📌 Remember: BIOFILM - Bacteria In Organized Fortresses Increase Lethality Massively - These structures increase antimicrobial resistance by 10-1,000 fold compared to planktonic bacteria
Biofilms consist of structured microbial communities embedded within a self-produced extracellular polymeric matrix. This matrix comprises 85-95% water and 5-15% solid components including polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. The architecture creates distinct microenvironments with varying oxygen gradients, pH levels, and nutrient availability.
- Structural Components
- Surface layer: Initial bacterial adhesion zone (1-5 μm thick)
- Base layer: Dense bacterial population with limited metabolic activity
- Cell density: 10^8-10^9 CFU/cm²
- Oxygen concentration: <5% of surface levels
- Intermediate zones: Metabolically active bacterial clusters
- Growth rate: 50-80% of planktonic bacteria
- Nutrient flow: Channeled through water channels
- Surface layer: Highly active bacterial populations
- Oxygen levels: Near atmospheric (21%)
- Dispersal zone: Active shedding of planktonic bacteria
| Biofilm Zone | Depth (μm) | O₂ Level (%) | Growth Rate | Resistance Factor | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | 0-10 | 18-21 | 90-100% | 10-50x | Dispersal source |
| Intermediate | 10-50 | 5-15 | 50-80% | 100-500x | Treatment failure |
| Base | 50-200 | 0-5 | 5-20% | 500-1000x | Persistence reservoir |
| Interface | 200+ | 0 | 0-5% | >1000x | Recurrence source |
The water channel system creates a primitive circulatory network, delivering nutrients and removing waste products. These channels occupy 15-25% of biofilm volume and maintain laminar flow patterns that optimize bacterial survival. Channel diameter ranges from 5-50 μm, allowing efficient mass transfer while protecting internal bacterial populations.
💡 Master This: Biofilm architecture creates concentration gradients - surface bacteria experience full antibiotic exposure while base layer bacteria receive <1% of administered drug concentrations, creating persistent infection reservoirs
Understanding this architectural complexity reveals why single-dose antimicrobial therapy fails and why biofilm-associated infections require prolonged treatment protocols with combination therapy approaches. The structural sophistication of these microbial cities demands equally sophisticated therapeutic strategies.
Connect biofilm architecture through formation mechanisms to understand how these complex structures develop from single bacterial cells into treatment-resistant communities.
🏗️ Biofilm Architecture: The Microbial Metropolis
⚙️ Formation Dynamics: The Five-Stage Construction Protocol
📌 Remember: STAGE - Surface Testing, Adhesion Gains, Expansion - The first 30 minutes determine biofilm success, with irreversible commitment occurring within 2-4 hours
Stage 1: Reversible Attachment (0-30 minutes)
- Initial contact: Bacteria approach surfaces via Brownian motion and chemotaxis
- Weak interactions: Van der Waals forces and electrostatic interactions
- Attachment strength: <10 pN (easily reversed)
- Success rate: Only 5-15% of bacteria achieve stable contact
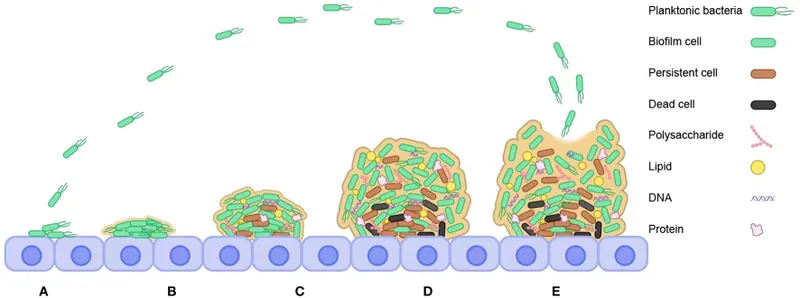
Stage 2: Irreversible Attachment (30 minutes - 4 hours)
- Molecular adhesins: Pili, fimbriae, and surface proteins engage
- Binding strength: >100 pN (permanent commitment)
- Gene expression: >50 adhesion genes upregulated
- Surface modification: Bacteria begin conditioning film production
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The 2-4 hour window represents the critical intervention period - antimicrobial prophylaxis is >95% effective before irreversible attachment but drops to <30% efficacy afterward
| Formation Stage | Duration | Key Molecules | Binding Strength | Intervention Success | Clinical Window |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reversible | 0-30 min | Van der Waals | <10 pN | >95% | Prophylaxis optimal |
| Irreversible | 30 min-4 hr | Adhesins/Pili | >100 pN | 60-80% | Early treatment |
| Microcolony | 4-12 hr | EPS matrix | >1000 pN | 30-50% | Aggressive therapy |
| Maturation | 12-48 hr | Quorum signals | >5000 pN | 10-20% | Combination therapy |
| Dispersal | 48+ hr | Dispersins | Variable | <10% | Chronic management |
- Cell division: Attached bacteria undergo rapid proliferation
- EPS production: Extracellular polymeric substances begin matrix formation
- Microcolony size: 10-50 μm diameter clusters
- Population density: 10^6-10^7 CFU/cm²
Stage 4: Maturation (12-48 hours)
- Three-dimensional architecture: Complex tower and mushroom structures
- Quorum sensing activation: Cell density >10^8 CFU/cm² triggers signaling
- Metabolic stratification: Distinct zones with specialized functions
- Maximum thickness: 100-500 μm depending on species and conditions
💡 Master This: Quorum sensing at 10^8 CFU/cm² triggers virulence factor production and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms - this population threshold explains why early intervention prevents treatment-resistant infections
Stage 5: Dispersal (48+ hours)
- Active dispersal: Enzymatic matrix degradation releases planktonic bacteria
- Passive shedding: Mechanical forces detach surface bacteria
- Dispersal rate: 1-5% of biofilm population per day
- Infection spread: Dispersed bacteria seed new infection sites
The formation timeline varies significantly with environmental conditions. Temperature >37°C accelerates formation by 2-3 fold, while low oxygen conditions (<5%) promote denser biofilm architecture. Surface roughness >0.2 μm increases attachment success by 5-10 fold.
Understanding formation dynamics reveals critical intervention windows and explains why device-related infections require immediate aggressive therapy rather than watchful waiting approaches.
Connect formation mechanisms through resistance strategies to understand how mature biofilms develop extraordinary antimicrobial tolerance and immune evasion capabilities.
⚙️ Formation Dynamics: The Five-Stage Construction Protocol
🛡️ Resistance Arsenal: The Fortress Defense Systems
- Physical Barrier Mechanisms
- EPS matrix: Polysaccharide networks bind and neutralize antimicrobials
- Alginate in P. aeruginosa: Reduces β-lactam penetration by 90%
- Poly-N-acetylglucosamine: Cationic antimicrobial sequestration
- Diffusion limitation: Tortuous pathways slow drug penetration
- Effective diffusion: 10-50% of free solution rates
- Concentration gradients: Base layer receives <1% of surface concentrations
- EPS matrix: Polysaccharide networks bind and neutralize antimicrobials
📌 Remember: MATRIX - Molecules Are Trapped, Resistance Increases Xponentially - EPS matrix reduces antimicrobial penetration by 50-95% depending on drug charge and molecular weight
| Resistance Mechanism | Effectiveness | Primary Target | Clinical Impact | Overcome Strategy | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPS sequestration | 50-95% reduction | Cationic drugs | Treatment failure | High-dose therapy | 20-40% |
| Diffusion limitation | 90-99% reduction | Large molecules | Chronic infection | Penetration enhancers | 30-50% |
| Metabolic dormancy | >99% protection | All antimicrobials | Persistence | Metabolic activation | 10-30% |
| Efflux pumps | 10-100x MIC | Multiple classes | Resistance evolution | Pump inhibitors | 40-60% |
| Stress responses | 5-50x tolerance | Oxidative stress | Immune evasion | Combination therapy | 50-70% |
- Persister cells: 1-5% of biofilm population enters dormant state
- Metabolic activity: <5% of active bacteria
- Antimicrobial tolerance: >1000-fold increased survival
- Recovery time: 6-24 hours post-stress removal
- Oxygen gradients: Create anaerobic zones resistant to oxygen-dependent killing
- Aminoglycoside resistance: Requires oxygen-dependent uptake
- Base layer protection: >99% survival in anaerobic conditions
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Persister cells explain recurrent infections after apparently successful treatment - these dormant bacteria reactivate when antimicrobial pressure is removed, causing clinical relapse in 30-60% of biofilm infections
Active Resistance Systems
- Efflux pump upregulation: 2-10 fold increased expression
- MexAB-OprM in P. aeruginosa: Broad-spectrum antimicrobial export
- AcrAB-TolC in E. coli: Multiple drug class resistance
- Enzymatic inactivation: β-lactamase concentration in EPS matrix
- Local enzyme concentration: 10-100x higher than planktonic
- Substrate protection: Continuous drug degradation
Stress Response Coordination
- Quorum sensing regulation: Population-wide stress response activation
- Signal threshold: 10^8 CFU/cm² triggers coordinated resistance
- Response genes: >200 genes involved in stress tolerance
- Biofilm-specific regulons: Specialized gene networks for sessile lifestyle
- RpoS regulation: Stationary phase sigma factor upregulation
- SOS response: DNA repair and mutagenesis enhancement
The combination of these mechanisms creates extraordinary antimicrobial tolerance. Standard MIC testing underestimates biofilm resistance by 10-1000 fold, explaining why clinically achievable concentrations often fail against biofilm-associated infections.
💡 Master This: Biofilm MIC values are 10-1000x higher than planktonic MIC - this explains why standard susceptibility testing poorly predicts clinical outcomes in device-related and chronic infections
Understanding resistance mechanisms reveals why biofilm infections require novel therapeutic approaches including combination therapy, biofilm-penetrating agents, and anti-biofilm compounds rather than traditional antimicrobial monotherapy.
Connect resistance strategies through clinical manifestations to understand how biofilm defenses translate into specific disease patterns and therapeutic challenges in real-world infections.
🛡️ Resistance Arsenal: The Fortress Defense Systems
🎯 Clinical Battlegrounds: High-Stakes Infection Territories
- Device-Related Infection Hotspots
- Central venous catheters: 5-15% infection rate, >90% biofilm-associated
- Coagulase-negative staphylococci: 60-70% of infections
- Treatment failure: 40-60% with antimicrobial therapy alone
- Device removal: Required in >80% of cases for cure
- Prosthetic joints: 1-3% infection rate, >95% biofilm-mediated
- Late infections (>2 years): >99% biofilm-associated
- Revision surgery: Required in 70-90% of cases
- Antimicrobial duration: 6-12 weeks minimum
- Central venous catheters: 5-15% infection rate, >90% biofilm-associated
📌 Remember: DEVICE - Difficult Eradication, Very Insidious, Chronic Evolution - Device-related infections have >90% biofilm involvement and <20% cure rates without device removal
| Clinical Site | Biofilm Prevalence | Primary Pathogens | Treatment Failure | Recurrence Rate | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVCs | >90% | CoNS, S. aureus | 40-60% | 30-50% | Device removal usually required |
| Prosthetic joints | >95% | S. epidermidis, S. aureus | 60-80% | 40-70% | Surgical debridement essential |
| Heart valves | >85% | S. aureus, Enterococci | 20-40% | 15-30% | Valve replacement often needed |
| Urinary catheters | >80% | E. coli, Enterococci | 50-70% | 60-80% | Catheter change required |
| Chronic wounds | 60-80% | P. aeruginosa, S. aureus | 70-90% | 80-95% | Debridement plus antimicrobials |
- Cystic fibrosis pulmonary infections: >95% biofilm-mediated by age 18
- P. aeruginosa biofilms: Alginate overproduction creates mucoid phenotype
- Antimicrobial tolerance: >100-fold increased MIC values
- Chronic inflammation: Persistent neutrophil infiltration with tissue damage
- Chronic otitis media: 60-80% biofilm involvement
- Polymicrobial biofilms: 2-4 species per infection
- Treatment duration: 4-6 weeks often required
- Surgical intervention: 30-50% require tympanoplasty
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Chronic infections lasting >4 weeks have >80% probability of biofilm involvement - this explains why standard 7-14 day antimicrobial courses fail and extended therapy is required
Diagnostic Challenges
- Culture limitations: Standard cultures detect <10% of biofilm bacteria
- Planktonic shedding: Intermittent positive cultures from chronic biofilms
- Viable but non-culturable: Stressed bacteria fail to grow on standard media
- Imaging findings: Biofilms often radiologically silent
- CT sensitivity: <30% for early biofilm infections
- MRI enhancement: Variable patterns depending on biofilm maturity
Treatment Resistance Patterns
- Antimicrobial failure: Standard dosing achieves <1% of required concentrations
- Biofilm MIC: 10-1000x higher than planktonic MIC
- Penetration barriers: EPS matrix blocks drug diffusion
- Immune evasion: Biofilm architecture protects from host defenses
- Neutrophil frustration: Ineffective phagocytosis of matrix-embedded bacteria
- Complement resistance: EPS binding neutralizes complement activation
Clinical Recognition Criteria
- Persistent symptoms despite appropriate antimicrobial therapy
- Recurrent infections at same anatomical site
- Device-associated infections with negative blood cultures
- Chronic wounds with delayed healing despite adequate debridement
💡 Master This: Clinical biofilm infections require paradigm shift from acute treatment models to chronic disease management - success depends on combination therapy, extended duration, and often surgical intervention
Understanding clinical patterns reveals why biofilm infections demand specialized diagnostic approaches and novel treatment strategies that address biofilm-specific pathophysiology rather than traditional planktonic-based protocols.
Connect clinical manifestations through therapeutic strategies to understand how modern anti-biofilm approaches overcome traditional treatment limitations and improve clinical outcomes.
🎯 Clinical Battlegrounds: High-Stakes Infection Territories
⚔️ Therapeutic Warfare: Advanced Anti-Biofilm Strategies
- Matrix Disruption Strategies
- DNase therapy: Dornase alfa degrades extracellular DNA scaffolding
- Biofilm reduction: 60-80% biomass decrease
- Antimicrobial synergy: 10-100 fold improved drug penetration
- Clinical application: Cystic fibrosis and chronic wounds
- Dispersin B: β-hexosaminidase cleaves PNAG matrix
- Staphylococcal biofilms: >90% disruption efficacy
- Combination therapy: Enhanced vancomycin activity by 50-fold
- DNase therapy: Dornase alfa degrades extracellular DNA scaffolding
📌 Remember: DISRUPT - Degrade Infrastructure, Stop Resistance, Unlock Penetration, Target - Matrix disruption agents increase antimicrobial efficacy by 10-1000 fold in biofilm infections
| Anti-Biofilm Strategy | Mechanism | Efficacy | Clinical Application | Combination Benefit | Resistance Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNase | DNA degradation | 60-80% reduction | CF, chronic wounds | 10-100x synergy | Low |
| Dispersin B | PNAG cleavage | >90% disruption | Staphylococcal infections | 50x enhancement | Minimal |
| Quorum inhibitors | Signal blocking | 40-70% reduction | P. aeruginosa infections | 5-20x synergy | Moderate |
| Iron chelation | Metabolic stress | 50-80% killing | Chronic infections | 2-10x enhancement | Low |
| Nitric oxide | Multiple targets | 70-95% reduction | Device infections | Variable synergy | Very low |
- Signal molecule analogs: Competitive inhibition of autoinducer binding
- Furanone compounds: AHL analog inhibitors for Gram-negative biofilms
- Efficacy: 40-70% biofilm reduction with preserved antimicrobial susceptibility
- Enzyme degradation: Lactonases and acylases degrade signaling molecules
- AiiA lactonase: Hydrolyzes AHL signals preventing quorum activation
- Clinical potential: Combination therapy with β-lactams shows 5-20 fold synergy
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Quorum sensing inhibitors prevent biofilm maturation without bactericidal activity - this reduces selection pressure for resistance development while enhancing conventional antimicrobial efficacy
Metabolic Manipulation Approaches
- Iron chelation therapy: Lactoferrin and EDTA create metabolic stress
- Biofilm disruption: 50-80% reduction in iron-dependent biofilms
- Persister cell activation: Forces dormant bacteria into metabolically active state
- Antimicrobial synergy: 2-10 fold enhancement of bactericidal activity
- Nitric oxide therapy: Multiple anti-biofilm mechanisms
- Direct antimicrobial: Oxidative stress and DNA damage
- Dispersal induction: Triggers biofilm dispersal mechanisms
- Efficacy: 70-95% biofilm reduction in device-related infections
Enhanced Drug Delivery Systems
- Liposomal formulations: Improved biofilm penetration and sustained release
- Liposomal amikacin: >10 fold higher biofilm concentrations
- Clinical success: 60-80% cure rates in chronic P. aeruginosa infections
- Nanoparticle carriers: Targeted delivery to biofilm matrix
- Silver nanoparticles: Broad-spectrum anti-biofilm activity
- Polymeric carriers: Controlled release with matrix penetration
Clinical Implementation Protocols
- Combination therapy sequencing: Matrix disruption followed by antimicrobial therapy
- Pre-treatment: DNase or dispersin B for 2-4 hours
- Antimicrobial phase: High-dose therapy for extended duration
- Success rates: 70-85% versus <30% with monotherapy
- Device-related infections: Anti-biofilm lock therapy
- High-concentration antimicrobials with matrix-disrupting agents
- Dwell time: 12-24 hours for optimal biofilm penetration
- Device salvage: 60-80% success rates avoiding device removal
💡 Master This: Successful biofilm therapy requires sequential combination approaches - matrix disruption creates antimicrobial access, quorum inhibition prevents resistance development, and metabolic manipulation eliminates persister cells
Emerging Therapeutic Targets
- Biofilm-specific enzymes: c-di-GMP phosphodiesterases regulate biofilm formation
- Efflux pump inhibitors: Restore antimicrobial susceptibility in biofilm bacteria
- Immunomodulatory approaches: Enhance host defenses against biofilm infections
Understanding advanced therapeutic strategies reveals how modern anti-biofilm medicine transforms previously incurable chronic infections into manageable conditions through scientifically-designed combination protocols.
Connect therapeutic strategies through integration principles to understand how biofilm knowledge revolutionizes infection prevention, diagnostic approaches, and treatment paradigms across multiple medical specialties.
⚔️ Therapeutic Warfare: Advanced Anti-Biofilm Strategies
🌐 Systems Integration: The Biofilm-Medicine Interface
- Cross-Specialty Integration Points
- Infectious Disease + Surgery: Biofilm-guided surgical timing and antimicrobial selection
- Debridement protocols: Biofilm-specific techniques improve cure rates by 40-60%
- Prophylaxis strategies: Anti-biofilm agents reduce device infections by 50-70%
- Critical Care + Microbiology: Biofilm-aware diagnostics and therapeutic monitoring
- Rapid detection: Biofilm-specific assays guide early intervention
- Treatment duration: Biofilm burden determines antimicrobial course length
- Infectious Disease + Surgery: Biofilm-guided surgical timing and antimicrobial selection
📌 Remember: INTEGRATE - Infectious Needs Timing, Every Group Requires Adaptation, Team Effort - Biofilm medicine requires multidisciplinary coordination with >3 specialties involved in complex cases
| Integration Domain | Specialties Involved | Shared Protocols | Outcome Improvement | Implementation Challenges | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device infections | ID, Surgery, ICU | Anti-biofilm prophylaxis | 50-70% reduction | Cost, training | Infection rates |
| Chronic wounds | Dermatology, Surgery, ID | Biofilm debridement | 40-60% healing | Technique standardization | Healing time |
| CF management | Pulmonology, ID, Pharmacy | Anti-biofilm therapy | 30-50% improvement | Drug availability | Lung function |
| Endocarditis | Cardiology, ID, Surgery | Biofilm-guided timing | 20-40% better outcomes | Surgical decision-making | Mortality rates |
| Osteomyelitis | Orthopedics, ID, Radiology | Extended therapy | 60-80% cure rates | Duration compliance | Recurrence rates |
- Surface modification technologies: Anti-biofilm coatings for medical devices
- Silver-impregnated catheters: 60-80% reduction in biofilm formation
- Antimicrobial-releasing surfaces: Sustained protection for 7-30 days
- Cost-effectiveness: $2,000-5,000 savings per prevented infection
- Prophylactic protocols: Biofilm-specific prevention strategies
- Pre-operative optimization: Biofilm screening and decolonization
- Perioperative timing: Anti-biofilm agents during critical windows
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Biofilm prevention is 10-100 times more cost-effective than treatment - investing $100-500 in prevention strategies saves $10,000-50,000 in treatment costs per avoided biofilm infection
Diagnostic Integration Advances
- Point-of-care biofilm detection: Rapid assays for clinical decision-making
- Fluorescent staining: 5-minute biofilm identification
- Molecular diagnostics: PCR-based biofilm gene detection
- Clinical impact: Same-day treatment optimization
- Imaging integration: Biofilm-specific radiological protocols
- PET-CT biofilm imaging: Metabolic activity mapping
- Contrast-enhanced MRI: Biofilm architecture visualization
Treatment Integration Protocols
- Multidisciplinary biofilm teams: Coordinated care for complex infections
- Team composition: ID physician, surgeon, pharmacist, microbiologist
- Decision algorithms: Evidence-based protocols for treatment selection
- Outcome tracking: Standardized metrics across specialties
- Therapeutic drug monitoring: Biofilm-adjusted dosing strategies
- Target concentrations: 10-100x higher than standard MIC
- Duration optimization: Biofilm burden-guided treatment length
- Combination protocols: Sequential and simultaneous agent selection
Research Integration Opportunities
- Translational biofilm research: Bench-to-bedside protocol development
- Clinical trial design: Biofilm-specific endpoints and outcome measures
- Biomarker development: Biofilm burden and treatment response indicators
- Technology integration: AI-assisted biofilm diagnosis and treatment optimization
- Machine learning: Pattern recognition for biofilm identification
- Decision support: Algorithm-guided treatment selection
💡 Master This: Biofilm medicine integration requires paradigm shift from single-specialty to team-based care - successful outcomes depend on coordinated protocols, shared decision-making, and unified treatment goals
Quality Improvement Integration
- Biofilm-specific metrics: Outcome measures that reflect biofilm pathophysiology
- Time to biofilm clearance: Novel endpoint for treatment success
- Recurrence rates: Long-term follow-up for biofilm eradication
- Cost-effectiveness analysis: Economic impact of biofilm-integrated care
- Prevention investments: ROI analysis for anti-biofilm strategies
- Treatment optimization: Cost per cure with biofilm-specific protocols
Understanding systems integration reveals how biofilm science creates unified medical approaches that transcend traditional specialty boundaries and optimize patient outcomes through coordinated, evidence-based care.
Connect integration principles through clinical mastery frameworks to understand how biofilm expertise becomes practical clinical competency through systematic knowledge application and evidence-based decision-making.
🌐 Systems Integration: The Biofilm-Medicine Interface
🎯 Clinical Mastery: The Biofilm Expertise Toolkit
- Essential Diagnostic Arsenal
- Clinical recognition patterns: "Red flag" indicators for biofilm involvement
- Device-related infections: >90% biofilm probability
- Chronic infections >4 weeks: >80% biofilm involvement
- Recurrent infections same site: >70% biofilm likelihood
- Rapid assessment tools: Point-of-care biofilm detection
- Congo red agar: Biofilm-producing organisms show black colonies
- Tube adherence test: >50% coverage indicates strong biofilm formation
- Clinical recognition patterns: "Red flag" indicators for biofilm involvement
📌 Remember: MASTER - Monitor Always, Suspect Treatment Escape, Recognize - Clinical mastery requires constant vigilance for biofilm indicators and treatment failure patterns
| Clinical Scenario | Biofilm Probability | Key Indicators | Diagnostic Approach | Treatment Modification | Success Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New device infection | >90% | Device present <30 days | Standard culture + biofilm assay | Combination therapy | 70-85% |
| Chronic wound | 60-80% | >4 weeks, poor healing | Tissue biopsy + microscopy | Debridement + anti-biofilm | 40-60% |
| Recurrent UTI | >70% | Same organism, catheter | Biofilm-specific culture | Extended therapy | 60-80% |
| CF exacerbation | >95% | Mucoid P. aeruginosa | Sputum biofilm staining | Anti-biofilm combination | 30-50% |
| Prosthetic joint | >95% | Late infection >2 years | Sonication + culture | Surgery + prolonged therapy | 70-90% |
- Biofilm-guided antimicrobial selection: Evidence-based drug choices
- High biofilm penetration: Fluoroquinolones, rifampin, linezolid
- Matrix-disrupting agents: DNase, dispersin B, EDTA
- Combination synergy: β-lactam + aminoglycoside for enhanced killing
- Duration optimization: Biofilm burden-guided treatment length
- Light biofilm burden: 2-4 weeks extended therapy
- Heavy biofilm burden: 6-12 weeks combination treatment
- Device-associated: Until device removal plus 2-4 weeks
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Biofilm treatment success correlates with early aggressive intervention - combination therapy initiated within 48-72 hours achieves 2-3 fold higher cure rates than delayed treatment
🎯 Clinical Mastery: The Biofilm Expertise Toolkit
Practice Questions: Biofilms
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 37-year-old woman with a history of anorectal abscesses complains of pain in the perianal region. Physical examination reveals mild swelling, tenderness, and erythema of the perianal skin. She is prescribed oral ampicillin and asked to return for follow-up. Two days later, the patient presents with a high-grade fever, syncope, and increased swelling. Which of the following would be the most common mechanism of resistance leading to the failure of antibiotic therapy in this patient?













