Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Medium vessel vasculitis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man with asthma comes to the physician because of a 1-month history of progressively worsening shortness of breath and cough. He also has a history of chronic sinusitis and foot drop. Current medications include an albuterol inhaler and inhaled corticosteroid. Physical examination shows diffuse wheezing over both lung fields and tender subcutaneous nodules on both elbows. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 23,000/mm3 with 26% eosinophils and a serum creatinine of 1.7 mg/dL. Urine microscopy shows red blood cell casts. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- B. Polyarteritis nodosa
- C. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Correct Answer)
- D. Microscopic polyangiitis
- E. Immunoglobulin A vasculitis
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)***
- The patient presents with **asthma**, **chronic sinusitis**, **eosinophilia** (26%), and symptoms of vasculitis including **foot drop** (neuropathy), **renal impairment** (elevated creatinine, RBC casts), and **subcutaneous nodules**. This constellation is highly characteristic of EGPA (formerly Churg-Strauss syndrome).
- EGPA is a **small-to-medium vessel vasculitis** defined by **asthma**, **eosinophilia**, and **granulomatous inflammation**.
*Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)*
- GPA typically involves the **upper and lower respiratory tracts** and **kidneys**, often presenting with chronic sinusitis, lung nodules, and glomerulonephritis.
- While GPA can cause renal impairment and neuropathy, it is not primarily characterized by **asthma** and profound **eosinophilia**, which are key features in this patient.
*Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)*
- PAN is a **necrotizing vasculitis of medium-sized arteries** that typically affects the kidneys, peripheral nerves, GI tract, and skin.
- PAN is not associated with **asthma** or significant **eosinophilia**, and it typically **spares the lungs**.
*Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)*
- MPA is a **small-vessel vasculitis** primarily affecting the kidneys and lungs, a common cause of **pulmonary-renal syndrome**.
- While MPA can cause renal failure, and sometimes pulmonary symptoms, it does not typically present with **asthma** or marked **eosinophilia**.
*Immunoglobulin A vasculitis (IgAV)*
- IgAV, also known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura, is characterized by classic triad of **palpable purpura**, **arthralgia**, and **abdominal pain**, and frequently involves the kidneys.
- IgAV primarily affects **small vessels** and is not associated with **asthma**, **eosinophilia**, or the specific neurological and skin manifestations seen in this patient.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 2: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents after 10 days of fever, varying from 38.0–40.0°C (100.4–104.0°F). On physical examination, the child is ill-looking with an extensive rash over his trunk with patchy desquamation. His hands are swollen, and he also shows signs of a bilateral conjunctivitis. The laboratory test results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 12.9 g/dL
Hematocrit 37.7%
Mean corpuscular volume 82.2 μm3
Leukocyte count 10,500/mm3
Neutrophils 65%
Lymphocytes 30%
Monocytes 5%
Platelet count 290,000/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 35 mm/h
What is the next best step in the management of this patient’s condition?
- A. High-dose aspirin (Correct Answer)
- B. Influenza vaccine
- C. Echocardiography
- D. Low-dose aspirin
- E. Corticosteroids
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***High-dose aspirin***
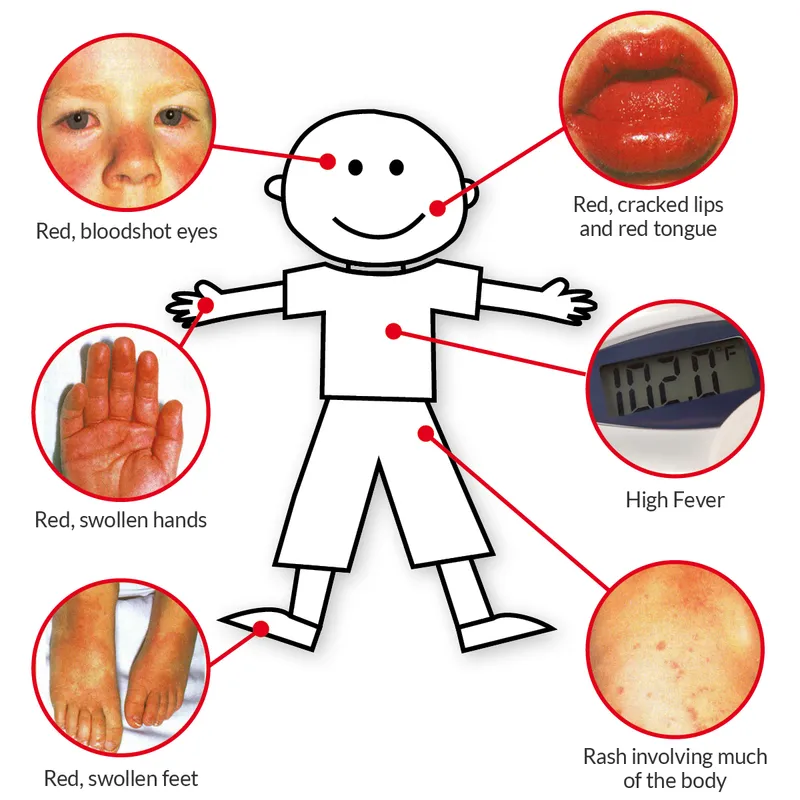
- This patient presents with classic **Kawasaki disease**: prolonged fever (10 days), bilateral conjunctivitis, rash with desquamation, and extremity changes (swollen hands).
- Standard treatment for Kawasaki disease includes **IVIG (2 g/kg) plus high-dose aspirin (80-100 mg/kg/day)**. While both should be given together, **high-dose aspirin** is the best *therapeutic* option among those listed.
- High-dose aspirin provides anti-inflammatory effects during the acute phase and helps reduce fever and systemic inflammation.
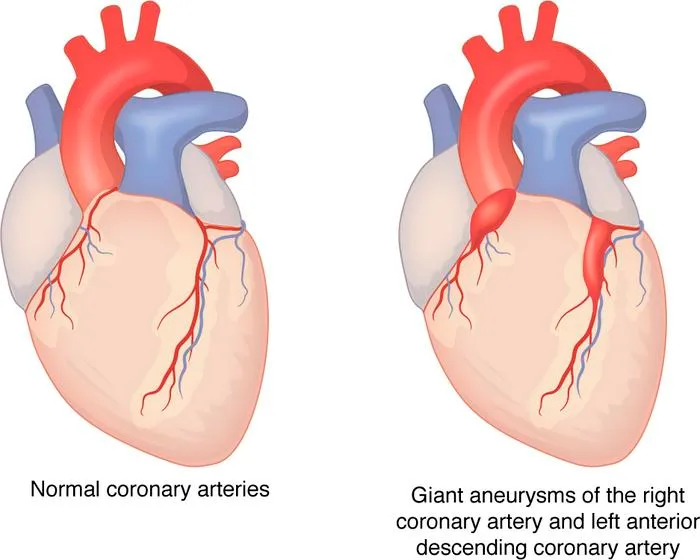
- Treatment should be initiated promptly (ideally within 10 days of fever onset) to reduce the risk of **coronary artery aneurysms**.
*Influenza vaccine*
- The influenza vaccine is not a treatment for acute illness and has no role in managing Kawasaki disease.
- Vaccination would not address the ongoing systemic inflammation or prevent cardiac complications.
*Echocardiography*
- **Echocardiography should be performed** in all cases of Kawasaki disease to assess for coronary artery abnormalities, both at diagnosis and during follow-up.
- However, it is a **diagnostic/monitoring tool**, not a therapeutic intervention. Medical treatment to reduce inflammation takes priority over imaging.
- The question asks for the "next best step in management," which implies therapeutic action rather than diagnostic testing.
*Low-dose aspirin*
- Low-dose aspirin (3-5 mg/kg/day) is used during the **convalescent phase** for its antiplatelet effects, typically after fever resolution.
- It is transitioned to after the acute inflammatory phase is controlled with high-dose aspirin.
- Not appropriate for initial acute management where anti-inflammatory dosing is needed.
*Corticosteroids*
- Corticosteroids are reserved for **IVIG-refractory cases** or patients with severe coronary artery involvement.
- They are not part of initial first-line therapy and should not be used before IVIG administration.
- Their use is indicated only when standard therapy fails.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 3: A previously healthy 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents because he has had a fever, diffuse joint pain, and a rash on his abdomen for the past week. Acetaminophen did not improve his symptoms. He emigrated from China with his family 2 years ago. He attends daycare. His immunization records are not available. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 125/min, and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Examination shows polymorphous truncal rash. The eyes are pink with no exudate. The tongue is shiny and red, and the lips are cracked. The hands and feet are red and swollen. There is right-sided anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. HHV-6 immunoglobulin M (IgM) detection
- B. ANA measurement
- C. Echocardiography (Correct Answer)
- D. Monospot test
- E. Antistreptolysin O titer measurement
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Echocardiography***
- This patient presents with classic symptoms of **Kawasaki disease**, including protracted fever (>5 days), polymorphous rash, conjunctival injection, cracked lips and red tongue (**strawberry tongue**), swollen hands and feet, and cervical lymphadenopathy.
- The diagnosis can be made clinically when fever ≥5 days plus ≥4 of 5 principal criteria are present, which this patient meets.
- **Echocardiography** is essential to establish a **baseline cardiac assessment** and screen for **coronary artery aneurysms**, which occur in 15-25% of untreated patients.
- Among the diagnostic options listed, echocardiography is the most appropriate next step, though in clinical practice, **treatment with IVIG and high-dose aspirin should be initiated promptly** (ideally within 10 days of fever onset) and should not be delayed pending echocardiography results.
*HHV-6 immunoglobulin M (IgM) detection*
- **Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6)** causes **roseola infantum** (exanthem subitum), which presents with high fever for 3-5 days followed by a rash that appears **as the fever resolves**.
- The mucocutaneous findings in this case (strawberry tongue, cracked lips, conjunctival injection, extremity swelling) are not consistent with roseola.
*ANA measurement*
- **Antinuclear antibody (ANA)** testing screens for **autoimmune diseases** such as systemic lupus erythematosus or juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
- While this patient has fever and joint pain, the specific mucocutaneous changes (strawberry tongue, cracked lips, conjunctival injection, polymorphous rash, extremity edema) and cervical lymphadenopathy are pathognomonic for Kawasaki disease, not typical autoimmune conditions.
*Monospot test*
- The **Monospot test** diagnoses **infectious mononucleosis** caused by **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**.
- While EBV can cause fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy (typically posterior cervical), the characteristic mucocutaneous findings of Kawasaki disease (strawberry tongue, cracked lips, conjunctival injection without exudate, extremity changes) are not seen in mononucleosis.
- Additionally, mononucleosis is uncommon in preschool-aged children.
*Antistreptolysin O titer measurement*
- **Antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer** detects recent **Group A Streptococcus** infection and can support a diagnosis of **acute rheumatic fever (ARF)**.
- ARF presents with migratory polyarthritis, carditis, and **erythema marginatum** (not a polymorphous rash), occurring 2-4 weeks after streptococcal pharyngitis.
- The mucocutaneous features in this case are specific to Kawasaki disease and not consistent with ARF.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 4: A 17-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of swelling of his face and legs for 5 days. He immigrated to the United States from Korea with his family 10 years ago. He has been healthy except for an episode of sore throat 2 weeks ago. His younger sister has type 1 diabetes mellitus. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 145/87 mm Hg. Examination shows periorbital edema and 3+ pitting edema of the lower extremities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.9 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8,100/mm3
Serum
Glucose 78 mg/dL
Albumin 2.4 g/dL
Hepatitis B surface antigen positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody negative
Complement C4 decreased
Urine
Blood negative
Protein 4+
Glucose negative
Protein/creatinine ratio 8.1 (N ≤ 0.2)
Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following additional findings?
- A. Increased IgA levels in serum
- B. Normal-appearing glomeruli on renal biopsy
- C. Subepithelial deposits on renal biopsy (Correct Answer)
- D. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody level in serum
- E. Eosinophilic nodules on renal biopsy
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Subepithelial deposits on renal biopsy***
- The patient presents with **nephrotic syndrome** (edema, proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia), a history of **hepatitis B infection** (HBsAg positive), and decreased **complement C4** levels. These findings are highly suggestive of **membranous nephropathy**, which is characterized by **subepithelial immune complex deposits**.
- **Membranous nephropathy** is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults and can be secondary to infections like **hepatitis B**, systemic lupus erythematosus, or certain medications.
*Increased IgA levels in serum*
- **Increased IgA levels** are characteristic of **IgA nephropathy**, which typically presents with recurrent episodes of **hematuria**, often following an upper respiratory infection.
- While there was a sore throat, the dominant presentation here is **nephrotic syndrome** with significant proteinuria and **hypocomplementemia**, which is not typical for IgA nephropathy.
*Normal-appearing glomeruli on renal biopsy*
- In cases of significant proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome, it is highly unlikely for the glomeruli to appear **normal** on biopsy.
- Conditions causing nephrotic syndrome, such as **minimal change disease**, do show normal glomeruli on light microscopy, but this patient's presentation with **Hepatitis B** and **hypocomplementemia** points away from minimal change disease.
*Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody level in serum*
- **Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs)** are associated with **vasculitic diseases** such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's), microscopic polyangiitis, and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss).
- These conditions typically present with **rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis** and systemic vasculitis, which is different from the predominant nephrotic syndrome seen in this patient.
*Eosinophilic nodules on renal biopsy*
- **Eosinophilic nodules**, also known as **Kimmelstiel-Wilson lesions**, are characteristic findings in **diabetic nephropathy**.
- Although the patient's sister has type 1 diabetes, there is no indication that the patient himself has diabetes (normal serum glucose), making this finding unlikely.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 5: A 32-year-old woman presents with new left-arm pain. She was previously well but for 2 months has had episodes of low-grade fever, night sweats, and dizziness. She works as a stock assistant and has noticed left arm pain when she stocks shelves. She is taking a multivitamin but no other medications. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 126/72 in her right arm, but it cannot be measured in her left arm. The left radial pulse is not detectable. There is a bruit over the left subclavian area. Femoral and pedal pulses are normal and no abdominal bruits are heard. The left hand is cool but has no other evidence of ischemia. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s condition?
- A. Raynaud’s phenomenon
- B. Fibromuscular dysplasia
- C. Subclavian steal syndrome
- D. Aortic coarctation
- E. Takayasu arteritis (Correct Answer)
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Takayasu arteritis***
- This **large-vessel vasculitis** predominantly affects **young women** (typically <40 years old) and involves the aorta and its major branches, including the subclavian arteries.
- The patient's **constitutional symptoms** (low-grade fever, night sweats) reflect the systemic inflammatory nature of the disease.
- The **absent left radial pulse**, **unmeasurable left arm blood pressure**, and **subclavian bruit** indicate significant stenosis or occlusion of the left subclavian artery, a hallmark of Takayasu arteritis.
- This arterial stenosis can lead to **subclavian steal syndrome** (a manifestation, not the etiology) and **arm claudication** with exertion (pain when stocking shelves).
- The **normal femoral and pedal pulses** help localize the pathology to the upper extremity vessels.
*Subclavian steal syndrome*
- This is a **hemodynamic phenomenon** (manifestation), not an underlying etiology.
- It occurs when subclavian artery stenosis causes retrograde flow from the vertebral artery to supply the affected arm, which can cause dizziness due to vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
- The underlying **cause** in this young woman with systemic symptoms is most likely Takayasu arteritis.
*Raynaud's phenomenon*
- Characterized by **episodic vasospasm** of digital arteries in response to cold or stress, causing color changes (white-blue-red).
- Does not cause **absent pulses**, **unequal blood pressures between arms**, **bruits**, or **constitutional symptoms**.
*Aortic coarctation*
- A **congenital narrowing of the aorta**, typically just distal to the left subclavian artery origin.
- Would cause **hypertension in both upper extremities** with **diminished lower extremity pulses and blood pressures** (upper-lower discrepancy, not left-right arm discrepancy).
- Does not explain the constitutional symptoms or isolated left arm findings.
*Fibromuscular dysplasia*
- A **noninflammatory arteriopathy** causing abnormal cellular proliferation in arterial walls, most commonly affecting **renal and carotid arteries**.
- Typically occurs in **middle-aged women** without systemic symptoms.
- While it can rarely affect subclavian arteries, the **constitutional symptoms** and pattern of large-vessel involvement strongly favor an inflammatory vasculitis like Takayasu arteritis.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 6: A 45-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and joint pain for 8 months. He has pain in both knees, both elbows, and diffuse muscle pain. He does not have dyspnea. He also had several episodes of a nonpruritic rash on his lower extremities. Eight years ago, the patient was diagnosed with hepatitis C. His temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Examination of the lower extremities shows raised purple papules that do not blanch when pressure is applied. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.9 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8,500/mm3
Platelets 160,000/mm3
Serum
Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
ALT 123 U/L
AST 113 U/L
Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Elevated IgA in serum
- B. Granulomatous inflammation of vessels
- C. Hypocomplementemia (Correct Answer)
- D. Elevated perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
- E. Positive pathergy test
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Hypocomplementemia***
- The patient's history of **hepatitis C** infection, along with **fatigue, polyarthralgia, elevated liver enzymes, and palpable purpura**, is classic for **HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia syndrome**.
- **Mixed cryoglobulinemia** (types II and III) involves immune complex deposition, which activates and consumes complement, leading to **low C3 and C4 levels** (hypocomplementemia).
- **Hypocomplementemia** is a hallmark laboratory finding and helps distinguish cryoglobulinemic vasculitis from other small vessel vasculitides.
*Elevated IgA in serum*
- Elevated IgA levels are characteristic of **IgA vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein purpura)**, which typically affects children and presents with palpable purpura, abdominal pain, and glomerulonephritis.
- While IgA vasculitis can occur in adults, the strong association with **hepatitis C infection** and the typical adult presentation point toward cryoglobulinemia rather than IgA vasculitis.
*Granulomatous inflammation of vessels*
- **Granulomatous inflammation of vessels** is a hallmark of **Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA)** or **Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA)**.
- These conditions typically present with upper/lower respiratory tract involvement, renal disease, and **ANCA positivity**, not the pattern seen here.
*Elevated perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies*
- **p-ANCA** (perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies) are primarily associated with **microscopic polyangiitis** and **eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)**.
- The clinical picture of **HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia** does not typically involve ANCA positivity; instead, **rheumatoid factor** and **cryoglobulins** would be the relevant serologic markers.
*Positive pathergy test*
- A **positive pathergy test** is characteristic of **Behçet's disease**, an inflammatory disorder causing recurrent oral and genital ulcers, skin lesions, and uveitis.
- This condition does not align with the patient's presentation of palpable purpura, polyarthralgia, and HCV-associated systemic symptoms.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 7: A 62-year-old man presents to the emergency department with hematuria and hemoptysis that started in the morning. He notes that he has had frequent lung infections throughout his adult life, the most recent being 2 weeks ago. He also mentions that he has had hematuria twice before but never as severe as he is having currently. His medical history is otherwise non-significant, and his only medication is acetaminophen as needed. His blood pressure is 136/92 mm Hg, heart rate is 86/min, respiratory rate is 16/min, and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). Chest radiography shows a resolving right middle lobe airspace opacity. His initial laboratory tests are notable for elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level. While in the examination room, the patient develops a spontaneous nosebleed. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Goodpasture syndrome
- B. IgA nephropathy
- C. Minimal change disease
- D. Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
- E. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Correct Answer)
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Granulomatosis with polyangiitis***
- This patient presents with a **triad of upper airway (nosebleed), lower airway (hemoptysis, recurrent lung infections), and renal involvement (hematuria)**, which is classic for granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), a form of ANCA-associated vasculitis.
- The elevated **ESR and CRP** indicate systemic inflammation, which is common in vasculitic conditions.
*Goodpasture syndrome*
- Characterized by **glomerulonephritis and pulmonary hemorrhage (hemoptysis)**, but typically does not involve the upper airways (e.g., nosebleeds).
- Diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of **anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies**, which often presents more acutely.
*IgA nephropathy*
- Often presents with **recurrent episodes of gross hematuria**, frequently following an upper respiratory tract infection.
- While it involves the kidneys, it **does not typically cause pulmonary or upper airway symptoms** such as hemoptysis or recurrent lung opacities.
*Minimal change disease*
- Characterized by **nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema)** and rarely presents with hematuria.
- **Does not cause pulmonary or upper airway manifestations** like hemoptysis or nosebleeds.
*Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis*
- Typically occurs **1-3 weeks after a streptococcal infection** and presents with acute nephritic syndrome (hematuria, proteinuria, edema, hypertension).
- **Does not involve recurrent lung infections or hemoptysis** and is less likely in an adult with recurrent hematuria episodes.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 8: A 27-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with worsening cough and asthma. The patient reports that he was in his usual state of health until 1 month ago, when he developed a cold. Since then his cold has improved, but he continues to have a cough and worsening asthma symptoms. He says that he has been using his rescue inhaler 3 times a day with little improvement. He is studying for an accounting exam and states that his asthma is keeping him up at night and making it hard for him to focus during the day. The patient admits to smoking tobacco. His smoking has increased from a half pack per day since he was 17 years old to 1 pack per day during the past month to cope with the stress of his exam. The patient's temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 110/74 mmHg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 15/min with an oxygen saturation of 97% on room air. Physical examination is notable for mild expiratory wheezes bilaterally. Labs are obtained, as shown below:
Serum:
Na+: 144 mEq/L
Cl-: 95 mEq/L
K+: 4.3 mEq/L
HCO3-: 23 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 24 mg/dL
Glucose: 100 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.6 mg/dL
Leukocyte count and differential:
Leukocyte count: 13,000/mm^3
Segmented neutrophils: 63%
Eosinophils: 15%
Basophils: < 1%
Lymphocytes: 20%
Monocytes: 1.3%
Hemoglobin: 13.5 g/dL
Hematocrit: 50%
Platelets: 200,000/mm^3
Urinalysis reveals proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Which of the following is associated with the patient's most likely diagnosis?
- A. IgA deposits
- B. Smoking
- C. c-ANCA levels
- D. Hepatitis B surface antigen
- E. p-ANCA levels (Correct Answer)
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***p-ANCA levels***
- The patient presents with asthma, sinusitis-like symptoms (prior cold followed by worsening cough/asthma), eosinophilia (15%), and renal involvement (proteinuria, hematuria, elevated creatinine). This constellation of symptoms is highly suggestive of **Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA)**, formerly known as Churg-Strauss Syndrome.
- Approximately 30-40% of EGPA patients are positive for **p-ANCA (anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies)**, which are associated with the vasculitic phase and renal involvement.
*IgA deposits*
- **IgA deposits** are characteristic of **IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease)** or **Henoch-Schönlein purpura** (now IgA vasculitis), which typically present with hematuria and proteinuria, sometimes after an upper respiratory infection.
- However, these conditions do not typically cause severe asthma, significant eosinophilia, or a systemic vasculitis picture with pulmonary involvement as seen in this patient.
*Smoking*
- While the patient is a smoker and smoking can exacerbate asthma and contribute to chronic lung disease, it is not an *associated factor* with the underlying diagnosis of EGPA itself.
- Smoking is a risk factor for many respiratory illnesses but doesn't specifically point to EGPA in the context of the given clinical and laboratory findings.
*c-ANCA levels*
- **c-ANCA (anti-proteinase 3 antibodies)** are primarily associated with **Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA)**, formerly Wegener's granulomatosis.
- While GPA can present with kidney involvement and pulmonary symptoms, it typically involves the upper airways (sinusitis, otitis), lungs, and kidneys, but is usually *not* associated with severe asthma or prominent eosinophilia, which are key features in this patient.
*Hepatitis B surface antigen*
- **Hepatitis B surface antigen** positivity is associated with **polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)** due to immune complex deposition.
- PAN is a necrotizing vasculitis that can affect multiple organs but typically spare the lungs and is not associated with asthma or eosinophilia.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 9: A 40-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of difficulty walking for the past 4 hours. She first noticed her symptoms after getting up this morning and her foot dragging while walking. She feels tired. She has a history of chronic sinusitis. Six months ago, she was diagnosed with asthma. Current medications include an albuterol inhaler and inhaled corticosteroids. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), pulse is 80/min, and her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Auscultation of her lungs shows diffuse wheezing over bilateral lung fields. Physical examination shows tender subcutaneous nodules on the extensor surfaces of the elbows. There are palpable, non-blanching erythematous lesions on both shins. Dorsiflexion of the right foot is impaired. Sensation to pinprick, light touch, and vibration is decreased over the ulnar aspect of the left forearm. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.3 g/dL
Leukocyte count 24,500
Segmented neutrophils 48%
Eosinophils 29%
Lymphocytes 19%
Monocytes 4%
Platelet count 290,000/mm3
Serum
Urea nitrogen 32 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.85 mg/dL
Urine
Blood 2+
Protein 3+
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- B. Excessive glucocorticoid use
- C. Goodpasture syndrome
- D. Henoch-Schönlein purpura
- E. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Correct Answer)
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)***
- This patient presents with a classic triad: **asthma**, **eosinophilia** (29%), and **multisystem vasculitis** as evidenced by mononeuropathy, skin lesions (nodules and palpable purpura), and kidney involvement.
- The history of chronic sinusitis, new-onset foot drop (mononeuropathy), **palpable purpura**, and elevated creatinine with proteinuria strongly point towards EGPA.
*Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)*
- While GPA can cause sinusitis, kidney disease, and neuropathy, it typically presents with **neutrophilic inflammation** and **c-ANCA** positivity, not prominent eosinophilia or severe asthma.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis typically involves the **upper and lower respiratory tracts** and kidneys but lacks the pronounced eosinophilia and severe asthma seen here.
*Excessive glucocorticoid use*
- This condition is associated with Cushingoid features, **osteoporosis**, and immunosuppression, none of which fully explain the patient's acute neurological deficits, eosinophilia, or vasculitic manifestations.
- Although the patient has asthma, her symptoms are not consistent with the side effects of inhaled corticosteroids or chronic systemic glucocorticoid use.
*Goodpasture syndrome*
- Goodpasture syndrome is characterized by **recurrent pulmonary hemorrhage** and rapidly progressive **glomerulonephritis** due to anti-GBM antibodies.
- It does not explain the prominent eosinophilia, asthma, or the presence of subcutaneous nodules and palpable purpura.
*Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP)*
- HSP typically presents in children with **palpable purpura** on the buttocks and lower extremities, **arthralgias**, abdominal pain, and **IgA nephropathy**.
- It does not involve significant eosinophilia, severe asthma, or mononeuropathy as seen in this adult patient.
Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG Question 10: A 32-year-old woman who recently emigrated to the USA from Japan comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of night sweats, malaise, and joint pain. During this time, she has also had a 6-kg (13-lb) weight loss. Physical examination shows weak brachial and radial pulses. There are tender subcutaneous nodules on both legs. Carotid bruits are heard on auscultation bilaterally. Laboratory studies show an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 96 mm/h. A CT scan of the chest shows thickening and narrowing of the aortic arch. Microscopic examination of the aortic arch is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Fibrinoid necrosis of the intima and media
- B. Calcification of the media
- C. Granulomatous inflammation of the media (Correct Answer)
- D. Subendothelial hyaline deposition
- E. Subendothelial immune complex deposition
Medium vessel vasculitis Explanation: ***Granulomatous inflammation of the media***
- The clinical presentation, including **night sweats, malaise, weight loss, weak brachial and radial pulses** (pulseless disease), and **thickening and narrowing of the aortic arch**, is highly suggestive of **Takayasu arteritis**.
- **Takayasu arteritis** is a **large-vessel vasculitis** characterized pathologically by **granulomatous inflammation** primarily affecting the **tunica media** of the aorta and its major branches.
*Fibrinoid necrosis of the intima and media*
- **Fibrinoid necrosis** is typically seen in **small-to-medium vessel vasculitides** (e.g., polyarteritis nodosa) or in severe **hypertensive vasculopathy**.
- It involves the deposition of **fibrin-like material** in the vessel wall, which is not the primary histological feature of Takayasu arteritis.
*Calcification of the media*
- **Medial calcification** (Mönckeberg arteriosclerosis) primarily affects **muscular arteries** and is typically seen in older individuals, often incidentally.
- It does not cause significant luminal narrowing, inflammation, or the systemic symptoms described in this patient.
*Subendothelial hyaline deposition*
- **Hyaline deposition** in the subendothelium is characteristic of **hyaline arteriolosclerosis**, commonly seen in **benign hypertension** or **diabetes mellitus**, affecting small arteries and arterioles.
- This finding is not consistent with the specific large-vessel inflammatory process seen in Takayasu arteritis.
*Subendothelial immune complex deposition*
- **Immune complex deposition** in the subendothelium is typical of **Type III hypersensitivity reactions**, such as those seen in **lupus nephritis** or **Type II cryoglobulinemia**, often affecting glomeruli or small vessels.
- While Takayasu arteritis is immune-mediated, its hallmark is **granulomatous inflammation**, not primary immune complex deposition in the vessel wall.
More Medium vessel vasculitis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.