Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Inflammatory myopathies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
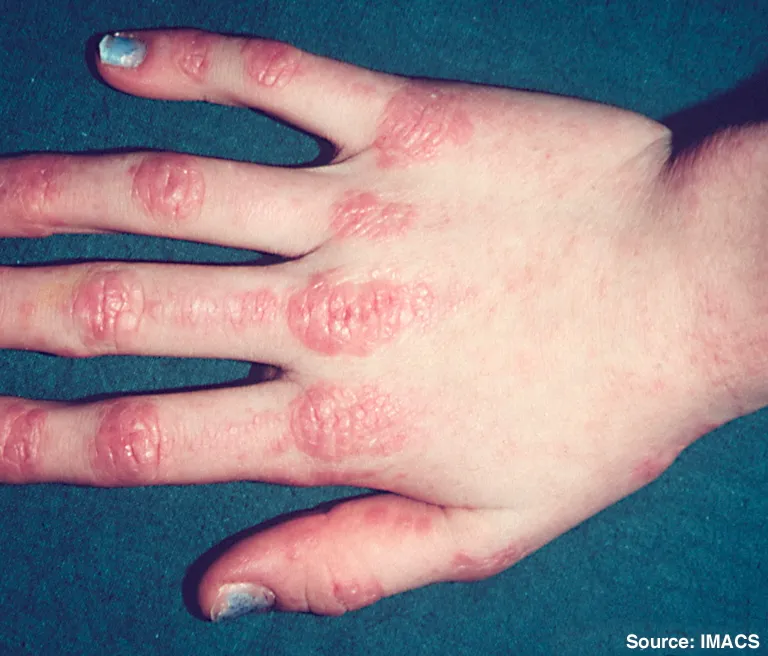
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 1: A 35-year-old woman presents for evaluation of symmetric proximal muscle weakness. The patient also presents with a blue-purple discoloration of the upper eyelids accompanied by rashes on the knuckles, as shown in the picture below. What is the most likely cause?
- A. Dermatomyositis (Correct Answer)
- B. Inclusion body myositis
- C. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- D. Polymyositis
- E. Hypothyroidism
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Dermatomyositis***
- This condition is characterized by **symmetric proximal muscle weakness** accompanied by distinctive skin manifestations, such as a **heliotrope rash** (blue-purple discoloration of the upper eyelids) and **Gottron's papules** (rashes on the knuckles).
- These classic features are almost pathognomonic for dermatomyositis, an **autoimmune inflammatory myopathy**.
*Inclusion body myositis*
- Inclusion body myositis typically presents with **asymmetric distal muscle weakness** and **atrophy**, a pattern different from the symmetric proximal weakness described.
- It primarily affects older individuals and does **not involve skin manifestations**.
*Duchenne muscular dystrophy*
- This is a **genetic disorder** primarily affecting young boys, presenting with progressive muscle weakness that is often noted in early childhood.
- It is characterized by **proximal muscle wasting** and does not present with the specific dermatological findings of heliotrope rash or Gottron's papules.
*Polymyositis*
- Polymyositis also presents with **symmetric proximal muscle weakness**, similar to dermatomyositis, but it **lacks the characteristic skin manifestations** described in the patient.
- The absence of the heliotrope rash and Gottron's papules helps differentiate it from dermatomyositis.
*Hypothyroidism*
- Hypothyroidism can cause **muscle weakness**, myalgia, and cramps, but these symptoms are usually insidious and accompanied by other systemic symptoms like **fatigue**, **weight gain**, and **cold intolerance**.
- It does **not cause the specific skin rashes** (heliotrope rash, Gottron's papules) seen in this patient.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 2: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of body aches for the past 9 months. She also has stiffness of the shoulders and knees that is worse in the morning and tingling in the upper extremities. Examination shows marked tenderness over the posterior neck, bilateral mid trapezius, and medial aspect of the left knee. A complete blood count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are within the reference ranges. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- B. Fibromyalgia (Correct Answer)
- C. Rheumatoid arthritis
- D. Polymyositis
- E. Major depressive disorder
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Fibromyalgia***
- The patient's presentation of widespread **body aches for 9 months**, morning **stiffness**, and **multiple tender points** (posterior neck, bilateral mid trapezius, medial aspect of the knee) in the absence of inflammatory markers (normal ESR, normal CBC) is highly characteristic of **fibromyalgia**.
- **Paresthesias** (tingling in the upper extremities) are a common associated feature in fibromyalgia.
- Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome diagnosed clinically based on widespread pain and tender points, with normal laboratory findings.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- SLE typically presents with **systemic inflammation**, often involving joints, skin, and kidneys, along with abnormalities in inflammatory markers (e.g., elevated ESR, positive ANA, cytopenias).
- The widespread tender points and completely normal inflammatory markers make SLE very unlikely.
*Rheumatoid arthritis*
- RA primarily affects the **synovial joints** symmetrically, leading to joint swelling, warmth, and morning stiffness, typically accompanied by elevated ESR and CRP.
- The examination findings show specific **tender points** rather than objective joint swelling, and the normal ESR rules against active RA.
*Polymyositis*
- Polymyositis is characterized by **proximal muscle weakness** (not diffuse body aches) and is associated with elevated muscle enzymes (CK, aldolase) and inflammatory changes on muscle biopsy.
- This patient has pain and tenderness without weakness, and her laboratory tests are normal.
*Major depressive disorder*
- While **fatigue**, body aches, and sleep disturbances can be symptoms of major depressive disorder, the presence of specific, well-defined **tender points on examination** points towards a primary pain syndrome.
- Fibromyalgia often coexists with depression, but the objective physical findings of multiple tender points are more consistent with fibromyalgia as the primary diagnosis.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 3: A 48-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of muscle stiffness, myalgia, and a 7-kg (15-lb) weight gain. Her last menstrual period was 4 months ago. Physical examination shows cold, dry skin, and proximal muscle weakness. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+ bilaterally, with delayed relaxation. The creatine kinase level is 2,940 U/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Thyroid function tests (Correct Answer)
- B. Repetitive nerve stimulation
- C. Serum electrolytes
- D. Muscle biopsy
- E. Serum assay for muscle specific tyrosine kinase antibody
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Thyroid function tests***
- The patient's symptoms (muscle stiffness, myalgia, weight gain, cold/dry skin, proximal muscle weakness, delayed deep tendon reflex relaxation, and elevated CK) are highly suggestive of **hypothyroidism**.
- Measuring **TSH** and **free T4** is crucial to confirm or rule out this diagnosis and it is the most appropriate next step in the diagnostic workup.
*Repetitive nerve stimulation*
- This test is primarily used to diagnose disorders of the **neuromuscular junction**, such as **myasthenia gravis** or **Lambert-Eaton syndrome**.
- The patient's clinical picture, particularly the delayed deep tendon reflex relaxation and muscle stiffness, is not typical for these conditions.
*Serum electrolytes*
- While electrolytes can be abnormal in various conditions, they are unlikely to directly explain the constellation of symptoms (muscle stiffness, weight gain, cold/dry skin, delayed reflexes) and the high **creatine kinase** level in this patient.
- While a basic metabolic panel is often part of a general workup, it is not the most specific or appropriate *next step* for this clinical presentation.
*Muscle biopsy*
- A muscle biopsy is an **invasive procedure** typically reserved for diagnosing specific **myopathies** (e.g., inflammatory myopathies, muscular dystrophies) when less invasive tests have not yielded a diagnosis.
- Given the strong indicators for hypothyroidism, a muscle biopsy would be premature before evaluating thyroid function.
*Serum assay for muscle specific tyrosine kinase antibody*
- This antibody is a marker for a subtype of **myasthenia gravis** (**MuSK-associated myasthenia gravis**), a disorder of the neuromuscular junction.
- As with repetitive nerve stimulation, the patient's symptoms, especially the delayed deep tendon reflexes and myxedema-like features, do not primarily point towards myasthenia gravis.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old man presents to clinic complaining of increasing difficulty climbing stairs and standing up from sitting in his chair. On exam you perceive his strength to be 5/5 distally, but only 3/5 in proximal muscle groups bilaterally. There is a distinctive rash on his upper eyelids and around his eyes. Examination of the fingers is most likely to reveal which of the following?
- A. Enlargement of the PIP
- B. Ulnar deviation of the fingers
- C. Dactylitis
- D. Violaceous papules over the MCP and PIP joints (Correct Answer)
- E. Nail pitting with oil spots
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Violaceous papules over the MCP and PIP joints***
- The patient's symptoms of **proximal muscle weakness** and characteristic rash (rash on upper eyelids, i.e., **heliotrope rash**) are highly suggestive of **dermatomyositis**.
- **Gottron's papules**, which are violaceous papules over the **extensor surfaces** of the **metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints**, are a **pathognomonic cutaneous finding** in dermatomyositis.
- These lesions may also appear over the elbows and knees, and occasionally over the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints, but MCP and PIP involvement is most characteristic.
*Enlargement of the PIP*
- **Enlargement of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints** is more characteristic of **osteoarthritis** (Bouchard's nodes) or **rheumatoid arthritis**, which typically presents with symmetric joint involvement and different cutaneous manifestations.
- This finding does not align with the patient's pattern of proximal muscle weakness and distinctive rash.
*Ulnar deviation of the fingers*
- **Ulnar deviation of the fingers** is a classic deformity seen in advanced **rheumatoid arthritis**, which primarily affects joints symmetrically and is not associated with the proximal muscle weakness and specific facial rash described.
- The patient's symptoms point away from an inflammatory arthropathy like rheumatoid arthritis.
*Dactylitis*
- **Dactylitis** (swelling of an entire digit, giving a **"sausage digit"** appearance) is characteristic of **psoriatic arthritis** or **spondyloarthropathies** (such as reactive arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis).
- It is not a feature of dermatomyositis and does not fit the overall clinical picture of proximal muscle weakness and heliotrope rash.
*Nail pitting with oil spots*
- **Nail pitting** and **oil spots** (yellow-brown discoloration under the nail) are characteristic dermatological manifestations of **psoriasis** and **psoriatic arthritis**.
- These findings are not associated with dermatomyositis, whose dermatological features include Gottron's papules and heliotrope rash.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 5: A 33-year-old woman comes to the clinic for a follow-up visit after recently starting high dose corticosteroids for a newly diagnosed autoimmune condition. She was first evaluated a month ago due to fatigue, muscle weakness, and a scaly rash on both hands. On examination, muscle strength was rated 2 out of 5 in the upper extremities. Creatine kinase-MB was elevated, and anti-Jo-1 antibodies were observed. A muscle biopsy later showed perimysial inflammation and treatment was initiated. Today, the patient says that her symptoms have not improved despite treatment with corticosteroids. It is agreed upon to initiate methotrexate with the hopes of achieving better symptom control. Which of the following is most often associated with this patient’s condition?
- A. Ovarian cancer
- B. Arthritis
- C. Lung cancer
- D. Raynaud's phenomenon
- E. Interstitial lung disease (Correct Answer)
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Interstitial lung disease***
- The patient's condition, characterized by **fatigue**, **muscle weakness**, **scaly rash** (likely **Gottron's papules** or **heliotrope rash**), **elevated CK-MB**, and **anti-Jo-1 antibodies**, strongly suggests **dermatomyositis**, which is frequently associated with **interstitial lung disease (ILD)**.
- Approximately 70% of patients with **anti-Jo-1 antibodies** develop **ILD**, which can manifest as chronic cough and dyspnea.
*Ovarian cancer*
- While dermatomyositis is associated with an **increased risk of malignancy**, particularly in older patients, **ovarian cancer** is not the *most common* or *most frequently associated* manifestation of the disease overall, especially given the patient's age (33).
- The risk of malignancy is higher in adults with dermatomyositis and polymyositis, with various cancers observed, but no single cancer type predominates as a universal association.
*Arthritis*
- **Arthritis** can occur in dermatomyositis and polymyositis, but it is typically **non-erosive** and **non-deforming**, affecting small and large joints.
- While a possible feature, it is less specific and less frequently highlighted as a major systemic complication compared to interstitial lung disease in the context of anti-Jo-1 antibodies.
*Lung cancer*
- Similar to ovarian cancer, **lung cancer** is a potential malignancy associated with dermatomyositis, especially in older patients and smokers.
- However, for a 33-year-old woman with anti-Jo-1 antibodies, **interstitial lung disease** is a more direct and prevalent associated complication than **lung cancer**.
*Raynaud's phenomenon*
- **Raynaud's phenomenon** (episodic digital ischemia) is observed in a subset of patients with dermatomyositis, often those with features of overlap syndromes.
- While present in some cases, it is not as highly prevalent or as clinically significant as **interstitial lung disease** in patients with anti-Jo-1 antibodies.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 6: A 32-year-old woman comes to the physician because of increasing muscle weakness in her shoulders and legs for 6 weeks. She is unable to climb stairs or comb her hair. She has also had difficulty swallowing food for the past week. Her symptoms do not improve with rest. Physical examination shows normal muscle tone. There is bilateral weakness of the iliopsoas, hamstring, deltoid, and biceps muscles. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+ bilaterally. Sensation to pinprick, temperature, and vibration is intact. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.7 g/dL
Leukocyte count 10.800/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 100 mm/h
Serum
Glucose 60 mg/dL
Creatine kinase 7047 U/L
Lactate dehydrogenase 2785 U/L
Thyroid-stimulating hormone 4.0 μU/mL
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Temporal artery biopsy
- B. Lumbar puncture
- C. Tensilon test
- D. Electromyography (Correct Answer)
- E. Skin biopsy
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Electromyography***
- Electromyography (EMG) can help confirm the diagnosis by demonstrating characteristic **myopathic changes**, such as short-duration, low-amplitude motor unit potentials, and increased insertional activity. This helps differentiate myopathy from other neuromuscular disorders.
- The patient's presentation with **proximal muscle weakness**, dysphagia, and significantly elevated muscle enzymes (CK and LDH) strongly suggests an inflammatory myopathy like polymyositis or dermatomyositis, for which EMG is a crucial diagnostic step.
*Temporal artery biopsy*
- This procedure is primarily used to diagnose **giant cell arteritis**, a condition presenting with headache, jaw claudication, and visual disturbances, which are not described in this patient.
- While an elevated ESR is present, it is a non-specific inflammatory marker and, in this context, points more towards a systemic inflammatory process affecting muscles.
*Lumbar puncture*
- A lumbar puncture is used to analyze **cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)** and is indicated for suspected infections (meningitis, encephalitis) or inflammatory conditions of the central nervous system.
- The patient's symptoms are localized to muscle weakness, with intact sensation and reflexes, making a primary CNS cause less likely at this stage.
*Tensilon test*
- The Tensilon test (edrophonium test) is used to diagnose **myasthenia gravis**, a neuromuscular junction disorder characterized by fluctuating muscle weakness that *improves with rest* and worsens with activity.
- This patient's symptoms do not improve with rest, and the significantly elevated muscle enzymes point away from a neuromuscular junction disorder and towards a primary muscle pathology.
*Skin biopsy*
- A skin biopsy is useful for diagnosing dermatological conditions, including **dermatomyositis**, if a characteristic rash (e.g., heliotrope eruption, Gottron's papules) is present.
- While dermatomyositis is a possibility, the question focuses on muscle weakness and enzyme elevation, suggesting that a muscle-specific investigative tool (like EMG or muscle biopsy) is a more direct next step for characterizing the primary muscle involvement.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 7: A 13-year-old girl is admitted to the hospital due to muscle weakness, pain, and arthralgia in her wrist joints. The patient says, "I am having trouble walking home after school, especially climbing steep hills." She also complains of malaise. On physical examination, a heliotrope rash is observed around her eyes, and multiple hyperkeratotic, flat, red papules with central atrophy are present on the back of the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. Deposits of calcium are also noted on the pads of her fingers. Her serum creatine kinase levels are elevated. Which of the following antibodies is most likely to be found in this patient?
- A. Anti-centromere
- B. Anti-histone
- C. Anti-Jo-1 (Correct Answer)
- D. Anti-Scl-70
- E. Anti-Sm
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Anti-Jo-1***
- This patient presents with classic signs and symptoms of **juvenile dermatomyositis**, including **proximal muscle weakness**, **arthralgia**, elevated **creatine kinase**, **heliotrope rash** (periorbital violaceous rash), **Gottron's papules** (hyperkeratotic papules over MCP/IP joints), and **calcinosis**.
- Among the given options, **anti-Jo-1** is the most appropriate antibody, though it should be noted that anti-Jo-1 antibodies are **relatively uncommon in juvenile dermatomyositis** (found in <5% of pediatric cases) compared to adult dermatomyositis/polymyositis (20-30% of cases).
- **Anti-Jo-1** (anti-histidyl-tRNA synthetase) is an **anti-synthetase antibody** associated with myositis, particularly when accompanied by **interstitial lung disease, Raynaud's phenomenon, arthritis, and "mechanic's hands"** (anti-synthetase syndrome).
- The most common antibodies in **juvenile dermatomyositis** are actually **anti-Mi-2, anti-TIF1-gamma (p155/140), and anti-NXP2**, which are more specific for the pediatric form and associated with calcinosis.
*Anti-centromere*
- **Anti-centromere antibodies** are characteristic of **limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (CREST syndrome)**, which includes **C**alcinosis, **R**aynaud's phenomenon, **E**sophageal dysmotility, **S**clerodactyly, and **T**elangiectasias.
- While calcinosis is present in this patient, the other key features of CREST syndrome (sclerodactyly, telangiectasias, esophageal symptoms) are absent, and the **heliotrope rash and Gottron's papules are pathognomonic for dermatomyositis**, not scleroderma.
*Anti-histone*
- **Anti-histone antibodies** are primarily associated with **drug-induced lupus erythematosus** (DILE), commonly caused by medications like procainamide, hydralazine, isoniazid, or quinidine.
- This patient's presentation with **proximal muscle weakness, markedly elevated creatine kinase, heliotrope rash, and Gottron's papules** is characteristic of inflammatory myopathy, not drug-induced lupus.
*Anti-Scl-70*
- **Anti-Scl-70 antibodies** (anti-topoisomerase I) are highly specific for **diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis**, which presents with widespread skin thickening, Raynaud's phenomenon, and internal organ involvement.
- While systemic sclerosis can involve muscle weakness, the **heliotrope rash and Gottron's papules are pathognomonic for dermatomyositis**, not scleroderma, making this diagnosis unlikely.
*Anti-Sm*
- **Anti-Sm antibodies** (anti-Smith) are highly specific for **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)** and are one of the diagnostic criteria.
- While SLE can cause myalgia, arthralgia, and various rashes, the **markedly elevated creatine kinase** (indicating true myositis), along with the **pathognomonic heliotrope rash and Gottron's papules**, clearly point to dermatomyositis rather than SLE.
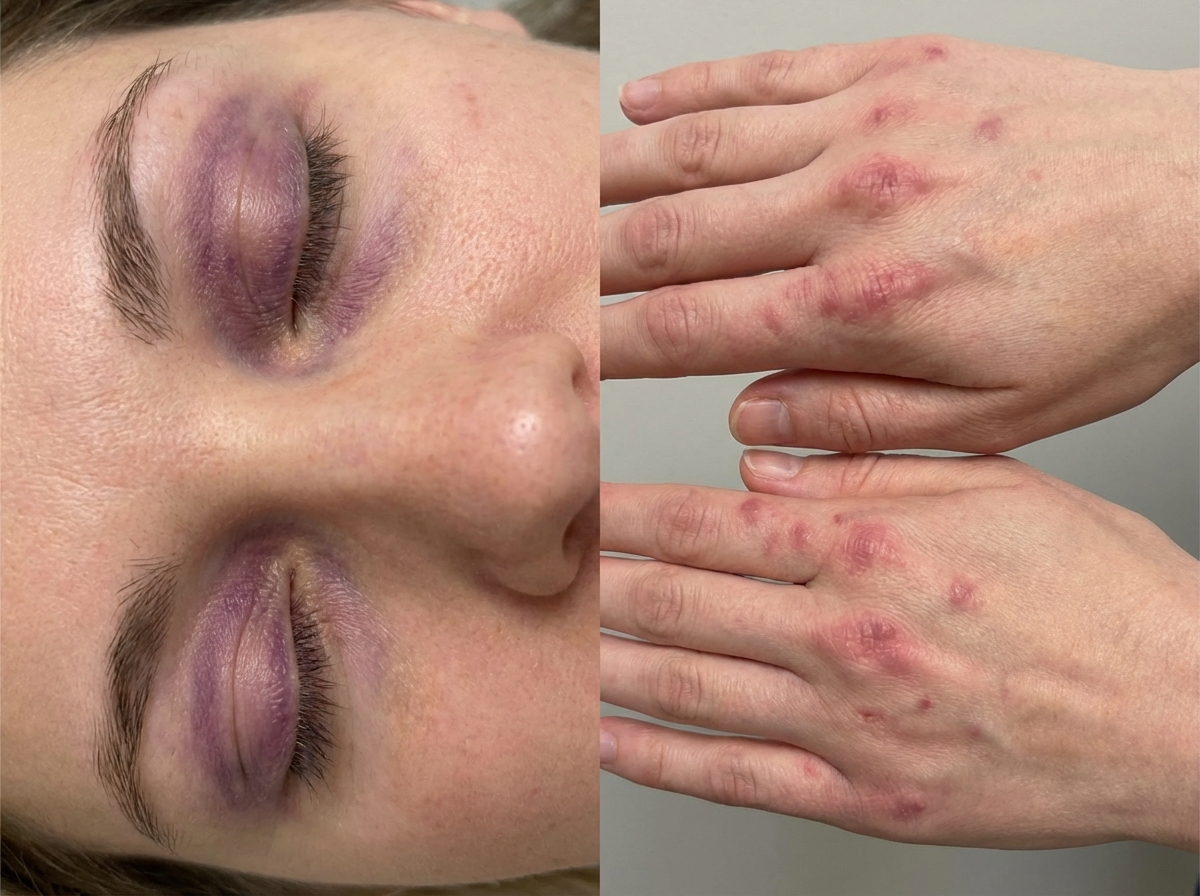
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 8: A 38-year-old woman presents with progressive muscle weakness. The patient says that symptoms onset a couple of weeks ago and have progressively worsened. She says she hasn’t been able to lift her arms to comb her hair the past few days. No significant past medical history and no current medications. Family history is significant for her mother with scleroderma and an aunt with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). On physical examination, strength is 2 out of 5 in the upper extremities bilaterally. There is an erythematous area, consisting of alternating hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation with telangiectasias, present on the extensor surfaces of the arms, the upper chest, and the neck in a ‘V-shaped’ distribution. Additional findings are presented in the exhibit (see image). Laboratory tests are significant for a positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) and elevated creatinine phosphokinase. Which of the following is the most appropriate first-line treatment for this patient?
- A. Methotrexate
- B. Hydroxychloroquine
- C. High-dose corticosteroids (Correct Answer)
- D. Infliximab
- E. Intravenous immunoglobulin
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***High-dose corticosteroids***
- This patient presents with **proximal muscle weakness**, characteristic skin findings (**heliotrope rash** and **Gottron papules** based on the image exhibit), elevated **creatinine phosphokinase**, and positive **ANA**, which are highly suggestive of **dermatomyositis**.
- **High-dose corticosteroids** are the cornerstone of initial treatment for dermatomyositis due to their potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, rapidly controlling disease activity and improving muscle strength.
*Methotrexate*
- **Methotrexate** is an immunosuppressant often used as a **second-line agent** or in combination with corticosteroids for dermatomyositis, especially in patients who do not respond adequately to steroids alone or require steroid-sparing agents.
- It works more slowly than corticosteroids and is not typically used for initial acute management of severe symptoms due to its delayed onset of action.
*Hydroxychloroquine*
- **Hydroxychloroquine** is primarily used for the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis or lupus, and is not sufficiently potent to treat the muscle weakness or systemic involvement characteristic of active dermatomyositis.
- It would be considered for **mild cutaneous disease** or as an adjunct, but not as the initial first-line treatment for multiorgan involvement.
*Infliximab*
- **Infliximab** is a **TNF-alpha inhibitor** used in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is **not indicated** for dermatomyositis.
- TNF-alpha inhibitors are generally not used in the management of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, and there is no evidence to support its role as a first-line treatment for dermatomyositis.
*Intravenous immunoglobulin*
- **Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)** is a treatment option for **refractory dermatomyositis**, or in cases of severe, life-threatening disease not responding to corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants.
- While effective, it is not considered first-line due to its cost, potential side effects, and the need for immediate, potent immunosuppression provided by corticosteroids.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 9: A 45-year-old woman presents to the clinic complaining of weakness that has progressively worsened over the past 2 weeks. She states that she has a hard time lifting both her arms but that they function normally. She notes no history of trauma or other deficits. On examination, that patient has 2/5 muscle strength on shoulder shrug and arm abduction bilaterally, but all other neurological exam findings are normal. You notice some skin changes and ask the patient about them. She states that she has had a rash around her eyes as well as on her lower face, going down to her neck and chest. She notes that the rashes started around the same time as the weakness began. Labs are drawn and a complete blood count and basic metabolic panel are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Dermatomyositis (Correct Answer)
- B. Polymyalgia rheumatica
- C. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)
- D. Fibromyalgia
- E. Myasthenia gravis
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Dermatomyositis***
- The presentation of **proximal muscle weakness** (difficulty lifting arms, weak shoulder shrug and arm abduction) combined with **characteristic skin rashes** (heliotrope rash around eyes, shawl sign on neck/chest) is highly indicative of dermatomyositis.
- Dermatomyositis is a **systemic autoimmune disease** characterized by inflammation of the muscles and skin, often associated with elevated muscle enzymes, although not mentioned as abnormal here, the clinical picture is classic.
*Polymyalgia rheumatica*
- Polymyalgia rheumatica also causes **proximal muscle pain and stiffness**, particularly in the shoulders and hips, but usually without significant weakness.
- It is not associated with the specific **skin manifestations** described, and typically occurs in older individuals (over 50).
*Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)*
- LEMS causes **proximal muscle weakness** that typically **improves with exercise** and is often associated with **autonomic dysfunction** (e.g., dry mouth, erectile dysfunction) and **small cell lung cancer**.
- The specific skin rashes observed and the progressive worsening of weakness are inconsistent with LEMS.
*Fibromyalgia*
- Fibromyalgia is characterized by **widespread musculoskeletal pain**, fatigue, and tender points, but typically **does not involve objective muscle weakness** or the specific skin rashes seen in this patient.
- The muscle strength findings (2/5) rule out fibromyalgia as the primary diagnosis.
*Myasthenia gravis*
- Myasthenia gravis causes **fluctuating muscle weakness** that worsens with activity and improves with rest, often affecting **ocular and bulbar muscles** first.
- While it can cause proximal limb weakness, it is not associated with the specific **skin rashes** described.
Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG Question 10: A 56-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with muscle weakness. She reports her symptoms have progressively worsened over the course of 2 weeks and are most significant in her lower extremities. She also notices increased urinary frequency. Approximately 1 month ago she was diagnosed with a calcium phosphate nephrolithiasis. Medical history is significant for rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed approximately 10 years ago treated with methotrexate, and type II diabetes mellitus treated with metformin. Her temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 138/92 mmHg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 17/min. On physical exam, there is mild tenderness to palpation of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. There is 4/5 power throughout the lower extremity. Laboratory testing is shown.
Serum:
Na+: 137 mEq/L
Cl-: 106 mEq/L
K+: 2.9 mEq/L
HCO3-: 18 mEq/L
Glucose: 115 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL
Urine pH: 5.6
Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Administer intravenous sodium bicarbonate
- B. Increase the methotrexate dose
- C. Administer intravenous insulin
- D. Begin potassium replacement therapy with dextrose (Correct Answer)
- E. Administer hydrochlorothiazide
Inflammatory myopathies Explanation: ***Begin potassium replacement therapy with dextrose***
- The patient presents with **muscle weakness**, **hypokalemia** (2.9 mEq/L), and **metabolic acidosis** (HCO3- 18 mEq/L, normal anion gap since Na - Cl - HCO3 = 137 - 106 - 18 = 13). These findings, along with a history of calcium phosphate nephrolithiasis and relatively alkaline urine (pH 5.6) in the presence of acidosis, point to **distal renal tubular acidosis (Type 1 RTA)**.
- **Potassium replacement** is crucial given the severe hypokalemia, which is likely contributing to the muscle weakness. Potassium is typically administered in dextrose-containing fluids to provide a vehicle for safe intravenous administration and prevent venous irritation from concentrated potassium solutions.
*Administer intravenous sodium bicarbonate*
- While the patient has **metabolic acidosis**, sodium bicarbonate is not the immediate priority and could worsen hypokalemia by driving potassium intracellularly through alkalinization.
- The primary issue is the **renal inability to excrete acid** *and* conserve potassium. Both potassium repletion and bicarbonate therapy will ultimately be needed for Type 1 RTA, but **potassium repletion is the immediate priority** given the severe hypokalemia and muscle weakness.
*Increase the methotrexate dose*
- The patient's **rheumatoid arthritis** is treated with methotrexate, but there is no indication that her current symptoms are related to RA flare or that her methotrexate dose is insufficient.
- Increasing methotrexate would not address the **hypokalemia**, **metabolic acidosis**, or **muscle weakness**.
*Administer intravenous insulin*
- The patient has type II diabetes, but her **blood glucose** (115 mg/dL) is well-controlled and does not warrant immediate intravenous insulin.
- **Insulin would be contraindicated** in this setting as it drives potassium into cells, which would worsen the patient's life-threatening hypokalemia.
*Administer hydrochlorothiazide*
- **Hydrochlorothiazide** is a thiazide diuretic that causes **hypokalemia** and **metabolic alkalosis**.
- Administering hydrochlorothiazide would be contraindicated in this patient as it would exacerbate her existing hypokalemia and would not address the underlying **Type 1 RTA** or metabolic acidosis.
More Inflammatory myopathies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.