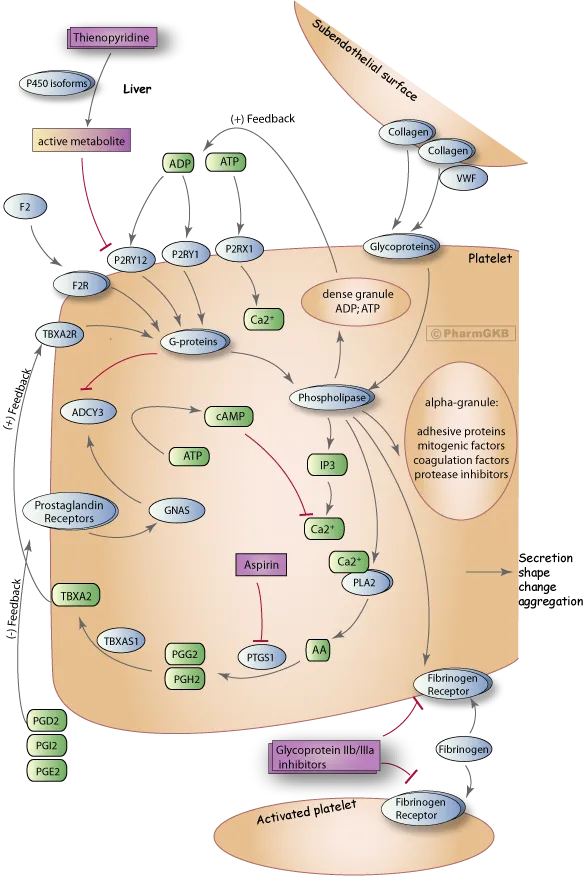
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antithrombotic therapies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 1: An 11-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department after she fell during a dance class. She was unable to stand after the accident and has a painful and swollen knee. On presentation she says that she has had 2 previous swollen joints as well as profuse bleeding after minor cuts. Based on her presentation, a panel of bleeding tests is obtained with the following results:
Bleeding time: 11 minutes
Prothrombin time: 12 seconds
Partial thromboplastin time: 52 seconds
Which of the following treatments would be most effective in treating this patient's condition?
- A. Vitamin K
- B. Factor VIII repletion
- C. Factor VII repletion
- D. Desmopressin (Correct Answer)
- E. Platelet infusion
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Desmopressin***
- The patient's history of **easy bruising and bleeding**, along with a **prolonged bleeding time** and **normal PT/prolonged PTT**, is highly suggestive of **von Willebrand disease (vWD)**, specifically type 1 given the bleeding time.
- **Desmopressin (DDAVP)** is the treatment of choice for vWD, as it stimulates the release of **endogenous von Willebrand factor (vWF)** and factor VIII from endothelial cells, improving both primary hemostasis and the intrinsic coagulation pathway.
*Vitamin K*
- **Vitamin K** is essential for the synthesis of functioning **coagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X**, as well as proteins C and S.
- This patient's **normal prothrombin time (PT)** suggests that the extrinsic and common pathways, which are dependent on adequate levels of vitamin K-dependent factors, are functioning adequately.
*Factor VIII repletion*
- Isolated **Factor VIII deficiency** (hemophilia A) would present with a **prolonged PTT** and **normal bleeding time**, as primary hemostasis (platelet plug formation) would be unaffected.
- In this patient, the **prolonged bleeding time** indicates a primary hemostasis defect, which is not directly corrected by Factor VIII repletion alone.
*Factor VII repletion*
- **Factor VII deficiency** primarily affects the **extrinsic coagulation pathway**, which would result in a **prolonged prothrombin time (PT)**.
- This patient has a **normal PT**, ruling out Factor VII deficiency as the primary cause of her bleeding disorder.
*Platelet infusion*
- A **prolonged bleeding time** can indicate a **quantitative (thrombocytopenia)** or **qualitative (platelet dysfunction)** defect in platelets.
- While platelet dysfunction is characteristic of vWD due to impaired platelet adhesion, **platelet infusions are generally not indicated for vWD** unless other therapies fail or in severe, life-threatening bleeding with very low vWF levels, as the issue is typically not a lack of platelets themselves but rather a lack of functional vWF to mediate their adhesion.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 2: A 60-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with chest pain that started 20 minutes ago while watching television at home. The pain is substernal and squeezing in nature. She rates the pain as 6/10 and admits to having similar pain in the past with exertion. Her past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus that is controlled with metformin. The physical examination is unremarkable. An electrocardiogram (ECG) shows ST-segment depression in the lateral leads. She is started on aspirin, nitroglycerin, metoprolol, unfractionated heparin, and insulin. She is asked not to take metformin while at the hospital. Three sets of cardiac enzymes are negative.
Lab results are given below:
Serum glucose 88 mg/dL
Sodium 142 mEq/L
Potassium 3.9 mEq/L
Chloride 101 mEq/L
Serum creatinine 1.2 mg/dL
Blood urea nitrogen 22 mg/dL
Cholesterol, total 170 mg/dL
HDL-cholesterol 40 mg/dL
LDL-cholesterol 80 mg/dL
Triglycerides 170 mg/dL
Hematocrit 38%
Hemoglobin 13 g/dL
Leucocyte count 7,500/mm3
Platelet count 185,000 /mm3
Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) 30 seconds
Prothrombin time (PT) 12 seconds
Urinalysis
Glucose negative
Ketones negative
Leucocytes negative
Nitrites negative
Red blood cells (RBC) negative
Casts negative
An echocardiogram reveals left ventricular wall motion abnormalities. With the pain subsiding, she was admitted and the medications were continued. A coronary angiography is planned in 4 days. In addition to regular blood glucose testing, which of the following should be closely monitored in this patient?
- A. Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) alone
- B. Prothrombin time alone
- C. aPTT and platelet count (Correct Answer)
- D. Platelet count alone
- E. Prothrombin time and platelet count
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***aPTT and platelet count***
- The patient is receiving **unfractionated heparin**, which requires monitoring of **aPTT** to ensure therapeutic anticoagulation and prevent bleeding complications.
- Heparin can also induce **heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)**, necessitating close monitoring of the **platelet count**.
*Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) alone*
- While **aPTT** monitoring is crucial for unfractionated heparin, it does not account for the risk of **heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)**.
- Monitoring platelet count is equally important alongside aPTT in patients receiving heparin.
*Prothrombin time alone*
- **Prothrombin time (PT)** is used to monitor **warfarin** therapy, not unfractionated heparin.
- Monitoring PT in this context would be inappropriate and would not provide information about the efficacy or safety of the prescribed heparin.
*Platelet count alone*
- Monitoring **platelet count** is important for detecting **heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)**, but it does not assess the therapeutic effect of heparin.
- **aPTT** monitoring is essential to ensure adequate anticoagulation and prevent thrombotic events.
*Prothrombin time and platelet count*
- **Prothrombin time (PT)** is irrelevant for unfractionated heparin monitoring, as it measures the extrinsic pathway and is used for warfarin.
- Although **platelet count** monitoring is important, relying on PT is incorrect for unfractionated heparin management.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 3: A 59-year-old woman comes to the physician because of left leg swelling that started after a transcontinental flight. A duplex ultrasound of the left leg shows a noncompressible popliteal vein. A drug is prescribed that inhibits the coagulation cascade. Two weeks later, laboratory studies show:
Platelet count 210,000/mm3
Partial thromboplastin time 28 seconds (normal: 25-35)
Prothrombin time 12 seconds (normal: 11-13)
Thrombin time 15 seconds (control: 15 seconds)
Which of the following drugs was most likely prescribed?
- A. Unfractionated heparin
- B. Apixaban
- C. Aspirin
- D. Warfarin
- E. Low molecular weight heparin (Correct Answer)
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Low molecular weight heparin***
- **LMWH (e.g., enoxaparin) is the first-line treatment for acute DVT** in ambulatory patients and is the most likely drug prescribed in this outpatient scenario
- LMWH enhances **antithrombin activity primarily against Factor Xa** (more than Factor IIa/thrombin), which is why it has **minimal effect on routine coagulation tests** (PT, PTT, TT)
- **Monitoring of LMWH is done via anti-Xa levels**, not PTT, PT, or TT, explaining why all these values remain normal two weeks after initiation
- The normal coagulation studies are **expected and consistent** with therapeutic LMWH use
*Unfractionated heparin*
- Unfractionated heparin (UFH) acts by enhancing **antithrombin activity against both Factor Xa and Factor IIa (thrombin)**, which significantly **prolongs PTT** (typically 1.5-2x control when therapeutic)
- UFH requires **IV administration and hospital monitoring**, making it unlikely for this ambulatory post-flight DVT patient
- If the patient were currently on UFH, the **PTT would be prolonged** (not normal as shown); if discontinued, this wouldn't be "the drug prescribed" for ongoing DVT treatment
*Apixaban*
- Apixaban is a **direct Factor Xa inhibitor** that would cause **mild prolongation of PT** and possibly PTT at therapeutic levels
- While it's a reasonable outpatient DVT treatment, the completely normal PT argues against current apixaban use
- Apixaban doesn't require routine monitoring, but when measured, coagulation times would typically show some abnormality
*Warfarin*
- Warfarin is a **vitamin K antagonist** that inhibits synthesis of factors II, VII, IX, and X, causing **significant PT/INR prolongation** (target INR 2-3 for DVT)
- The **normal PT (12 seconds) excludes warfarin** as the current medication
- Warfarin requires regular INR monitoring and would not show normal values at therapeutic doses
*Aspirin*
- Aspirin is an **antiplatelet agent** (COX-1 inhibitor) that affects platelet aggregation, **not the coagulation cascade**
- It has **no effect on PT, PTT, or TT** and is **inadequate monotherapy for DVT treatment**
- While it may have a role in extended VTE prevention, it would not be the primary drug prescribed for acute DVT
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 4: A 54-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after the sudden onset of shortness of breath, severe chest pain, and sweating. He has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He has smoked one pack and a half of cigarettes daily for 20 years. An ECG shows ST-segment elevations in leads II, III, and avF. The next hospital with a cardiac catheterization unit is more than 2 hours away. Reperfusion pharmacotherapy is initiated. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this medication?
- A. Conversion of plasminogen to plasmin (Correct Answer)
- B. Inhibition of glutamic acid residue carboxylation
- C. Blocking of adenosine diphosphate receptors
- D. Direct inhibition of thrombin activity
- E. Prevention of thromboxane formation
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Conversion of plasminogen to plasmin***
- **Fibrinolytic** (thrombolytic) drugs, like **tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)**, work by converting plasminogen to plasmin, which then degrades the **fibrin mesh** of a **blood clot**.
- This action helps to **restore blood flow** in cases of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) where primary **percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)** is not immediately available.
*Inhibition of glutamic acid residue carboxylation*
- This is the mechanism of action of **warfarin**, an anticoagulant that inhibits the synthesis of **vitamin K-dependent clotting factors** (II, VII, IX, X, protein C, and protein S).
- While important for long-term anticoagulation, it does not provide immediate reperfusion in an acute STEMI.
*Blocking of adenosine diphosphate receptors*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **P2Y12 inhibitors** such as **clopidogrel**, **prasugrel**, and **ticagrelor**.
- These drugs are **antiplatelet agents** that prevent platelet aggregation, but they do not directly dissolve an existing thrombus to restore blood flow in STEMI.
*Direct inhibition of thrombin activity*
- This is the mechanism of action of **direct thrombin inhibitors** like **dabigatran** and **bivalirudin**.
- These drugs primarily prevent clot formation or extension and are not used as primary reperfusion agents for acute STEMI due to an existing occlusive thrombus.
*Prevention of thromboxane formation*
- This is the primary mechanism of action of **aspirin**, which irreversibly inhibits **cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1)**, thereby reducing the production of thromboxane A2.
- Aspirin is an important antiplatelet drug in STEMI management but does not provide reperfusion by dissolving the clot.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 5: Drug A is an experimental compound being investigated for potential use as a protectant against venous thrombosis. Binding assays reveal that the drug’s primary mechanism of action is to block carboxylation of glutamic acid residues in certain serum proteins. Drug A is most similar to which of the following:
- A. Streptokinase
- B. Bivalirudin
- C. Warfarin (Correct Answer)
- D. Heparin
- E. Rivaroxaban
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Warfarin***
- Warfarin inhibits **vitamin K epoxide reductase**, enzyme responsible for regenerating active vitamin K.
- Active vitamin K is a cofactor for the **gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues** on factors II, VII, IX, X and protein C and S. Thus, warfarin blocks their activation, inhibiting coagulation.
*Steptokinase*
- **Streptokinase** is a **thrombolytic drug** that catalyzes the conversion of **plasminogen to plasmin**, an enzyme that degrades fibrin clots.
- Its mechanism of action is focused on **breaking down existing clots**, rather than preventing their formation by affecting coagulation factor synthesis.
*Bivalirudin*
- **Bivalirudin** is a direct **thrombin inhibitor**, binding directly to the active site and exosite I of thrombin to prevent its action.
- It does not interfere with the **carboxylation of glutamic acid residues** but rather directly inhibits the final common pathway of coagulation.
*Heparin*
- **Heparin** works by potentiating the action of **antithrombin III**, which in turn inactivates thrombin and factor Xa.
- Its mechanism involves accelerating the natural anticoagulant system, rather than inhibiting the **synthesis or activation of coagulation factors** through carboxylation.
*Rivaroxaban*
- **Rivaroxaban** is a **direct factor Xa inhibitor**, which blocks the activity of free and clot-bound factor Xa.
- It directly interferes with the coagulation cascade downstream of the carboxylation step, and does not affect the **vitamin K-dependent carboxylation process**.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 6: A 69-year-old man is brought by his son to the emergency department with weakness in his right arm and leg. The man insists that he is fine and blames his son for "creating panic". Four hours ago the patient was having tea with his wife when he suddenly dropped his teacup. He has had difficulty moving his right arm since then and cannot walk because his right leg feels stuck. He has a history of hypertension and dyslipidemia, for which he currently takes lisinopril and atorvastatin, respectively. He is allergic to aspirin and peanuts. A computerized tomography (CT) scan shows evidence of an ischemic stroke. Which medication would most likely prevent such attacks in this patient in the future?
- A. Celecoxib
- B. Abciximab
- C. Urokinase
- D. Clopidogrel (Correct Answer)
- E. Alteplase
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Clopidogrel***
- This patient has suffered an **ischemic stroke** and has a **contraindication to aspirin** due to allergy. **Clopidogrel**, an **alternative antiplatelet agent**, is the most appropriate long-term secondary prevention medication to reduce the risk of future thrombotic events.
- As a **P2Y12 inhibitor**, clopidogrel prevents platelet aggregation, thereby reducing the likelihood of clot formation in patients at high risk for cardiovascular events.
*Celecoxib*
- **Celecoxib** is a **COX-2 selective NSAID** primarily used for pain and inflammation. It has no role in the prevention of ischemic stroke.
- While NSAIDs can have antiplatelet effects through COX-1 inhibition, **COX-2 selective inhibitors like celecoxib generally have a prothrombotic effect** and are not indicated for stroke prevention.
*Abciximab*
- **Abciximab** is a **glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor** that potently prevents platelet aggregation. It is typically used in acute settings, such as during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and not for long-term stroke prevention.
- Its potent antiplatelet effect and **risk of bleeding** make it unsuitable for chronic outpatient management.
*Urokinase*
- **Urokinase** is a **thrombolytic agent** used to dissolve existing blood clots in acute conditions like pulmonary embolism or acute myocardial infarction. It is not indicated for the prevention of future ischemic strokes.
- Thrombolytics carry a **significant risk of hemorrhage** and are solely for acute clot lysis, not chronic prevention.
*Alteplase*
- **Alteplase** is a **tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)**, a thrombolytic used in the **acute treatment of ischemic stroke** within a specific time window to dissolve clots and restore blood flow.
- It is an **acute rescue therapy** and is not used for long-term secondary prevention of stroke due to its high bleeding risk and short duration of action.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 7: A 73-year-old man presents to the outpatient clinic complaining of chest pain with exertion. He states that resting for a few minutes usually resolves the chest pain. Currently, he takes 81 mg of aspirin daily. He has a blood pressure of 127/85 mm Hg and heart rate of 75/min. Physical examination reveals regular heart sounds and clear lung sounds bilateral. Which medication regimen below should be added?
- A. Metoprolol and a statin daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed. (Correct Answer)
- B. Clopidogrel and amlodipine daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.
- C. Amlodipine and a statin daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.
- D. Amlodipine daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.
- E. Metoprolol and ranolazine daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Metoprolol and a statin daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.***
- This patient presents with symptoms consistent with **stable angina** (**chest pain with exertion, relieved by rest**). The recommended medical therapy includes **antiplatelet agents** (aspirin, already prescribed), **beta-blockers** (metoprolol) for symptom control and improved survival post-MI, and **high-intensity statins** for lipid management and plaque stabilization. **Sublingual nitroglycerin** is crucial for acute symptom relief.
- Beta-blockers like metoprolol decrease myocardial **oxygen demand** by reducing heart rate and contractility, effectively treating angina. Statins are essential for **atherosclerosis management**.
*Clopidogrel and amlodipine daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.*
- While clopidogrel is an **antiplatelet agent**, aspirin is typically the first-line choice for stable angina unless there's an intolerance or compelling reason for dual antiplatelet therapy (e.g., recent stent placement), which is not indicated here.
- Amlodipine, a **calcium channel blocker**, can be used for angina but is usually a second-line agent if beta-blockers are contraindicated or insufficient; it doesn't offer the mortality benefit seen with beta-blockers post-MI.
*Amlodipine and a statin daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.*
- This regimen includes a **statin** and sublingual nitroglycerin, which are appropriate. However, it uses amlodipine instead of a beta-blocker, which is generally the preferred initial therapy for angina due to its benefits in reducing myocardial oxygen demand and improving outcomes, especially in patients with a history of MI or heart failure.
- Beta-blockers provide superior **mortality reduction benefits** in patients with coronary artery disease compared to calcium channel blockers.
*Amlodipine daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.*
- This option misses two critical components of comprehensive treatment for stable angina: a **statin** for lipid management and plaque stabilization, and a **beta-blocker** for primary symptom control and long-term cardiac protection.
- Relying solely on amlodipine and sublingual nitroglycerin would leave the patient incompletely treated for their underlying **coronary artery disease**.
*Metoprolol and ranolazine daily. Sublingual nitroglycerin as needed.*
- This option lacks a **statin**, which is a cornerstone of therapy for stable angina to manage atherosclerosis.
- While metoprolol is appropriate and ranolazine can be used as an add-on therapy for refractory angina, it's not typically a first-line agent and doesn't replace the need for a statin.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 8: A 70-year-old man with diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease (eGFR 35 mL/min/1.73m²) presents with NSTEMI. Troponin is elevated at 8.5 ng/mL. ECG shows 2mm ST depression in V2-V5. GRACE score is 165 (high risk). He is hemodynamically stable. Cardiologist recommends early invasive strategy within 24 hours. Nephrologist is concerned about contrast-induced nephropathy potentially requiring dialysis. Patient is on metformin. Evaluate the management strategy integrating multiple specialist perspectives and evidence.
- A. Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin (Correct Answer)
- B. Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography
- C. Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration
- D. Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast
- E. Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Proceed with angiography within 24 hours using iso-osmolar contrast and intravenous hydration, hold metformin***
- High-risk NSTEMI patients with a **GRACE score >140** benefit from an **early invasive strategy** within 24 hours to reduce ischemic events and mortality.
- Renal protection is maximized through **pre-procedural hydration** and **iso-osmolar contrast**, while **metformin** must be held to avoid the risk of lactic acidosis if acute kidney injury occurs.
*Perform coronary CT angiography as alternative to invasive angiography*
- **Coronary CTA** is primarily used for ruling out coronary artery disease in low-to-intermediate risk stable patients, not for high-risk **NSTEMI**.
- This modality still requires **iodinated contrast** and does not provide the therapeutic benefit of percutaneous coronary intervention (**PCI**).
*Delay catheterization for 72 hours to optimize renal function with hydration*
- Delaying the procedure in a high-risk patient increases the risk of **re-infarction** and **cardiovascular death**, outweighing the minor benefits of prolonged hydration.
- Evidence suggests that optimization of renal status should happen concurrently with the preparation for **early intervention** in high-risk ACS.
*Prophylactic hemodialysis before and after catheterization to remove contrast*
- **Prophylactic hemodialysis** has not been proven to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy and may actually increase the risk of adverse events.
- High-volume **intravenous hydration** with isotonic saline remains the gold standard for preventing renal injury in patients with **CKD**.
*Medical management only with dual antiplatelet therapy, avoid catheterization*
- While **dual antiplatelet therapy** is essential, medical management alone is inferior to an invasive strategy in patients with **high GRACE scores**.
- Avoiding catheterization based solely on **renal impairment** results in "renalism," where patients are undertreated for their life-threatening cardiac condition.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 9: A 58-year-old woman with anterior STEMI underwent primary PCI with drug-eluting stent placement. Post-procedure echocardiogram shows left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% with apical akinesis. She is started on aspirin, ticagrelor, high-intensity statin, and ACE inhibitor. On hospital day 3, she develops atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. CHA2DS2-VASc score is 4. Creatinine is normal. Evaluate the optimal antithrombotic strategy balancing ischemic and bleeding risk.
- A. Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely
- B. Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely
- C. Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk
- D. Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor
- E. Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone (Correct Answer)
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Triple therapy for 1 month, then apixaban and clopidogrel for 11 months, then apixaban alone***
- In patients with **Atrial Fibrillation** (CHA2DS2-VASc ≥2) undergoing **PCI**, current guidelines recommend minimizing the duration of **triple therapy** (aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitor, and anticoagulant) to 1 week to 1 month to reduce **bleeding risk**.
- Transitioning to **dual therapy** with a **NOAC** (like apixaban) and a P2Y12 inhibitor (preferably **clopidogrel**) for up to 12 months, followed by NOAC monotherapy, provides an optimal balance between preventing **stent thrombosis** and systemic **thromboembolism**.
*Triple therapy with aspirin, ticagrelor, and apixaban indefinitely*
- Indefinite **triple therapy** carries a prohibitively high risk of life-threatening **major bleeding** without added benefit for stroke prevention.
- **Ticagrelor** is generally avoided in triple therapy regimens due to a significantly higher bleeding profile compared to **clopidogrel**.
*Triple therapy for 6 months, then aspirin and apixaban indefinitely*
- **Triple therapy** for 6 months is rarely indicated and significantly increases the risk of **gastrointestinal and intracranial hemorrhage** compared to the 1-month strategy.
- Aspirin is usually discontinued after the first year in favor of **anticoagulant monotherapy**, as the latter is sufficient for both AF and stable CAD protection.
*Aspirin and ticagrelor only, hold anticoagulation due to bleeding risk*
- This approach leaves the patient with a high **CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4** unprotected against **cardioembolic stroke**, which carries high morbidity and mortality.
- Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) alone is significantly less effective than **oral anticoagulants** for stroke prevention in the setting of atrial fibrillation.
*Warfarin with INR 2-3 plus aspirin, discontinue ticagrelor*
- **NOACs** (like apixaban) are now preferred over **Warfarin** for non-valvular AF due to a superior safety profile, including a lower risk of **intracranial hemorrhage**.
- Discontinuing the P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor) immediately post-PCI in favor of aspirin and warfarin significantly increases the risk of **stent thrombosis**.
Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG Question 10: A 60-year-old man with inferoposterior STEMI presents to a rural hospital. The nearest PCI-capable facility is 3 hours away. He arrives 90 minutes after symptom onset. Blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg, heart rate 88/min, oxygen saturation 96% on room air. He has no contraindications to fibrinolysis. The transfer team can arrive in 30 minutes. Evaluate the evidence-based approach considering time metrics and available resources.
- A. Immediate fibrinolytic therapy followed by transfer (Correct Answer)
- B. Helicopter transfer to reduce transfer time, then primary PCI
- C. Administer half-dose fibrinolytic and transfer for immediate PCI
- D. Fibrinolytic therapy at rural hospital, transfer only if fails
- E. Wait for transfer team and proceed directly to PCI facility
Antithrombotic therapies Explanation: ***Immediate fibrinolytic therapy followed by transfer***
- In a STEMI patient where the expected **door-to-balloon time** exceeds **120 minutes**, and the patient is seen within **12 hours** of symptom onset, **fibrinolytic therapy** is the preferred reperfusion strategy.
- Following fibrinolysis, a **pharmacoinvasive strategy** is recommended, involving a routine transfer to a PCI-capable center for angiography within **3 to 24 hours**.
*Helicopter transfer to reduce transfer time, then primary PCI*
- Even with expedited transport, the distance and total time likely still exceed the recommended **120-minute window** for primary PCI superiority over fibrinolysis.
- Choosing transfer over immediate thrombolysis in a rural setting when delays are significant increases the risk of **myocardial necrosis**.
*Administer half-dose fibrinolytic and transfer for immediate PCI*
- **Half-dose fibrinolytics** are generally only considered in specific subsets like elderly patients (over 75) to reduce **intracranial hemorrhage** risk, which does not apply here.
- Combining half-dose thrombolysis with immediate PCI (facilitated PCI) has not shown superior outcomes and may increase **bleeding complications**.
*Fibrinolytic therapy at rural hospital, transfer only if fails*
- Modern guidelines recommend a **pharmacoinvasive approach**, meaning all patients should be transferred for **coronary angiography** regardless of clinical success of fibrinolysis.
- Waiting only for "failure" (rescue PCI) ignores the benefit of definitive **revascularization** and stabilization provided by routine post-thrombolysis PCI.
*Wait for transfer team and proceed directly to PCI facility*
- Delaying reperfusion for a 3-hour transport window violates the "**time is muscle**" principle, as the patient is currently in the highly time-sensitive **early window** (under 3 hours).
- Failure to administer fibrinolytics when the **PCI-related delay** is over 90-120 minutes is a deviation from standard **STEMI management protocols**.
More Antithrombotic therapies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.