Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Arrhythmic complications management. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 1: A 39-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after her husband found her unconscious on the living room floor. She does not report having experienced light-headedness, nausea, sweating, or visual disturbance before losing consciousness. Three weeks ago, she was diagnosed with open-angle glaucoma and began treatment with an antiglaucoma drug in the form of eye drops. She last used the eye drops 1 hour ago. Examination shows pupils of normal size that are reactive to light. An ECG shows sinus bradycardia. This patient is most likely undergoing treatment with which of the following drugs?
- A. Brimonidine
- B. Dorzolamide
- C. Latanoprost
- D. Pilocarpine
- E. Timolol (Correct Answer)
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Timolol***
- **Timolol** is a **non-selective beta-blocker** used to treat open-angle glaucoma by reducing aqueous humor production
- Can be **systemically absorbed** from eye drops, causing cardiac side effects including **bradycardia, hypotension, and syncope**
- The patient's presentation of **sudden unconsciousness without prodromal symptoms** plus **sinus bradycardia** is classic for beta-blocker toxicity
- Systemic absorption is enhanced with frequent dosing and can occur even with topical ophthalmic use
*Brimonidine*
- **Brimonidine** is an **alpha-2 adrenergic agonist** that reduces aqueous humor production and increases uveoscleral outflow
- Systemic absorption can cause CNS depression, fatigue, and hypotension, but **bradycardia is not a prominent feature**
- Would not typically present with syncope as the primary manifestation
*Dorzolamide*
- **Dorzolamide** is a **carbonic anhydrase inhibitor** that reduces aqueous humor production
- Systemic side effects include metabolic acidosis and electrolyte disturbances with chronic use
- **Not associated with significant bradycardia or acute syncope**
*Latanoprost*
- **Latanoprost** is a **prostaglandin F2-alpha analog** that increases uveoscleral outflow to lower intraocular pressure
- Side effects are primarily local (iris pigmentation, eyelash growth, conjunctival hyperemia)
- Has **minimal systemic absorption** and would not cause bradycardia or syncope
*Pilocarpine*
- **Pilocarpine** is a **muscarinic cholinergic agonist** that causes miosis and increases trabecular outflow
- Can cause cholinergic side effects including bradycardia, but typically accompanied by **miosis, salivation, lacrimation, nausea, and sweating**
- Patient has **normal-sized reactive pupils** and no cholinergic symptoms, ruling this out
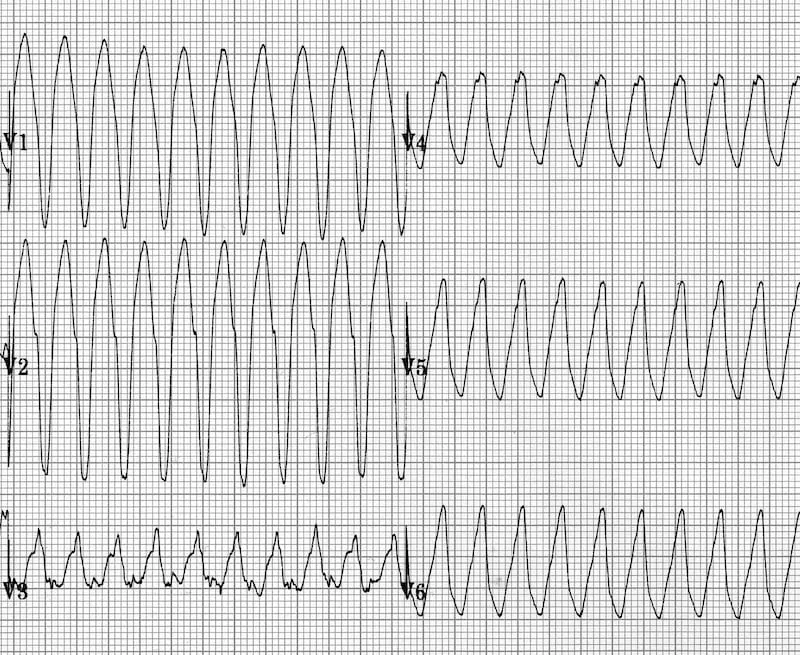
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 2: A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of syncope. He reports sudden onset of palpitations followed by loss of consciousness while carrying his groceries to his car. He is unable to recall any further details and does not have any chest pain or dizziness. He has a history of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, gastroparesis, and osteoarthritis of the knees. Medications include lisinopril, metformin, and ondansetron as needed for nausea. He also takes methadone daily for chronic pain. Apart from an abrasion on his forehead, he appears well. His temperature is 37.2 °C (98.9 F), heart rate is 104/min and regular, and blood pressure is 135/70 mm Hg. While he is in the emergency department, he loses consciousness again. Telemetry shows polymorphic ventricular tachycardia with cyclic alteration of the QRS axis that spontaneously resolves after 30 seconds. Results of a complete blood count, serum electrolyte concentrations, and serum thyroid studies show no abnormalities. Cardiac enzymes are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's syncope?
- A. Prinzmetal angina
- B. Fast accessory conduction pathway
- C. Brugada syndrome
- D. Prolonged QT interval (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypomagnesemia
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Prolonged QT interval***
- The patient experienced **polymorphic ventricular tachycardia** with cyclic alteration of the **QRS axis** (Torsades de Pointes), which is characteristic of a prolonged QT interval.
- **Methadone is known to prolong the QT interval**, and the patient's history of syncope preceded by palpitations is consistent with this arrhythmia.
*Prinzmetal angina*
- Prinzmetal angina involves **coronary artery spasm**, leading to **transient myocardial ischemia**, typically causing chest pain, not primarily syncope from polymorphic VT.
- While it can cause arrhythmias, the characteristic EKG finding would be **ST-segment elevation during pain**, which is not described.
*Fast accessory conduction pathway*
- A fast accessory pathway (e.g., in Wolfe-Parkinson-White syndrome) can lead to **AV reentrant tachycardia** or **pre-excitation** with atrial fibrillation, but not typically polymorphic VT with cyclic QRS alteration.
- The EKG would show a **delta wave** and a short PR interval, which is not mentioned.
*Brugada syndrome*
- Brugada syndrome is an inherited channelopathy **characterized by specific EKG patterns** (e.g., coved-type ST elevation in V1-V3) and an increased risk of sudden cardiac death due to ventricular arrhythmias.
- The patient's EKG findings of polymorphic VT with cyclic QRS alteration are not typical of Brugada syndrome-induced arrhythmia.
*Hypomagnesemia*
- While **hypomagnesemia can prolong the QT interval** and lead to Torsades de Pointes, the patient's **serum electrolyte concentrations were normal**, ruling out this direct cause.
- Magnesium levels would need to be critically low for such an effect, and this is typically detected on blood tests.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 3: A 63-year-old man with a history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation is brought into the emergency room and found to have a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Ibutilide is discontinued and the patient is switched to another drug that also prolongs the QT interval but is associated with a decreased risk of torsades de pointes. Which drug was most likely administered in this patient?
- A. Esmolol
- B. Digoxin
- C. Sotalol
- D. Amiodarone (Correct Answer)
- E. Quinidine
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Amiodarone***
- **Amiodarone** prolongs the **QT interval** but has a lower risk of **torsades de pointes** compared to other **Class III antiarrhythmics** due to its mixed ion channel blocking properties and consistent action potential prolongation.
- It's a broad-spectrum **antiarrhythmic drug** effective for both **atrial** and **ventricular arrhythmias**, making it a good choice for someone with a history of **atrial fibrillation** presenting with **ventricular tachyarrhythmia**.
*Esmolol*
- **Esmolol** is a **beta-blocker** that does not prolong the **QT interval**; it is used to slow heart rate and can be used for rhythm control but not by **QT prolongation**.
- Its primary action is on **beta-1 receptors**, reducing **myocardial contractility** and **heart rate**, primarily used for acute control of **tachyarrhythmias** or **hypertensive emergencies**.
*Digoxin*
- **Digoxin** is a **cardiac glycoside** that does not prolong the **QT interval**; it primarily works by inhibiting the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump** and increasing **vagal tone**.
- It is used to control **ventricular rate** in **atrial fibrillation** and to manage **heart failure**, but it is not an **antiarrhythmic** in the sense of directly terminating **ventricular tachyarrhythmias** by affecting **QT prolongation**.
*Sotalol*
- **Sotalol** is a **beta-blocker** with **Class III antiarrhythmic properties** that prolongs the **QT interval** and has a significant **dose-related risk of torsades de pointes**, particularly at higher doses.
- While it's effective for both **ventricular** and **supraventricular arrhythmias**, its risk of **TdP** is a major concern, making **amiodarone** a safer alternative when **TdP risk** is to be minimized.
*Quinidine*
- **Quinidine** is a **Class IA antiarrhythmic** that significantly prolongs the **QT interval** and is known for a high risk of causing **torsades de pointes**.
- It primarily blocks **fast sodium channels** and also **potassium channels**, contributing to its **proarrhythmic effects** and making it a less favored option when **TdP risk** needs to be decreased.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old man with hypertension and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation presents to his cardiologist for follow-up after recently starting metoprolol for rate control. His EKG shows an atrial rate of 260/min with ventricular rate of 50/min on an irregular baseline. An echocardiogram from his previous visit revealed no evidence of hypokinesis or hypertrophy with functionally intact valves. The patient does not drink alcohol and had no evidence of liver dysfunction in prior studies. What is the best medication for rhythm control in this patient?
- A. Amiodarone
- B. Flecainide (Correct Answer)
- C. Procainamide
- D. Verapamil
- E. Mexiletine
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Flecainide***
- **Flecainide** is a **Class IC antiarrhythmic** medication that is effective for rhythm control in patients with **paroxysmal atrial fibrillation** and no structural heart disease.
- The patient's echocardiogram showed no evidence of hypokinesis or hypertrophy, with functionally intact valves, indicating the **absence of structural heart disease**, which is a prerequisite for using Class IC agents like flecainide.
*Amiodarone*
- **Amiodarone** is a potent antiarrhythmic but is associated with numerous significant **extracardiac side effects**, including **pulmonary fibrosis**, **thyroid dysfunction**, and liver toxicity.
- It is generally reserved for patients with structural heart disease or those who have failed other antiarrhythmic therapies due to its extensive side effect profile.
*Procainamide*
- **Procainamide** is a **Class IA antiarrhythmic** that has a high incidence of side effects, including **drug-induced lupus**, and is typically used for acute management of arrhythmias, not long-term rhythm control in this setting.
- Its use is limited by its short half-life and significant proarrhythmic potential, especially in patients with structural heart disease or LV dysfunction.
*Verapamil*
- **Verapamil** is a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** primarily used for **rate control** in atrial fibrillation, not rhythm control.
- The patient is already on metoprolol for rate control, and the question specifically asks for a medication for rhythm control.
*Mexiletine*
- **Mexiletine** is a **Class IB antiarrhythmic** agent primarily used for treating **ventricular arrhythmias**, particularly in the setting of myocardial infarction.
- It is not typically used for rhythm control in atrial fibrillation and has limited efficacy in this context.
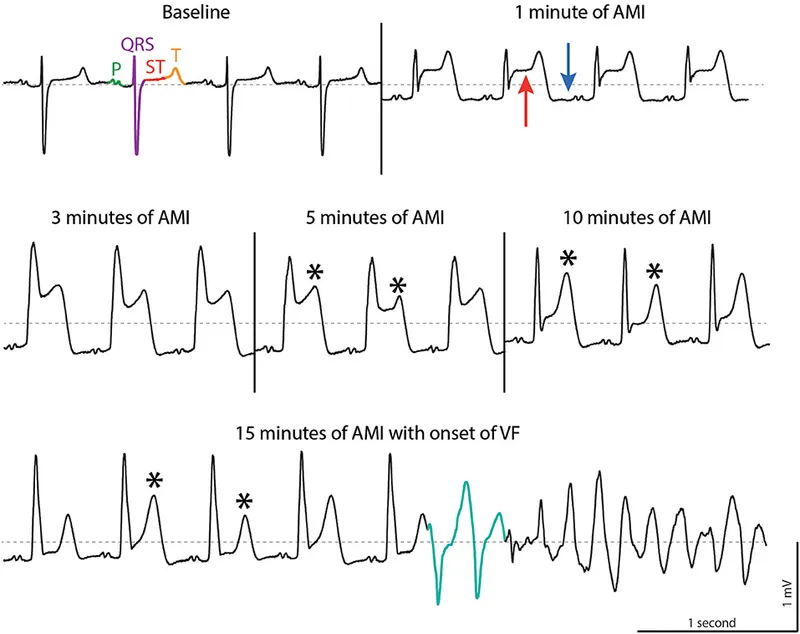
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 5: A 61-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance because of severe retrosternal chest pain and shortness of breath for 30 minutes. Paramedics report that an ECG recorded en route to the hospital showed ST-segment elevation in I, aVL, and the precordial leads. On arrival, the patient is unresponsive to painful stimuli. Examination shows neither respiration nor pulse. Despite appropriate lifesaving measures, he dies 10 minutes later. Which of the following is the most likely cause of death in this patient?
- A. Left ventricular failure
- B. Cardiac free wall rupture
- C. Ventricular fibrillation (Correct Answer)
- D. Ventricular aneurysm
- E. Hemorrhagic stroke
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Ventricular fibrillation***
- The rapid onset of symptoms, severe chest pain, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) involving extensive leads (I, aVL, and precordial), and sudden cardiac arrest without pulse or respiration strongly indicate a **malignant arrhythmia**, specifically ventricular fibrillation.
- In a STEMI, **ischemia** can rapidly trigger electrical instability in the myocardium, leading to disorganized electrical activity and immediate hemodynamic collapse.
*Left ventricular failure*
- While a large anterior STEMI could lead to **left ventricular failure**, the patient's immediate collapse and absence of respiration and pulse suggest sudden electrical rather than mechanical failure.
- **Left ventricular failure** typically manifests with progressive symptoms like severe dyspnea, pulmonary edema, and cardiogenic shock, which often allows for some period of clinical deterioration before death.
*Cardiac free wall rupture*
- **Cardiac free wall rupture** is a mechanical complication of MI that usually occurs several days post-infarction, though it can rarely occur acutely.
- It typically presents with **sudden severe chest pain**, hypotension, and rapid death due to **cardiac tamponade**, but the immediate timeline and ECG findings of extensive STEMI followed by sudden arrest are more consistent with an electrical event.
*Ventricular aneurysm*
- A **ventricular aneurysm** is a late complication of an MI, developing weeks to months after the event.
- It presents with symptoms like **heart failure**, arrhythmias, or mural thrombus formation, not as an acute cause of death within minutes of symptom onset.
*Hemorrhagic stroke*
- A **hemorrhagic stroke** would present with sudden neurological deficits, such as severe headache, altered consciousness, and focal neurological signs.
- While it can cause sudden death, the prominent chest pain and the ECG findings of widespread ST-segment elevation are indicative of a primary cardiac event.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 6: An 8-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother. She is concerned that her son has had intermittent periods of severe abdominal pain over the past several days that has been associated with emesis and "currant jelly" stool. Of note, the family lives in a rural part of the state, requiring a 2 hour drive to the nearest hospital. He currently appears to be in significant pain and has vomited twice in the past hour. On physical examination, a sausage-shaped mass is noted on palpation of the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. Ultrasound of the abdomen was consistent with a diagnosis of intussusception. An air-contrast barium enema was performed, which confirmed the diagnosis and also successfully reduced the intussusception. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Keep patient NPO and initiate work-up to identify lead-point
- B. Admit to hospital for 24 hour observation for complications and/or recurrence (Correct Answer)
- C. Pursue urgent surgical reduction with resection of necrotic segments of bowel
- D. Repeat barium enema q6 hrs to monitor for recurrence
- E. Discharge to home with follow-up in 3 weeks in an outpatient pediatric gastroenterology clinic
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Admit to hospital for 24 hour observation for complications and/or recurrence***
- Following successful non-operative reduction of intussusception, there is a risk of **recurrence** (approximately 5-10%) and potential for **perforation** or other delayed complications, necessitating close hospital observation.
- The patient's presentation with significant pain and vomiting, coupled with the long travel time to the hospital, further supports the need for **hospital admission** to monitor for stability and potential early recurrence.
*Keep patient NPO and initiate work-up to identify lead-point*
- While keeping the patient NPO (nil per os) might be appropriate initially, a work-up for a **lead point** is generally performed if there are multiple recurrences or in older children, as most intussusceptions in infants are idiopathic.
- Doing this immediately without observation can delay identification of recurrence and prompt intervention.
*Pursue urgent surgical reduction with resection of necrotic segments of bowel*
- Surgical reduction is indicated if **non-operative reduction fails**, if there are signs of **perforation**, diffuse peritonitis, or if there is clinical evidence of **bowel necrosis**.
- Since the intussusception was successfully reduced by air-contrast enema and there are no signs of perforation or necrosis currently, urgent surgery is not the immediate next step.
*Repeat barium enema q6 hrs to monitor for recurrence*
- Repeated enemas carry risks such as **radiation exposure** and potential for perforation, and are not a standard monitoring strategy for recurrence.
- Clinical observation and physical examination are generally sufficient for monitoring during the initial 24-hour period.
*Discharge to home with follow-up in 3 weeks in an outpatient pediatric gastroenterology clinic*
- Discharging the patient home so soon after reduction is unsafe due to the significant risk of **early recurrence** (especially within the first 24-48 hours) or development of complications.
- A follow-up in 3 weeks is too delayed for immediate post-reduction concerns.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 7: A 70-year-old man with diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease (eGFR 35 mL/min/1.73m²) presents with NSTEMI. Troponin is elevated at 8.5 ng/mL. ECG shows 2mm ST depression in V2-V5. GRACE score is 165 (high risk). He is hemodynamically stable. Cardiologist recommends early invasive strategy within 24 hours. Nephrologist is concerned about contrast-induced nephropathy potentially requiring dialysis. Patient is on metformin. Evaluate the management strategy integrating multiple specialist perspectives and evidence.
- A. Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin (Correct Answer)
- B. Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography
- C. Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration
- D. Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast
- E. Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin***
- High-risk NSTEMI patients with a **GRACE score >140** benefit from an **early invasive strategy** within 24 hours to reduce ischemic events and mortality.
- Renal protection is maximized through **pre-procedural hydration** and **iso-osmolar contrast**, while **metformin** must be held to avoid the risk of lactic acidosis if acute kidney injury occurs.
*Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography*
- **Coronary CTA** is primarily used for ruling out coronary artery disease in low-to-intermediate risk stable patients, not for high-risk **NSTEMI**.
- This modality still requires **iodinated contrast** and does not provide the therapeutic benefit of percutaneous coronary intervention (**PCI**).
*Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration*
- Delaying the procedure in a high-risk patient increases the risk of **re-infarction** and **cardiovascular death**, outweighing the minor benefits of prolonged hydration.
- Evidence suggests that optimization of renal status should happen concurrently with the preparation for **early intervention** in high-risk ACS.
*Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast*
- **Prophylactic hemodialysis** has not been proven to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy and may actually increase the risk of adverse events.
- High-volume **intravenous hydration** with isotonic saline remains the gold standard for preventing renal injury in patients with **CKD**.
*Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization*
- While **dual antiplatelet therapy** is essential, medical management alone is inferior to an invasive strategy in patients with **high GRACE scores**.
- Avoiding catheterization based solely on **renal impairment** results in "renalism," where patients are undertreated for their life-threatening cardiac condition.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 8: A 58-year-old woman with anterior STEMI underwent primary PCI with drug-eluting stent placement. Post-procedure echocardiogram shows left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% with apical akinesis. She is started on aspirin, ticagrelor, high-intensity statin, and ACE inhibitor. On hospital day 3, she develops atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. CHA2DS2-VASc score is 4. Creatinine is normal. Evaluate the optimal antithrombotic strategy balancing ischemic and bleeding risk.
- A. Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely
- B. Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely
- C. Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk
- D. Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor
- E. Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone (Correct Answer)
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone***
- In patients with **Atrial Fibrillation** (CHA2DS2-VASc ≥2) undergoing **PCI**, current guidelines recommend minimizing the duration of **triple therapy** (aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitor, and anticoagulant) to 1 week to 1 month to reduce **bleeding risk**.
- Transitioning to **dual therapy** with a **NOAC** (like apixaban) and a P2Y12 inhibitor (preferably **clopidogrel**) for up to 12 months, followed by NOAC monotherapy, provides an optimal balance between preventing **stent thrombosis** and systemic **thromboembolism**.
*Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely*
- Indefinite **triple therapy** carries a prohibitively high risk of life-threatening **major bleeding** without added benefit for stroke prevention.
- **Ticagrelor** is generally avoided in triple therapy regimens due to a significantly higher bleeding profile compared to **clopidogrel**.
*Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely*
- **Triple therapy** for 6 months is rarely indicated and significantly increases the risk of **gastrointestinal and intracranial hemorrhage** compared to the 1-month strategy.
- Aspirin is usually discontinued after the first year in favor of **anticoagulant monotherapy**, as the latter is sufficient for both AF and stable CAD protection.
*Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk*
- This approach leaves the patient with a high **CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4** unprotected against **cardioembolic stroke**, which carries high morbidity and mortality.
- Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) alone is significantly less effective than **oral anticoagulants** for stroke prevention in the setting of atrial fibrillation.
*Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor*
- **NOACs** (like apixaban) are now preferred over **Warfarin** for non-valvular AF due to a superior safety profile, including a lower risk of **intracranial hemorrhage**.
- Discontinuing the P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor) immediately post-PCI in favor of aspirin and warfarin significantly increases the risk of **stent thrombosis**.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 9: A 60-year-old man with inferoposterior STEMI presents to a rural hospital. The nearest PCI-capable facility is 3 hours away. He arrives 90 minutes after symptom onset. Blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg, heart rate 88/min, oxygen saturation 96% on room air. He has no contraindications to fibrinolysis. The transfer team can arrive in 30 minutes. Evaluate the evidence-based approach considering time metrics and available resources.
- A. Immediate fibrinolytic therapy followed by transfer (Correct Answer)
- B. Helicopter transfer to reduce transfer time, then primary PCI
- C. Administer half-dose fibrinolytic and transfer for immediate PCI
- D. Fibrinolytic therapy at rural hospital, transfer only if fails
- E. Wait for transfer team and proceed directly to PCI facility
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Immediate fibrinolytic therapy followed by transfer***
- In a STEMI patient where the expected **door-to-balloon time** exceeds **120 minutes**, and the patient is seen within **12 hours** of symptom onset, **fibrinolytic therapy** is the preferred reperfusion strategy.
- Following fibrinolysis, a **pharmacoinvasive strategy** is recommended, involving a routine transfer to a PCI-capable center for angiography within **3 to 24 hours**.
*Helicopter transfer to reduce transfer time, then primary PCI*
- Even with expedited transport, the distance and total time likely still exceed the recommended **120-minute window** for primary PCI superiority over fibrinolysis.
- Choosing transfer over immediate thrombolysis in a rural setting when delays are significant increases the risk of **myocardial necrosis**.
*Administer half-dose fibrinolytic and transfer for immediate PCI*
- **Half-dose fibrinolytics** are generally only considered in specific subsets like elderly patients (over 75) to reduce **intracranial hemorrhage** risk, which does not apply here.
- Combining half-dose thrombolysis with immediate PCI (facilitated PCI) has not shown superior outcomes and may increase **bleeding complications**.
*Fibrinolytic therapy at rural hospital, transfer only if fails*
- Modern guidelines recommend a **pharmacoinvasive approach**, meaning all patients should be transferred for **coronary angiography** regardless of clinical success of fibrinolysis.
- Waiting only for "failure" (rescue PCI) ignores the benefit of definitive **revascularization** and stabilization provided by routine post-thrombolysis PCI.
*Wait for transfer team and proceed directly to PCI facility*
- Delaying reperfusion for a 3-hour transport window violates the "**time is muscle**" principle, as the patient is currently in the highly time-sensitive **early window** (under 3 hours).
- Failure to administer fibrinolytics when the **PCI-related delay** is over 90-120 minutes is a deviation from standard **STEMI management protocols**.
Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old man with extensive anterior STEMI underwent PCI 6 hours after symptom onset due to delayed presentation. Peak troponin was significantly elevated. Three days later, he develops progressive dyspnea. Examination reveals a new holosystolic murmur at the apex radiating to the axilla. Echocardiogram shows severe mitral regurgitation with flail posterior leaflet and hyperdynamic left ventricle. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure tracing shows prominent v waves. He is euvolemic on examination. Analyze this complication to determine timing of intervention.
- A. Immediate surgical mitral valve repair or replacement
- B. Aggressive diuresis and ACE inhibitor, reassess in 2 weeks
- C. Intra-aortic balloon pump with surgery within 24-48 hours (Correct Answer)
- D. Percutaneous mitral valve repair with MitraClip
- E. Medical management with afterload reduction for 6 weeks, then surgery
Arrhythmic complications management Explanation: ***Intra-aortic balloon pump with surgery within 24-48 hours***
- **Acute papillary muscle rupture** leads to severe mitral regurgitation and hemodynamic instability; an **IABP** provides essential **afterload reduction** and increases forward flow while reducing the regurgitant fraction.
- Providing a brief period of stabilization for 24-48 hours allows for therapeutic optimization before **urgent surgical intervention**, balancing the high risk of immediate surgery with the extreme mortality of medical delay.
*Immediate surgical mitral valve repair or replacement*
- Performing surgery immediately upon diagnosis carries an exceptionally high mortality rate due to the **friable, necrotic myocardial tissue** that is difficult to suture.
- While definitive, Proceeding without initial **hemodynamic stabilization** (like IABP) increases the risk of intraoperative cardiovascular collapse.
*Aggressive diuresis and ACE inhibitor, reassess in 2 weeks*
- This patient has a mechanical complication (flail leaflet); medical management alone for **acute MR** has a mortality rate exceeding 90%.
- **ACE inhibitors** may be poorly tolerated in the acute setting of a large MI if the patient becomes hypotensive, and waiting 2 weeks is far too long for a **mechanical emergency**.
*Percutaneous mitral valve repair with MitraClip*
- **MitraClip** is primarily indicated for chronic secondary MR or in patients with prohibitive surgical risk, rather than as first-line treatment for **acute post-MI papillary muscle rupture**.
- The necrotic and distorted nature of the **subvalvular apparatus** in an acute rupture makes it a poor substrate for percutaneous repair techniques.
*Medical management with afterload reduction for 6 weeks, then surgery*
- Delaying surgery for 6 weeks for "tissue healing" is inappropriate for **papillary muscle rupture** as the patient will likely suffer from progressive **pulmonary edema** or cardiogenic shock.
- While chronic MR can be managed medically, **acute structural failure** requires urgent mechanical correction once stable, not prolonged medical therapy.
More Arrhythmic complications management US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.