Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Altered mental status approach. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
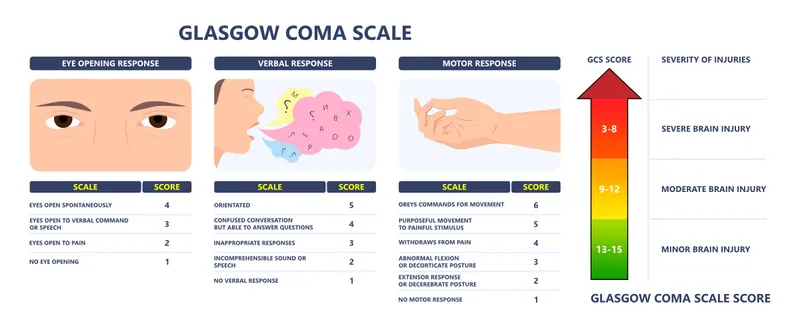
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 1: A 24-year-old man presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle collision. He was in the front seat and unrestrained driver in a head on collision. His temperature is 99.2°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 90/65 mmHg, pulse is 152/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a young man who opens his eyes spontaneously and is looking around. He answers questions with inappropriate responses but discernible words. He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement. Which of the following is this patient's Glasgow coma scale?
- A. 9
- B. 15
- C. 7
- D. 11 (Correct Answer)
- E. 13
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***11***
- **Eye-opening (E)**: The patient opens his eyes spontaneously, scoring **E4**.
- **Verbal response (V)**: He gives inappropriate responses but discernible words, scoring **V3**.
- **Motor response (M)**: He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement, scoring **M4**.
- Therefore, the total Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is **E4 + V3 + M4 = 11**.
*9*
- This score would imply a lower verbal or motor response, such as **incomprehensible sounds (V2)** or **abnormal flexion (M3)**, which is not consistent with the patient's presentation.
- For example, E4 + V2 + M3 would equal 9.
*15*
- A GCS of 15 indicates **normal neurological function**, meaning the patient would be fully oriented, obey commands, and open eyes spontaneously, which is not the case here.
- This score is for a patient who is fully conscious and responsive.
*7*
- A GCS of 7 suggests a **severe brain injury**, which would typically present with a much poorer response, such as **no verbal response (V1)** or **abnormal extension (M2)**.
- For example, E4 + V1 + M2 would equal 7.
*13*
- This score would mean a higher level of consciousness, such as **confused conversation (V4)** or **localizing pain (M5)**, which is better than the patient's described responses.
- For example, E4 + V4 + M5 would equal 13.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 2: A 42-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of a 1-day history of progressive confusion. He recently lost his job. He has a history of chronic alcoholism and has been drinking 14 beers daily for the past week. Before this time, he drank 6 beers daily. He appears lethargic. His vital signs are within normal limits. Serum studies show a sodium level of 111 mEq/L and a potassium level of 3.7 mEq/L. Urgent treatment for this patient's current condition increases his risk for which of the following adverse events?
- A. Wernicke encephalopathy
- B. Osmotic myelinolysis (Correct Answer)
- C. Cerebral edema
- D. Cardiac arrhythmia
- E. Hyperglycemia
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***Osmotic myelinolysis***
* **Rapid correction of severe hyponatremia** (serum sodium <120 mEq/L), especially when chronic, can cause **osmotic demyelination syndrome** (also known as central pontine myelinolysis).
* This condition results from a sudden shift in osmolality, causing water to leave brain cells, leading to neuronal damage and severe neurological deficits.
*Wernicke encephalopathy*
* **Wernicke encephalopathy** is caused by **thiamine deficiency**, common in chronic alcoholics.
* While he is at risk for Wernicke encephalopathy, the urgent treatment for his hyponatremia (rapid correction) is more likely to cause osmotic myelinolysis, not directly trigger Wernicke encephalopathy.
*Cerebral edema*
* **Cerebral edema** is a direct consequence of **severe, acute hyponatremia** (as fluid shifts into brain cells), not a risk of its *treatment*.
* The question asks about the risk of urgent treatment, which aims to *reduce* cerebral edema.
*Cardiac arrhythmia*
* While severe electrolyte imbalances can cause **cardiac arrhythmias**, the **rapid correction of hyponatremia** does not directly or primarily increase the risk of arrhythmias.
* The immediate risk associated with hyponatremia correction is neurological, related to osmotic shifts.
*Hyperglycemia*
* **Hyperglycemia** is a condition of high blood glucose and is not directly related to or caused by the **rapid correction of hyponatremia**.
* Although chronic alcohol abuse can affect glucose metabolism, hyperglycemia is not an acute adverse event of treating hyponatremia.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 3: An 82-year-old woman comes to the physician because of difficulty sleeping and increasing fatigue. Over the past 3 months she has been waking up early and having trouble falling asleep at night. During this period, she has had a decreased appetite and a 3.2-kg (7-lb) weight loss. Since the death of her husband one year ago, she has been living with her son and his wife. She is worried and feels guilty because she does not want to impose on them. She has stopped going to meetings at the senior center because she does not enjoy them anymore and also because she feels uncomfortable asking her son to give her a ride, especially since her son has had a great deal of stress lately. She is 155 cm (5 ft 1 in) tall and weighs 51 kg (110 lb); BMI is 21 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. On mental status examination, she is tired and has a flattened affect. Cognition is intact. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Begin mirtazapine therapy
- B. Begin cognitive-behavioral therapy
- C. Notify adult protective services
- D. Assess for suicidal ideation (Correct Answer)
- E. Recommend relocation to a nursing home
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***Assess for suicidal ideation***
- The patient exhibits several **risk factors for depression**, including **insomnia**, **early morning awakening**, **anorexia**, **weight loss**, and significant **anhedonia** (lack of enjoyment in activities).
- Given her age, recent loss of her husband, social withdrawal, feelings of guilt, and significant emotional distress, it is crucial to first assess for **suicidal ideation** before initiating other treatments.
- **Elderly patients with depression have elevated suicide risk**, especially with recent bereavement and social isolation. Safety assessment is the **mandatory first step** in managing any patient with major depressive symptoms.
*Begin mirtazapine therapy*
- While **mirtazapine** is an effective antidepressant that could address several of her symptoms (insomnia, poor appetite, depression), it should only be considered after a **thorough safety assessment**, particularly for suicide risk.
- Starting medication without assessing for immediate danger may overlook critical safety concerns.
*Begin cognitive-behavioral therapy*
- **Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)** is an effective treatment for depression and could be beneficial for this patient.
- However, similar to medication, it is a subsequent treatment step. The immediate priority is to rule out **suicidal intent** given the severity of her depressive symptoms.
*Notify adult protective services*
- There is no direct evidence of **abuse or neglect** in the provided information that would warrant involving adult protective services.
- Her feelings of guilt and worry about burdening her family, while contributing to her depression, do not indicate that her son or daughter-in-law are harming her.
*Recommend relocation to a nursing home*
- While the patient is elderly and potentially depressed, there is no medical or social necessity presented that indicates she requires or would benefit from a **nursing home** at this stage.
- This step would be premature and does not address the immediate mental health concerns or potential safety issues.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 4: A 20-year-old college student is brought to the ED after a motor vehicle accident. Primary and secondary surveys reveal no significant compromise to his airway, his cardiovascular system, or to his motor function. However, his conjunctiva appear injected and he maintains combative behavior towards staff. What is the gold standard confirmatory test for substance use?
- A. Gas chromatography / mass spectrometry (GC/MS) (Correct Answer)
- B. Urine immunoassay
- C. Western blot
- D. Breath alcohol test
- E. Polymerase chain reaction
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***Gas chromatography / mass spectrometry (GC/MS)***
- **GC/MS** is considered the **gold standard** for confirming substance use due to its high specificity and sensitivity in identifying and quantifying various substances.
- It effectively separates individual compounds in a complex mixture and identifies them based on their unique mass spectra, making it highly reliable for forensic and clinical toxicology.
*Urine immunoassay*
- **Urine immunoassays** are typically used as **screening tests** for substances because they are rapid and relatively inexpensive, but they can produce false positives.
- While useful for initial detection, they require confirmatory testing, often by GC/MS, due to their lower specificity.
*Western blot*
- **Western blot** is primarily used to detect **specific proteins** in a sample, especially in the diagnosis of infectious diseases or autoimmune conditions, not for substance identification.
- It involves separating proteins by gel electrophoresis and then transferring them to a membrane for antibody-based detection.
*Breath alcohol test*
- A **breath alcohol test** is specifically designed to measure **alcohol concentration** in the breath, which correlates with blood alcohol content.
- It is not used for detecting other illicit substances and would not provide a comprehensive toxicology profile.
*Polymerase chain reaction*
- **Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)** is a molecular biology technique used to amplify **DNA or RNA sequences**, primarily for detecting genetic material from pathogens or for genetic analysis.
- It has no role in the direct detection of drugs or their metabolites in biological samples.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 5: A 60-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by police officers because he was acting strangely in public. The patient was found talking nonsensically to characters on cereal boxes in the store. Past medical history is significant for multiple hospitalizations for alcohol-related injuries and seizures. The patient’s vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows a disheveled male who is oriented to person, but not time or place. Neurologic examination shows nystagmus and severe gait ataxia. A T1/T2 MRI is performed and demonstrates evidence of damage to the mammillary bodies. The patient is given the appropriate treatment for recovering most of his cognitive functions. However, significant short-term memory deficits persist. The patient remembers events from his past such as the school and college he attended, his current job, and the names of family members quite well. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Schizophrenia
- B. Korsakoff's syndrome (Correct Answer)
- C. Wernicke encephalopathy
- D. Delirium
- E. Delirium tremens
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***Korsakoff's syndrome***
- The patient's history of **chronic alcohol abuse**, along with **gait ataxia**, **nystagmus**, and most notably, significant **anterograde amnesia** (inability to form new long-term memories) despite preserved remote memory, points to Korsakoff's syndrome.
- **Damage to the mammillary bodies** on MRI is a classic finding in Korsakoff's syndrome, a direct result of **thiamine deficiency**.
- The patient demonstrates the characteristic pattern: **impaired new memory formation** while retaining memories from his past (school, college, job, family names).
*Schizophrenia*
- Schizophrenia typically presents with **hallucinations and delusions** (e.g., talking to cereal box characters), but it is not commonly associated with physical signs like **nystagmus** or **gait ataxia**, nor with MRI findings of mammillary body damage.
- While the initial presentation of talking to cereal box characters might suggest psychosis, the complete clinical picture, especially the neurological deficits and persistent memory impairment, points away from schizophrenia as the primary diagnosis.
*Wernicke encephalopathy*
- Wernicke encephalopathy shares symptoms like **nystagmus** and **ataxia** with this patient and is also due to **thiamine deficiency** in alcoholics.
- However, Wernicke encephalopathy typically presents with more acute and severe symptoms, including **global confusion** and **ophthalmoplegia**, and represents the acute phase. The dominant chronic **anterograde amnesia** described here is characteristic of Korsakoff's syndrome, which represents the chronic sequela.
*Delirium*
- Delirium is characterized by an **acute disturbance in attention and cognition**, often with a fluctuating course, and can be seen in alcohol withdrawal.
- While the patient shows some disorientation, the chronic nature of the symptoms, the specific neurological deficits (nystagmus, ataxia), and particularly the persistent, isolated **anterograde amnesia** are not typical features of delirium.
*Delirium tremens*
- Delirium tremens is a severe form of **alcohol withdrawal** characterized by **autonomic hyperactivity**, severe delirium, hallucinations, and seizures.
- While the patient has a history of alcohol-related seizures, his current vital signs are normal, and the persistent, chronic memory deficits and specific MRI findings are not hallmarks of acute delirium tremens but rather a chronic neurological complication.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 6: A 48-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife 20 minutes after she witnessed him vigorously shaking for about 1 minute. During this episode, he urinated on himself. He feels drowsy and has nausea. He has a history of chronic alcoholism; he has been drinking 15 beers daily for the past 3 days. Before this time, he drank 8 beers daily. His last drink was 2 hours ago. He appears lethargic. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical and neurologic examinations show no other abnormalities. On mental status examination, he is confused and not oriented to time. Laboratory studies show:
Hematocrit 44.0%
Leukocyte count 12,000/mm3
Platelet count 320,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 112 mEq/L
Cl- 75 mEq/L
K+ 3.8 mEq/L
HCO3- 13 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 6 mEq/L
Creatinine 0.6 mg/dL
Albumin 2.1 g/dL
Glucose 80 mg/dL
Urgent treatment for this patient's current condition puts him at increased risk for which of the following adverse events?
- A. Cardiac arrhythmia
- B. Osmotic myelinolysis (Correct Answer)
- C. Cerebral edema
- D. Wernicke encephalopathy
- E. Hyperglycemia
Altered mental status approach Explanation: **Osmotic myelinolysis**
- The severe **hyponatremia (Na+ 112 mEq/L)** in a chronic alcoholic, likely due to increased ADH from excessive beer intake (beer potomania) and possible malnutrition, places him at risk.
- **Rapid correction** of chronic hyponatremia can cause water to leave brain cells too quickly, leading to **demyelination** of neurons, particularly in the pons.
*Cardiac arrhythmia*
- While severe **electrolyte imbalances** such as hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia can cause cardiac arrhythmias, his potassium is normal, and there's no indication of magnesium deficiency.
- **Alcohol withdrawal** can also cause arrhythmias, but the immediate treatment for his hyponatremia does not directly increase this risk.
*Cerebral edema*
- **Cerebral edema** is a risk of **untreated severe hyponatremia**, where water shifts into brain cells, causing swelling.
- However, the question asks about the risk associated with **urgent treatment** for the condition, which, in this case, would involve raising serum sodium.
*Wernicke encephalopathy*
- **Wernicke encephalopathy** is caused by **thiamine deficiency**, common in chronic alcoholics, and presents with gait ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, and confusion.
- While this patient is at risk, treating hyponatremia does not directly increase the risk of Wernicke encephalopathy; rather, thiamine administration is part of routine care for alcoholics.
*Hyperglycemia*
- **Hyperglycemia** is not a common adverse event of correcting hyponatremia in a patient with a normal blood glucose level.
- Insulin resistance or glucose intolerance might be present in chronic alcoholics, but the urgent treatment for hyponatremia itself does not typically induce hyperglycemia.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 7: A 57-year-old man was brought into the emergency department unconscious 2 days ago. His friends who were with him at that time say he collapsed on the street. Upon arrival to the ED, he had a generalized tonic seizure. At that time, he was intubated and is being treated with diazepam and phenytoin. A noncontrast head CT revealed hemorrhages within the pons and cerebellum with a mass effect and tonsillar herniation. Today, his blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, heart rate is 65/min, respiratory rate is 12/min (intubated, ventilator settings: tidal volume (TV) 600 ml, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 5 cm H2O, and FiO2 40%), and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). On physical examination, the patient is in a comatose state. Pupils are 4 mm bilaterally and unresponsive to light. Cornea reflexes are absent. Gag reflex and cough reflex are also absent. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Second opinion from a neurologist
- B. Withdraw ventilation support and mark time of death
- C. Electroencephalogram
- D. Repeat examination in several hours
- E. Apnea test (Correct Answer)
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***Apnea test***
- The patient exhibits classic signs of **brain death**, including a **coma**, fixed and dilated pupils, and absent brainstem reflexes (corneal, gag, cough). The next step is to perform an apnea test to confirm the absence of spontaneous respiratory drive.
- An apnea test confirms brain death by demonstrating the **absence of respiratory effort** despite a rising pCO2, provided that spinal cord reflexes are not mistaken for respiratory efforts.
*Second opinion from a neurologist*
- While consulting a neurologist is often helpful in complex neurological cases, the current clinical picture presents such clear signs of brain death that **further confirmatory testing** for brain death (like the apnea test) is more immediately indicated before seeking additional opinions on diagnosis.
- A second opinion would typically be sought to confirm the diagnosis or guide management, but establishing brain death requires a specific protocol which is incomplete without the apnea test.
*Withdraw ventilation support and mark time of death*
- It is **premature to withdraw ventilation** before brain death is unequivocally confirmed by all necessary clinical and confirmatory tests, including the apnea test.
- Withdrawing support without full confirmation could lead to ethical and legal issues, as the patient might still have residual brainstem function, however minimal.
*Electroencephalogram*
- An **EEG** can show absent electrical activity, supporting brain death, but it is **not a mandatory part of the core brain death criteria** in many protocols, especially when clinical signs are clear and an apnea test can be performed.
- The primary diagnostic criteria for brain death usually prioritize clinical examination and the apnea test for proving irreversible cessation of all brain functions.
*Repeat examination in several hours*
- Repeating the examination in several hours is typically done if there are **confounding factors** (e.g., severe hypothermia, drug intoxication) that might mimic brain death, or if the initial assessment is incomplete.
- In this case, there are no mentioned confounding factors, and the immediate priority is to complete the brain death protocol with an apnea test, given the current clear clinical picture.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old man presents to the emergency department with altered mental status. The patient is non-verbal at baseline, but his caretakers at the nursing home noticed he was particularly somnolent recently. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes and Alzheimer dementia. His temperature is 99.7°F (37.6°C), blood pressure is 157/98 mmHg, pulse is 150/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Laboratory values are obtained and shown below.
Hemoglobin: 9 g/dL
Hematocrit: 33%
Leukocyte count: 8,500/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 197,000/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 139 mEq/L
Cl-: 102 mEq/L
K+: 4.3 mEq/L
HCO3-: 25 mEq/L
BUN: 37 mg/dL
Glucose: 99 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.4 mg/dL
Ca2+: 12.2 mg/dL
The patient has lost 20 pounds over the past month. His parathyroid hormone is within normal limits, and his urinary calcium is increased. Physical exam demonstrates discomfort when the patient's lower back and extremities are palpated. Which of the following is the most accurate diagnostic test for this patient's underlying diagnosis?
- A. Peripheral blood smear
- B. Urine protein levels
- C. Bone marrow biopsy (Correct Answer)
- D. Radiograph of the lumbar spine
- E. Urine, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid cultures
Altered mental status approach Explanation: **Bone marrow biopsy**
- The patient presents with **hypercalcemia**, **elevated creatinine** (acute kidney injury), **anemia**, **weight loss**, and bony pain, which are classic features of **multiple myeloma**; a bone marrow biopsy is crucial for diagnosis and staging by identifying plasma cell infiltration.
- Identification of > **10% clonal plasma cells** in the bone marrow confirms the diagnosis of multiple myeloma in patients with myeloma-defining events (e.g., hypercalcemia, renal failure, anemia, bone lesions).
*Peripheral blood smear*
- While a peripheral blood smear might show **rouleaux formation** in multiple myeloma due to increased plasma proteins, it is not specific or diagnostic as rouleaux can be seen in other conditions like inflammation.
- It does not quantify the percentage of **clonal plasma cells**, which is essential for diagnosing multiple myeloma.
*Urine protein levels*
- **Urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP)** and **immunofixation** are important for detecting Bence-Jones proteinuria (clonal free light chains) which supports the diagnosis of multiple myeloma, but quantifying general urine protein levels (e.g., with a 24-hour collection) is not as specific or diagnostic.
- While **elevated urine protein** is expected in multiple myeloma due to light chain excretion, it doesn't provide definitive evidence of plasma cell dyscrasia or bone marrow involvement.
*Radiograph of the lumbar spine*
- **Skeletal surveys** (including radiographs) are used to identify **lytic bone lesions** characteristic of multiple myeloma, which contribute to pain and hypercalcemia.
- Although important for identifying bone involvement, radiographs are not the most accurate diagnostic test for the underlying disease itself, as they do not directly evaluate the presence of **clonal plasma cells**.
*Urine, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid cultures*
- These cultures are primarily used to diagnose **infections**, which can cause altered mental status and fever.
- While infection is a consideration, the constellation of hypercalcemia, renal failure, anemia, and bone pain points strongly toward multiple myeloma, making cultures less likely to reveal the primary underlying diagnosis.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old man is brought into the emergency department by ambulance. The patient was at an appointment to receive welfare when he began acting abnormally. The patient was denied welfare. Shortly afterwards, he no longer responded to questions and stared blankly off into space, not responding to verbal stimuli. Other than odd lip-smacking behavior, he was motionless. Several minutes later, he became responsive but seemed confused. The patient has a past medical history of drug abuse and homelessness and is not currently taking any medications. His temperature is 98.9°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 124/78 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical exam reveals cranial nerves II-XII as grossly intact with 5/5 strength in the upper and lower extremities and a stable gait. The patient seems confused when answering questions and has trouble remembering the episode. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Absence seizure
- B. Malingering
- C. Focal impaired awareness seizure (Correct Answer)
- D. Transient ischemic attack
- E. Generalized seizure
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***Focal impaired awareness seizure***
- The patient's presentation with a period of **unresponsiveness**, **staring blankly**, repetitive **lip-smacking automatisms**, and subsequent **postictal confusion** and **amnesia of the event** are highly characteristic of a focal impaired awareness seizure (formerly called complex partial seizure).
- This seizure type originates from a **focal area of the brain** (often temporal lobe) and involves **impaired consciousness** during the episode.
- The context of significant stress (welfare denial) can sometimes precipitate seizures in susceptible individuals, although it is not a direct cause.
- **Automatisms** (repetitive purposeless movements like lip-smacking) are a hallmark feature.
*Absence seizure*
- Absence seizures are typically **brief (seconds)**, characterized by a sudden **cessation of activity and blank stares**, without automatisms like lip-smacking.
- Patients usually have **no postictal confusion** or memory loss of the event, which contradicts this patient's presentation.
- More common in **children** rather than adults.
*Malingering*
- Malingering involves the **intentional feigning of symptoms** for secondary gain, but the presence of automatisms like lip-smacking and the postictal state are objective neurological signs not easily faked.
- The lack of responsiveness to verbal stimuli and subsequent confusion are clinical features inconsistent with volitional control.
*Transient ischemic attack*
- TIAs present with **focal neurological deficits** (e.g., weakness, speech disturbance, visual loss) that resolve completely within 24 hours, often without confusion.
- The symptoms described (staring, lip-smacking, generalized unresponsiveness, and confusion) are not typical of a TIA.
- More common in **older patients** with vascular risk factors.
*Generalized seizure*
- A generalized seizure, such as a tonic-clonic seizure, would involve **loss of consciousness** with **tonic and clonic movements** of the extremities, which are not described here.
- While postictal confusion is common, the focal automatisms and lack of widespread motor activity point away from a primary generalized seizure.
- Generalized seizures involve **both hemispheres** from onset, unlike this focal presentation.
Altered mental status approach US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Altered mental status approach Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
More Altered mental status approach US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.