ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for ECG interpretation in MI. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
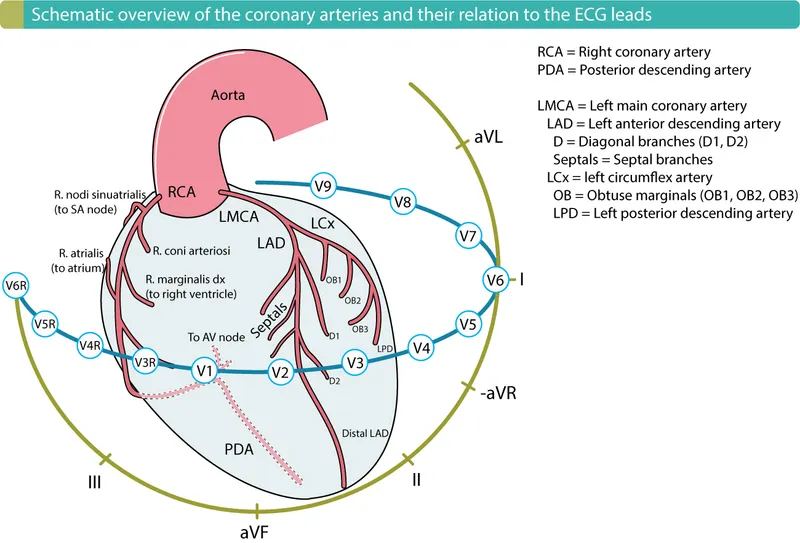
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 1: A 53-year-old man with a past medical history significant for hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and hyperhomocysteinemia presents to the emergency department complaining of 10/10 crushing, left-sided chest pain radiating down his left arm and up his neck into the left side of his jaw. His ECG shows ST-segment elevation in leads V2-V4. He is taken to the cardiac catheterization laboratory for successful balloon angioplasty and stenting of a complete blockage in his left anterior descending coronary artery. Echocardiogram the following day shows decreased left ventricular function and regional wall motion abnormalities. A follow-up echocardiogram 14 days later shows a normal ejection fraction and no regional wall motion abnormalities. This post-infarct course illustrates which of the following concepts?
- A. Coronary collateral circulation
- B. Ventricular remodeling
- C. Myocardial hibernation
- D. Myocardial stunning (Correct Answer)
- E. Reperfusion injury
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Myocardial stunning***
- This refers to a temporary **post-ischemic contractile dysfunction** that persists even after blood flow has been restored following an acute ischemic event.
- The return to normal left ventricular function and absence of regional wall motion abnormalities after successful reperfusion indicates that the initial dysfunction was transient and not due to permanent myocardial damage.
- Classic timeframe: recovery occurs over **days to weeks** after reperfusion, as seen in this patient (14 days).
*Coronary collateral circulation*
- This involves the development of alternative pathways for blood supply to the myocardium when the primary coronary arteries are occluded.
- While it can mitigate the extent of myocardial injury, it generally doesn't explain the reversal of severe regional wall motion abnormalities and low ejection fraction to normal in such a short period after a complete blockage.
*Ventricular remodeling*
- This refers to changes in the **size, shape, and function of the ventricles** in response to myocardial injury or chronic pressure/volume overload, often leading to progressive heart failure.
- It typically involves *persistent* and *often detrimental* changes, which is contrary to the improvement seen in this patient's echocardiogram.
*Myocardial hibernation*
- This is a state of **persistently impaired myocardial function at rest** due to **chronic inadequate blood flow** that can improve with revascularization.
- Hibernation requires **pre-existing chronic ischemia** with baseline dysfunction prior to intervention, not an acute complete occlusion presenting as STEMI.
- This patient had an **acute presentation** with complete blockage and no history suggesting chronic stable ischemia, making stunning (not hibernation) the correct answer.
*Reperfusion injury*
- This is damage to the myocardial tissue that occurs **after blood flow is restored** to an ischemic area, often involving oxidative stress and inflammation.
- While it can worsen myocardial function, it is a complication of reperfusion that causes *additional damage*, not a phenomenon that explains the *recovery* of cardiac function after reperfusion.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 2: A 43-year-old woman presents to a physician with weakness and fatigue for a week. She mentions that she has been taking oral fluconazole for the last 4 weeks for the treatment of tinea capitis. She also says that she loves coffee and usually consumes 4–6 cups of coffee every day. On physical examination, her vital signs are stable and examination of all systems, including nervous system, is normal. Her laboratory evaluation reveals that her serum potassium level is 3.1 mmol/L (3.1 mEq/L). The physician orders an ECG. Which of the following findings is most likely to be present?
- A. Shortened QT interval
- B. Tall peaked T waves
- C. Disappearing P waves
- D. Depression of ST segment (Correct Answer)
- E. Widening of QRS complexes
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Depression of ST segment***
- The patient presents with **hypokalemia** (serum potassium 3.1 mmol/L), which is commonly associated with **ST segment depression** on an ECG.
- Fluconazole can cause hypokalemia, and coffee consumption can exacerbate it due to its diuretic effect, further contributing to the likelihood of this ECG finding.
*Shortened QT interval*
- A **shortened QT interval** is typically associated with **hypercalcemia** rather than hypokalemia.
- Hypokalemia is more commonly associated with **QT prolongation** or prominent U waves, not shortening.
*Tall peaked T waves*
- **Tall, peaked T waves** are characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, which is the opposite of the patient's condition.
- In hypokalemia, T waves tend to be flattened or inverted.
*Disappearing P waves*
- **Disappearing P waves** are often seen in conditions like **atrial fibrillation** or severe hyperkalemia, where atrial activity is affected.
- They are not a characteristic finding of hypokalemia.
*Widening of QRS complexes*
- **Widening of QRS complexes** is typically associated with conditions like **bundle branch blocks**, certain intoxications, or severe **hyperkalemia**, not hypokalemia.
- Hypokalemia does not directly lead to a widened QRS complex.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 3: A 41-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with chest pain. She has had progressive substernal chest pain accompanied by weakness and mild shortness of breath for the past 2 hours. Her past medical history is notable for poorly controlled systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren syndrome, and interstitial lung disease. She was hospitalized last year with pericarditis presumed to be from SLE. Her temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 106/56 mmHg, pulse is 132/min, and respirations are 26/min. On exam, the skin overlying the internal jugular vein fills at 9 cm above the sternal angle and distant heart sounds are appreciated. There is no friction rub. She is given 1000cc of intravenous fluids with no appreciable change in her blood pressure. An electrocardiogram in this patient would most likely reveal which of the following findings?
- A. Polymorphic P waves
- B. ST elevations in leads II, III, and aVF
- C. Peaked T waves
- D. Wide QRS complexes with no P waves
- E. Electrical alternans (Correct Answer)
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Electrical alternans***
- The patient's symptoms (chest pain, shortness of breath, **hypotension**, **tachycardia**, **elevated JVP**, and **distant heart sounds**) in the context of a history of **pericarditis** and **SLE** are highly suggestive of **cardiac tamponade.**
- **Electrical alternans**, characterized by alternating QRS complex heights due to the swinging motion of the heart in a large pericardial effusion, is a classic EKG finding for cardiac tamponade.
- This finding reflects the mechanical swinging of the heart within the pericardial fluid, causing beat-to-beat variation in QRS amplitude.
*Polymorphic P waves*
- **Polymorphic P waves** (multifocal atrial tachycardia) occur when there are at least three different P wave morphologies on the EKG, indicating multiple ectopic atrial foci.
- This is typically seen in patients with severe lung disease or other conditions causing increased atrial stretch, but it is not a direct consequence or typical finding of cardiac tamponade.
*ST elevations in leads II, III, and aVF*
- **ST elevations in leads II, III, and aVF** indicate an **inferior myocardial infarction**, which is caused by coronary artery occlusion.
- While chest pain is present, the patient's other signs (elevated JVP, distant heart sounds, hypotension not responding to fluids, history of pericarditis/SLE) point away from an acute MI and strongly towards cardiac tamponade.
*Peaked T waves*
- **Peaked T waves** are characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, a condition of excessively high potassium levels in the blood.
- While hyperkalemia can cause cardiac symptoms, it does not typically present with the specific hemodynamic compromise and physical exam findings (elevated JVP, distant heart sounds) described, which are classic for cardiac tamponade.
*Wide QRS complexes with no P waves*
- **Wide QRS complexes with no P waves** are characteristic of a **ventricular arrhythmia**, such as ventricular tachycardia or idioventricular rhythm.
- While the patient is hypotensive and tachycardic, the presenting symptoms and physical exam findings are not directly indicative of a primary ventricular arrhythmia, but rather suggest an extracardiac compression of the heart due to tamponade.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 4: A 49-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of increasing shortness of breath. He has also had chest pain that is exacerbated by deep inspiration. He has had recurrent episodes of pain in his fingers for the past 2 years. Two years ago, he was treated for a deep vein thrombosis. He has hypertension and anxiety. Current medications include enalapril, St John's wort, and ibuprofen. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Examination shows pale conjunctiva. There is tenderness to palpation of the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints of both hands. Heart sounds are distant. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.9 g/dL
Leukocyte count 4200/mm3
Platelet count 330,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 136 mEq/L
K+ 4.3 mEq/L
Antinuclear antibodies 1: 320
Anti-Sm antibodies positive
Anti-CCP antibodies negative
An x-ray of the chest is shown. Which of the following is most likely to be seen on this patient's ECG?
- A. Deep Q wave
- B. Pseudo right bundle branch block
- C. Increased QT interval
- D. S1Q3T3 pattern
- E. Electrical alternans (Correct Answer)
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Electrical alternans***
- **Electrical alternans** is the classic ECG finding in **pericardial effusion with cardiac tamponade**, which this patient likely has based on distant heart sounds, dyspnea, and pleuritic chest pain
- This phenomenon reflects **beat-to-beat variations in QRS complex amplitude or axis**, caused by the heart swinging within a large pericardial effusion
- The patient has **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)** evidenced by positive ANA and anti-Sm antibodies, which commonly causes **serositis including pericarditis**
- **Distant heart sounds** are a key physical exam finding indicating significant pericardial effusion
*Deep Q wave*
- Deep Q waves typically indicate **prior myocardial infarction** due to transmural myocardial necrosis
- The patient's clinical presentation with distant heart sounds, pleuritic pain, and SLE points to a **pericardial process rather than ischemic heart disease**
- No clinical features suggest acute or chronic MI in this case
*Pseudo right bundle branch block*
- Pseudo RBBB patterns can be seen in conditions like **pulmonary embolism** (S1Q3T3 pattern) or Brugada syndrome
- While the patient has a history of DVT, the **primary findings of distant heart sounds and SLE-related serositis** make pericardial effusion the more likely diagnosis
- No signs of acute right heart strain from PE
*Increased QT interval*
- A prolonged QT interval is associated with increased risk of **torsades de pointes** and can be caused by medications or electrolyte abnormalities
- This is **not a characteristic finding of pericardial effusion or cardiac tamponade**
- The patient's medications (enalapril, St John's wort, ibuprofen) are not typical causes of QT prolongation
*S1Q3T3 pattern*
- The S1Q3T3 pattern (deep S wave in lead I, Q wave in lead III, inverted T wave in lead III) is suggestive of **acute pulmonary embolism**
- While the patient has a history of DVT, the **absence of hypoxemia, presence of distant heart sounds, and SLE diagnosis** make pericardial effusion with tamponade a more fitting diagnosis
- PE would typically present with more prominent respiratory symptoms and signs of right heart strain
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 5: A 50-year-old man presents the emergency department for intense chest pain, profuse sweating, and shortness of breath. The onset of these symptoms was 3 hours ago. The chest pain began after a heated discussion with a colleague at the community college where he is employed. Upon arrival, he is found conscious and responsive; the vital signs include a blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg, a heart rate at 90/min, a respiratory rate at 20/min, and a body temperature of 36.4°C (97.5°F). His medical history is significant for hypertension diagnosed 7 years ago, which is well-controlled with a calcium channel blocker. The initial electrocardiogram (ECG) shows ST-segment depression in multiple consecutive leads, an elevated cardiac troponin T level, and normal kidney function. Which of the following would you expect to find in this patient?
- A. Subendocardial necrosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Transmural necrosis
- C. Incomplete occlusion of a coronary artery
- D. Coronary artery spasm
- E. Ventricular pseudoaneurysm
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Subendocardial necrosis***
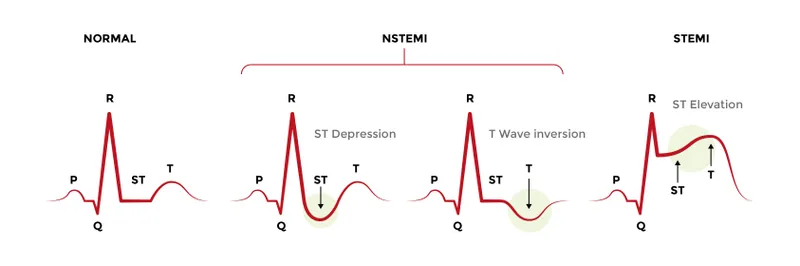
- This patient's presentation with **ST-segment depression** and **elevated troponin T** indicates a **Non-ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)**, which typically results from subendocardial ischemia and necrosis.
- Subendocardial tissue is most vulnerable to ischemia due to its high oxygen demand and distal location from the coronary arteries, making it the first region to suffer damage when oxygen supply is compromised.
*Transmural necrosis*
- **Transmural necrosis** is characteristic of a **ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)**, which presents with persistent **ST-segment elevation** on ECG.
- This patient's ECG shows **ST-segment depression**, ruling out transmural involvement at the time of presentation.
*Incomplete occlusion of a coronary artery*
- While an NSTEMI usually involves an **incomplete occlusion** or **critical stenosis** of a coronary artery, the question asks what would be *found* in the patient's heart tissue, not the mechanism.
- The direct tissue consequence of incomplete occlusion leading to NSTEMI is **subendocardial necrosis**, which is a more specific answer about the pathological finding.
*Coronary artery spasm*
- Although **coronary artery spasm (Prinzmetal angina)** can cause chest pain and ECG changes, it typically presents with **transient ST-segment elevation** (not depression) and often resolves spontaneously.
- The elevated troponin T indicates myocardial necrosis, which is not typically a feature of uncomplicated coronary artery spasm, and the duration of symptoms (3 hours) suggests a more sustained event than a transient spasm.
*Ventricular pseudoaneurysm*
- A **ventricular pseudoaneurysm** is a **late complication of myocardial infarction**, typically occurring weeks to months after the acute event, due to rupture of the ventricular free wall contained by pericardium.
- Given the 3-hour symptom onset, it is highly unlikely to be present in the acute phase of myocardial infarction.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 6: A 70-year-old man with diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease (eGFR 35 mL/min/1.73m²) presents with NSTEMI. Troponin is elevated at 8.5 ng/mL. ECG shows 2mm ST depression in V2-V5. GRACE score is 165 (high risk). He is hemodynamically stable. Cardiologist recommends early invasive strategy within 24 hours. Nephrologist is concerned about contrast-induced nephropathy potentially requiring dialysis. Patient is on metformin. Evaluate the management strategy integrating multiple specialist perspectives and evidence.
- A. Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin (Correct Answer)
- B. Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography
- C. Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration
- D. Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast
- E. Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin***
- High-risk NSTEMI patients with a **GRACE score >140** benefit from an **early invasive strategy** within 24 hours to reduce ischemic events and mortality.
- Renal protection is maximized through **pre-procedural hydration** and **iso-osmolar contrast**, while **metformin** must be held to avoid the risk of lactic acidosis if acute kidney injury occurs.
*Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography*
- **Coronary CTA** is primarily used for ruling out coronary artery disease in low-to-intermediate risk stable patients, not for high-risk **NSTEMI**.
- This modality still requires **iodinated contrast** and does not provide the therapeutic benefit of percutaneous coronary intervention (**PCI**).
*Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration*
- Delaying the procedure in a high-risk patient increases the risk of **re-infarction** and **cardiovascular death**, outweighing the minor benefits of prolonged hydration.
- Evidence suggests that optimization of renal status should happen concurrently with the preparation for **early intervention** in high-risk ACS.
*Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast*
- **Prophylactic hemodialysis** has not been proven to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy and may actually increase the risk of adverse events.
- High-volume **intravenous hydration** with isotonic saline remains the gold standard for preventing renal injury in patients with **CKD**.
*Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization*
- While **dual antiplatelet therapy** is essential, medical management alone is inferior to an invasive strategy in patients with **high GRACE scores**.
- Avoiding catheterization based solely on **renal impairment** results in "renalism," where patients are undertreated for their life-threatening cardiac condition.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 7: A 58-year-old woman with anterior STEMI underwent primary PCI with drug-eluting stent placement. Post-procedure echocardiogram shows left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% with apical akinesis. She is started on aspirin, ticagrelor, high-intensity statin, and ACE inhibitor. On hospital day 3, she develops atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. CHA2DS2-VASc score is 4. Creatinine is normal. Evaluate the optimal antithrombotic strategy balancing ischemic and bleeding risk.
- A. Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely
- B. Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely
- C. Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk
- D. Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor
- E. Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone (Correct Answer)
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone***
- In patients with **Atrial Fibrillation** (CHA2DS2-VASc ≥2) undergoing **PCI**, current guidelines recommend minimizing the duration of **triple therapy** (aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitor, and anticoagulant) to 1 week to 1 month to reduce **bleeding risk**.
- Transitioning to **dual therapy** with a **NOAC** (like apixaban) and a P2Y12 inhibitor (preferably **clopidogrel**) for up to 12 months, followed by NOAC monotherapy, provides an optimal balance between preventing **stent thrombosis** and systemic **thromboembolism**.
*Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely*
- Indefinite **triple therapy** carries a prohibitively high risk of life-threatening **major bleeding** without added benefit for stroke prevention.
- **Ticagrelor** is generally avoided in triple therapy regimens due to a significantly higher bleeding profile compared to **clopidogrel**.
*Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely*
- **Triple therapy** for 6 months is rarely indicated and significantly increases the risk of **gastrointestinal and intracranial hemorrhage** compared to the 1-month strategy.
- Aspirin is usually discontinued after the first year in favor of **anticoagulant monotherapy**, as the latter is sufficient for both AF and stable CAD protection.
*Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk*
- This approach leaves the patient with a high **CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4** unprotected against **cardioembolic stroke**, which carries high morbidity and mortality.
- Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) alone is significantly less effective than **oral anticoagulants** for stroke prevention in the setting of atrial fibrillation.
*Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor*
- **NOACs** (like apixaban) are now preferred over **Warfarin** for non-valvular AF due to a superior safety profile, including a lower risk of **intracranial hemorrhage**.
- Discontinuing the P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor) immediately post-PCI in favor of aspirin and warfarin significantly increases the risk of **stent thrombosis**.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 8: A 60-year-old man with inferoposterior STEMI presents to a rural hospital. The nearest PCI-capable facility is 3 hours away. He arrives 90 minutes after symptom onset. Blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg, heart rate 88/min, oxygen saturation 96% on room air. He has no contraindications to fibrinolysis. The transfer team can arrive in 30 minutes. Evaluate the evidence-based approach considering time metrics and available resources.
- A. Immediate fibrinolytic therapy followed by transfer (Correct Answer)
- B. Helicopter transfer to reduce transfer time, then primary PCI
- C. Administer half-dose fibrinolytic and transfer for immediate PCI
- D. Fibrinolytic therapy at rural hospital, transfer only if fails
- E. Wait for transfer team and proceed directly to PCI facility
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Immediate fibrinolytic therapy followed by transfer***
- In a STEMI patient where the expected **door-to-balloon time** exceeds **120 minutes**, and the patient is seen within **12 hours** of symptom onset, **fibrinolytic therapy** is the preferred reperfusion strategy.
- Following fibrinolysis, a **pharmacoinvasive strategy** is recommended, involving a routine transfer to a PCI-capable center for angiography within **3 to 24 hours**.
*Helicopter transfer to reduce transfer time, then primary PCI*
- Even with expedited transport, the distance and total time likely still exceed the recommended **120-minute window** for primary PCI superiority over fibrinolysis.
- Choosing transfer over immediate thrombolysis in a rural setting when delays are significant increases the risk of **myocardial necrosis**.
*Administer half-dose fibrinolytic and transfer for immediate PCI*
- **Half-dose fibrinolytics** are generally only considered in specific subsets like elderly patients (over 75) to reduce **intracranial hemorrhage** risk, which does not apply here.
- Combining half-dose thrombolysis with immediate PCI (facilitated PCI) has not shown superior outcomes and may increase **bleeding complications**.
*Fibrinolytic therapy at rural hospital, transfer only if fails*
- Modern guidelines recommend a **pharmacoinvasive approach**, meaning all patients should be transferred for **coronary angiography** regardless of clinical success of fibrinolysis.
- Waiting only for "failure" (rescue PCI) ignores the benefit of definitive **revascularization** and stabilization provided by routine post-thrombolysis PCI.
*Wait for transfer team and proceed directly to PCI facility*
- Delaying reperfusion for a 3-hour transport window violates the "**time is muscle**" principle, as the patient is currently in the highly time-sensitive **early window** (under 3 hours).
- Failure to administer fibrinolytics when the **PCI-related delay** is over 90-120 minutes is a deviation from standard **STEMI management protocols**.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 9: A 65-year-old man with extensive anterior STEMI underwent PCI 6 hours after symptom onset due to delayed presentation. Peak troponin was significantly elevated. Three days later, he develops progressive dyspnea. Examination reveals a new holosystolic murmur at the apex radiating to the axilla. Echocardiogram shows severe mitral regurgitation with flail posterior leaflet and hyperdynamic left ventricle. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure tracing shows prominent v waves. He is euvolemic on examination. Analyze this complication to determine timing of intervention.
- A. Immediate surgical mitral valve repair or replacement
- B. Aggressive diuresis and ACE inhibitor, reassess in 2 weeks
- C. Intra-aortic balloon pump with surgery within 24-48 hours (Correct Answer)
- D. Percutaneous mitral valve repair with MitraClip
- E. Medical management with afterload reduction for 6 weeks, then surgery
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Intra-aortic balloon pump with surgery within 24-48 hours***
- **Acute papillary muscle rupture** leads to severe mitral regurgitation and hemodynamic instability; an **IABP** provides essential **afterload reduction** and increases forward flow while reducing the regurgitant fraction.
- Providing a brief period of stabilization for 24-48 hours allows for therapeutic optimization before **urgent surgical intervention**, balancing the high risk of immediate surgery with the extreme mortality of medical delay.
*Immediate surgical mitral valve repair or replacement*
- Performing surgery immediately upon diagnosis carries an exceptionally high mortality rate due to the **friable, necrotic myocardial tissue** that is difficult to suture.
- While definitive, Proceeding without initial **hemodynamic stabilization** (like IABP) increases the risk of intraoperative cardiovascular collapse.
*Aggressive diuresis and ACE inhibitor, reassess in 2 weeks*
- This patient has a mechanical complication (flail leaflet); medical management alone for **acute MR** has a mortality rate exceeding 90%.
- **ACE inhibitors** may be poorly tolerated in the acute setting of a large MI if the patient becomes hypotensive, and waiting 2 weeks is far too long for a **mechanical emergency**.
*Percutaneous mitral valve repair with MitraClip*
- **MitraClip** is primarily indicated for chronic secondary MR or in patients with prohibitive surgical risk, rather than as first-line treatment for **acute post-MI papillary muscle rupture**.
- The necrotic and distorted nature of the **subvalvular apparatus** in an acute rupture makes it a poor substrate for percutaneous repair techniques.
*Medical management with afterload reduction for 6 weeks, then surgery*
- Delaying surgery for 6 weeks for "tissue healing" is inappropriate for **papillary muscle rupture** as the patient will likely suffer from progressive **pulmonary edema** or cardiogenic shock.
- While chronic MR can be managed medically, **acute structural failure** requires urgent mechanical correction once stable, not prolonged medical therapy.
ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG Question 10: A 72-year-old man with inferior STEMI underwent successful PCI 5 days ago. He develops sudden onset dyspnea and hypotension. Blood pressure is 75/50 mmHg with pulsus paradoxus of 20 mmHg. Jugular venous pressure is elevated with prominent x descent. Emergent echocardiography shows large pericardial effusion with right atrial and ventricular diastolic collapse. The patient is on aspirin, clopidogrel, and therapeutic enoxaparin. Analyze the complication and optimal intervention strategy.
- A. Immediate surgical exploration and repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Administer protamine and fresh frozen plasma, then observe
- C. Discontinue anticoagulation and observe with serial echocardiograms
- D. Increase intravenous fluid administration
- E. Urgent pericardiocentesis followed by surgical evaluation
ECG interpretation in MI Explanation: ***Immediate surgical exploration and repair***
- The patient presents with **free wall rupture** leading to **cardiac tamponade**, a lethal post-MI complication typically occurring 3 to 7 days after the event.
- Definitive treatment for mechanical rupture requires **emergent surgery** to repair the defect, as conservative management carries a near 100% mortality rate.
*Administer protamine and fresh frozen plasma, then observe*
- While reversing **anticoagulation** is important, observation is inappropriate for a patient with **mechanical rupture** and obstructive shock.
- Delaying surgery for medical reversal will likely result in **cardiac arrest** due to rapid hemodynamic collapse.
*Discontinue anticoagulation and observe with serial echocardiograms*
- Discontinuing medication addresses the risk of hemorrhage but fails to manage the primary **ventricular wall defect**.
- **Serial echocardiograms** are indicated for stable pericarditis, not a patient with **hypotension** and right heart collapse.
*Increase intravenous fluid administration*
- IV fluids can be a temporary bridge to maintain **preload** during tamponade, but they are never a curative or primary strategy.
- Over-reliance on fluid resuscitation delays the necessary **surgical decompression** and defect repair required for survival.
*Urgent pericardiocentesis followed by surgical evaluation*
- While it can relieve pressure, **pericardiocentesis** is often contraindicated in free wall rupture as it can dislodge a clot and **exacerbate bleeding**.
- Immediate transition to the **operating room** is the priority over bedside drainage in the setting of post-MI mechanical complications.
More ECG interpretation in MI US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.