Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Sjögren's syndrome. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
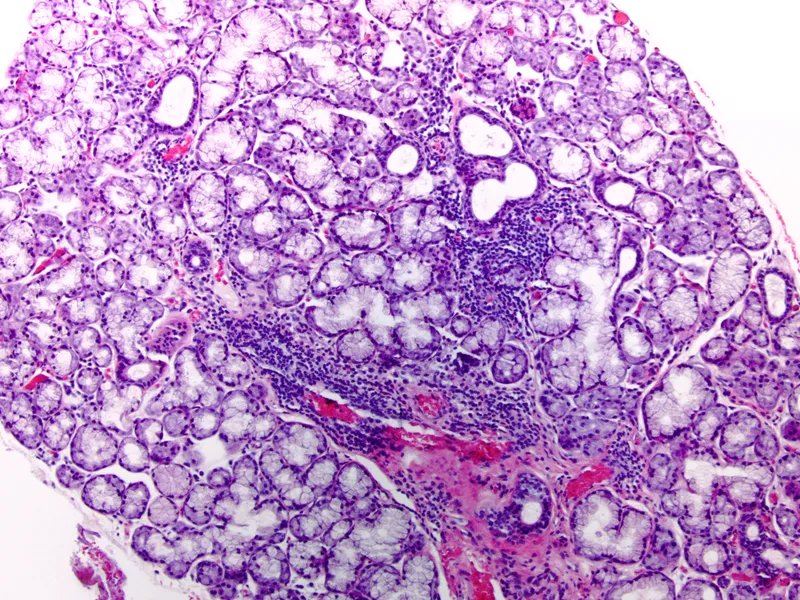
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 1: A 47-year-old woman presents to her physician for difficulty swallowing. She states that she intentionally delayed seeing a physician for this issue. She says her primary issue with swallowing is that her mouth always feels dry so she has difficulty chewing food to the point that it can be swallowed. On physical examination, her oral mucosa appears dry. Both of her eyes also appear dry. Several enlarged lymph nodes are palpated. Which of the following patterns of reactive lymphadenitis is most commonly associated with this patient’s presentation?
- A. Sinus hyperplasia
- B. Follicular hyperplasia (Correct Answer)
- C. Diffuse hyperplasia
- D. Mixed B and T cell hyperplasia
- E. Paracortical hyperplasia
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Follicular hyperplasia***
- The patient's symptoms of **dry mouth (xerostomia)** and **dry eyes (xerophthalmia)** strongly suggest **Sjögren syndrome**. This autoimmune disease selectively affects **exocrine glands**, particularly the salivary and lacrimal glands.
- Lymphoid hyperplasia, especially **follicular hyperplasia**, is a common feature in Sjögren syndrome due to chronic B-cell activation, which is linked to a higher risk of developing **MALT lymphoma**.
*Sinus hyperplasia*
- **Sinus hyperplasia**, also known as **reticular hyperplasia**, is characterized by an increase in the number and size of macrophages within the subcapsular and medullary sinuses of lymph nodes.
- It is typically associated with **lymph nodes draining a site of malignancy** or conditions involving histiocytic proliferation.
*Diffuse hyperplasia*
- **Diffuse hyperplasia** involves a generalized expansion of all lymphoid components within the lymph node, without a predominance of any specific area.
- This pattern is less specific and can be seen in various **chronic inflammatory conditions** or reactive processes, but it is not the most characteristic pattern for Sjögren syndrome.
*Mixed B and T cell hyperplasia*
- While both B and T cells are involved in immune responses, **mixed B and T cell hyperplasia** refers to the expansion of both populations in a less defined pattern than follicular or paracortical types.
- Conditions like **toxoplasmosis** can present with mixed hyperplasia, but it is not the classic pattern seen in Sjögren syndrome.
*Paracortical hyperplasia*
- **Paracortical hyperplasia** involves the expansion of the paracortical areas of the lymph node, which are rich in T-lymphocytes.
- This pattern is typically seen in response to **viral infections** (e.g., infectious mononucleosis) or certain drug reactions, where T-cell activation is a prominent feature.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old woman presents to the physician with a throbbing headache. She says she had it for the last year and it’s usually located in the right temporal area. There is localized tenderness over the scalp. During the last 2 weeks, she experienced 3 episodes of transient loss of vision on the right side, without ocular pain. On physical examination, her vital signs are normal. Palpation reveals that the pulsations of the superficial temporal artery on the right side are reduced in amplitude. Laboratory studies show:
Blood hemoglobin 10.7 g/dL (6.64 mmol/L)
Leukocyte count 8,000/mm3 (8.0 x 109/L)
Platelet count 470,000/mm3 (470 x 109/L)
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 60 mm/h (60 mm/h)
Which of the following conditions is most likely to co-exist with the presenting complaint in this woman?
- A. Amyloidosis
- B. Sjogren’s syndrome
- C. Fibromyalgia
- D. Polymyalgia rheumatica (Correct Answer)
- E. Dermatomyositis
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Polymyalgia rheumatica***
- This patient's symptoms are highly suggestive of **giant cell arteritis** (temporal arteritis) due to the throbbing headache, temporal tenderness, reduced temporal artery pulsation, **amaurosis fugax**, and elevated ESR.
- **Polymyalgia rheumatica** is closely associated with giant cell arteritis, often co-existing in up to 50% of patients. Both conditions are characterized by systemic inflammation.
*Amyloidosis*
- **Amyloidosis** is a disorder caused by the deposition of abnormal proteins in various tissues, leading to organ dysfunction.
- It does not typically present with the acute inflammatory symptoms or vascular complications seen in this patient, and there is no direct link to giant cell arteritis.
*Sjogren’s syndrome*
- **Sjogren's syndrome** is an autoimmune disease primarily affecting the **exocrine glands**, leading to dry eyes and dry mouth.
- While it can cause systemic symptoms, it does not typically manifest with temporal arteritis or its specific visual and cranial symptoms.
*Fibromyalgia*
- **Fibromyalgia** is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, often without clear inflammation markers.
- It is not associated with giant cell arteritis or the inflammatory markers (high ESR) and vascular occlusion symptoms (amaurosis fugax) seen in this patient.
*Dermatomyositis*
- **Dermatomyositis** is an inflammatory myopathy characterized by muscle weakness and distinctive skin rashes.
- While it is an inflammatory condition, it does not typically present with the specific headache, temporal artery abnormalities, or visual symptoms that are hallmarks of giant cell arteritis.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 3: A 51-year-old man is bitten by a cottonmouth viper and is successfully treated with sheep hyperimmune Fab antivenom. Three days later, the patient develops an abdominal itchy rash and re-presents to the emergency department for medical care. His medical history is significant for gout, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus type II, and multiple basal cell carcinomas on his face and neck. He currently smokes 1 pack of cigarettes per day, drinks a 6-pack of beer per day, and denies any current illicit drug use. His vital signs include: temperature 40.0°C (104.0°F), blood pressure 126/74 mm Hg, heart rate 111/min, and respiratory rate 23/min. On physical examination, his gait is limited by diffuse arthralgias, lung sounds are clear bilaterally, and he has normal heart sounds. The patient has a pruritic periumbilical serpiginous macular rash that has spread to involve the back, upper trunk, and extremities. Of the following options, which is the next best step in patient management?
- A. Glucocorticoid taper with antihistamines (Correct Answer)
- B. Plasmapheresis
- C. NSAIDs
- D. Antihistamines
- E. Dialysis
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Glucocorticoid taper with antihistamines***
- The patient's symptoms (rash, arthralgias, fever) developing several days after receiving **sheep hyperimmune Fab antivenom** are classic for **serum sickness**, a type III hypersensitivity reaction.
- Treatment for serum sickness typically involves **oral corticosteroids** (e.g., prednisone) to suppress the immune response and **antihistamines** to manage the pruritus.
*Plasmapheresis*
- This is reserved for **severe cases of serum sickness** when organ damage (e.g., renal failure, severe vasculitis, neurological involvement) is present or when steroid therapy is ineffective.
- The patient's symptoms, while bothersome, do not appear severe enough at this stage to warrant plasmapheresis.
*NSAIDs*
- While NSAIDs can help with arthralgias and fever, they do not address the underlying **immune complex deposition** that causes serum sickness.
- They are insufficient as monotherapy for managing the rash and other systemic symptoms.
*Antihistamines*
- Antihistamines can effectively alleviate the **pruritus** associated with the rash in serum sickness.
- However, they do not treat the **systemic inflammatory response** (fever, arthralgia) or prevent further immune complex deposition, making them inadequate as a primary treatment alone.
*Dialysis*
- Dialysis is indicated for **severe renal failure**, which is not described in this patient's presentation.
- While serum sickness can *rarely* cause glomerulonephritis, there is no evidence here to suggest a need for dialysis.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 4: A biology student is studying apoptosis pathways. One of the experiments conducted involves the binding of a ligand to a CD95 receptor. A defect of this pathway will most likely cause which of the conditions listed below?
- A. Chronic granulomatous disease
- B. Chédiak-Higashi syndrome
- C. Follicular lymphoma
- D. Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome***
- A defect in the **CD95 (Fas) receptor pathway** impairs the normal **apoptotic deletion of self-reactive lymphocytes**, leading to their accumulation.
- This accumulation results in **lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and autoimmune manifestations** due to uncontrolled lymphocyte proliferation.
*Chronic granulomatous disease*
- This condition is characterized by a defect in **NADPH oxidase**, leading to recurrent infections and granuloma formation due to the inability of phagocytes to produce **reactive oxygen species**.
- It does not primarily involve the CD95 apoptosis pathway.
*Chédiak-Higashi syndrome*
- This is an **autosomal recessive disorder** involving a defect in lysosomal trafficking, leading to impaired function of phagocytes, melanocytes, and platelets.
- Symptoms include **recurrent pyogenic infections, partial albinism, and neurological abnormalities**, not directly linked to the CD95 pathway.
*Follicular lymphoma*
- This is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma characterized by a **t(14;18) translocation**, which causes overexpression of the **BCL2 gene**, an anti-apoptotic protein.
- While it involves impaired apoptosis, the primary defect is not in the CD95 receptor itself but rather in the regulation of apoptosis through BCL2.
*Leukocyte adhesion deficiency*
- This is a rare **immunodeficiency disorder** characterized by defects in **leukocyte adhesion molecules (integrins)**, impairing the ability of white blood cells to adhere to endothelial surfaces and migrate to sites of infection.
- It results in **recurrent bacterial infections and impaired wound healing**, unrelated to the CD95 apoptosis pathway.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 5: A 51-year-old woman comes to the physician because of fatigue and progressive pain and stiffness in her hands for 3 months. She used to play tennis but stopped 1 month ago because of difficulties holding the racket and her skin becoming “very sensitive to sunlight.” Her last menstrual period was 1 year ago. She has diabetes mellitus controlled with insulin. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Vital signs are within normal limits. The patient appears tanned. The second and third metacarpophalangeal joints of both hands are tender to palpation and range of motion is limited. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Synovial fluid analysis
- B. Testing for parvovirus B19 antibodies
- C. Testing for rheumatoid factors
- D. Testing for anti-nuclear antibodies
- E. Iron studies (Correct Answer)
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Iron studies***
- The patient's presentation with **"tanned" appearance**, **diabetes mellitus**, and **arthropathy specifically involving the 2nd and 3rd metacarpophalangeal joints** is the **classic triad of hemochromatosis** (hereditary iron overload).
- The bronze/tan skin pigmentation results from **iron deposition in the skin**, while diabetes occurs from **iron deposition in the pancreas** ("bronze diabetes").
- **MCP 2 and 3 joint involvement** is pathognomonic for hemochromatosis arthropathy, distinguishing it from other arthritides.
- **Iron studies** (serum ferritin and transferrin saturation) are the most appropriate initial diagnostic tests, typically showing **elevated ferritin (>200 ng/mL in women) and transferrin saturation >45%**.
- Early diagnosis is crucial as hemochromatosis is treatable with phlebotomy, preventing progression to cirrhosis and cardiac complications.
*Testing for anti-nuclear antibodies*
- While **photosensitivity** could suggest **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**, the patient lacks other characteristic SLE features (malar rash, oral ulcers, serositis).
- The **"tanned" appearance** is not typical of photosensitivity, which usually manifests as a **rash or erythema with sun exposure**, not generalized hyperpigmentation.
- The **specific involvement of MCP 2 and 3 joints** is more characteristic of hemochromatosis than SLE, which typically has a more diffuse polyarticular pattern.
- ANA testing would be appropriate if other SLE features were present, but the constellation of findings here points to iron overload.
*Synovial fluid analysis*
- This test is performed to evaluate for **septic arthritis**, **crystal arthropathy (gout, pseudogout)**, or other inflammatory conditions when there is **acute monoarticular** or **oligoarticular** involvement.
- The patient's **chronic, symmetrical polyarticular** presentation and systemic features make a systemic metabolic disorder (hemochromatosis) more likely than conditions requiring synovial fluid analysis as the initial diagnostic step.
*Testing for parvovirus B19 antibodies*
- **Parvovirus B19** can cause acute arthropathy mimicking rheumatoid arthritis, typically following a viral prodrome.
- However, the **3-month chronicity**, **diabetes**, and **bronze pigmentation** are not explained by parvovirus infection, making this an unlikely diagnosis.
*Testing for rheumatoid factors*
- While **rheumatoid arthritis (RA)** can present with symmetrical small joint arthritis, it typically involves **PIP and MCP joints more diffusely**, not specifically MCP 2 and 3.
- RA does not explain the **tanned appearance** or the specific association with **diabetes mellitus** seen in this patient.
- The MCP 2 and 3 predilection is a distinguishing feature of hemochromatosis arthropathy.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 6: A previously healthy 30-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of a recurring rash that typically occurs on exposure to the sun and affects only the face. She also has noticed several nonpainful ulcers on the roof of her mouth. She is sexually active with one male partner and they use condoms inconsistently. Her mother has end-stage renal disease. The patient does not smoke or drink alcohol. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows an erythematous rash across the cheeks that spares the nasolabial folds. There are three small ulcers on the hard palate. Laboratory studies show:
Leukocyte count 3,000/mm3
Platelet count 70,000/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 80 mm/h
Serum
Antinuclear antibodies 1:320
Anti-Smith antibodies positive
Urine
Protein 3+
RBC casts negative
RBCs none
WBCs 10–15/hpf
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Renal biopsy (Correct Answer)
- B. Pathergy skin testing
- C. Administration of hydroxychloroquine
- D. Skin biopsy
- E. Administration of azathioprine
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Renal biopsy***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**, including photosensitive malar rash, oral ulcers, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated ESR, positive ANA, and positive anti-Smith antibodies. The presence of **proteinuria** (3+) and **pyuria** (WBCs 10-15/hpf) indicates significant renal involvement, likely **lupus nephritis**.
- A **renal biopsy** is essential to determine the **class of lupus nephritis**, which guides treatment and prognosis. This is a critical next step before initiating specific immunosuppressive therapy.
*Pathergy skin testing*
- **Pathergy testing** is used to diagnose **Behcet's disease**, an inflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent oral and genital ulcers, skin lesions, and uveitis.
- While oral ulcers are present, the overall clinical picture, particularly the photosensitive rash, positive ANA and anti-Smith antibodies, and significant hematologic and renal abnormalities, points away from Behcet's disease and towards SLE.
*Administration of hydroxychloroquine*
- **Hydroxychloroquine** is a standard treatment for SLE, particularly for cutaneous symptoms, musculoskeletal involvement, and for preventing disease flares and organ damage.
- However, given the evidence of **significant renal involvement** (proteinuria, pyuria) and the need to classify the lupus nephritis, a renal biopsy is a more immediate and crucial step before initiating general SLE treatment.
*Skin biopsy*
- A **skin biopsy** could confirm lupus-related skin changes (e.g., discoid lupus or subacute cutaneous lupus), but the diagnosis of SLE is already strongly suggested by the other clinical and serological findings.
- A skin biopsy would not provide information about the **severity or type of renal involvement**, which is critical for guiding immediate and specific treatment for lupus nephritis.
*Administration of azathioprine*
- **Azathioprine** is an immunosuppressant used in SLE, particularly for lupus nephritis or other severe organ involvement, often as maintenance therapy or in combination with corticosteroids.
- Similar to hydroxychloroquine, while it may be part of the future treatment plan, initiating this medication without first classifying the **lupus nephritis via renal biopsy** would be premature and potentially suboptimal. The specific class of lupus nephritis determines the most appropriate and aggressive immunosuppressive regimen.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 7: A 42-year-old woman presents complaining of pain in her hands. She reports that the pain is in both hands, and that it is usually worse in the morning. She reports that her hands are also stiff in the morning, but that this gradually improves throughout the morning. She notes, however, that her symptoms seem to be getting worse over the last three months. What is the most likely pathogenesis of her disease process?
- A. Production of antibodies against smooth muscle
- B. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody production
- C. Production of antibodies against antibodies (Correct Answer)
- D. Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
- E. Repetitive microtrauma
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Production of antibodies against antibodies***
- The patient's symptoms of **bilateral hand pain and morning stiffness** improving with activity, worsening over three months, are classic for **Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)**.
- RA is characterized by the production of **rheumatoid factor (RF)**, an antibody (typically IgM) directed against the Fc portion of IgG, which is essentially an antibody against an antibody.
*Production of antibodies against smooth muscle*
- This describes the presence of **anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA)**, which are characteristic of **Autoimmune Hepatitis type 1**.
- Autoimmune hepatitis primarily affects the liver, leading to symptoms like fatigue, jaundice, and elevated liver enzymes, not primarily joint pain.
*Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody production*
- This refers to **ANCA (anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies)**, which are associated with various forms of **vasculitis**, such as Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener's), Microscopic Polyangiitis, and Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss).
- While vasculitis can cause systemic symptoms, the patient's presentation of symmetric, inflammatory arthritis is not typical for primary ANCA-associated vasculitis.
*Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction*
- A **type I hypersensitivity reaction** involves IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation, leading to immediate allergic reactions like asthma, anaphylaxis, or hives.
- This mechanism is completely unrelated to the pathogenesis of an autoimmune, chronic inflammatory arthritis like Rheumatoid Arthritis.
*Repetitive microtrauma*
- Repetitive microtrauma is more consistent with **osteoarthritis** or **occupational overuse injuries**.
- Osteoarthritis typically presents with pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest, **morning stiffness lasting less than 30 minutes**, and often affects weight-bearing joints or specific joints due to trauma or wear and tear, rather than the inflammatory pattern described.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 8: A 53-year-old woman presents to her primary care provider complaining of fatigue for the last several months. She reports feeling tired all day, regardless of her quality or quantity of sleep. On further questioning, she has also noted constipation and a 4.5 kg (10 lb) weight gain. She denies shortness of breath, chest pain, lightheadedness, or blood in her stool. At the doctor’s office, the vital signs include: pulse 58/min, blood pressure 104/68 mm Hg, and oxygen saturation 98% on room air. The physical exam shows only slightly dry skin. The complete blood count (CBC) is within normal limits. Which of the following best describes the pathogenesis of this patient's condition?
- A. Chronic blood loss
- B. Bone marrow failure
- C. Autoimmune attack on endocrine tissue (Correct Answer)
- D. Nutritional deficiency
- E. Iatrogenesis
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Autoimmune attack on endocrine tissue***
- The patient's symptoms of **fatigue**, **constipation**, **weight gain**, **bradycardia**, and dry skin are classic signs of **hypothyroidism**.
- The most common cause of hypothyroidism in developed countries is **Hashimoto's thyroiditis**, an **autoimmune disease** where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland (endocrine tissue).
*Chronic blood loss*
- This typically leads to **iron deficiency anemia**, which would likely manifest as a **low hemoglobin** or hematocrit on the CBC.
- While fatigue can be a symptom, constipation and weight gain are not typical presentations of chronic blood loss, and the CBC is within normal limits.
*Bone marrow failure*
- Bone marrow failure would result in **pancytopenia** (low red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets), which would be evident on the CBC.
- The patient's CBC is normal, ruling out this condition as the primary cause of her symptoms.
*Nutritional deficiency*
- While certain nutritional deficiencies (e.g., **Vitamin B12 deficiency**) can cause fatigue and constipation, they do not typically cause weight gain or bradycardia.
- The patient's symptom constellation points more specifically to an endocrine disorder.
*Iatrogenesis*
- Iatrogenic causes refer to conditions resulting from medical intervention or treatment.
- There is no information in the vignette to suggest any recent medical procedures or medications that would account for this specific constellation of symptoms.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 9: Match the following: A) Caplan syndrome- 1) Found first in coal worker B) Asbestosis- 2) Upper lobe predominance C) Mesothelioma- 3) Involves lower lobe D) Sarcoidosis- 4) Pleural effusion is seen
- A. A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
- B. A-1, B-4, C-3, D-2 (Correct Answer)
- C. A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
- D. A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: **A-1, B-4, C-3, D-2**
- **Caplan syndrome** was first described in **coal workers** with **rheumatoid arthritis** and progressive massive fibrosis.
- **Asbestosis** is often associated with **pleural effusion**, which can be benign or malignant.
- **Mesothelioma** typically involves the **lower lobes** of the lungs, specifically the pleura, and is strongly linked to asbestos exposure.
- **Sarcoidosis** is characterized by **non-caseating granulomas**, which have a predilection for the **upper lobes** of the lungs.
*A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1*
- This option incorrectly states that Caplan syndrome involves the lower lobe; **Caplan syndrome** is defined by the presence of large nodules in the lungs of coal workers with rheumatoid arthritis, and their specific lobar distribution is not a defining characteristic.
- This option incorrectly states that Mesothelioma has an upper lobe predominance; **Mesothelioma** is a pleural malignancy and typically involves the **lower lobes**, extending along the pleura.
*A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1*
- This option incorrectly associates Caplan syndrome with pleural effusion; **Caplan syndrome** manifests as rheumatoid nodules in the lungs, not primarily pleural effusion.
- This option incorrectly states that Asbestosis has an upper lobe predominance; **Asbestosis** predominantly affects the **lower lobes** of the lungs, causing interstitial fibrosis.
*A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1*
- This option incorrectly states that Caplan syndrome has an upper lobe predominance; the defining feature of **Caplan syndrome** is the combination of rheumatoid arthritis and pneumoconiosis, not specific lobar involvement.
- This option correctly identifies pleural effusion with asbestosis and lower lobe involvement with mesothelioma, but **Caplan syndrome** is not characterized by upper lobe predominance.
Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG Question 10: A 55-year-old woman presents to the office complaining of leg ulcers for the past 6 months. She has a chronic history of severe rheumatoid arthritis controlled with methotrexate. She does not drink alcohol or smoke cigarettes. Her vitals are normal. Her lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is soft and non-tender with a palpable spleen tip on inspiration. Skin examination shows scattered ulcers on the legs in various stages of healing. Additionally, metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints are tender. Varicose veins are not observed. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 10.5 g/dL
MCV 74 fl
Platelets 226,000/mm3
White blood cells 2500/mm3
Neutrophils 20%
Alanine aminotransferase 36 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase 39 U/L
Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
HIV test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Venous stasis and valve insufficiency
- B. Drug toxicity
- C. Caplan syndrome
- D. Vitamin deficiency
- E. Felty syndrome (Correct Answer)
Sjögren's syndrome Explanation: ***Felty syndrome***
- The patient's presentation with severe, long-standing **rheumatoid arthritis**, **leg ulcers**, **splenomegaly** (palpable spleen tip), and **neutropenia** (WBC 2500, neutrophils 20%) is highly characteristic of **Felty syndrome**.
- **Felty syndrome** is a rare, severe complication of rheumatoid arthritis, defined by the triad of **rheumatoid arthritis, neutropenia, and splenomegaly**. The neutropenia increases susceptibility to infections and can contribute to chronic leg ulcers.
*Venous stasis and valve insufficiency*
- This condition typically presents with **venous stasis ulcers** that are often located in the **gaiter area** (around the ankles) and accompanied by signs of chronic venous insufficiency, such as **edema**, **skin discoloration**, and **varicose veins**, which are noted as absent in this patient.
- It does not explain the patient's systemic symptoms like **splenomegaly** or **neutropenia**.
*Drug toxicity*
- While methotrexate can cause **bone marrow suppression** leading to cytopenias, and liver enzyme elevations, it typically doesn't cause **splenomegaly** or chronic leg ulcers in this specific constellation without other clear signs of severe toxicity.
- The liver enzymes are within normal limits, making significant hepatotoxicity unlikely, and the chronic nature of the leg ulcers along with splenomegaly points away from isolated methotrexate toxicity as the primary cause.
*Caplan syndrome*
- **Caplan syndrome** is characterized by the presence of **pneumoconiosis** (e.g., coal worker's pneumoconiosis) and **rheumatoid arthritis**, resulting in distinctive pulmonary nodules.
- This patient has no history of occupational exposure to dusts and her lungs are clear to auscultation, making **Caplan syndrome** an unlikely diagnosis.
*Vitamin deficiency*
- While certain vitamin deficiencies (e.g., **Vitamin C** causing scurvy) can lead to skin manifestations and impaired wound healing, they do not typically cause the combination of **splenomegaly**, **neutropenia**, and severe leg ulcers in the context of rheumatoid arthritis.
- The specific laboratory findings and the clinical picture are more indicative of a distinct rheumatologic complication.
More Sjögren's syndrome US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.