Stroke

On this page
🧠 Stroke: The Cerebrovascular Emergency Masterclass
Stroke remains one of neurology's most time-sensitive emergencies, where minutes determine whether brain tissue survives or dies. You'll master the pathophysiology driving ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, sharpen your clinical eye with rapid recognition tools, discriminate between critical subtypes, and command evidence-based treatment algorithms that can reverse disability. By integrating prehospital systems, acute interventions, and long-term prevention strategies, you'll build the comprehensive skillset needed to save brain tissue and transform outcomes when every second counts.
Stroke represents the ultimate neurological emergency, demanding immediate recognition, rapid assessment, and time-critical interventions. Understanding stroke pathophysiology, recognition patterns, and management algorithms transforms chaotic emergency presentations into systematic, life-saving protocols.
⭐ Critical Concept: Stroke kills 1.9 million neurons per minute during acute ischemia, making time-to-treatment the most crucial prognostic factor
The stroke care continuum spans from pre-hospital recognition through acute intervention to long-term rehabilitation, requiring mastery of multiple clinical domains. Each phase demands specific knowledge frameworks, from FAST screening protocols to complex endovascular procedures.
📌 Remember: BEFAST - Balance, Eyes, Face, Arms, Speech, Time (expanded stroke recognition mnemonic covering posterior circulation and visual field defects)
| Stroke Type | Incidence | Mortality | Key Mechanism | Time Window | Primary Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ischemic | 87% | 10-15% | Thromboembolism | 4.5 hours | IV thrombolysis |
| ICH | 10% | 40-50% | Vessel rupture | <6 hours | BP control |
| SAH | 3% | 25-50% | Aneurysm rupture | <24 hours | Aneurysm securing |
-
Acute Recognition
- FAST/BEFAST screening protocols with 85% sensitivity
- NIHSS scoring for severity assessment (0-42 scale)
- Door-to-needle targets of <60 minutes
- CT interpretation within 25 minutes
- Laboratory results within 45 minutes
- Physician assessment within 10 minutes
-
Therapeutic Interventions
- IV alteplase for eligible patients (6-13% of all strokes)
- Mechanical thrombectomy for large vessel occlusions (10-15% of strokes)
- Blood pressure management with specific targets per stroke type
💡 Master This: Time is brain - every 15-minute delay in treatment reduces good outcomes by 4%, making systematic protocols essential for optimal results
Connect these foundational concepts through pathophysiology mechanisms to understand how different stroke types require distinct management approaches.
🧠 Stroke: The Cerebrovascular Emergency Masterclass
⚡ Stroke Pathophysiology: The Vascular Catastrophe Engine
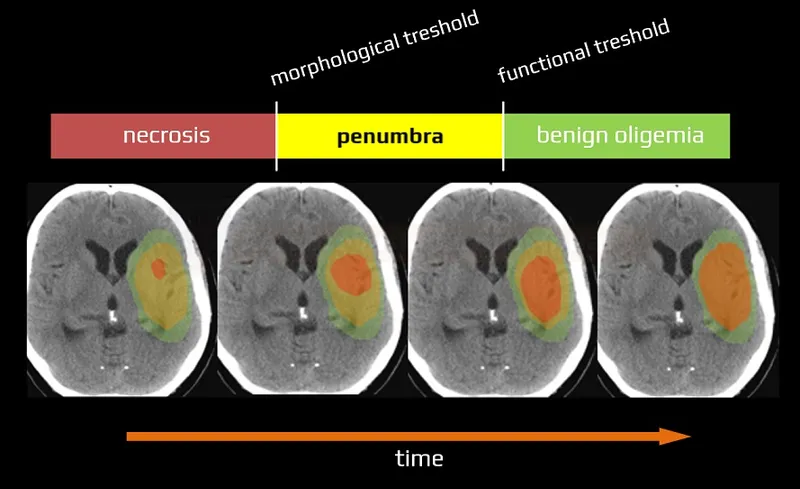
Stroke pathophysiology centers on the ischemic cascade - a series of cellular events triggered when cerebral blood flow falls below critical thresholds. Understanding this cascade explains why time-sensitive interventions work and guides therapeutic targeting.
📌 Remember: PENUMBRA - Potentially Endangered Neurons Under Metabolic Burden Requiring Acute intervention (the salvageable brain tissue surrounding infarct core)
The ischemic cascade progresses through distinct phases:
-
Immediate Phase (0-6 minutes)
- ATP depletion within 2-4 minutes
- Na+/K+ pump failure leading to cellular swelling
- Membrane depolarization with massive K+ efflux
- Extracellular K+ rises from 3 mEq/L to >50 mEq/L
- Cellular swelling increases tissue volume by 10-15%
- Glutamate release increases 10-fold above baseline
-
Early Phase (6 minutes-2 hours)
- Excitotoxicity from glutamate release (>100 μM concentrations)
- Calcium influx triggering enzymatic cascades
- Free radical formation with lipid peroxidation
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The penumbra can survive up to 6-8 hours in some patients, explaining why extended time windows for thrombectomy (up to 24 hours) can still provide benefit
| CBF Threshold | Tissue State | Clinical Significance | Intervention Window |
|---|---|---|---|
| >50 mL/100g/min | Normal function | Asymptomatic | Prevention focus |
| 20-50 mL/100g/min | Penumbra | Salvageable | <6-24 hours |
| 10-20 mL/100g/min | Severe ischemia | Rapid progression | <4.5 hours |
| <10 mL/100g/min | Core infarction | Irreversible | Supportive care |
-
Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH)
- Direct tissue destruction from mass effect
- Secondary injury from perihematomal edema (peaks at 24-48 hours)
- Inflammatory cascade with microglial activation
- Hematoma expansion in 20-30% of patients within 6 hours
- Perihematomal edema increases volume by 75-100% over 72 hours
-
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
- Vasospasm affecting 30-70% of patients (days 4-14)
- Delayed cerebral ischemia in 20-30% of cases
- Hydrocephalus requiring intervention in 15-20%
💡 Master This: Collateral circulation determines penumbra survival - patients with robust leptomeningeal collaterals can maintain viable tissue for 12-24 hours, explaining individual variation in treatment windows
Understanding these pathophysiological mechanisms through clinical recognition patterns reveals why rapid assessment and intervention protocols save brain tissue and improve outcomes.
⚡ Stroke Pathophysiology: The Vascular Catastrophe Engine
🎯 Stroke Recognition: The FAST-Track Diagnostic Arsenal

Stroke recognition transforms from chaotic emergency presentations into systematic diagnostic frameworks through validated screening tools and structured assessments. Mastering these tools enables rapid triage and appropriate intervention selection.
📌 Remember: BEFAST - Balance (ataxia), Eyes (visual field cuts), Face (droop), Arms (weakness), Speech (aphasia), Time (onset) - captures 95% of stroke presentations including posterior circulation
BEFAST Screening Protocol provides systematic stroke recognition:
-
Balance - Sudden loss of coordination
- Tests cerebellar and brainstem function
- Positive in 85% of posterior circulation strokes
- Often missed by traditional FAST screening
- Acute vertigo with nystagmus
- Truncal ataxia preventing sitting
- Limb dysmetria on finger-nose testing
-
Eyes - Visual field defects or diplopia
- Homonymous hemianopia in 30% of strokes
- Diplopia suggests brainstem involvement
- Gaze deviation toward lesion side
- Conjugate gaze palsy in 40% of large MCA strokes
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia in brainstem strokes
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Gaze preference toward the lesion occurs in 60% of large hemispheric strokes and correlates with NIHSS >15 and poor outcomes
| BEFAST Component | Sensitivity | Specificity | Key Clinical Signs | Time to Assess |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balance | 85% | 70% | Ataxia, vertigo | 30 seconds |
| Eyes | 75% | 85% | Field cuts, diplopia | 45 seconds |
| Face | 90% | 80% | Asymmetric droop | 15 seconds |
| Arms | 95% | 75% | Unilateral weakness | 30 seconds |
| Speech | 85% | 90% | Slurred, absent | 30 seconds |
- Consciousness Assessment (Items 1a-1c)
- 1a: Level of consciousness (0-3 scale)
- 1b: Orientation questions (0-2 scale)
- 1c: Commands (0-2 scale)
- NIHSS 0-4: Minor stroke (90% good outcomes)
- NIHSS 5-15: Moderate stroke (60% good outcomes)
- NIHSS 16-20: Moderate-severe (30% good outcomes)
- NIHSS >20: Severe stroke (<15% good outcomes)
Stroke Mimics account for 25-30% of stroke alerts and require systematic exclusion:
-
Metabolic Causes (40% of mimics)
- Hypoglycemia (<50 mg/dL) causing focal deficits
- Hyponatremia (<120 mEq/L) with altered mental status
- Uremia with encephalopathy and focal signs
- Seizure with Todd's paralysis (15% of mimics)
- Migraine with aura (10% of mimics)
- Conversion disorder (8% of mimics)
-
Infectious/Inflammatory (20% of mimics)
- Encephalitis with focal neurological signs
- Brain abscess mimicking acute stroke
- Multiple sclerosis exacerbation
💡 Master This: NIHSS >15 with large vessel territory symptoms triggers immediate CTA and thrombectomy team activation - don't wait for IV tPA completion
Advanced recognition patterns through systematic assessment frameworks enable rapid differentiation between stroke types and guide appropriate therapeutic interventions.
🎯 Stroke Recognition: The FAST-Track Diagnostic Arsenal
🔬 Stroke Subtype Analysis: The Pathological Discrimination Matrix
📌 Remember: HEMORRHAGE - Headache, Elevated BP, Meningismus, Obtundation, Rapid onset, Reduced consciousness, Hypertensive history, Age >55, GCS <15, Emesis (clinical predictors of ICH)
Ischemic Stroke Patterns (87% of all strokes) demonstrate characteristic clinical and imaging features:
-
Large Vessel Occlusion (15-20% of ischemic strokes)
- NIHSS typically >6 with cortical signs
- Dense hemiplegia with cortical dysfunction
- Gaze deviation toward lesion (60% of cases)
- MCA occlusion: Hemiplegia + aphasia/neglect
- ICA occlusion: NIHSS >15 with multi-territory involvement
- Basilar occlusion: Coma or locked-in syndrome
-
Small Vessel Disease (25% of ischemic strokes)
- Pure motor or pure sensory syndromes
- Lacunar syndromes with NIHSS <5
- No cortical signs (aphasia, neglect, hemianopia)
- Hypertensive history in >80%
- Diabetes present in >60%
- Chronic kidney disease in >40%
| Stroke Subtype | Clinical Pattern | NIHSS Range | Key Imaging | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Vessel | Cortical signs | >6 | Vessel occlusion | 30% good outcome |
| Small Vessel | Pure syndromes | <5 | Small infarcts | >80% good outcome |
| Cardioembolic | Sudden, maximal | Variable | Multiple territories | 50% good outcome |
| ICH | Headache, ↓GCS | >10 | Hyperdense lesion | 40% mortality |
| SAH | Thunderclap HA | Variable | Subarachnoid blood | 25% mortality |
-
Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) (10% of strokes)
- Gradual onset over minutes to hours
- Headache in 50%, nausea/vomiting in 40%
- Decreased consciousness more common than ischemic
- Hypertensive ICH: Basal ganglia (40%), thalamus (15%)
- Lobar ICH: Consider amyloid angiopathy (age >70)
- Cerebellar ICH: Hydrocephalus risk, surgical emergency
-
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) (3% of strokes)
- Thunderclap headache - "worst headache of life"
- Sudden onset reaching maximum intensity in <1 minute
- Meningeal signs in >80% within 6 hours
- Hunt-Hess Grade 1-2: Good prognosis (>90% survival)
- Hunt-Hess Grade 4-5: Poor prognosis (<30% good outcome)
Advanced Discrimination Techniques enhance diagnostic accuracy:
- Clinical Scoring Systems
- SEDAN Score for ICH expansion risk (0-6 scale)
- ICH Score for 30-day mortality (0-6 scale)
- ABCD2 Score for TIA stroke risk (0-7 scale)
- SEDAN ≥2: High expansion risk (>50%)
- ICH Score ≥4: High mortality (>80%)
- ABCD2 ≥4: High stroke risk (>8% at 48 hours)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Microbleeds on gradient echo MRI predict ICH risk with thrombolysis - >10 microbleeds increases ICH risk 3-fold
💡 Master This: Time of onset determination drives all therapeutic decisions - last known normal time defines treatment windows, not symptom discovery time
Systematic subtype analysis through evidence-based discrimination frameworks enables precise therapeutic targeting and accurate prognostic assessment for optimal stroke outcomes.
🔬 Stroke Subtype Analysis: The Pathological Discrimination Matrix
⚕️ Stroke Treatment Algorithms: The Therapeutic Command Center
📌 Remember: CLOTS - CT scan, Labs, Obtain IV access, Time of onset, Start treatment (parallel processing for stroke workup efficiency)
IV Thrombolysis Protocol represents the cornerstone of acute ischemic stroke treatment:
-
Inclusion Criteria (must meet ALL)
- Age ≥18 years with ischemic stroke
- Onset <4.5 hours from last known normal
- NIHSS ≥4 (or disabling deficit)
- Measurable neurological deficit
- No rapidly improving symptoms
- No minor, isolated symptoms
-
Absolute Contraindications (any ONE excludes treatment)
- ICH on imaging or prior ICH history
- Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis
- Recent surgery (<14 days) or trauma (<3 months)
- Platelet count <100,000/μL
- INR >1.7 or PT >15 seconds
- Heparin use with elevated aPTT
Mechanical Thrombectomy Indications extend treatment windows for selected patients:
-
Core Criteria (must meet ALL)
- Large vessel occlusion (ICA, M1, M2, basilar)
- NIHSS ≥6 with disabling deficit
- ASPECTS ≥6 or favorable perfusion imaging
- 0-6 hours: Clinical + non-contrast CT sufficient
- 6-24 hours: Perfusion imaging required
- Basilar occlusion: Consider up to 24 hours
-
Extended Window Criteria (6-24 hours)
- DAWN criteria: Age-adjusted NIHSS thresholds
- DEFUSE-3 criteria: Mismatch ratio ≥1.8
- Ischemic core <70 mL on CT perfusion
- Age <80 with NIHSS ≥10
- Age ≥80 with NIHSS ≥20
- Mismatch volume ≥15 mL
| Time Window | Imaging Required | NIHSS Threshold | Success Rate | Good Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-6 hours | Non-contrast CT | ≥6 | 85-90% | 45-50% |
| 6-16 hours | CT/MR perfusion | ≥10 | 80-85% | 35-40% |
| 16-24 hours | MR perfusion | ≥20 | 75-80% | 25-30% |
-
Ischemic Stroke - Permissive hypertension
- Target <185/110 mmHg before thrombolysis
- Target <180/105 mmHg after thrombolysis
- Avoid aggressive lowering (may worsen penumbra)
- Labetalol 10-20 mg IV every 10-20 minutes
- Nicardipine 5 mg/hr IV titrated by 2.5 mg/hr
- Clevidipine 1-2 mg/hr IV doubled every 2-5 minutes
-
Hemorrhagic Stroke - Aggressive lowering
- ICH target: SBP <140 mmHg within 1 hour
- SAH target: SBP <160 mmHg (unless vasospasm)
- Rapid, sustained reduction prevents expansion
- Nicardipine or clevidipine preferred
- Avoid sublingual nifedipine (precipitous drops)
- Monitor neurological status during reduction
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Door-to-needle <60 minutes achieved in >75% of stroke centers improves outcomes by 15-20% compared to longer intervals
💡 Master This: Bridging therapy (IV tPA + thrombectomy) provides better outcomes than thrombectomy alone for large vessel occlusions - don't delay tPA while preparing for thrombectomy
Advanced treatment algorithms through systematic intervention protocols maximize therapeutic benefit while minimizing complications across the acute stroke care continuum.
⚕️ Stroke Treatment Algorithms: The Therapeutic Command Center
🔄 Stroke Systems Integration: The Comprehensive Care Network
Stroke systems integration transforms fragmented care episodes into coordinated, evidence-based pathways that span from acute intervention through long-term recovery. This integration optimizes outcomes through systematic care coordination and standardized protocols.
📌 Remember: STROKE TEAM - Specialists, Therapists, Rapid response, Organized care, Kinetic rehabilitation, Education, Transition planning, Emergency protocols, Assessment tools, Monitoring systems (comprehensive care elements)
Acute Care Integration coordinates multiple simultaneous interventions:
-
Emergency Department Protocols
- Stroke alert activation within 15 minutes of arrival
- CT completion within 25 minutes of arrival
- Laboratory results within 45 minutes
- Glucose, CBC, PT/INR, aPTT
- Basic metabolic panel with creatinine
- Troponin and ECG for cardiac evaluation
- Pregnancy test for women of childbearing age
-
Specialist Consultation Pathways
- Neurology evaluation within 60 minutes
- Neurosurgery for ICH >30 mL or cerebellar stroke
- Interventional neuroradiology for thrombectomy candidates
- Telemedicine consultation for remote hospitals
- Transfer protocols for comprehensive stroke centers
- Critical care management for severe strokes
Stroke Unit Care provides specialized monitoring and intervention:
-
Multidisciplinary Team Composition
- Stroke-trained nurses with 1:4 patient ratios
- Physical therapy assessment within 24 hours
- Occupational therapy for ADL evaluation
- Speech-language pathology for swallowing assessment
- Social work for discharge planning
- Pharmacy for medication reconciliation
- Nutrition for dysphagia management
-
Monitoring Protocols (first 72 hours)
- Neurological checks every 2-4 hours
- Blood pressure monitoring every 15 minutes (post-tPA)
- Glucose management (target 140-180 mg/dL)
- Temperature control (<100.4°F)
- Oxygen saturation monitoring (>94%)
- Cardiac monitoring for arrhythmias
| Care Component | Timeline | Success Metric | Outcome Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Treatment | 0-24 hours | Door-to-needle <60 min | 15-20% better outcomes |
| Stroke Unit | 1-7 days | Early mobilization | 25% mortality reduction |
| Rehabilitation | 3-90 days | Therapy intensity | 30% functional improvement |
| Secondary Prevention | Lifelong | Risk factor control | 80% recurrence reduction |
-
Early Mobilization (within 24-48 hours)
- Progressive mobility from bed to chair
- Swallowing assessment before oral intake
- Fall prevention protocols for safety
- Physical therapy 3-5 sessions/week
- Occupational therapy for ADL training
- Speech therapy for communication/swallowing
-
Discharge Planning (begins day 1)
- Functional assessment using modified Rankin Scale
- Home safety evaluation and equipment needs
- Caregiver training for assistance requirements
- Medication management education
- Follow-up appointments scheduling
- Emergency contact information
Secondary Prevention Systems prevent recurrent events:
-
Risk Factor Management
- Blood pressure target <130/80 mmHg
- LDL cholesterol target <70 mg/dL
- HbA1c target <7% for diabetics
- Antiplatelet therapy (aspirin 75-100 mg daily)
- Statin therapy (high-intensity for most patients)
- Anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation
-
Lifestyle Interventions
- Smoking cessation programs (reduces risk 50%)
- Cardiac rehabilitation for exercise training
- Dietary counseling for Mediterranean diet
- Weight management (BMI <25 kg/m²)
- Alcohol moderation (<2 drinks/day men, <1 drink/day women)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Stroke unit care reduces death or dependency by 25% compared to general medical wards, regardless of patient age or stroke severity
💡 Master This: Comprehensive stroke centers achieve 40% better functional outcomes for large vessel occlusions compared to primary stroke centers - transfer protocols save lives
Integrated stroke systems through coordinated care pathways optimize outcomes across the entire continuum from acute intervention through long-term recovery and secondary prevention.
🔄 Stroke Systems Integration: The Comprehensive Care Network
🎯 Stroke Mastery: The Clinical Excellence Toolkit
📌 Remember: MASTER STROKE - Monitor vitals, Assess deficits, Systematic imaging, Time-critical decisions, Emergency protocols, Rehabilitation planning, Secondary prevention, Team coordination, Risk stratification, Outcome optimization, Knowledge integration, Evidence application (comprehensive mastery framework)
Essential Clinical Arsenal for stroke expertise:
-
Time-Critical Thresholds
- Door-to-CT: <25 minutes
- Door-to-needle: <60 minutes
- Door-to-groin: <90 minutes
- Last known normal to IV tPA: <4.5 hours
- Symptom onset to thrombectomy: <24 hours (selected)
- ICH expansion risk highest: <6 hours
-
Critical Assessment Scores
- NIHSS 0-4: Minor stroke (>90% good outcome)
- NIHSS 5-15: Moderate stroke (60% good outcome)
- NIHSS >20: Severe stroke (<15% good outcome)
- ASPECTS ≥6: Thrombectomy candidate
- mRS 0-2: Functional independence
- ICH Score ≥4: >80% mortality
| Clinical Tool | Application | Key Thresholds | Decision Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| BEFAST | Recognition | 85% sensitivity | Stroke activation |
| NIHSS | Severity | >6 for LVO | Treatment selection |
| ASPECTS | Imaging | ≥6 for EVT | Thrombectomy decision |
| mRS | Outcome | 0-2 independence | Prognosis/goals |
-
Hemorrhage Exclusion (<15 minutes)
- Non-contrast CT interpretation
- Hyperdense lesions indicate ICH
- Subarachnoid blood in cisterns/sulci
- Hypodense areas suggest established infarct
- Normal CT within 6 hours of ischemic stroke
- Mass effect indicates large territory involvement
-
Treatment Pathway Selection
- IV tPA eligible: Standard protocol
- Large vessel occlusion: Thrombectomy pathway
- ICH: Blood pressure and reversal agents
- Minor stroke (NIHSS <4): Rapid discharge planning
- Stroke mimic: Alternative diagnosis workup
- Wake-up stroke: Advanced imaging for tissue selection
Prognostic Assessment Tools guide realistic goal-setting:
-
Functional Outcome Predictors
- Age >80: Reduced recovery potential
- Pre-stroke mRS >2: Limited improvement expected
- NIHSS >15: High disability risk
- Diabetes: Slower recovery patterns
- Atrial fibrillation: Higher recurrence risk
- Prior stroke: Cumulative deficits
-
Complication Risk Stratification
- Malignant edema: Age <60, >50% MCA territory
- Hemorrhagic transformation: Large infarcts, anticoagulation
- Pneumonia: Dysphagia, decreased consciousness
- DVT/PE: Immobilization >3 days
- Depression: >30% of stroke survivors
- Seizures: Cortical involvement, hemorrhagic stroke
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Golden Hour protocols achieving door-to-needle <60 minutes improve good outcomes by 15-20% - every 15-minute delay reduces benefit by 4%
💡 Master This: Stroke systems of care with comprehensive protocols reduce mortality by 25% and disability by 30% - systematic approaches save brains and lives
Quality Metrics for stroke care excellence:
-
Process Measures
- IV tPA rate: >15% of ischemic strokes
- Door-to-needle time: >75% within 60 minutes
- Thrombectomy rate: >2% of all strokes
- Stroke unit admission: >80% of patients
- Dysphagia screening: >95% before oral intake
- Discharge on antithrombotic: >95% of ischemic strokes
-
Outcome Measures
- Symptomatic ICH: <6% with IV tPA
- Good functional outcome: >40% at 90 days
- Mortality: <10% for ischemic, <30% for ICH
- Length of stay: <5 days median
- Readmission rate: <15% at 30 days
- Patient satisfaction: >90% recommend hospital
Stroke mastery through systematic knowledge integration and evidence-based protocols transforms complex neurological emergencies into manageable, outcome-optimized care pathways.
🎯 Stroke Mastery: The Clinical Excellence Toolkit
Practice Questions: Stroke
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 78-year-old woman is accompanied by her family for a routine visit to her primary care provider. The family states that 5 months prior, the patient had a stroke and is currently undergoing physical therapy. Today, her temperature is 98.2°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 112/72 mmHg, pulse is 64/min, and respirations are 12/min. On exam, she is alert and oriented with no deficits in speech. Additionally, her strength and sensation are symmetric and preserved bilaterally. However, on further neurologic testing, she appears to have some difficulty with balance and a propensity to fall to her right side. Which of the following deficits does the patient also likely have?











