Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Initial assessment and triage. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
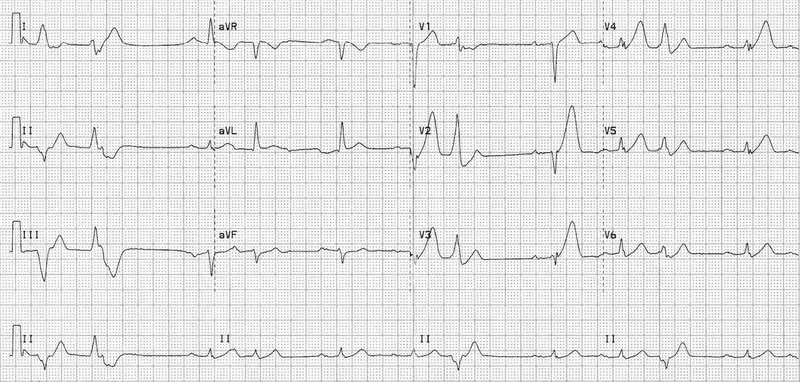
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 1: Two days after admission for myocardial infarction and subsequent coronary angioplasty, a 65-year-old man becomes distressed and diaphoretic in the cardiac intensive care unit. Suddenly he is no longer responsive. Pulse oximetry does not show a tracing. He has a history of hypertension and depression. Prior to his admission, his medication included ramipril and aripiprazole. Examination shows no carotid pulse. An ECG is shown. After beginning chest compressions, which of the following is the most appropriate step in management of the patient?
- A. Intravenous procainamide
- B. Cardiac catheterization
- C. Intravenous amiodarone
- D. Intravenous magnesium sulfate
- E. Defibrillation (Correct Answer)
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Defibrillation***
- The ECG shows a **wide complex tachycardia** consistent with either **ventricular fibrillation (VF)** or **pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT)**.
- In a patient who is **unresponsive and pulseless**, both VF and pulseless VT are treated identically with **immediate unsynchronized defibrillation** after initiating CPR, according to **ACLS guidelines**.
- **Defibrillation** is the definitive treatment to restore a perfusing rhythm and is the priority intervention after chest compressions have begun.
*Intravenous procainamide*
- **Procainamide** is an antiarrhythmic drug used for certain types of **stable ventricular tachycardia** or wide-complex tachycardia of uncertain type when the patient has a pulse.
- It is **contraindicated** in pulseless arrhythmias like VF or pulseless VT, where electrical therapy (defibrillation) is paramount.
- Administration would cause dangerous delay in definitive treatment.
*Cardiac catheterization*
- **Cardiac catheterization** is an invasive diagnostic and interventional procedure typically performed to evaluate and treat coronary artery disease.
- It is **not an immediate life-saving intervention** for a patient in **cardiac arrest**, which requires immediate electrical therapy.
- Catheterization may be considered after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) to address underlying ischemia.
*Intravenous amiodarone*
- **Amiodarone** is an antiarrhythmic agent used in **VF/pulseless VT that is refractory to initial defibrillation attempts** and after epinephrine administration.
- It is administered **after initial defibrillation attempts have failed**, not as the primary or first-line treatment.
- The ACLS algorithm recommends amiodarone after the third shock if VF/pulseless VT persists.
*Intravenous magnesium sulfate*
- **Magnesium sulfate** is the treatment of choice for **Torsades de Pointes**, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia often associated with **prolonged QT interval**.
- The clinical presentation and ECG do not suggest Torsades de Pointes, and magnesium is not indicated as the initial treatment for VF or monomorphic VT.
- Magnesium may also be considered for refractory VF/VT with suspected hypomagnesemia.
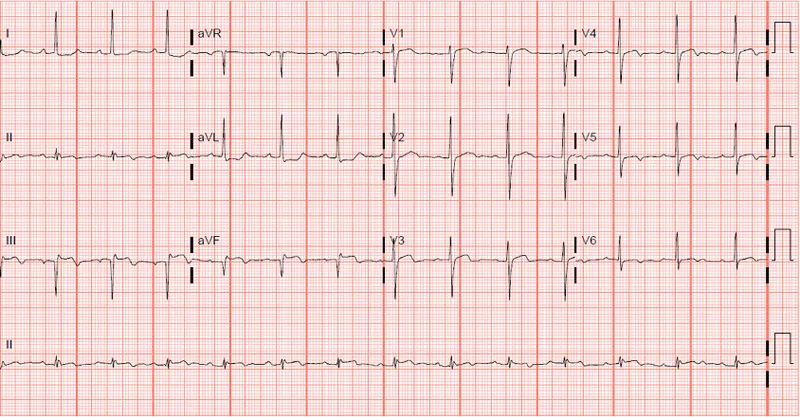
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 2: A 57-year-old man with a known angina pectoris starts to experience a severe burning retrosternal pain that radiates to his left hand. After 2 consecutive doses of sublingual nitroglycerin taken 5 minutes apart, there is no improvement in his symptoms, and the patient calls an ambulance. Emergency medical service arrives within 10 minutes and begins evaluation and prehospital management. The vital signs include: blood pressure 85/50 mm Hg, heart rate 96/min, respiratory rate 19/min, temperature 37.1℃ (98.9℉), and SpO2 89% on ambient air. Oxygen supply and intravenous access are established. An ECG shows the findings in the given image. Which of the following is a part of a proper further prehospital management strategy for this patient?
- A. Administer nitroglycerin and transport to percutaneous coronary intervention center
- B. Perform pre-hospital thrombolysis and transport to a percutaneous coronary intervention center
- C. Administer aspirin 325 mg and transport to percutaneous coronary intervention center (Correct Answer)
- D. Administer aspirin 81 mg and transport to a percutaneous coronary intervention center
- E. Perform pre-hospital thrombolysis and transport to emergency department irrespective of percutaneous coronary intervention center presence
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Administer aspirin 325 mg and transport to percutaneous coronary intervention center***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of an acute myocardial infarction (AMI), namely **retrosternal chest pain radiating to the left hand**, unrelieved by nitroglycerin. The ECG would likely confirm **ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)**, necessitating urgent reperfusion.
- **Aspirin 325 mg** is the recommended initial dose for suspected AMI due to its **antiplatelet effects**, which help prevent further thrombus formation, and the patient should be transported to a **percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) center**, as this is the preferred reperfusion strategy for STEMI.
*Administer nitroglycerin and transport to percutaneous coronary intervention center*
- The patient has already received two doses of sublingual nitroglycerin without improvement, and his **blood pressure is 85/50 mm Hg**, indicating **hypotension**.
- Administering further nitroglycerin would be **contraindicated due to hypotension** and unlikely to be effective.
*Perform pre-hospital thrombolysis and transport to a percutaneous coronary intervention center*
- While pre-hospital thrombolysis can be an option in certain settings, **PCI is the preferred reperfusion strategy for STEMI** if it can be performed within recommended timeframes. Given the option of a PCI center, thrombolysis is secondary.
- Additionally, thrombolysis carries **risks of bleeding** and is typically reserved for situations where PCI is not readily available.
*Administer aspirin 81 mg and transport to a percutaneous coronary intervention center*
- While aspirin is crucial, the initial loading dose for acute coronary syndrome (**ACS**) is typically **325 mg** (or 162 mg chewable) to achieve rapid antiplatelet effect, not 81 mg.
- The 81 mg dose is commonly used for **maintenance therapy** or chronic prevention, not for initial acute management.
*Perform pre-hospital thrombolysis and transport to emergency department irrespective of percutaneous coronary intervention center presence*
- Thrombolysis is generally performed only if a PCI center is not accessible within a specific timeframe; transporting directly to an ED irrespective of PCI capabilities is suboptimal if a PCI center is available.
- The goal is **rapid reperfusion**, and direct transport to a PCI center is preferred over thrombolysis if the time to PCI is short.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 3: A 66-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 1-day history of chest pain, palpitations, and dyspnea on exertion. He had a similar episode 3 days ago and was diagnosed with an inferior wall myocardial infarction. He was admitted and a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty was successfully done that day. A fractional flow reserve test during the procedure showed complete resolution of the stenosis. Laboratory tests including serum glucose, lipids, and blood count were within normal limits. He was discharged the day after the procedure on a drug regimen of aspirin, simvastatin, and isosorbide dinitrate. At the time of discharge, he had no chest pain or dyspnea. Presently, his vitals are normal and ECG at rest shows new T-wave inversion. Which of the following is the most reliable test for rapidly establishing the diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Creatine kinase MB
- B. Lactate dehydrogenase
- C. Copeptin
- D. Aspartate aminotransferase
- E. Cardiac troponin T (Correct Answer)
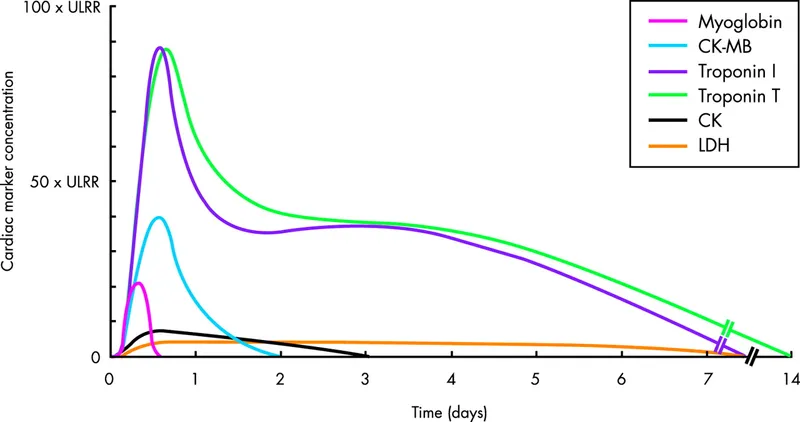
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Cardiac troponin T***
- **Cardiac troponin T** is a highly sensitive and specific biomarker for **myocardial injury**, making it the most reliable test for rapidly diagnosing acute coronary syndrome or re-infarction.
- Its elevation indicates ongoing **myocardial necrosis**, even after a recent MI, and is crucial for guiding immediate management.
*Creatine kinase MB*
- While CK-MB is used for diagnosing myocardial infarction, its levels can also be elevated in cases of **skeletal muscle injury** or **after cardiac procedures**, reducing its specificity in this context.
- CK-MB also has a **shorter window of elevation** compared to troponins, potentially missing later presentations of myocardial injury.
*Lactate dehydrogenase*
- **LDH** is a relatively **nonspecific marker** that can elevate due to various conditions affecting different organs (e.g., liver disease, hemolysis, renal injury).
- Its elevation onset is **slower** and its diagnostic window is longer, making it less suitable for rapid diagnosis of acute myocardial injury.
*Copeptin*
- **Copeptin** is a marker of **endogenous stress** and is often used in conjunction with troponins to rule out NSTEMI, especially at early presentation.
- However, it is not a direct marker of myocardial necrosis itself and is **not as specific** as troponin for diagnosing a re-infarction.
*Aspartate aminotransferase*
- **AST** is a **nonspecific enzyme** found in various tissues, including the liver, skeletal muscle, and heart.
- Elevated AST levels are frequently seen in **liver damage** and are not a primary biomarker for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction or re-infarction.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 4: A 66-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 3-hour history of crushing chest pain radiating to the left shoulder and neck. Patient states that the pain began suddenly when he was taking a walk around the block and has not improved with rest. He also mentions difficulty breathing and prefers to sit leaning forward. He denies ever having similar symptoms before. Past medical history is significant for hypertension, diagnosed 10 years ago, and hyperlipidemia diagnosed 8 years ago. Current medications are atorvastatin. Patient is also prescribed hydrochlorothiazide as an antihypertensive but is not compliant because he says it makes him urinate too often.
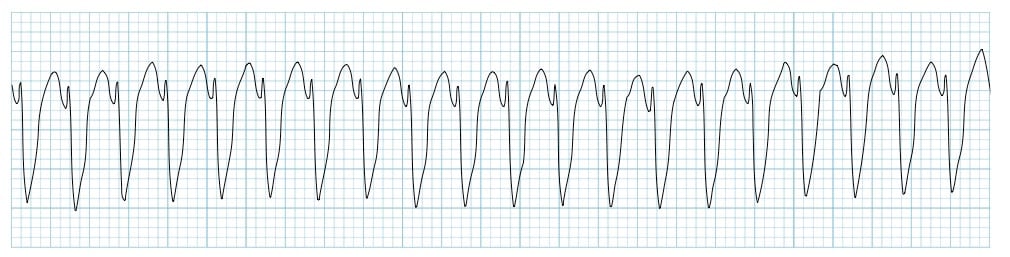
Vitals show a blood pressure of 152/90 mm Hg, pulse of 106/min, respirations of 22/min and oxygen saturation of 97% on room air. On physical exam, patient is profusely diaphoretic and hunched over in distress. Cardiac exam is unremarkable and lungs are clear to auscultation. During your examination, the patient suddenly becomes unresponsive and a pulse cannot be palpated. A stat ECG shows the following (see image). Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. Synchronized cardioversion
- B. Administer amiodarone
- C. Urgent echocardiography
- D. Administer epinephrine
- E. Unsynchronized cardioversion (Correct Answer)
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Unsynchronized cardioversion***
- The ECG shows **ventricular fibrillation (VF)**, a chaotic electrical activity with no coordinated contractions, which leads to immediate cardiac arrest.
- In a patient who is unresponsive and pulseless with VF, **immediate unsynchronized defibrillation** (cardioversion) is the definitive treatment to restore a perfusing rhythm.
*Synchronized cardioversion*
- **Synchronized cardioversion** delivers an electrical shock timed to the QRS complex, used for unstable patients with a pulse and organized tachyarrhythmias (e.g., ventricular tachycardia with a pulse, atrial flutter, or atrial fibrillation).
- This patient is **pulseless** and in **ventricular fibrillation**, making synchronized cardioversion inappropriate and ineffective.
*Administer amiodarone*
- **Amiodarone** is an antiarrhythmic drug used in cardiac arrest protocols for **refractory VF/pulseless VT** after initial defibrillation attempts and epinephrine have failed.
- It is not the *initial* best step in a pulseless patient with VF, as electrical defibrillation is paramount.
*Urgent echocardiography*
- While an echocardiogram might be useful in identifying the underlying cause (e.g., myocardial infarction leading to VF), it is **not the immediate life-saving intervention** for a patient in cardiac arrest from VF.
- Delaying defibrillation for an echocardiogram would significantly worsen the patient's prognosis.
*Administer epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is a vasoconstrictor and cardiac stimulant used during **cardiac arrest**, typically given after the initial defibrillation attempt for VF/pulseless VT.
- It helps improve myocardial and cerebral blood flow but is **secondary to immediate defibrillation** in VF.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 5: A cardiologist is studying how a new virus that infects the heart affects the electrical conduction system of the cardiac myocytes. He decides to obtain electrocardiograms on patients with this disease in order to see how the wave patterns and durations change over time. While studying these records, he asks a medical student who is working with him to interpret the traces. Specifically, he asks her to identify the part that represents initial ventricular depolarization. Which of the following characteristics is most consistent with this feature of the electrocardiogram?
- A. Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart
- B. Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia
- C. Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia
- D. Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds (Correct Answer)
- E. Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds***
- The question asks for the representation of **initial ventricular depolarization**, which corresponds to the **QRS complex** on an ECG.
- The normal duration of the **QRS complex** is typically less than **0.12 seconds (120 milliseconds)**, reflecting efficient ventricular depolarization.
*Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart*
- This description refers to the **ST segment elevation** seen in **ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)**, which represents myocardial injury, not initial ventricular depolarization.
- While related to cardiac electrical activity, **ST segment elevation** is a consequence of injury and refers to repolarization abnormalities, not the QRS complex itself.
*Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia*
- **Peaked T waves** are characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, indicating altered ventricular repolarization, not ventricular depolarization.
- The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, and its morphology changes significantly with potassium imbalances.
*Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia*
- A **prominent U wave** is sometimes observed in **hypokalemia**, which follows the T wave and is thought to represent repolarization of Purkinje fibers.
- The U wave is distinct from the QRS complex and does not represent initial ventricular depolarization.
*Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds*
- A duration of less than 200 milliseconds (0.20 seconds) typically refers to the normal duration of the **PR interval**, which represents atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node.
- The **QRS complex** (initial ventricular depolarization) has a shorter normal duration, typically less than 120 milliseconds.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 6: A 67-year-old man presents to the emergency department for squeezing and substernal chest pain. He states that he was at home eating dinner when his symptoms began. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. He is currently taking atorvastatin, lisinopril, insulin, metformin, metoprolol, and aspirin. Six days ago he underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 197/118 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam reveals an uncomfortable elderly man who is sweating. An ECG is ordered. Which of the following is the best next step in management for this patient?
- A. Stress testing
- B. Angiography (Correct Answer)
- C. Cardiac troponins
- D. Creatine kinase-MB
- E. Myoglobin
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Correct: Angiography***
- This patient presenting with **acute chest pain 6 days post-PCI** is at high risk for **stent thrombosis or acute in-stent restenosis**, which represents a life-threatening emergency.
- Given the **clinical instability** (severe hypertension 197/118, tachycardia 120/min, diaphoresis) and classic ACS symptoms in the immediate post-PCI period, **urgent coronary angiography** is the best next step in management.
- While ECG and troponins are important diagnostic tools, this patient requires **immediate intervention** to evaluate the recent PCI site and potentially perform emergent revascularization.
- In the setting of suspected **acute stent thrombosis**, time to reperfusion is critical, and angiography allows both diagnosis and treatment.
*Incorrect: Cardiac troponins*
- While troponins are essential biomarkers for myocardial injury and should be obtained, they are a **diagnostic test** rather than definitive management.
- Waiting for troponin results would delay definitive management in a patient with clear clinical evidence of ACS.
- In this high-risk post-PCI patient with active symptoms, management should not wait for biomarker confirmation.
*Incorrect: Stress testing*
- Stress testing is **absolutely contraindicated** in patients with active chest pain and suspected acute MI.
- It could precipitate further myocardial ischemia, arrhythmias, or cardiac arrest.
- Stress testing is reserved for risk stratification in stable patients or after ACS has been ruled out.
*Incorrect: Creatine kinase-MB*
- CK-MB is less sensitive and specific than troponins for myocardial injury, as it can be elevated in skeletal muscle conditions.
- It has a shorter elevation window and has largely been replaced by troponins in modern practice.
- Like troponins, it would not change the immediate management need in this clinically unstable patient.
*Incorrect: Myoglobin*
- Myoglobin lacks cardiac specificity (present in both cardiac and skeletal muscle) and has poor diagnostic accuracy for MI.
- Its rapid rise and fall make it unreliable, and it generates many false positives.
- It has no role in guiding management decisions in suspected ACS.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 7: Serum studies show a troponin T concentration of 6.73 ng/mL (N < 0.01), and fingerstick blood glucose concentration of 145 mg/dL. The cardiac catheterization team is activated. Treatment with unfractionated heparin, aspirin, ticagrelor, and sublingual nitroglycerin is begun, and the patient's pain subsides. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 65/min, respirations are 23/min, and blood pressure is 91/60 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 96%. Which of the following is the most appropriate additional pharmacotherapy?
- A. Intravenous morphine
- B. Intravenous furosemide
- C. Intravenous insulin
- D. Oral atorvastatin (Correct Answer)
- E. Intravenous nitroglycerin
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Oral atorvastatin***
- All patients with **acute coronary syndrome (ACS)** should receive high-intensity statin therapy, such as **atorvastatin 80 mg daily**, as early as possible.
- Statins stabilize plaques, reduce inflammation, and improve endothelial function, which are crucial in the acute setting of a myocardial infarction.
*Intravenous morphine*
- Morphine can be used for persistent chest pain refractory to nitroglycerin, but its routine use is now questioned due to potential adverse effects like hypotension and delayed antiplatelet absorption.
- The patient's pain has already subsided with initial treatment, and his blood pressure is already low (91/60 mm Hg), making morphine less appropriate.
*Intravenous furosemide*
- Furosemide is a loop diuretic primarily used for treating **fluid overload** and **pulmonary edema**, which are not indicated by the patient's current presentation (oxygen saturation 96%, no mention of crackles or dyspnea).
- Its use in a patient with **borderline hypotension** could worsen hemodynamic stability.
*Intravenous insulin*
- While the patient has elevated fingerstick glucose (145 mg/dL), this level does not immediately require intravenous insulin unless there is evidence of **diabetic ketoacidosis** or **hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state**, or persistent severe hyperglycemia.
- More moderate hyperglycemia can often be managed with subcutaneous insulin or diet in the acute phase, and focuses remain on cardiac stabilization.
*Intravenous nitroglycerin*
- Intravenous nitroglycerin is indicated for ongoing ischemic chest pain or uncontrolled hypertension in ACS, but the patient's pain has subsided and he is **hypotensive** (91/60 mm Hg).
- Administering more nitroglycerin would likely worsen his hypotension and could compromise coronary perfusion.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 8: A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department with progressive dyspnea for the last 3 weeks. He complains of shortness of breath while lying flat and reports nighttime awakenings due to shortness of breath for the same duration. The patient has been a smoker for the last 30 years. Past medical history is significant for myocardial infarction 7 months ago. Current medications include metoprolol, aspirin, and rosuvastatin, but the patient is noncompliant with his medications. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), the blood pressure is 150/115 mm Hg, the pulse is 110/min, and the respiratory rate is 24/min. Oxygen saturation on room air is 88%. Chest auscultation reveals bilateral crackles and an S3 gallop. On physical examination, the cardiac apex is palpated in left 6th intercostal space. Bilateral pitting edema is present, and the patient is in moderate distress. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of the patient?
- A. Intravenous beta blockers
- B. Intravenous diuretics (Correct Answer)
- C. Echocardiography
- D. Cardiac stress testing
- E. Intravenous inotropes
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Intravenous diuretics***
- The patient presents with classic signs and symptoms of **acute decompensated heart failure**, such as progressive dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, bilateral crackles, S3 gallop, pitting edema, and elevated blood pressure with elevated heart rate due to fluid overload.
- **Intravenous loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide) are the most appropriate initial therapy to reduce preload, alleviate pulmonary and systemic congestion, and improve oxygenation.
*Intravenous beta blockers*
- While beta-blockers are a cornerstone of chronic heart failure management, **starting or acutely increasing beta-blocker dosage in acute decompensated heart failure** can worsen cardiac output and lead to symptomatic hypotension or cardiogenic shock.
- Beta-blockers should generally be withheld or reduced during acute exacerbations and reinstituted once the patient is stable.
*Echocardiography*
- While an **echocardiogram** is essential for diagnosing the underlying cause and assessing cardiac function in heart failure, it is not the *best next step* in a patient presenting with acute, severe symptoms requiring immediate stabilization.
- The patient's acute respiratory distress and hypoxemia necessitate immediate medical intervention to reduce fluid overload before detailed diagnostic imaging.
*Cardiac stress testing*
- **Cardiac stress testing** is used to evaluate for inducible ischemia in stable patients and is not appropriate in the setting of acute decompensated heart failure.
- Performing a stress test on a patient with signs of fluid overload and respiratory distress would be dangerous and could exacerbate their condition.
*Intravenous inotropes*
- **Intravenous inotropes** (e.g., dobutamine, milrinone) are typically reserved for patients with evidence of **cardiogenic shock** or severe heart failure with persistent hypoperfusion despite optimal fluid management and diuretic therapy.
- This patient, while acutely ill, primarily exhibits signs of fluid overload without clear evidence of severe hypoperfusion compromising end-organ function.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 9: A 70-year-old man with diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease (eGFR 35 mL/min/1.73m²) presents with NSTEMI. Troponin is elevated at 8.5 ng/mL. ECG shows 2mm ST depression in V2-V5. GRACE score is 165 (high risk). He is hemodynamically stable. Cardiologist recommends early invasive strategy within 24 hours. Nephrologist is concerned about contrast-induced nephropathy potentially requiring dialysis. Patient is on metformin. Evaluate the management strategy integrating multiple specialist perspectives and evidence.
- A. Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin (Correct Answer)
- B. Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography
- C. Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration
- D. Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast
- E. Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin***
- High-risk NSTEMI patients with a **GRACE score >140** benefit from an **early invasive strategy** within 24 hours to reduce ischemic events and mortality.
- Renal protection is maximized through **pre-procedural hydration** and **iso-osmolar contrast**, while **metformin** must be held to avoid the risk of lactic acidosis if acute kidney injury occurs.
*Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography*
- **Coronary CTA** is primarily used for ruling out coronary artery disease in low-to-intermediate risk stable patients, not for high-risk **NSTEMI**.
- This modality still requires **iodinated contrast** and does not provide the therapeutic benefit of percutaneous coronary intervention (**PCI**).
*Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration*
- Delaying the procedure in a high-risk patient increases the risk of **re-infarction** and **cardiovascular death**, outweighing the minor benefits of prolonged hydration.
- Evidence suggests that optimization of renal status should happen concurrently with the preparation for **early intervention** in high-risk ACS.
*Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast*
- **Prophylactic hemodialysis** has not been proven to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy and may actually increase the risk of adverse events.
- High-volume **intravenous hydration** with isotonic saline remains the gold standard for preventing renal injury in patients with **CKD**.
*Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization*
- While **dual antiplatelet therapy** is essential, medical management alone is inferior to an invasive strategy in patients with **high GRACE scores**.
- Avoiding catheterization based solely on **renal impairment** results in "renalism," where patients are undertreated for their life-threatening cardiac condition.
Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old woman with anterior STEMI underwent primary PCI with drug-eluting stent placement. Post-procedure echocardiogram shows left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% with apical akinesis. She is started on aspirin, ticagrelor, high-intensity statin, and ACE inhibitor. On hospital day 3, she develops atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. CHA2DS2-VASc score is 4. Creatinine is normal. Evaluate the optimal antithrombotic strategy balancing ischemic and bleeding risk.
- A. Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely
- B. Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely
- C. Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk
- D. Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor
- E. Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone (Correct Answer)
Initial assessment and triage Explanation: ***Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone***
- In patients with **Atrial Fibrillation** (CHA2DS2-VASc ≥2) undergoing **PCI**, current guidelines recommend minimizing the duration of **triple therapy** (aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitor, and anticoagulant) to 1 week to 1 month to reduce **bleeding risk**.
- Transitioning to **dual therapy** with a **NOAC** (like apixaban) and a P2Y12 inhibitor (preferably **clopidogrel**) for up to 12 months, followed by NOAC monotherapy, provides an optimal balance between preventing **stent thrombosis** and systemic **thromboembolism**.
*Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely*
- Indefinite **triple therapy** carries a prohibitively high risk of life-threatening **major bleeding** without added benefit for stroke prevention.
- **Ticagrelor** is generally avoided in triple therapy regimens due to a significantly higher bleeding profile compared to **clopidogrel**.
*Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely*
- **Triple therapy** for 6 months is rarely indicated and significantly increases the risk of **gastrointestinal and intracranial hemorrhage** compared to the 1-month strategy.
- Aspirin is usually discontinued after the first year in favor of **anticoagulant monotherapy**, as the latter is sufficient for both AF and stable CAD protection.
*Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk*
- This approach leaves the patient with a high **CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4** unprotected against **cardioembolic stroke**, which carries high morbidity and mortality.
- Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) alone is significantly less effective than **oral anticoagulants** for stroke prevention in the setting of atrial fibrillation.
*Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor*
- **NOACs** (like apixaban) are now preferred over **Warfarin** for non-valvular AF due to a superior safety profile, including a lower risk of **intracranial hemorrhage**.
- Discontinuing the P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor) immediately post-PCI in favor of aspirin and warfarin significantly increases the risk of **stent thrombosis**.
More Initial assessment and triage US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.