Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Initial resuscitation in sepsis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 1: A 61-year-old female with congestive heart failure and type 2 diabetes is brought to the emergency room by her husband because of an altered mental status. He states he normally helps her be compliant with her medications, but he had been away for several days. On physical exam, her temperature is 37.2 C, BP 85/55, and HR 130. Serum glucose is 500 mg/dL. Which of the following is the first step in the management of this patient?
- A. IV ½ NS
- B. IV insulin
- C. Subcutaneous insulin injection
- D. IV NS (Correct Answer)
- E. IV D5W
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***IV NS***
- The patient presents with **hypotension (85/55 mmHg)** and **tachycardia (130 bpm)**, indicating significant **volume depletion** despite a history of congestive heart failure.
- **Isotonic intravenous fluids (e.g., normal saline)** are crucial in the initial management of **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** or **hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)** to restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion.
*IV ½ NS*
- **Hypotonic solutions** such as IV ½ NS are typically used later in DKA/HHS management, once the patient's **hemodynamic stability** has been achieved and serum sodium levels are stable or elevated.
- Administering hypotonic fluids to an already **hypotensive and volume-depleted patient** could worsen hypotension and potentially lead to cerebral edema if not carefully monitored.
*IV insulin*
- While insulin is essential for correcting hyperglycemia, it is administered **after or concurrently with fluid resuscitation** to avoid worsening hypovolemia as it drives glucose and potassium into cells, potentially causing **hypokalemia** and further **hemoconcentration**.
- **Fluid resuscitation** should always precede or be initiated simultaneously with insulin therapy, especially in cases of hemodynamic instability.
*Subcutaneous insulin injection*
- **Subcutaneous insulin** is not appropriate for initial management in this critically ill patient due to its **slower onset of action** and potentially **erratic absorption** in hypotensive and poorly perfused states.
- **Intravenous insulin** is preferred in DKA/HHS for its rapid, titratable effect.
*IV D5W*
- **Dextrose 5% in water (D5W)** is a hypotonic solution primarily used when **blood glucose levels fall below 250 mg/dL** during DKA/HHS treatment to prevent hypoglycemia.
- Administering D5W in a patient with a **serum glucose of 500 mg/dL** would further elevate blood sugar and worsen the hyperosmolar state.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of a 1-month history of worsening fatigue, loss of appetite, and decreased energy. More recently, she has also had intermittent abdominal pain and nausea. She is at the 50th percentile for height and 15th percentile for weight. Her pulse is 119/min and blood pressure is 85/46 mm Hg. Physical examination shows darkened skin and bluish-black gums. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Serum studies show:
Sodium 133 mEq/L
Potassium 5.3 mEq/L
Bicarbonate 20 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 16 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
Glucose 72 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Succimer
- B. Deferoxamine
- C. Norepinephrine
- D. Isoniazid + rifampin + pyrazinamide + ethambutol
- E. Glucocorticoids (Correct Answer)
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Glucocorticoids***
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, anorexia, abdominal pain, hypotension, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia) combined with **darkened skin** and **bluish-black gums** are highly suggestive of **adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease)**. The blackened gums are due to increased **melanin deposition**.
- **Glucocorticoid replacement therapy** (e.g., hydrocortisone) is the mainstay treatment for adrenal insufficiency to replace deficient hormones.
*Succimer*
- This is a **chelating agent** used for **lead poisoning**, which presents with symptoms like abdominal pain, fatigue, and neurological issues, but not typically darkened skin or characteristic electrolyte imbalances and gum findings seen here.
- While lead poisoning can cause **encephalopathy** and developmental delays, it doesn't cause the distinct presentation of Addison's crisis.
*Deferoxamine*
- This is a **chelating agent** primarily used for **iron overload** (hemochromatosis or acute iron poisoning), which can cause fatigue and abdominal pain, but not the specific skin pigmentation, hypotension, and electrolyte disturbances of adrenal insufficiency.
- Iron overload can damage organs like the liver and heart but does not typically cause adrenal crisis.
*Norepinephrine*
- While the patient is hypotensive, **norepinephrine** is a **vasopressor** used to acutely manage severe hypotension, typically in shock states.
- It would not address the underlying **hormone deficiency** in adrenal insufficiency, which requires glucocorticoid replacement.
*Isoniazid + rifampin + pyrazinamide + ethambutol*
- This is the standard 4-drug regimen for treating **active tuberculosis**.
- Although tuberculosis can rarely lead to adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease) as a secondary complication, the primary treatment for the adrenal crisis itself is **glucocorticoid replacement**, not anti-tuberculosis drugs in the acute setting unless active TB is confirmed and directly causing the insufficiency.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 3: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency room because of severe, acute diarrhea. He is drowsy with a dull, lethargic appearance. He has sunken eyes, poor skin turgor, and dry oral mucous membranes and tongue. He has a rapid, thready pulse with a systolic blood pressure of 60 mm Hg and his respirations are 33/min. His capillary refill time is 6 sec. He has had no urine output for the past 24 hours. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in treatment?
- A. Start IV fluid resuscitation by administering colloid solutions
- B. Provide oral rehydration therapy to correct dehydration
- C. Give initial IV bolus of 2 L of Ringer’s lactate, followed by packed red cells, fresh frozen plasma, and platelets in a ratio of 1:1:1
- D. Start IV fluid resuscitation with normal saline or Ringer’s lactate, along with monitoring of vitals and urine output (Correct Answer)
- E. Give antidiarrheal drugs
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Start IV fluid resuscitation with normal saline or Ringer's lactate, along with monitoring of vitals and urine output***
- This patient presents with **severe dehydration** and **hypovolemic shock** (lethargy, sunken eyes, poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, rapid thready pulse, hypotension [systolic BP 60 mmHg], tachypnea, prolonged capillary refill >5 seconds, and anuria).
- According to **PALS guidelines**, the immediate priority is rapid intravenous administration of **isotonic crystalloids** (normal saline or Ringer's lactate) given as **20 mL/kg boluses** over 5-20 minutes, repeated as needed based on clinical response.
- Close monitoring of vital signs, mental status, perfusion (capillary refill), and urine output is essential to assess response to resuscitation and guide further fluid management.
*Start IV fluid resuscitation by administering colloid solutions*
- While colloids (albumin, synthetic colloids) can expand intravascular volume, **isotonic crystalloids** are preferred for initial resuscitation in severe dehydration per **WHO and PALS guidelines**.
- Crystalloids are equally effective, more readily available, less expensive, and have fewer potential adverse effects compared to colloids in pediatric dehydration.
- There is no proven survival benefit of colloids over crystalloids in this clinical scenario.
*Provide oral rehydration therapy to correct dehydration*
- **Oral rehydration therapy (ORT)** is the appropriate first-line treatment for **mild to moderate dehydration** in children who can tolerate oral intake.
- However, ORT is **contraindicated** in patients with **severe dehydration** or **hypovolemic shock**, particularly those with altered mental status, inability to drink, or hemodynamic instability.
- This patient's drowsiness, hypotension, and signs of shock require immediate IV resuscitation; ORT would be too slow and potentially dangerous.
*Give initial IV bolus of 2 L of Ringer's lactate, followed by packed red cells, fresh frozen plasma, and platelets in a ratio of 1:1:1*
- A 2-liter bolus is **excessive and dangerous** for a 7-year-old child (average weight ~23 kg); the appropriate initial bolus is **20 mL/kg** (~460 mL), which can be repeated based on response.
- The **1:1:1 massive transfusion protocol** (packed RBCs, FFP, platelets) is indicated for **hemorrhagic shock** with significant blood loss, not for hypovolemic shock from dehydration.
- There is no evidence of bleeding or coagulopathy in this patient; blood products are not indicated.
*Give antidiarrheal drugs*
- **Antidiarrheal agents** (loperamide, diphenoxylate) are **contraindicated** in young children with acute infectious diarrhea, as they can prolong illness, increase risk of complications (toxic megacolon, bacterial overgrowth), and mask serious underlying conditions.
- The priority in severe dehydration is **fluid and electrolyte resuscitation**, not stopping the diarrhea.
- The diarrhea typically resolves once the underlying infection is controlled and hydration is restored.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 4: A 23-year-old man presents to the emergency department with shortness of breath. The patient was at a lunch hosted by his employer. He started to feel his symptoms begin when he started playing football outside with a few of the other employees. The patient has a past medical history of atopic dermatitis and asthma. His temperature is 98.3°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 87/58 mmHg, pulse is 150/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 85% on room air. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Albuterol and prednisone
- B. IV epinephrine
- C. IV fluids and 100% oxygen
- D. Albuterol and norepinephrine
- E. IM epinephrine (Correct Answer)
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***IM epinephrine***
- The patient presents with **signs of anaphylaxis**, including acute onset shortness of breath, hypotension (BP 87/58 mmHg), tachycardia (HR 150/min), and hypoxia (SpO2 85%). Given his history of atopic dermatitis and asthma, he is at high risk for severe allergic reactions.
- **Intramuscular epinephrine** is the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis as it acts rapidly to constrict blood vessels, relax airway smooth muscle, and reduce swelling, addressing both cardiovascular collapse and respiratory distress.
*Albuterol and prednisone*
- While **albuterol** (a bronchodilator) might help with bronchoconstriction, and **prednisone** (a corticosteroid) can reduce inflammation, these are not the immediate priority for severe anaphylaxis.
- They act too slowly to counteract the rapid, systemic effects of anaphylaxis, particularly the life-threatening hypotension and airway compromise.
*IV epinephrine*
- **Intravenous epinephrine** is reserved for severe, refractory cases of anaphylaxis, or for patients already receiving IV infusions in a critical care setting.
- Administering IV epinephrine requires careful titration due to the risk of arrhythmias and hypertension, and IM administration is preferred as the initial rapid response.
*IV fluids and 100% oxygen*
- **IV fluids** are crucial to address the distributive shock and hypotension in anaphylaxis, and **100% oxygen** is essential for hypoxia, but these are supportive measures.
- They do not address the underlying immunological mechanism driving the severe allergic reaction as directly and effectively as epinephrine.
*Albuterol and norepinephrine*
- **Albuterol** can help with bronchospasm, but it is insufficient for systemic anaphylaxis. **Norepinephrine** is a potent vasopressor used for severe shock.
- While norepinephrine can raise blood pressure, it does not have the broader beneficial effects of epinephrine on mast cell degranulation, airway dilation, and stabilization of vascular permeability, making it a secondary agent.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 5: A 57-year-old man is admitted to the burn unit after he was brought to the emergency room following an accidental fire in his house. His past medical history is unknown due to his current clinical condition. Currently, his blood pressure is 75/40 mmHg, pulse rate is 140/min, and respiratory rate is 17/min. The patient is subsequently intubated and started on aggressive fluid resuscitation. A Swan-Ganz catheter is inserted to clarify his volume status. Which of the following hemodynamic parameters would you expect to see in this patient?
- A. Cardiac output: ↓, systemic vascular resistance: ↔, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔
- B. Cardiac output: ↑, systemic vascular resistance: ↑, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔
- C. Cardiac output: ↑, systemic vascular resistance: ↓, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔
- D. Cardiac output: ↓, systemic vascular resistance: ↑, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↓ (Correct Answer)
- E. Cardiac output: ↔, systemic vascular resistance: ↔, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Cardiac output: ↓, systemic vascular resistance: ↑, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↓***
- The patient's **hypotension (75/40 mmHg)** and **tachycardia (140/min)**, combined with severe burns, indicate **hypovolemic shock** due to massive fluid loss from damaged capillaries.
- In response to decreased cardiac output and hypovolemia, the body compensates by increasing **systemic vascular resistance (SVR)** to maintain perfusion to vital organs, and **pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP)** will be low due to reduced intravascular volume.
*Cardiac output: ↓, systemic vascular resistance: ↔, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔*
- This option incorrectly suggests that systemic vascular resistance and pulmonary artery wedge pressure would be normal, which is inconsistent with **hypovolemic shock**.
- In shock, the body's compensatory mechanisms would lead to significant changes in SVR and PAWP, not maintain them at baseline.
*Cardiac output: ↑, systemic vascular resistance: ↑, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔*
- Increased cardiac output is usually seen in **distributive shock** (e.g., septic shock) where vasodilation leads to reduced SVR, not increased SVR as suggested here.
- An elevated SVR coupled with an increased cardiac output would typically result in a higher blood pressure unless there is a compensatory drop in other parameters.
*Cardiac output: ↑, systemic vascular resistance: ↓, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔*
- This pattern (high cardiac output, low SVR) is characteristic of **distributive shock**, such as **septic shock** or anaphylactic shock, rather than the hypovolemic shock expected in a burn patient.
- Severe burns primarily cause massive fluid shifts, leading to hypovolemia and a reduced cardiac output, not an elevated one.
*Cardiac output: ↔, systemic vascular resistance: ↔, pulmonary artery wedge pressure: ↔*
- This scenario represents **normal hemodynamic parameters**, which would not be expected in a patient experiencing severe shock from extensive burns.
- The patient's clinical presentation (hypotension, tachycardia) clearly indicates a state of hemodynamic instability.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 6: A 68-year-old woman presents to the hospital for an elective right hemicolectomy. She is independently mobile and does her own shopping. She has had type 2 diabetes mellitus for 20 years, essential hypertension for 15 years, and angina on exertion for 6 years. She has a 30-pack-year history of smoking. The operation was uncomplicated. On post-op day 5, she becomes confused. She has a temperature of 38.5°C (101.3°F), respiratory rate of 28/min, and oxygen saturation of 92% on 2 L of oxygen. She is tachycardic at 118/min and her blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg. On chest auscultation, she has coarse crackles in the right lung base. Her surgical wound appears to be healing well, and her abdomen is soft and nontender. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Malignant hyperthermia
- B. Drug-induced fever
- C. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
- D. Sepsis (Correct Answer)
- E. Non-infectious systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Sepsis***
- The patient exhibits several signs of **systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)** (fever, tachycardia, tachypnea) coupled with evidence of infection (coarse crackles in the lung base suggests **pneumonia**).
- The combination of **SIRS criteria** and a likely infection source in a postoperative patient strongly points to sepsis, a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection.
*Malignant hyperthermia*
- This is a rare, life-threatening condition typically triggered by **volatile anesthetic agents** or **succinylcholine** during surgery.
- It usually presents **intraoperatively or immediately postoperatively** with rapid onset of hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, and metabolic acidosis, which is not consistent with a presentation on post-op day 5.
*Drug-induced fever*
- While drug-induced fever is possible, particularly in polymedicated patients, it would be a **diagnosis of exclusion** when other more likely causes of fever, such as infection, are present.
- There are no specific clinical features in this case that strongly suggest a drug as the singular cause of fever and the systemic inflammatory response.
*Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome*
- **MODS** is the progressive failure of two or more organ systems and is often a **complication of severe sepsis or septic shock**, rather than an initial diagnosis.
- While the patient is unwell, her current presentation describes a potential precursor (sepsis) rather than established multi-organ dysfunction.
*Non-infectious systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)*
- SIRS caused by non-infectious etiologies (e.g., pancreatitis, trauma, burns) can occur, but the presence of **localized lung crackles** and a **postoperative fever** makes an infectious etiology much more likely.
- Postoperative SIRS can occur due to surgical stress, but the signs of infection (especially respiratory) shift the diagnosis towards sepsis.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 7: A 35-year-old woman volunteers for a study on respiratory physiology. Pressure probes A and B are placed as follows:
Probe A: between the parietal and visceral pleura
Probe B: within the cavity of an alveolus
The probes provide a pressure reading relative to atmospheric pressure. To obtain a baseline reading, she is asked to sit comfortably and breathe normally. Which of the following sets of values will most likely be seen at the end of inspiration?
- A. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- C. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg
- D. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- E. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg***
- At the **end of inspiration**, the **intrapleural pressure (Probe A)** is at its most negative, typically around -6 to -8 cm H2O (equivalent to -4 to -6 mmHg), reflecting the maximum expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- At the **end of inspiration**, just before exhalation begins, there is **no airflow**, so the **intrapulmonary pressure (Probe B)** equalizes with atmospheric pressure, resulting in a 0 mm Hg reading.
*Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of 0 mm Hg** would indicate a **pneumothorax** since it should always be negative to prevent lung collapse.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** would indicate that **inspiration is still ongoing**, as air would be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapulmonary pressure of 0 mm Hg** is correct at the end of inspiration, an **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is typical for the **end of expiration (Functional Residual Capacity)** during quiet breathing, not the end of inspiration.
- The **intrapleural pressure becomes more negative** during inspiration due to increased thoracic volume, so -4 mm Hg would be insufficient.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is the normal pressure at the **end of expiration**, not the end of inspiration, where it becomes more negative.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** indicates that **inspiration is still in progress**, not at its end, as air would still be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapleural pressure of -6 mm Hg** is consistent with the end of inspiration, an **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** means that **airflow is still occurring into the lungs**.
- At the **very end of inspiration**, just before the start of exhalation, airflow momentarily ceases, and intrapulmonary pressure becomes zero relative to the atmosphere.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 8: A 68-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after she was found down by her daughter. She lives alone in her apartment so it is unclear when she began to develop symptoms. Her medical history is significant for cardiac arrhythmias, diabetes, pericarditis, and a stroke 2 years ago. On presentation her temperature is 98.1°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 88/51 mmHg, pulse is 137/min, and respirations are 18/min. On physical exam her skin is cold and clammy. If special tests were obtained, they would reveal dramatically decreased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, increased systemic vascular resistance, and mildly decreased cardiac output. Which of the following treatments would most directly target the cause of this patient's low blood pressure?
- A. Vasopressors
- B. Intravenous fluids (Correct Answer)
- C. Antibiotic administration
- D. Relieve obstruction
- E. Intravenous inotropes
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Intravenous fluids***
- The patient exhibits signs of **hypovolemic shock**, including **hypotension** (BP 88/51 mmHg), **tachycardia** (pulse 137/min), and **cold, clammy skin**. The dramatically decreased **pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)** indicates low preload, which is characteristic of hypovolemia.
- Administration of intravenous fluids directly addresses the underlying cause of this patient's low blood pressure by increasing intravascular volume, thereby improving **cardiac preload** and ultimately **cardiac output** and blood pressure.
*Vasopressors*
- While vasopressors can temporarily increase blood pressure by causing **vasoconstriction**, they do not address the root cause of hypovolemic shock, which is insufficient circulating blood volume.
- Using vasopressors without adequate fluid resuscitation in hypovolemic shock can lead to further **organ hypoperfusion** due to increased afterload on an already compromised heart.
*Antibiotic administration*
- Although the patient's presentation with hypotension and tachycardia could raise suspicion for **sepsis**, there is no explicit evidence of infection presented (e.g., fever, focal source).
- The **decreased PCWP** points more strongly towards hypovolemic shock rather than septic shock, where PCWP can be variable or even normal/elevated.
*Relieve obstruction*
- Obstruction, such as in **cardiac tamponade** or **pulmonary embolism**, can cause obstructive shock, which presents with hypotension.
- However, the dramatically **decreased PCWP** is not typically seen in obstructive shock, where PCWP would likely be normal or elevated due to impedance to cardiac filling or outflow.
*Intravenous inotropes*
- **Inotropes** like dobutamine increase myocardial contractility and are primarily indicated in **cardiogenic shock** or severe heart failure with reduced ejection fraction to improve cardiac output.
- While cardiac output is mildly decreased, the primary issue is reduced preload as indicated by the very low PCWP, making fluid resuscitation a more appropriate initial step than directly increasing contractility.
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 9: A previously healthy 17-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of fever, nausea, and myalgia for the past day. His temperature is 39.5°C (103.1°F), pulse is 112/min, and blood pressure is 77/55 mm Hg. Physical examination shows scattered petechiae over the anterior chest and abdomen. Blood culture grows an organism on Thayer-Martin agar. Which of the following virulence factors of the causal organism is most likely responsible for the high mortality rate associated with it?
- A. Immunoglobulin A protease
- B. Lipooligosaccharide (Correct Answer)
- C. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1
- D. Lipoteichoic acid
- E. Erythrogenic exotoxin A
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Lipooligosaccharide***
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **hypotension**, and **petechiae**, along with a positive blood culture on Thayer-Martin agar, points to **meningococcemia** caused by *Neisseria meningitidis*.
- **Lipooligosaccharide (LOS)** acts as an **endotoxin**, triggering an excessive inflammatory response that leads to widespread vascular damage, **capillary leakage**, and **septic shock**, accounting for the high mortality.
*Immunoglobulin A protease*
- While *N. meningitidis* produces **IgA protease** to cleave secretory IgA and evade host defenses on mucosal surfaces, this factor is primarily involved in colonization and initial invasion rather than the systemic severity and mortality of septic shock.
- Its role is to help the bacteria **adhere and penetrate** host mucous membranes, but it does not directly cause the shock and petechiae seen in this severe presentation.
*Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1*
- **Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1)** is a **superantigen** produced by *Staphylococcus aureus* that causes **toxic shock syndrome**, which can present with fever, rash, and hypotension.
- However, the organism grown on **Thayer-Martin agar** is characteristic of *Neisseria meningitidis*, not *Staphylococcus aureus*.
*Lipoteichoic acid*
- **Lipoteichoic acid** is a major component of the cell wall of **Gram-positive bacteria**, acting as a potent proinflammatory molecule and contributing to septic shock in those infections.
- *Neisseria meningitidis* is a **Gram-negative bacterium**, and therefore does not possess lipoteichoic acid.
*Erythrogenic exotoxin A*
- **Erythrogenic exotoxin A** is primarily produced by ***Streptococcus pyogenes*** and is responsible for the characteristic rash of **scarlet fever**.
- While *S. pyogenes* can cause invasive infections, the clinical picture and the specific growth on **Thayer-Martin agar** are not consistent with streptococcal infection.
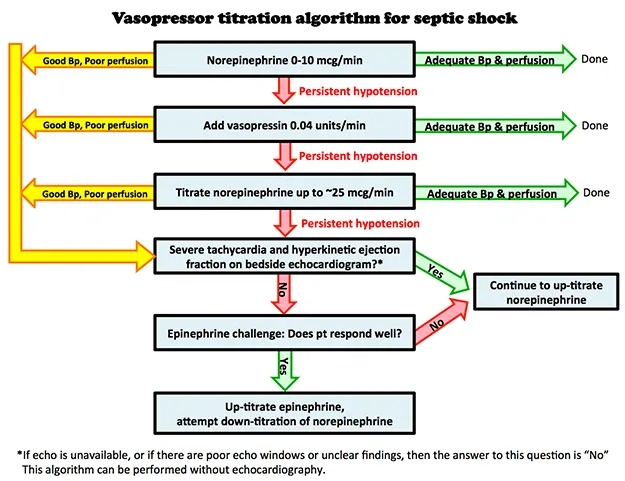
Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG Question 10: A 38-year-old previously healthy woman develops septic shock from necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity. Despite three debridements, broad-spectrum antibiotics (vancomycin, meropenem, clindamycin), IVIG, and aggressive critical care support, she develops refractory shock requiring norepinephrine 1.2 mcg/kg/min, vasopressin 0.04 units/min, and epinephrine 0.1 mcg/kg/min. Lactate is 15 mmol/L. Surgical team recommends hemipelvectomy as last option for source control. Family is devastated. ICU team notes SOFA score of 18. Synthesize an approach to management and decision-making.
- A. Transfer to ECMO center for consideration of VA-ECMO as bridge to hemipelvectomy
- B. Multidisciplinary meeting with surgery, ICU, palliative care, and family to discuss realistic outcomes, quality of life, and patient values before decision (Correct Answer)
- C. Continue medical management for 24 hours and proceed with hemipelvectomy only if shock improves
- D. Decline surgery based on futility given SOFA score >15 and initiate comfort care
- E. Proceed with hemipelvectomy immediately as only chance for survival with informed consent from family
Initial resuscitation in sepsis Explanation: ***Multidisciplinary meeting with surgery, ICU, palliative care, and family to discuss realistic outcomes, quality of life, and patient values before decision***
- In high-acuity cases with refractory shock and high **SOFA scores (>15)**, shared decision-making is essential to align surgical intervention with the patient’s **goals of care**.
- This approach ensures that the **prognosis**, which carries a high risk of mortality and morbidity from **hemipelvectomy**, is transparently communicated by the entire medical team.
*Transfer to ECMO center for consideration of VA-ECMO as bridge to hemipelvectomy*
- **VA-ECMO** is generally not indicated in septic shock with refractory vasoplegia and severe multi-organ failure as it doesn't solve the **source control** issue.
- The logistics and physiological stress of a transfer in the setting of **1.2 mcg/kg/min norepinephrine** would be highly unstable and likely fatal.
*Continue medical management for 24 hours and proceed with hemipelvectomy only if shock improves*
- Delaying source control in **necrotizing fasciitis** while shock is worsening usually leads to death, as medical management alone cannot overcome the focus of infection.
- Waiting for improvement in the setting of a **lactate of 15 mmol/L** and triple vasopressors is unrealistic without definitive surgical intervention.
*Decline surgery based on futility given SOFA score >15 and initiate comfort care*
- While the **SOFA score** indicates a very high mortality risk, unilateral physician declaration of **medical futility** is ethically complex and can damage family trust.
- Comfort care should remain a possibility, but first requires a thorough **interdisciplinary discussion** to ensure legal and ethical standards are met.
*Proceed with hemipelvectomy immediately as only chance for survival with informed consent from family*
- Performing such a **mutilating surgery** without a detailed discussion of the expected **quality of life** and long-term functional loss is poor surgical practice.
- Immediate surgery without addressing the massive **operative mortality** risk ignores the patient's potential preference for a dignified death over a futile procedure.
More Initial resuscitation in sepsis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.