Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Acute ischemic stroke management. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
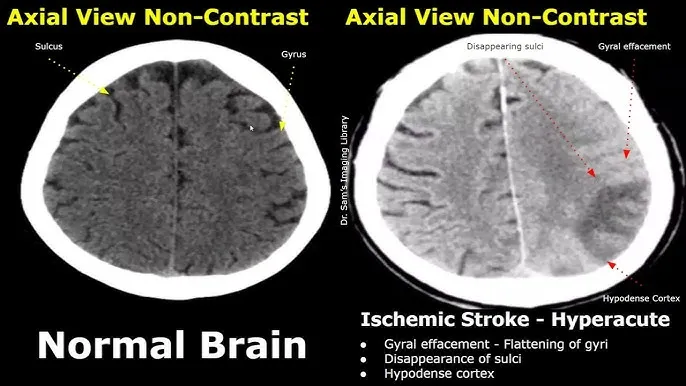
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 1: A 69-year-old man is brought in by his wife with acute onset aphasia for the past 5 hours. The patient's wife says that they were sitting having dinner when suddenly he was not able to speak. They delayed coming to the hospital because he had a similar episode 2 months ago which resolved within an hour. His past medical history is significant for hypercholesterolemia, managed with rosuvastatin, and a myocardial infarction (MI) 2 months ago, status post percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty complicated by residual angina. His family history is significant for his father who died of MI at age 60. The patient reports a 15-pack-year smoking history but denies any alcohol or recreational drug use. The vital signs include: temperature 37.0℃ (98.6℉), blood pressure 125/85 mm Hg, pulse 96/min, and respiratory rate 19/min. On physical examination, the patient has expressive aphasia. There is a weakness of the right-sided lower facial muscles. The strength in his upper and lower extremities is 4/5 on the right and 5/5 on the left. There is also a decreased sensation on his right side. A noncontrast computed tomography (CT) scan of the head is unremarkable. CT angiography (CTA) and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain are acquired, and the findings are shown in the exhibit (see image). Which of the following is the best course of treatment in this patient?
- A. Aspirin
- B. Mannitol
- C. Mechanical thrombectomy (Correct Answer)
- D. IV tPA
- E. Low molecular weight heparin
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Mechanical thrombectomy***
- The patient presents with **acute ischemic stroke** symptoms (aphasia, right-sided weakness, sensory deficits) at **5 hours from symptom onset**. Imaging (CTA showing large vessel occlusion and MRI confirming diffusion restriction) demonstrates a **large vessel occlusion**, making him a candidate for **mechanical thrombectomy**.
- Since the patient is **beyond the 4.5-hour window for IV tPA**, mechanical thrombectomy is the **primary reperfusion therapy** indicated for large vessel occlusion strokes up to **24 hours** (with appropriate imaging showing salvageable tissue).
- Mechanical thrombectomy offers the best chance for complete recanalization and improved neurological outcomes in large vessel occlusion strokes, particularly when IV tPA is not an option.
*Aspirin*
- While **aspirin** is crucial for **secondary stroke prevention**, it is not the primary acute treatment for a large vessel occlusion stroke due to its limited ability to achieve rapid and complete recanalization.
- Aspirin (or other antiplatelet therapy) is typically initiated **within 24-48 hours after stroke onset**, but only after excluding hemorrhagic transformation and after acute reperfusion therapies have been considered or completed.
*Mannitol*
- **Mannitol** is an osmotic diuretic used to reduce **intracranial pressure (ICP)** in cases of severe cerebral edema, which can be a complication of large ischemic strokes.
- It is not a primary treatment for the acute ischemic event itself, but rather a supportive measure used to manage life-threatening complications if **cerebral edema** develops and causes significant mass effect or herniation risk.
*IV tPA*
- **Intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (IV tPA)** is the first-line pharmacologic treatment for acute ischemic stroke if administered **within 4.5 hours of symptom onset** in eligible patients.
- This patient presents at **5 hours**, which is **beyond the approved time window** for IV tPA administration, making him **ineligible** for thrombolytic therapy.
- Even if within the time window, patients with large vessel occlusion often require mechanical thrombectomy in addition to or instead of IV tPA for optimal outcomes.
*Low molecular weight heparin*
- **Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)** is primarily used for **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)** prophylaxis in immobilized patients or for the treatment of established DVT/pulmonary embolism.
- It is generally **not recommended for acute ischemic stroke treatment** due to an increased risk of hemorrhagic transformation without proven benefit in recanalization or clinical outcomes.
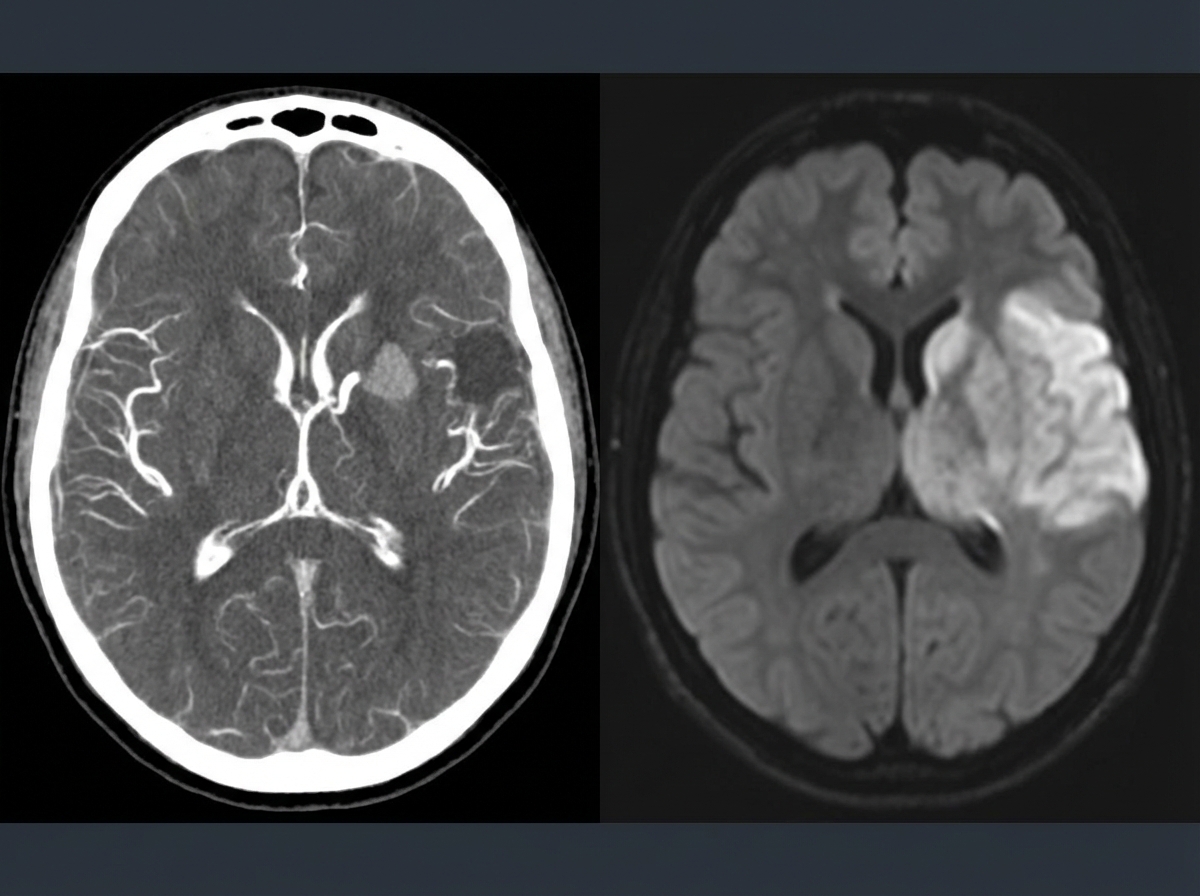
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old man presents to the clinic concerned about his health after his elder brother recently became bed-bound due to a brain condition. He has also brought a head CT scan of his brother to reference, as shown in the picture. The patient has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, osteoarthritis, and hypercholesterolemia. His medication list includes aspirin, diclofenac sodium, metformin, and ramipril. He leads a sedentary lifestyle and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. He also drinks 4–5 cups of red wine every weekend. His BMI is 33.2 kg/m2. His blood pressure is 164/96 mm Hg, the heart rate is 84/min, and the respiratory rate is 16/min. Which of the following interventions will be most beneficial for reducing the risk of developing the disease that his brother has?
- A. Statin therapy
- B. Quit smoking
- C. Stop aspirin
- D. Blood sugar control
- E. Blood pressure control (Correct Answer)
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Blood pressure control***
- The brother's CT scan shows features of **white matter hyperintensities (WMH)**, indicative of **cerebral small vessel disease**, a significant risk factor for **neurodegenerative conditions** and dementia, which can cause a patient to become bedridden.
- **Hypertension** is the most potent and modifiable risk factor for the development and progression of WMH and other forms of cerebral small vessel disease; therefore, strict **blood pressure control** is the most beneficial intervention.
*Statin therapy*
- Statins are crucial for managing **hypercholesterolemia** and reducing the risk of **atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease** and stroke.
- While beneficial for overall vascular health, **dyslipidemia** is less strongly associated with WMH and cerebral small vessel disease than hypertension.
*Quit smoking*
- **Smoking** is a significant risk factor for **stroke**, **atherosclerosis**, and several neurodegenerative disorders.
- While important for overall health, **smoking cessation** has a less direct and immediate impact on the progression of existent WMH compared to **blood pressure control**.
*Stop aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is used for **primary or secondary prevention** of cardiovascular events due to its **antiplatelet effects**.
- There is no indication that stopping aspirin would benefit in preventing further cerebral small vessel disease; rather, it could increase the risk of other vascular events in this patient with multiple risk factors.
*Blood sugar control*
- **Type 2 diabetes mellitus** is a known risk factor for **vascular dementia** and can contribute to small vessel disease.
- While important for long-term health, the impact of **blood sugar control** on WMH progression is less substantial compared to **blood pressure control**.
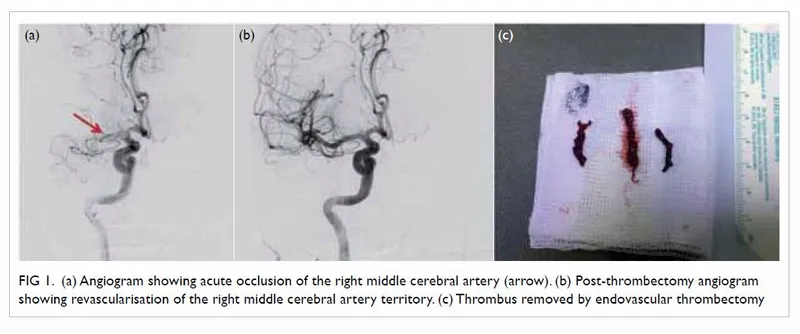
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 3: A 79-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after he noted the abrupt onset of weakness accompanied by decreased sensation on his left side. His symptoms developed rapidly, peaked within 1 minute, and began to spontaneously resolve 10 minutes later. Upon arrival in the emergency room 40 minutes after the initial onset of symptoms, they had largely resolved. The patient has essential hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and a 50 pack-year smoking history. He also had an ST-elevation myocardial infarction 3 years ago. His brain CT scan without contrast is reported as normal. Carotid duplex ultrasonography reveals 90% stenosis of the right internal carotid. His transthoracic echocardiogram does not reveal any intracardiac abnormalities. Which of the following interventions is most appropriate for this patient's condition?
- A. Carotid stenting (Correct Answer)
- B. Warfarin
- C. Low molecular weight heparin
- D. Hypercoagulability studies
- E. Aspirin and clopidogrel
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Carotid stenting***
- The patient experienced a **transient ischemic attack (TIA)** with **90% stenosis of the right internal carotid artery**, which is a high-grade stenosis.
- **Carotid revascularization** is highly recommended for symptomatic patients with **high-grade carotid stenosis** (70–99%) to prevent future strokes.
- Both **carotid endarterectomy (CEA)** and **carotid stenting** are acceptable options. In this elderly patient (79 years) with significant comorbidities (COPD, prior MI, 50 pack-year smoking history), **carotid stenting** may be preferred as it avoids the surgical risks of general anesthesia and neck dissection.
*Warfarin*
- **Warfarin** is primarily used for preventing strokes in patients with **atrial fibrillation** or mechanical heart valves.
- It is **not the first-line treatment** for stroke prevention directly caused by symptomatic carotid artery stenosis.
*Low molecular weight heparin*
- **Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)** is typically used for acute treatment of **deep vein thrombosis** and **pulmonary embolism**, or in certain acute coronary syndromes.
- It does not address the underlying **structural issue of severe carotid stenosis** for long-term stroke prevention.
*Hypercoagulability studies*
- While hypercoagulability can cause strokes, the patient's symptoms are clearly attributed to **severe carotid stenosis**.
- These studies are usually reserved for patients with strokes of **unexplained etiology**, especially younger patients, or those with unusual clot locations.
*Aspirin and clopidogrel*
- **Dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin and clopidogrel)** is often used after a TIA or minor stroke, but typically for a limited duration (e.g., 21-90 days), and it is an adjunct to revascularization in severe carotid stenosis.
- Although important for **secondary stroke prevention**, it does not address the critical **90% carotid stenosis** that warrants revascularization.
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 4: A 74-year-old man is rushed to the emergency department with left-sided weakness, facial deviation, and slurred speech. His wife first noticed these changes about an hour ago. The patient is having difficulty communicating. He can answer questions by nodding his head, and his wife is providing detailed information. He denies fever, loss of consciousness, head injury, bleeding, or seizures. Past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, ischemic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, and osteoarthritis. He had a heart attack 6 weeks ago. Baseline creatinine is 2.5 mg/dL, and he is not on hemodialysis. Medications include aspirin, clopidogrel, metoprolol, ramipril, rosuvastatin, and insulin detemir. Blood pressure is 175/95 mm Hg and the heart rate is 121/min. Muscle strength is decreased in both the upper and lower extremities on the left-side. A forehead sparing left sided facial weakness is also appreciated. An ECG reveals atrial fibrillation. An urgent head CT shows a hypodense area in the right parietal cortex with no indication of hemorrhage. Treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is deferred due to which condition?
- A. History of myocardial infarction 6 weeks ago (Correct Answer)
- B. Chronic kidney disease
- C. Atrial fibrillation on electrocardiogram
- D. Raised blood pressures
- E. Aspirin and clopidogrel use
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***History of myocardial infarction 6 weeks ago***
- Recent **myocardial infarction (MI)**, especially within the last 3 months, is a relative contraindication for tPA due to the increased risk of hemorrhage. The patient's MI 6 weeks ago falls within this critical window.
- While not an absolute contraindication, the increased risk of hemorrhagic complications from tPA outweighs potential benefits in this specific scenario.
*Chronic kidney disease*
- **Chronic kidney disease (CKD)** itself is not a contraindication to tPA administration.
- The elevated creatinine and CKD stage do not directly increase the risk of hemorrhage from tPA in the absence of other bleeding diatheses.
*Atrial fibrillation on electrocardiogram*
- **Atrial fibrillation (AFib)** is a common cause of embolic stroke and does not contraindicate tPA.
- In fact, identifying AFib helps confirm the likely cardioembolic etiology of the stroke, making tPA a potentially beneficial treatment if other contraindications are absent.
*Raised blood pressures*
- While BP above 185/110 mm Hg is an absolute contraindication for tPA, the patient's current BP of **175/95 mm Hg** can typically be managed pharmacologically to below the threshold before tPA administration.
- **Hypertension** itself can be treated to enable tPA, it is not an intrinsic contraindication provided it can be lowered.
*Aspirin and clopidogrel use*
- Concurrent use of **antiplatelet agents** like aspirin and clopidogrel is not an absolute or relative contraindication for tPA.
- The combination of antiplatelets does not significantly increase the risk of hemorrhage with tPA to the extent that it would prompt deferral.
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 5: A 69-year-old male presents to the emergency department for slurred speech and an inability to use his right arm which occurred while he was eating dinner. The patient arrived at the emergency department within one hour. A CT scan was performed of the head and did not reveal any signs of hemorrhage. The patient is given thrombolytics and is then managed on the neurology floor. Three days later, the patient is recovering and is stable. He seems depressed but is doing well with his symptoms gradually improving as compared to his initial presentation. The patient complains of neck pain that has worsened slowly over the past few days for which he is being given ibuprofen. Laboratory values are ordered and return as indicated below:
Serum:
Na+: 130 mEq/L
K+: 3.7 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 7 mg/dL
Glucose: 70 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL
Ca2+: 9.7 mg/dL
Urine:
Appearance: dark
Glucose: negative
WBC: 0/hpf
Bacterial: none
Na+: 320 mEq/L/24 hours
His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), pulse is 95/min, blood pressure is 129/70 mmHg, respirations are 10/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Demeclocycline
- B. Fluid restriction (Correct Answer)
- C. Oral salt tablets
- D. Continue conservative management
- E. Conivaptan
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Fluid restriction***
- The patient presents with **hyponatremia** (Na+ 130 mEq/L) and elevated urine sodium (320 mEq/L/24 hours) in the setting of recent stroke and possible SIADH (**Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone secretion**).
- **Fluid restriction** is the initial and most crucial step in managing euvolemic hyponatremia due to SIADH, reducing water intake to allow the kidney to excrete excess water and correct serum sodium.
*Demeclocycline*
- **Demeclocycline** is a tetracycline derivative that inhibits the action of ADH on renal tubules, used in chronic or refractory cases of SIADH.
- It is *not* the first-line treatment for acute, moderate hyponatremia, especially when fluid restriction has not yet been attempted.
*Oral salt tablets*
- **Oral salt tablets** would increase the solute load but would also draw water, potentially worsening hyponatremia if unrestricted fluid intake persists in SIADH.
- This intervention is generally not appropriate for **euvolemic hyponatremia** where the primary issue is excess free water.
*Continue conservative management*
- With a sodium level of 130 mEq/L, this is considered **mild to moderate hyponatremia** and requires active intervention to prevent potential neurological complications.
- Simply continuing conservative management without addressing the underlying **hyponatremia** or its cause would be inadequate and potentially harmful.
*Conivaptan*
- **Conivaptan** is an ADH receptor antagonist that can be used for persistent or significant hyponatremia in SIADH.
- It is typically reserved for more severe or refractory cases of hyponatremia and is usually administered intravenously, making it less suitable as a first-line outpatient management strategy.
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 6: A 77-year-old woman is brought by ambulance to the emergency department after she developed weakness of her right arm along with a right-sided facial droop. By the time the ambulance arrived, she was having difficulty speaking. Past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus type II, and hyperlipidemia. She takes lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, metformin, and atorvastatin. On arrival to the emergency department, her vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, she is awake and alert but the right side of her mouth is dropping, making it difficult for her to speak clearly. Her heart has a regular rate and rhythm and her lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Fingerstick glucose is 85 mg/dL. Her right upper extremity strength is 2/5 and her left upper extremity strength is 5/5. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Obtain transcranial doppler
- B. Start tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
- C. Consult cardiology
- D. Intubate the patient
- E. Obtain noncontrast CT of the brain (Correct Answer)
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Obtain noncontrast CT of the brain***
- An **urgent noncontrast CT of the brain** is the **most crucial initial step** in managing acute neurological deficits suggestive of stroke.
- This imaging is essential to **rule out hemorrhagic stroke** before considering thrombolytic therapy like tPA.
*Obtain transcranial doppler*
- **Transcranial Doppler (TCD)** can be used to assess cerebral blood flow and identify vascular stenosis but is not the immediate first-line diagnostic imaging for an acute stroke presentation.
- TCD is typically performed **after initial imaging** to determine the presence of large vessel occlusion or monitor for vasospasm, not to differentiate between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
*Start tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)*
- While **tPA** is a treatment for acute ischemic stroke, it is **contraindicated in hemorrhagic stroke**.
- Without a **noncontrast CT scan to rule out hemorrhage**, administering tPA can be life-threatening.
*Consult cardiology*
- Consulting cardiology is important for evaluating potential cardiac sources of emboli (e.g., atrial fibrillation) as a cause of stroke but it is **not the immediate next step** in managing acute stroke symptoms.
- The **immediate priority is diagnosing the type of stroke** and determining eligibility for acute interventions.
*Intubate the patient*
- **Intubation** is reserved for patients with compromise of their **airway, breathing, or circulation (ABCs)**, or a significantly decreased level of consciousness (e.g., GCS < 8).
- This patient is described as **awake and alert**, making intubation unnecessary at this stage.
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 7: A 73-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after being found to be non-communicative by his family during dinner. On presentation he appears to be alert, though he is confused and cannot follow instructions. When he tries to speak, he vocalizes a string of fluent but unintelligible syllables. Given this presentation, his physician decides to administer tissue plasminogen activator to this patient. This intervention best represents which of the following principles?
- A. Tertiary prevention
- B. Primary prevention
- C. This does not represent prevention (Correct Answer)
- D. Quaternary prevention
- E. Secondary prevention
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***This does not represent prevention***
- The administration of **tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)** during an **acute stroke** is a **therapeutic intervention**, not a form of prevention.
- **Prevention** refers to actions taken to prevent disease occurrence, detect it early, or prevent complications after recovery. Treating an acute, symptomatic event is **acute treatment**, not prevention.
- This is an active medical intervention to treat an ongoing, symptomatic disease process (acute ischemic stroke), which falls under **therapeutic management** rather than any category of prevention.
*Secondary prevention*
- **Secondary prevention** involves **early detection** and treatment of asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic disease to prevent progression (e.g., screening mammography, colonoscopy).
- For stroke specifically, secondary prevention would include interventions **after** the acute event to **prevent recurrence**, such as starting antiplatelet therapy (aspirin, clopidogrel), anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation, statin therapy, or carotid endarterectomy after TIA.
- tPA is given during the acute symptomatic phase, making it treatment rather than secondary prevention.
*Tertiary prevention*
- **Tertiary prevention** focuses on **rehabilitation** and managing established disease to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
- Examples after stroke include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and managing post-stroke complications like depression or spasticity.
- This occurs in the recovery phase, not during acute treatment.
*Primary prevention*
- **Primary prevention** aims to prevent disease before it occurs in healthy individuals.
- Examples include controlling hypertension, managing diabetes, smoking cessation, exercise, and healthy diet - all interventions that reduce stroke risk **before** any event occurs.
*Quaternary prevention*
- **Quaternary prevention** protects patients from **overmedicalization** and excessive or harmful medical interventions.
- It involves avoiding unnecessary testing or treatment that may cause more harm than benefit.
- Administering tPA for acute stroke (when indicated) is evidence-based treatment, not overtreatment.
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 8: A 77-year-old man with a history of hypertension and a 46 pack-year smoking history presents to the emergency department from an extended care facility with acute onset of headache, nausea, vomiting, and neck pain which started 6 hours ago and has persisted since. He is alert, but his baseline level of consciousness is slightly diminished per the nursing home staff. His temperature is 99.0°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 164/94 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient's neurological exam is unremarkable with cranial nerves II-XII grossly intact and with stable gait with a walker. He is immediately sent for a head CT which is normal. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Ultrasound
- B. Lumbar puncture (Correct Answer)
- C. Alteplase
- D. Ibuprofen, acetaminophen, metoclopramide, and diphenhydramine
- E. MRI
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Lumbar puncture***
- The patient's symptoms (acute severe headache, nausea, vomiting, neck pain) and risk factors (hypertension, smoking history) are highly suggestive of a **subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)**, even with a normal initial **non-contrast head CT**.
- A **lumbar puncture (LP)** is the next critical diagnostic step to detect **xanthochromia** (due to bilirubin degradation from red blood cells) or elevated red blood cell count in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which would confirm SAH.
- CT has approximately **95% sensitivity in the first 6 hours**, but sensitivity decreases over time, making LP essential when clinical suspicion remains high.
*Ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** is not a standard diagnostic tool for acute neurological symptoms like severe headache or suspected SAH.
- It is primarily used for evaluating soft tissues, abdominal organs, and vascular structures like carotid arteries, but offers limited utility for intracranial bleeding.
*Alteplase*
- **Alteplase** (tissue plasminogen activator, tPA) is a thrombolytic agent used in acute ischemic stroke, characterized by focal neurological deficits due to arterial occlusion.
- Administering alteplase in the setting of headache and neck pain without focal deficits, while SAH is suspected, could be fatal as it would worsen bleeding.
*Ibuprofen, acetaminophen, metoclopramide, and diphenhydramine*
- This combination of medications is used for **symptomatic relief** of headache and nausea but does not address the underlying potentially life-threatening cause.
- Treating symptoms without a definitive diagnosis in suspected SAH could lead to delayed intervention and worse outcomes.
*MRI*
- While **MRI with specific sequences (FLAIR, GRE, SWI)** has high sensitivity for detecting SAH and is increasingly used in clinical practice, **lumbar puncture remains the traditional and most widely recommended next step** after a negative CT in suspected SAH.
- LP directly detects **xanthochromia** (present 6-12 hours after bleeding) and RBCs in CSF, providing definitive evidence of SAH.
- MRI may not always be readily available in the emergency setting, takes longer to perform, and requires patient stability and cooperation.
- For standardized exams, **LP is the classic correct answer** when CT is negative but clinical suspicion for SAH remains high.
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 9: A 72-year-old man is brought into clinic by his daughter for increasing confusion. The daughter states that over the past 2 weeks, she has noticed that the patient “seems to stare off into space.” She reports he has multiple episodes a day during which he will walk into a room and forget why. She is also worried about his balance. She endorses that he has had several falls, the worst being 3 weeks ago when he tripped on the sidewalk getting the mail. The patient denies loss of consciousness, pre-syncope, chest pain, palpitations, urinary incontinence, or bowel incontinence. He complains of headache but denies dizziness. He reports nausea and a few episodes of non-bloody emesis but denies abdominal pain, constipation, or diarrhea. The patient’s medical history is significant for atrial fibrillation, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and osteoarthritis. He takes aspirin, warfarin, insulin, lisinopril, simvastatin, and ibuprofen. He drinks a half glass of whisky after dinner every night and smokes a cigar on the weekends. On physical examination, he is oriented to name and place but not to date. He is unable to spell "world" backward. When asked to remember 3 words, he recalls only 2. There are no motor or sensory deficits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Ischemic stroke
- B. Subdural hematoma (Correct Answer)
- C. Vitamin B12 deficiency
- D. Alzheimer disease
- E. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Subdural hematoma***
- The patient's presentation with **gradual onset of confusion**, increasing forgetfulness, and **balance issues with falls** over a couple of weeks, especially after a fall three weeks prior, is highly suggestive of a subdural hematoma.
- His use of **warfarin** and **aspirin** significantly increases his risk for bleeding, and the **headache and nausea/vomiting** are common symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
*Ischemic stroke*
- An ischemic stroke typically presents with **acute, focal neurological deficits**, which are not described here.
- While the patient has risk factors for stroke (atrial fibrillation, hypertension, diabetes), the **gradual onset** of symptoms over weeks makes it less likely.
*Vitamin B12 deficiency*
- Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause **cognitive impairment** and neurological symptoms, but it usually develops **insidiously over months to years**, not acutely over 2 weeks.
- It is also associated with **peripheral neuropathy and megaloblastic anemia**, which are not reported.
*Alzheimer disease*
- Alzheimer's disease causes **progressive cognitive decline** over many years, starting with memory issues that gradually worsen.
- The **relatively rapid 2-week progression** of symptoms and the clear precipitating factor of a fall make Alzheimer's less likely in this acute context.
*Normal pressure hydrocephalus*
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) classically presents with a triad of **gait disturbance, urinary incontinence, and dementia**.
- While the patient has gait issues and cognitive changes, the **absence of urinary incontinence** and the relatively rapid onset after a fall makes NPH less probable.
Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old man presents to the emergency department with dizziness. He states he has experienced a sustained sensation of the room spinning that is low grade and constant since this morning. The patient occasionally feels nauseous and has been taking diphenydramine to sleep which helps with his symptoms. The patient is generally healthy, has no other medical conditions, and only endorses eating more garlic recently to get over a cold he had a few days ago. His temperature is 98.7°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 122/81 mmHg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 15/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a healthy man. The patient is sat upright, his head is turned slightly to the right, and he is laid back flat rapidly. This does not provoke any symptoms even when repeated on the left side. A nystagmus is notable on cranial nerve exam as well as bilateral decreased hearing. The patient’s tandem gait is unstable; however, his baseline gait appears unremarkable despite the patient stating he has a sustained sensation of imbalance. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Labyrinthitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Vertebrobasilar stroke
- C. Vestibular neuritis
- D. Meniere disease
- E. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
Acute ischemic stroke management Explanation: ***Labyrinthitis***
- The patient presents with **vertigo, nystagmus, and bilateral decreased hearing** following a recent cold, which is highly suggestive of **labyrinthitis**.
- **Labyrinthitis** is typically caused by a viral infection of the inner ear, affecting both the **vestibular and cochlear functions**.
*Vertebrobasilar stroke*
- While a **vertebrobasilar stroke** can cause dizziness and nystagmus, it would typically present with **focal neurological deficits** such as ataxia, dysarthria, or diplopia, which are absent here.
- The patient's otherwise healthy status and the history of a recent infection make a stroke less likely in this young individual.
*Vestibular neuritis*
- **Vestibular neuritis** presents with sudden, severe vertigo and nystagmus, but it **does not involve hearing loss**, unlike labyrinthitis.
- The patient's complaint of **bilateral decreased hearing** rules out isolated vestibular neuritis.
*Meniere disease*
- **Meniere disease** is characterized by recurrent episodes of vertigo, fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, and aural fullness.
- The patient's symptoms are described as a **sustained, constant sensation of spinning** and not episodic, making Meniere disease less likely.
*Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo*
- **BPPV** causes brief episodes of vertigo triggered by specific head movements, and it is usually diagnosed with a **positive Dix-Hallpike test**.
- The patient's symptoms are **constant and sustained**, and the **Dix-Hallpike maneuver did not provoke symptoms**, ruling out BPPV.
More Acute ischemic stroke management US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.