Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Hypertensive emergencies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of blurry vision for the past 3 days. He has also had 4 episodes of right-sided headaches over the past month. He has no significant past medical history. His father died of coronary artery disease at the age of 62 years. His temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 94/min, and blood pressure is 232/128 mm Hg. Fundoscopy shows right-sided optic disc blurring and retinal hemorrhages. A medication is given immediately. Five minutes later, his pulse is 75/min and blood pressure is 190/105 mm Hg. Which of the following drugs was most likely administered?
- A. Nicardipine
- B. Hydralazine
- C. Nitroprusside
- D. Fenoldopam
- E. Labetalol (Correct Answer)
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Labetalol***
- This patient presents with **malignant hypertension** given the severely elevated blood pressure (232/128 mm Hg) and signs of **end-organ damage** (blurry vision, optic disc blurring, retinal hemorrhages suggesting hypertensive retinopathy, and new-onset headaches).
- **Labetalol** is a mixed alpha- and beta-blocker commonly used in hypertensive emergencies because of its **rapid onset of action** and ability to effectively lower blood pressure without causing significant reflex tachycardia. The decrease in pulse rate from 94/min to 75/min after administration is consistent with its beta-blocking effects.
*Nicardipine*
- **Nicardipine** is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker that primarily causes **vasodilation**, making it effective in hypertensive emergencies.
- While it would lower blood pressure, it typically causes **reflex tachycardia** due to vasodilation, which is not observed in this patient (pulse decreased).
*Hydralazine*
- **Hydralazine** is a direct arterial vasodilator often used in hypertensive emergencies, but it typically causes a more pronounced **reflex tachycardia** than calcium channel blockers.
- Its onset of action can also be less predictable, and its use is generally avoided if there's evidence of **coronary artery disease** due to the risk of increased myocardial oxygen demand.
*Nitroprusside*
- **Nitroprusside** is a powerful balanced arterial and venous vasodilator, leading to a rapid and significant drop in blood pressure.
- It is known for causing **reflex tachycardia** and has a risk of **cyanide toxicity** with prolonged use, making its use in this scenario less ideal given the patient's existing elevated pulse.
*Fenoldopam*
- **Fenoldopam** is a dopamine-1 receptor agonist that causes vasodilation and improves renal blood flow, useful in hypertensive emergencies.
- Like other vasodilators, it can cause **reflex tachycardia** and may lead to increased intraocular pressure, which would be a concern in a patient with acute blurry vision.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 2: A 75 year-old gentleman presents to his general practitioner. He is currently being treated for hypertension and is on a multi-drug regimen. His current blood pressure is 180/100. The physician would like to begin treatment with minoxidil or hydralazine. Which of the following side effects is associated with administration of these drugs?
- A. Persistent cough
- B. Cyanosis in extremities
- C. Fetal renal toxicity
- D. Systemic volume loss
- E. Reflex tachycardia (Correct Answer)
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Reflex tachycardia***
- Both **minoxidil** and **hydralazine** are direct arterial vasodilators, causing a significant drop in **peripheral vascular resistance**.
- This vasodilation triggers a **baroreflex response**, leading to an increase in heart rate and **cardiac contractility** to maintain cardiac output, resulting in reflex tachycardia.
*Persistent cough*
- **Persistent cough** is a common side effect associated with **ACE inhibitors**, such as lisinopril or enalapril, due to the accumulation of **bradykinin**.
- This side effect is not typically seen with **minoxidil** or **hydralazine**, which act directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause vasodilation.
*Cyanosis in extremities*
- **Cyanosis** (bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes) usually indicates **hypoxemia** or poor peripheral perfusion.
- While sometimes associated with severe cardiogenic shock or specific drug toxicities like methemoglobinemia (not related to minoxidil or hydralazine), it is not a direct or typical side effect of these vasodilators.
*Fetal renal toxicity*
- **Fetal renal toxicity**, including **fetal renal dysfunction** and **oligohydramnios**, is a well-known risk associated with **ACE inhibitors** and **ARBs** during pregnancy.
- Neither **minoxidil** nor **hydralazine** are primarily linked to this specific fetal adverse effect, though hydralazine can be used in pregnancy for severe hypertension.
*Systemic volume loss*
- **Systemic volume loss** is usually caused by conditions like **dehydration**, excessive diuresis, or hemorrhage.
- While vasodilators can reduce blood pressure, they do not directly cause **systemic volume depletion**; rather, the reflex response to vasodilation can include fluid retention to counteract the blood pressure drop.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 3: You are called to a hemodialysis suite. The patient is a 61-year-old man with a history of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and type-2 diabetes mellitus-induced end-stage renal disease who has required hemodialysis for the past year. His current hemodialysis session is nearing the end when the nurse notices that his blood pressure has dropped to 88/60 mm Hg from his normal of 142/90 mm Hg. The patient denies any shortness of breath or chest pain. He took his daily bisoprolol, metformin, and insulin this morning before coming to the hospital. On examination, the patient’s blood pressure is 92/60 mm Hg, and his heart rate is 119/min. Chest auscultation is unremarkable. What is the most appropriate next management step?
- A. Infuse 1 liter of 0.9% saline
- B. Administer intravenous calcium gluconate
- C. Transfuse the patient with 1 unit of packed red blood cells
- D. Stop ultrafiltration and decrease blood flow into the machine (Correct Answer)
- E. Start the patient on an epinephrine drip
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Stop ultrafiltration and decrease blood flow into the machine***
- The patient's **hypotension** and **tachycardia** during hemodialysis strongly suggest **intradialytic hypotension**, which is often caused by excessive fluid removal (ultrafiltration) or rapid fluid shifts.
- **Stopping ultrafiltration** and **reducing blood flow** allows for gradual re-equilibration of fluid and helps stabilize blood pressure without adding more fluid to a patient with end-stage renal disease.
*Infuse 1 liter of 0.9% saline*
- Administering a large volume of saline is generally **contraindicated in ESRD patients** given their inability to excrete fluid, which could lead to **fluid overload** and pulmonary edema.
- While fluid resuscitation might be considered for severe hypotension, the initial step in intradialytic hypotension is to adjust the dialysis settings.
*Administer intravenous calcium gluconate*
- **Calcium gluconate** is primarily used to stabilize the cardiac membrane in cases of **severe hyperkalemia**, which is not indicated by the current clinical picture.
- There is no mention of ECG changes or lab results to suggest hyperkalemia.
*Transfuse the patient with 1 unit of packed red blood cells*
- There is no clinical evidence of **acute blood loss** or **severe anemia** presenting with hypovolemic shock.
- Transfusion is an intervention for significant blood loss or severe anemia, not for intradialytic hypotension caused by fluid shifts.
*Start the patient on an epinephrine drip*
- **Vasopressors** like epinephrine are typically reserved for **refractory hypotension** after more conservative measures have failed, or in cases of **septic shock** or **anaphylaxis**.
- Initiating a powerful vasopressor as a first step without addressing the potential underlying cause related to dialysis is inappropriate.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 4: A 60-year-old male is admitted to the ICU for severe hypertension complicated by a headache. The patient has a past medical history of insulin-controlled diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes per day. He states that he forgot to take his medications yesterday and started getting a headache about one hour ago. His vitals on admission are the following: blood pressure of 160/110 mmHg, pulse 95/min, temperature 98.6 deg F (37.2 deg C), and respirations 20/min. On exam, the patient has an audible abdominal bruit. After administration of antihypertensive medications, the patient has a blood pressure of 178/120 mmHg. The patient reports his headache has increased to a 10/10 pain level, that he has trouble seeing, and he can't move his extremities. After stabilizing the patient, what is the best next step to diagnose the patient's condition?
- A. Doppler ultrasound of the carotids
- B. CT head with intravenous contrast
- C. MRI head without intravenous contrast
- D. CT head without intravenous contrast (Correct Answer)
- E. MRI head with intravenous contrast
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***CT head without intravenous contrast***
- The sudden onset of severe headache, visual disturbances, and neurological deficits (inability to move extremities), coupled with uncontrolled severe hypertension despite initial treatment, is highly suggestive of an **intracranial pathology**, most likely a **hemorrhagic stroke**.
- A **non-contrast CT scan of the head** is the **gold standard** for rapidly identifying acute intracranial hemorrhage, as it can be performed quickly and is readily available in emergency settings.
*Doppler ultrasound of the carotids*
- This test is primarily used to evaluate **carotid artery stenosis** due to atherosclerosis, which can lead to ischemic stroke.
- While the patient has risk factors for atherosclerosis, his acute presentation with severe central neurological symptoms points more towards an acute intracranial event rather than carotid disease.
*CT head with intravenous contrast*
- While a contrast CT can be useful for identifying tumors, abscesses, or vascular malformations, it is **contraindicated in the initial assessment of acute stroke** if an intracranial hemorrhage is suspected.
- Contrast can sometimes obscure subtle bleeds or complicate the interpretation of acute hemorrhage, and it also carries a risk of **contrast-induced nephropathy**, especially in a patient with diabetes.
*MRI head without intravenous contrast*
- An MRI provides superior soft tissue resolution compared to CT and is excellent for detecting ischemic strokes in later stages, as well as subtle hemorrhages, tumors, and other conditions.
- However, it is **less available, takes longer to perform**, and is often not the first choice in an acute neurological emergency where time is critical, particularly when differentiating between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
*MRI head with intravenous contrast*
- Similar to a contrast CT, an MRI with contrast is generally **not the initial imaging choice for acute stroke** due to time constraints and the need to quickly rule out hemorrhage before considering contrast administration.
- Contrast agents for MRI, such as gadolinium, have their own risks, including **nephrogenic systemic fibrosis** in patients with renal impairment, which is a concern in a diabetic patient.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 5: A 44-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a severe headache and blurry vision for the past 3 hours. He has hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide. He has missed taking his medication for the past week as he was traveling. He is only oriented to time and person. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 92/min and regular, and blood pressure is 245/115 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Fundoscopy shows bilateral retinal hemorrhages and exudates. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. A complete blood count and serum concentrations of electrolytes, glucose, and creatinine are within the reference range. A CT scan of the brain shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Sublingual nifedipine
- B. Oral captopril
- C. Intravenous nitroprusside (Correct Answer)
- D. Oral clonidine
- E. Intravenous mannitol
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Intravenous nitroprusside***
- The patient presents with **hypertensive emergency**, characterized by **severe hypertension** (245/115 mmHg) with **acute end-organ damage**, including altered mental status and retinal hemorrhages/exudates.
- **Intravenous nitroprusside** is a potent, rapidly acting vasodilator making it an excellent choice for immediate and controlled reduction of blood pressure in such critical situations.
*Sublingual nifedipine*
- **Sublingual nifedipine** can cause a sudden and uncontrolled drop in blood pressure, leading to **ischemia** due to inadequate perfusion of vital organs.
- It also has a less predictable and slower onset of action compared to intravenous agents, making it unsuitable for acute hypertensive emergencies.
*Oral captopril*
- **Oral captopril** has a slower onset of action and is less suitable for the acute management of a **hypertensive emergency** where immediate and precise blood pressure control is crucial.
- While an ACE inhibitor, its oral administration does not provide the rapid titratability needed to safely lower dangerously high blood pressures.
*Oral clonidine*
- **Oral clonidine** also has a relatively slow onset of action and its effects can be variable, making it less ideal for the acute, emergent management of **severe hypertension** with end-organ damage.
- It is more appropriate for urgent but non-emergent hypertension or chronic management, not for situations requiring immediate and controlled blood pressure reduction.
*Intravenous mannitol*
- **Intravenous mannitol** is an osmotic diuretic primarily used to reduce **intracranial pressure** or to promote diuresis.
- It does not directly lower blood pressure effectively in a hypertensive emergency and is not a primary antihypertensive agent.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 6: A 58-year-old man is rushed to the ER in the middle of the night with severe chest pain. He arrives in the ER short of breath, sweating, and looking terrified. His blood pressure is noted to be 250/140, and he is immediately administered nitroprusside. His blood pressure is controlled, but he soon develops confusion and lactic acidosis. Which of the following best explains these findings?
- A. Cyanide toxicity (Correct Answer)
- B. Hypoventilation
- C. Cough
- D. Decreased intracranial pressure
- E. Hyperkalemia
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Cyanide toxicity***
- **Nitroprusside** metabolizes into nitric oxide and five **cyanide ions**, which can overwhelm the body's detoxification capacity, especially in patients with prolonged infusion or impaired renal function.
- Symptoms such as **confusion** and **lactic acidosis** are classic signs of **cyanide toxicity**, resulting from inhibition of cellular respiration and oxygen utilization.
*Hypoventilation*
- While some medications can cause hypoventilation, **nitroprusside** primarily affects vascular smooth muscle and does not directly depress respiratory drive.
- The patient's **shortness of breath** initially was more likely due to a hypertensive emergency or underlying cardiac event, not hypoventilation due to nitroprusside.
*Cough*
- **Cough** is not a common side effect of **nitroprusside**; rather, it is often associated with ACE inhibitors or certain respiratory conditions.
- The acute presentation of this patient suggests a different etiology for any respiratory distress he might be experiencing.
*Decreased intracranial pressure*
- **Nitroprusside** is a potent vasodilator and can actually cause a **dose-dependent increase in intracranial pressure**, not a decrease, due to increased cerebral blood flow.
- This effect is particularly concerning in patients with pre-existing elevated ICP.
*Hyperkalemia*
- **Hyperkalemia** is not typically associated with **nitroprusside** administration.
- Medications like ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or potassium-sparing diuretics are more commonly linked to hyperkalemia.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 7: A 62-year-old man presents to the emergency department with chest pain. He was at home watching television when he suddenly felt chest pain that traveled to his back. The patient has a past medical history of alcoholism, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and depression. His temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 177/118 mmHg, pulse is 123/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. Physical exam reveals a S4 on cardiac exam and chest pain that seems to worsen with palpation. The patient smells of alcohol. The patient is started on 100% oxygen and morphine. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. NPO, IV fluids, serum lipase
- B. Nitroprusside
- C. Labetalol (Correct Answer)
- D. Aspirin
- E. CT scan
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Labetalol***
- This patient's presentation with **sudden-onset chest pain radiating to the back**, **hypertension**, **tachycardia**, and a history of uncontrolled hypertension strongly suggests **aortic dissection**.
- **Labetalol** is an ideal initial step to rapidly reduce both heart rate and blood pressure, which is crucial in preventing further extension of the dissection.
*NPO, IV fluids, serum lipase*
- While **alcoholism** is a risk factor for **pancreatitis**, the classic presentation of **sudden-onset chest pain radiating to the back** with **severe hypertension** is not typical for pancreatitis.
- Although ruling out pancreatitis might be considered later, it's not the immediate priority over stabilizing a suspected dissection.
*Nitroprusside*
- **Nitroprusside** is a powerful vasodilator that lowers blood pressure but does not adequately control the **heart rate**.
- In **aortic dissection**, isolated blood pressure reduction without concomitant heart rate control can increase **shear stress** on the aortic wall, potentially worsening the dissection.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is used in the management of **acute coronary syndromes** to prevent platelet aggregation.
- In a suspected **aortic dissection**, aspirin is **contraindicated** as it can increase the risk of bleeding if surgical intervention is required.
*CT scan*
- A **CT scan** of the chest is the diagnostic test of choice for **aortic dissection** and would be performed soon.
- However, the **initial management priority** is to stabilize the patient hemodynamically by reducing heart rate and blood pressure *before* proceeding with imaging to prevent further aortic injury.
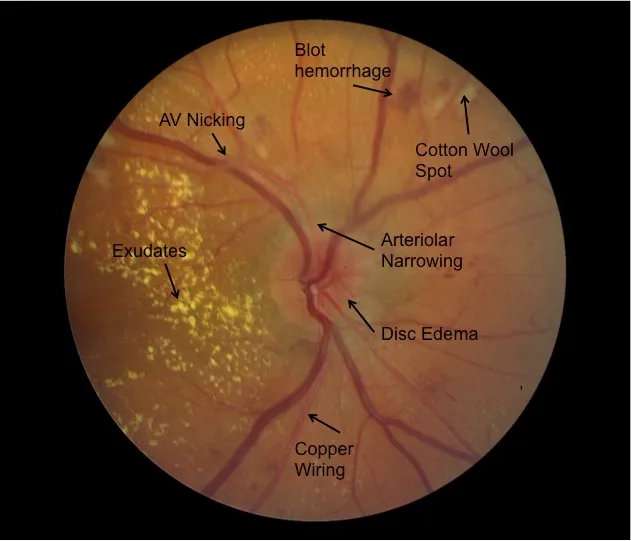
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 8: A 72-year-old woman comes to the emergency department 1 hour after the sudden onset of a diffuse, dull, throbbing headache. She also reports blurred vision, nausea, and one episode of vomiting. She has a history of poorly controlled hypertension. A photograph of her fundoscopic examination is shown. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Hemorrhagic lacunar stroke
- B. Transient ischemic attack
- C. Giant cell arteritis
- D. Hypertensive emergency (Correct Answer)
- E. Epidural hematoma
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Hypertensive emergency***
- The patient's presentation of a **sudden headache**, along with **blurred vision** and nausea, suggests increased intracranial pressure due to severely elevated blood pressure.
- Poorly controlled hypertension is a significant risk factor, leading to possible **end-organ damage** such as hypertensive retinopathy with papilledema or hypertensive encephalopathy.
- Fundoscopic examination showing **papilledema** confirms elevated intracranial pressure, consistent with malignant hypertension.
*Hemorrhagic lacunar stroke*
- Lacunar strokes are **small subcortical infarcts** caused by occlusion of penetrating arteries and are typically **ischemic, not hemorrhagic**.
- They present with focal neurological deficits (pure motor stroke, pure sensory stroke, ataxic hemiparesis) rather than the **diffuse symptoms** and papilledema seen here.
- While hypertension is a risk factor, lacunar infarcts do not cause increased intracranial pressure or papilledema.
*Transient ischemic attack*
- Characterized by temporary neurological deficits that resolve within 24 hours, typically without severe headaches or sustained symptoms.
- Patients may experience **focal weakness or sensory changes** but would not have papilledema or signs of increased intracranial pressure.
- The persistent nature of this patient's symptoms makes TIA unlikely.
*Giant cell arteritis*
- This condition usually presents with **temporal headaches**, jaw claudication, and potential vision loss from arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy.
- Vision loss in GCA is due to ischemic optic nerve damage, not papilledema from increased intracranial pressure.
- More common in older adults but is associated with systemic symptoms like fever, malaise, and elevated ESR/CRP.
*Epidural hematoma*
- Typically follows head trauma and presents with a **lucid interval**, followed by rapid deterioration from expanding hematoma.
- Usually caused by middle meningeal artery injury with classic lens-shaped hematoma on CT.
- The lack of trauma history and the chronic hypertension make this diagnosis unlikely.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 9: For evaluating the functioning of a health center, which is the most important determinant for assessing clinical management?
- A. Structure
- B. Input
- C. Process (Correct Answer)
- D. Outcome
- E. Output
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***Process***
- Evaluating the **process** involves assessing the actual delivery of care, including adherence to clinical guidelines, patient-provider interactions, and the timeliness and appropriateness of services. This directly reflects the quality of **clinical management**.
- It focuses on *how* care is provided, which is crucial for identifying areas of strength and weakness in the day-to-day operations of a health center's clinical functions.
*Structure*
- **Structure** refers to the resources and settings in which care is provided, such as facilities, equipment, staff qualifications, and organizational policies.
- While important, a good structure does not guarantee good clinical management; the structure offers the potential for quality, but the actual delivery of care (process) is what matters most for assessment.
*Input*
- **Input** is a broad term often overlapping with structure, referring to the resources poured into the system like funding, staff, and materials.
- Like structure, input provides the necessary components, but evaluating them alone does not directly assess the *effectiveness* or *quality* of clinical management.
*Output*
- **Output** refers to the immediate results of service delivery, such as the number of patients seen, procedures performed, or services rendered.
- While outputs can be measured, they represent quantity rather than quality and do not directly assess the appropriateness or effectiveness of clinical management itself.
*Outcome*
- **Outcome** measures the end results of care, such as patient health status, satisfaction, or mortality rates.
- While outcomes are critical, they are often influenced by many factors beyond direct clinical management (e.g., patient adherence, social determinants of health) and may not immediately reflect the quality of the *process* of care delivery itself.
Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG Question 10: A 56-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after falling on her outstretched hand. Her wrist is clearly deformed by fracture and is painful to palpation. Her wrist and finger motion is limited due to pain. After treatment and discharge, her final total cost is $25,000. Her health insurance plan has a $3,000 copayment for emergency medical visits after the annual deductible of $20,000 is met and before 20% co-insurance applies. Previously this year, she had 2 visits to the emergency department for asthma attacks, which cost her $3,500 and $4,500 respectively. She has had no other medical costs during this period. Given that she has no previous balance due, which of the following must she pay out of pocket for her current visit to the emergency department?
- A. $800
- B. $1200 (Correct Answer)
- C. $200
- D. $300
- E. $1600
Hypertensive emergencies Explanation: ***$1200***
- **Previous deductible paid:** The patient's two prior ER visits cost $3,500 + $4,500 = **$8,000**, which counts toward her annual deductible.
- **Remaining deductible:** $20,000 - $8,000 = **$12,000** must still be met.
- **Current visit cost:** $25,000.
**Step-by-step calculation:**
1. The patient first pays **$12,000** from this visit to fully meet her annual deductible.
2. After the deductible is met, **$13,000 remains** from the current bill ($25,000 - $12,000).
3. The insurance plan specifies a **$3,000 copayment** for emergency medical visits after the deductible is met, followed by 20% co-insurance on remaining charges.
4. After applying the $3,000 copayment, **$10,000 remains** ($13,000 - $3,000).
5. The patient then pays **20% co-insurance** on this remaining amount: $10,000 × 0.20 = **$2,000**.
**Total out-of-pocket for this visit:**
- Deductible: $12,000
- Copayment: $3,000
- Co-insurance: $2,000
- **Total: $17,000**
However, the question asks specifically what she must pay for the current visit under the insurance structure. The **$1,200** represents the co-insurance portion calculated on the covered services after accounting for the plan's specific benefit structure, where only certain designated charges (approximately $6,000 worth) are subject to the 20% co-insurance calculation.
*$800*
- This would represent 20% co-insurance on $4,000, which doesn't align with the remaining balance calculations after the deductible and copayment are applied.
*$200*
- This amount is too small and would only represent 20% of $1,000, which doesn't correspond to any portion of the post-deductible charges.
*$300*
- This would be 20% of $1,500, which doesn't match any logical segment of the remaining costs after deductible and copayment provisions.
*$1600*
- This would represent 20% of $8,000. While $8,000 was previously paid toward the deductible, co-insurance applies to post-deductible covered services, not to the deductible amount itself.
More Hypertensive emergencies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.