Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Acid-base monitoring and management. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 1: A 27-year-old man with a past medical history of type I diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with altered mental status. The patient was noted as becoming more lethargic and confused over the past day, prompting his roommates to bring him in. His temperature is 99.0°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 107/68 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Laboratory values are ordered as seen below.
Serum:
Na+: 144 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 6.3 mEq/L
HCO3-: 16 mEq/L
BUN: 20 mg/dL
Glucose: 599 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL
Ca2+: 10.2 mg/dL
Which of the following is the appropriate endpoint of treatment for this patient?
- A. Clinically asymptomatic
- B. Normal anion gap (Correct Answer)
- C. Normal glucose
- D. Vitals stable
- E. Normal potassium
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Normal anion gap***
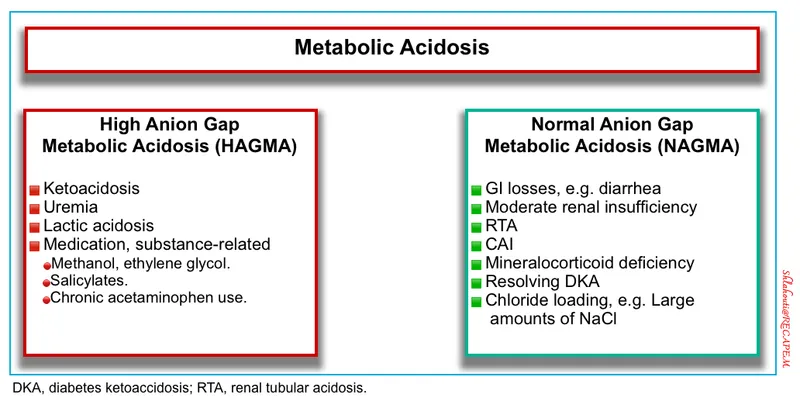
- A **normal anion gap** (approximately 8-12 mEq/L) indicates resolution of the **metabolic acidosis** characteristic of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). The current anion gap is high (Na - (Cl + HCO3) = 144 - (100 + 16) = 28 mEq/L).
- The patient's presentation with **type 1 diabetes** and **altered mental status**, coupled with **hyperglycemia** (599 mg/dL) and **low bicarbonate** (16 mEq/L), is highly suggestive of DKA, for which anion gap normalization is a key treatment endpoint.
*Clinically asymptomatic*
- While a desirable outcome, resolution of symptoms occurs gradually and is not the primary biochemical endpoint for DKA treatment.
- Patients may have residual symptoms even after metabolic derangements have significantly improved.
*Normal glucose*
- In DKA treatment, glucose is allowed to drop to a level (e.g., <200 mg/dL) but not necessarily to normal range, before initiating **dextrose-containing intravenous fluids** to prevent hypoglycemia while continuing insulin.
- **Normal glucose** alone does not guarantee resolution of ketoacidosis, which is the main life-threatening aspect of DKA.
*Vitals stable*
- **Stable vital signs** indicate hemodynamic stability, which is crucial but does not confirm the resolution of the underlying DKA metabolic derangements.
- Vitals can stabilize or worsen independently of acidosis resolution, especially if complications arise.
*Normal potassium*
- **Potassium levels** are critical to monitor and correct during DKA treatment, as insulin administration drives potassium into cells, potentially causing **hypokalemia**.
- While important for patient safety, achieving a normal potassium level is part of supportive care and not the primary endpoint for resolving the ketoacidotic state itself.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 2: A 19-year-old man with a history of type 1 diabetes presents to the emergency department for the evaluation of a blood glucose level of 492 mg/dL. Laboratory examination revealed a serum bicarbonate level of 13 mEq/L, serum sodium level of 122 mEq/L, and ketonuria. Arterial blood gas demonstrated a pH of 6.9. He is admitted to the hospital and given bicarbonate and then started on an insulin drip and intravenous fluid. Seven hours later when his nurse is making rounds, he is confused and complaining of a severe headache. Repeat sodium levels are unchanged, although his glucose level has improved. His vital signs include a temperature of 36.6°C (98.0°F), pulse 50/min, respiratory rate 13/min and irregular, and blood pressure 177/95 mm Hg. What other examination findings would be expected in this patient?
- A. Hypoglycemia
- B. Pupillary constriction
- C. Papilledema (Correct Answer)
- D. Pancreatitis
- E. Peripheral edema
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Papilledema***
- This patient's symptoms (confusion, severe headache, bradycardia, irregular respiration, hypertension) following treatment for **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** are highly suggestive of **cerebral edema**.
- **Papilledema** is a retinal finding resulting from increased intracranial pressure (ICP), which is a characteristic sign of cerebral edema.
*Hypoglycemia*
- While the patient's glucose level has improved, it is not described as being low enough to cause hypoglycemia, and the symptoms are more consistent with **increased ICP**.
- Symptoms of hypoglycemia (e.g., tremors, sweating, hunger, anxiety) are different from the patient's current presentation of confusion and severe headache.
*Pupillary constriction*
- **Pupillary constriction** (miosis) is typically not associated with cerebral edema; instead, **pupillary dilation** (mydriasis) can occur with severe increase in ICP due to uncal herniation.
- The combination of bradycardia, irregular respiration, and hypertension (Cushing's triad) is indicative of increased ICP, which would likely cause pupillary changes related to brainstem compression.
*Pancreatitis*
- Pancreatitis is a known complication of DKA, but it typically presents with **severe abdominal pain**, nausea, and vomiting, rather than cerebral symptoms.
- Although the patient had DKA, the current neurological symptoms point directly to an intracranial process rather than an abdominal issue.
*Peripheral edema*
- **Peripheral edema** results from fluid accumulation in peripheral tissues and is not a direct consequence or expected finding in cerebral edema.
- While fluid administration can cause some peripheral fluid retention, it typically does not lead to the acute neurological deterioration seen in this patient.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 3: A 16-year-old woman presents to the emergency department for evaluation of acute vomiting and abdominal pain. Onset was roughly 3 hours ago while she was sleeping. She has no known past medical history. Her family history is positive for hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus in her maternal grandmother. On examination, she is found to have fruity breath and poor skin turgor. She appears fatigued and her consciousness is slightly altered. Laboratory results show a blood glucose level of 691 mg/dL, sodium of 125 mg/dL, and elevated serum ketones. Of the following, which is the next best step in patient management?
- A. Administer IV fluids and insulin (Correct Answer)
- B. Initiate basal-bolus insulin regimen
- C. Initiate insulin glargine 10 units at bedtime only
- D. Initiate oral antidiabetic medications
- E. Initiate insulin aspart at mealtimes only
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Administer IV fluids and insulin***
- The patient presents with **fruity breath**, **altered consciousness**, **hyperglycemia (691 mg/dL)**, **hyponatremia**, and **elevated serum ketones**, which are classic signs of **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)**.
- The immediate management for DKA involves aggressive **intravenous fluid resuscitation** to correct dehydration and hypovolemia, followed by a continuous **intravenous insulin infusion** to lower blood glucose and suppress ketogenesis.
*Initiate basal-bolus insulin regimen*
- A **basal-bolus insulin regimen** is appropriate for long-term management of diabetes but is not the immediate treatment for acute DKA, which requires continuous intravenous insulin.
- This approach does not address the severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances seen in DKA, which need urgent fluid replacement.
*Initiate insulin glargine 10 units at bedtime only*
- **Insulin glargine** is a long-acting insulin used for basal insulin coverage, typically in the chronic management of diabetes.
- This dose is insufficient to manage acute DKA, and it also fails to address the critical need for fluid resuscitation.
*Initiate oral antidiabetic medications*
- **Oral antidiabetic medications** are suitable for individuals with type 2 diabetes or milder forms of insulin resistance, not for acute DKA.
- They are ineffective in severe hyperglycemia and metabolic acidosis characteristic of DKA, and do not address dehydration.
*Initiate insulin aspart at mealtimes only*
- **Insulin aspart** is a rapid-acting insulin used to cover mealtime glucose excursions.
- Administering it only at mealtimes is inadequate for acute DKA, which requires continuous insulin infusion and aggressive fluid management.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 4: A 14-year-old female with no past medical history presents to the emergency department with nausea and abdominal pain. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 78/65, her respiratory rate is 30, her breath has a fruity odor, and capillary refill is > 3 seconds. Serum glucose is 820 mg/dL. After starting IV fluids, what is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Intravenous Dextrose in water
- B. Subcutaneous insulin glargine
- C. Intravenous regular insulin (Correct Answer)
- D. Intravenous glucagon
- E. Subcutaneous insulin lispro
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Intravenous regular insulin***
- The patient presents with **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)**, characterized by **hyperglycemia**, **fruity breath** (due to ketones), and **hypotension**. Prompt administration of **intravenous regular insulin** is crucial to lower blood glucose and resolve ketoacidosis.
- **Regular insulin** is preferred intravenously due to its **rapid onset** and short duration of action, allowing for precise titration and continuous adjustment based on glucose levels.
*Intravenous Dextrose in water*
- **Dextrose** would further increase the already severely elevated blood glucose level in a patient with DKA, worsening the metabolic derangements.
- Dextrose is typically initiated only after blood glucose drops to safe levels (<200 mg/dL) to prevent **hypoglycemia** during insulin infusion.
*Subcutaneous insulin glargine*
- **Insulin glargine** is a **long-acting insulin** designed for basal insulin coverage, not for acute management of severe hyperglycemia or DKA.
- Its **slow onset of action** and prolonged effect make it unsuitable for the urgent and rapid glucose reduction required in DKA.
*Intravenous glucagon*
- **Glucagon** is a hormone that **raises blood glucose levels**, counteracting the effects of insulin.
- Administering glucagon would exacerbate the severe hyperglycemia present in DKA and is used only in cases of severe hypoglycemia.
*Subcutaneous insulin lispro*
- **Insulin lispro** is a **rapid-acting insulin analog** but is typically given subcutaneously.
- While faster than regular insulin subcutaneously, the **subcutaneous route** has variable absorption in critically ill patients, and the immediate and precisely controllable effect of intravenous regular insulin is needed in DKA.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 5: A 35-year-old patient with a history of diabetes presents to the ED with a myriad of systemic complaints. An arterial blood gas shows serum pH = 7.3, HCO3- = 13 mEq/L, PCO2 = 27 mmHg. Which of the following would you LEAST expect to observe in this patient?
- A. Increased anion gap
- B. Increased urine output
- C. Increased serum potassium
- D. Decreased respiratory rate (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased serum ketones
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Decreased respiratory rate***
- This patient has **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)**, which causes a metabolic acidosis. The body compensates for acidosis by increasing the respiratory rate (**Kussmaul respirations**) to blow off CO2, thus decreasing serum acidity.
- A decreased respiratory rate would worsen the acidosis by retaining CO2, which is contrary to the body's compensatory mechanism in DKA.
- This is what you would **LEAST expect** to observe in a patient with DKA.
*Increased anion gap*
- The patient's **pH of 7.3** and **HCO3- of 13 mEq/L** indicate a metabolic acidosis with a PCO2 of 27 mmHg showing respiratory compensation.
- DKA is characterized by the accumulation of **ketoacids** (acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate), which are unmeasured anions, leading to an **elevated anion gap**.
- This is an **expected finding** in DKA.
*Increased urine output*
- In DKA, **hyperglycemia** leads to an osmotic diuresis as excess glucose is filtered by the kidneys and draws water out, resulting in **polyuria** (increased urine output).
- This excessive urination contributes to **dehydration**, a common finding in DKA.
- This is an **expected finding** in DKA.
*Increased serum potassium*
- Despite total body potassium depletion, patients in DKA often present with **normal or elevated serum potassium** due to intracellular potassium shifting out of cells in exchange for hydrogen ions (to buffer acidosis).
- **Insulin deficiency** also contributes to this shift by impairing potassium uptake into cells.
- This is an **expected finding** in DKA, though potassium will drop with insulin treatment.
*Increased serum ketones*
- **Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** is fundamentally caused by insulin deficiency, leading to increased **lipolysis** and subsequent overproduction of **ketone bodies** (acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate) by the liver.
- These ketones accumulate in the blood, causing the characteristic metabolic acidosis and are measurable in serum and urine.
- This is an **expected finding** and diagnostic of DKA.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 6: A 52-year-old man with a history of Type 1 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency room with increasing fatigue. Two days ago, he ran out of insulin and has not had time to obtain a new prescription. He denies fevers or chills. His temperature is 37.2 degrees Celsius, blood pressure 84/56 mmHg, heart rate 100/min, respiratory rate 20/min, and SpO2 97% on room air. His physical exam is otherwise within normal limits. An arterial blood gas analysis shows the following:
pH 7.25, PCO2 29, PO2 95, HCO3- 15.
Which of the following acid-base disorders is present?
- A. Respiratory alkalosis with appropriate metabolic compensation
- B. Respiratory acidosis with appropriate metabolic compensation
- C. Mixed metabolic and respiratory acidosis
- D. Metabolic acidosis with appropriate respiratory compensation (Correct Answer)
- E. Metabolic alkalosis with appropriate respiratory compensation
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Metabolic acidosis with appropriate respiratory compensation***
- The patient's pH of 7.25 and HCO3- of 15 indicate **metabolic acidosis**, while the PCO2 of 29 indicates **respiratory compensation**.
- The compensation is **appropriate** as suggested by Winter's formula [Expected PCO2 = (1.5 x HCO3-) + 8 +/- 2; (1.5 x 15) + 8 = 30.5, which is close to 29].
*Respiratory alkalosis with appropriate metabolic compensation*
- This would involve a **pH > 7.45** and **low PCO2** with a secondary drop in HCO3-, which is not seen here.
- The patient's primary problem is a metabolic disturbance due to insulin deficiency.
*Respiratory acidosis with appropriate metabolic compensation*
- This disorder is characterized by a **low pH** and a **high PCO2**, with a secondary rise in HCO3-.
- The patient's PCO2 is low, indicating a compensatory response rather than a primary respiratory acidosis.
*Mixed metabolic and respiratory acidosis*
- A mixed disorder would show a **low pH** due to both **low HCO3-** and **high PCO2**.
- The patient's PCO2 is low, indicating a compensatory response to metabolic acidosis, not an additional respiratory acidosis.
*Metabolic alkalosis with appropriate respiratory compensation*
- This would present with a **high pH (>7.45)** and **high HCO3-**, with compensatory **elevated PCO2**.
- The patient's pH and HCO3- are low, indicating acidosis, not alkalosis.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 7: A 48-year-old man presents with DKA. Initial treatment is initiated with fluids and insulin infusion. Labs show glucose 460 mg/dL, pH 7.18, bicarbonate 10 mEq/L, potassium 4.5 mEq/L, and creatinine 2.8 mg/dL (baseline 1.0). After 4 hours, glucose decreases to 380 mg/dL but pH worsens to 7.12, bicarbonate drops to 8 mEq/L, and lactate is 5.2 mmol/L (initially 1.8). Blood pressure is 85/50 mmHg. Evaluate the clinical situation and necessary intervention.
- A. Administer additional fluid bolus for persistent hypotension
- B. Evaluate for sepsis or other concurrent illness causing lactic acidosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Increase insulin infusion rate to accelerate ketone clearance
- D. Add bicarbonate therapy for worsening acidosis
- E. Continue current management as DKA takes time to resolve
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Evaluate for sepsis or other concurrent illness causing lactic acidosis***
- While the blood glucose is responding to insulin, the **worsening metabolic acidosis** and significantly elevated **lactate (5.2 mmol/L)** indicate a secondary process such as **sepsis** or tissue hypoperfusion.
- **Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)** often has a precipitating factor; the combination of **hypotension** and rising lactate suggests **septic shock** or organic ischemia that requires urgent investigation and targeted treatment.
*Administer additional fluid bolus for persistent hypotension*
- Although fluid resuscitation is vital, simply giving more fluids without diagnosing the **underlying cause** of the rising lactate and refractory shock is insufficient.
- **Hypotension** in this context may be secondary to **septic shock** or systemic inflammatory response rather than simple volume depletion from DKA.
*Increase insulin infusion rate to accelerate ketone clearance*
- The current insulin infusion is successfully lowering the blood glucose, but the acidosis is worsening due to **lactic acid**, not just ketones.
- Increasing insulin will not resolve **Type A lactic acidosis** caused by **inadequate tissue oxygenation** or sepsis.
*Add bicarbonate therapy for worsening acidosis*
- **Bicarbonate therapy** is generally not recommended in DKA unless the pH is <6.9, as it can cause **paradoxical cerebral acidosis** and hypokalemia.
- Administering bicarbonate would provide a temporary buffer but would fail to address the **rising lactate** and underlying hemodynamic instability.
*Continue current management as DKA takes time to resolve*
- While DKA resolution is gradual, a **rising lactate** and **falling pH** despite therapy are red flags that indicate the clinical condition is deteriorating.
- Ignoring the **acute kidney injury** (Creatinine 2.8) and persistent **hypotension** increases the risk of multi-organ failure and mortality.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 8: A 25-year-old woman with type 1 diabetes presents with DKA. She admits to intentionally withholding insulin to lose weight. This is her fifth DKA admission in 8 months. Current pH is 7.14, glucose 520 mg/dL, bicarbonate 11 mEq/L. Medical costs exceed $150,000 for recurrent admissions. The team is frustrated. Evaluate the comprehensive management approach beyond acute DKA treatment.
- A. Referral to ethics committee for discussion of resource allocation
- B. Involuntary psychiatric commitment for non-compliance
- C. Insulin pump placement to prevent future manipulation
- D. Multidisciplinary approach including psychiatry, eating disorder specialist, diabetes educator, and close outpatient follow-up (Correct Answer)
- E. Standard DKA treatment with discharge to outpatient endocrinology
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Multidisciplinary approach including psychiatry, eating disorder specialist, diabetes educator, and close outpatient follow-up***
- This patient presents with **diabulimia**, a life-threatening eating disorder where Type 1 diabetics restrict insulin for weight control, requiring a **comprehensive care team** to address both physiologic and psychological needs.
- A **multidisciplinary strategy** is essential to reduce the high risk of mortality and frequent **recurrent DKA admissions** by targeting the root cause of non-compliance.
*Referral to ethics committee for discussion of resource allocation*
- While medical costs are high, **withholding treatment** based on cost or resource allocation for a life-threatening condition like DKA is generally unethical.
- The **ethics committee** may assist in complex care plans, but it does not address the primary clinical need for specialized psychiatric and nutritional intervention.
*Involuntary psychiatric commitment for non-compliance*
- **Involuntary commitment** typically requires the patient to be a danger to themselves or others due to a mental illness; insulin omission, while dangerous, often does not meet legal criteria if the patient has **decision-making capacity**.
- Simple **non-compliance** in an adult with capacity is not usually grounds for commitment, and long-term behavioral change is better achieved through voluntary therapeutic engagement.
*Insulin pump placement to prevent future manipulation*
- An **insulin pump** is not a solution as it can still be easily manipulated, disconnected, or the settings altered by a patient determined to restrict insulin.
- Introducing a medical device without addressing the **underlying eating disorder** may actually complicate management and increase the risk of device-related complications.
*Standard DKA treatment with discharge to outpatient endocrinology*
- Given five DKA admissions in 8 months, standard management has already proven **insufficient** and fails to address the unique psychiatric etiology of her condition.
- Discharging to **standard outpatient endocrinology** without specialized eating disorder support ignores the behavioral triggers that lead to recurrent life-threatening metabolic crises.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man with type 2 diabetes and end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis presents with DKA. Initial glucose is 580 mg/dL, pH 7.12, bicarbonate 10 mEq/L, and potassium 6.2 mEq/L. He is fluid overloaded with bilateral crackles and peripheral edema. His last dialysis was 3 days ago. Evaluate the optimal management strategy addressing both DKA and renal failure.
- A. Standard DKA protocol with furosemide for fluid management
- B. Bicarbonate therapy to correct acidosis without fluids
- C. Subcutaneous insulin with no IV fluids due to volume overload
- D. Insulin infusion with limited fluids and urgent hemodialysis (Correct Answer)
- E. Standard DKA protocol with aggressive fluid resuscitation
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Insulin infusion with limited fluids and urgent hemodialysis***
- Patients with **ESRD** and **DKA** who are **fluid overloaded** require **urgent hemodialysis** to safely correct metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia, and volume status.
- **Continuous insulin infusion** is essential to stop ketone production, but fluid resuscitation must be severely **restricted** to avoid worsening pulmonary edema.
*Standard DKA protocol with furosemide for fluid management*
- **Furosemide** is ineffective in patients with **end-stage renal disease** (ESRD) as they have minimal to no residual renal function.
- Standard DKA protocols prioritize aggressive IV fluids, which would be **life-threatening** for a patient already showing signs of volume overload and crackles.
*Bicarbonate therapy to correct acidosis without fluids*
- **Bicarbonate therapy** is generally not recommended for DKA unless the pH is below 6.9, and it can cause a **rebound worsening** of intracellular acidosis.
- It does not address the underlying **insulin deficiency** or the patient's massive **volume overload** and hyperkalemia.
*Subcutaneous insulin with no IV fluids due to volume overload*
- **Subcutaneous insulin** is inappropriate for severe DKA (pH 7.12); **intravenous insulin** is the standard for rapid titration and metabolic control.
- Complete avoidance of fluids may prevent correction of the **osmotic shift**, but the primary failure here is the omission of dialysis for a symptomatic ESRD patient.
*Standard DKA protocol with aggressive fluid resuscitation*
- Aggressive fluid administration is **contraindicated** in ESRD patients with clinical signs of **congestive heart failure** like crackles and peripheral edema.
- This approach carries a high risk of inducing **acute respiratory failure** or flash pulmonary edema.
Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG Question 10: A 38-year-old pregnant woman at 28 weeks gestation with type 1 diabetes presents with nausea and vomiting. Labs show glucose 310 mg/dL, pH 7.27, bicarbonate 15 mEq/L, and positive urine ketones. Fetal monitoring shows reactive non-stress test. She has been taking her insulin but unable to eat for 24 hours due to hyperemesis. Analyze the optimal management approach considering maternal and fetal risks.
- A. Standard DKA protocol with standard glucose targets (200-250 mg/dL)
- B. Aggressive DKA treatment with lower glucose targets (100-150 mg/dL) and close fetal monitoring (Correct Answer)
- C. Immediate cesarean delivery followed by DKA treatment
- D. Conservative management with oral intake and subcutaneous insulin
- E. Standard DKA protocol with delivery planning after stabilization
Acid-base monitoring and management Explanation: ***Aggressive DKA treatment with lower glucose targets (100-150 mg/dL) and close fetal monitoring***
- In pregnancy, **Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)** often presents with lower blood glucose levels due to increased **glucose utilization** by the fetus and placenta.
- Successful management requires **aggressive hydration**, **intravenous insulin**, and maintaining blood glucose between **100-150 mg/dL** to prevent fetal complications.
*Standard DKA protocol with standard glucose targets (200-250 mg/dL)*
- Standard targets for non-pregnant adults are too high for pregnancy and can lead to prolonged **fetal acidosis** and increased morbidity.
- Pregnancy-specific protocols prioritize tighter glycemic control to optimize the **maternal-fetal environment** during acute metabolic distress.
*Immediate cesarean delivery followed by DKA treatment*
- Surgery during **untreated DKA** carries extremely high maternal and fetal risk; the fetus should only be delivered for **obstetric indications** after maternal stabilization.
- **Fetal heart rate** abnormalities often resolve once the mother's **acidosis** and electrolyte imbalances are corrected with medical therapy.
*Conservative management with oral intake and subcutaneous insulin*
- Maternal **acidemia (pH 7.27)** and **ketonuria** indicate a medical emergency that cannot be safely managed with subcutaneous insulin or oral fluids.
- **Nausea and vomiting** from hyperemesis or the DKA itself necessitate **intravenous fluid resuscitation** and specialized inpatient monitoring.
*Standard DKA protocol with delivery planning after stabilization*
- While maternal stabilization is the primary goal, following a "standard" protocol ignores the need for **lower glucose targets** unique to pregnancy.
- **Delivery planning** at 28 weeks should only be considered if fetal distress persists after maternal metabolic status has returned to baseline.
More Acid-base monitoring and management US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.