Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
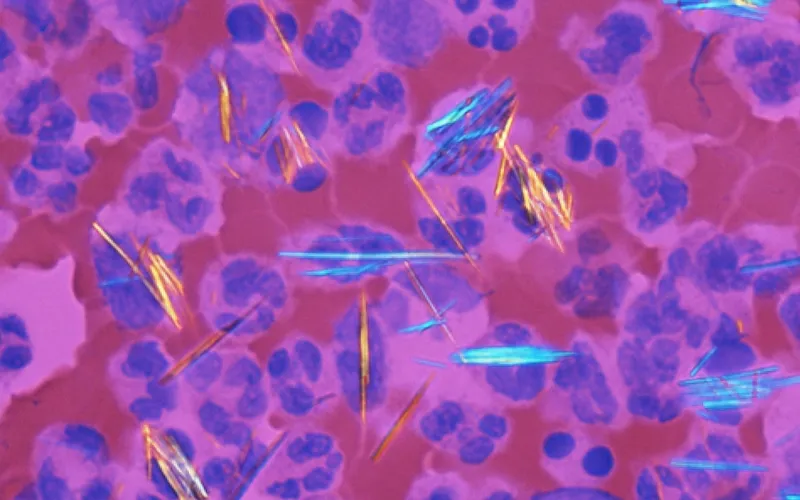
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 1: A 60-year-old man has had intermittent pain in his right great toe for the past 2 years. Joint aspiration and crystal analysis shows thin, tapered, needle shaped intracellular crystals that are strongly negatively birefringent. Radiograph demonstrates joint space narrowing of the 1st metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint with medial soft tissue swelling. What is the most likely cause of this condition?
- A. Tuberculosis
- B. Monosodium urate crystal deposition (Correct Answer)
- C. Calcium pyrophosphate deposition
- D. Rheumatoid arthritis
- E. Septic arthritis
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Monosodium urate crystal deposition***
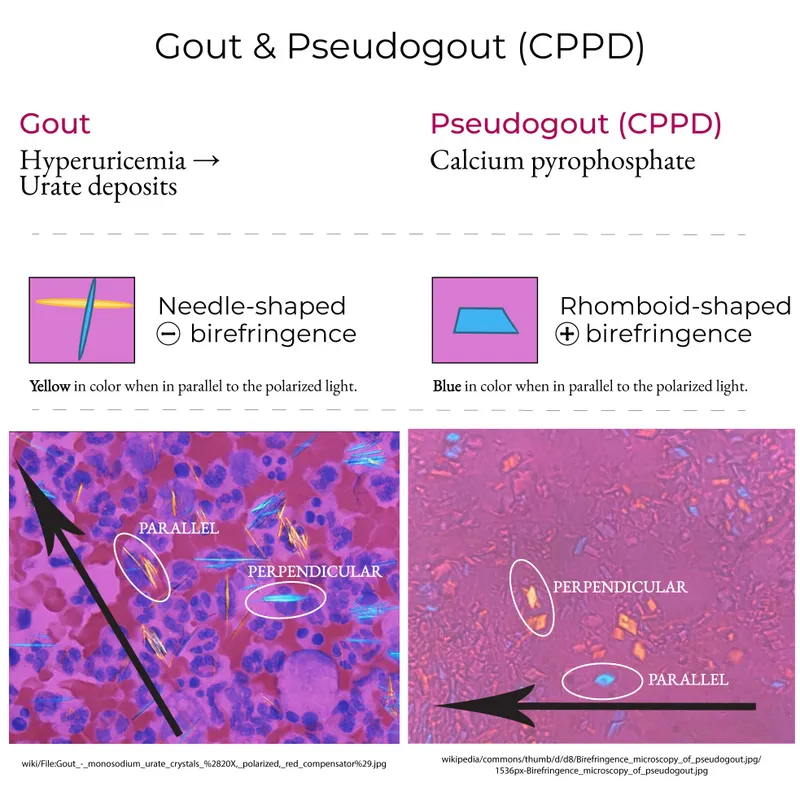
- The presence of **thin, tapered, needle-shaped intracellular crystals** that are **strongly negatively birefringent** on joint fluid analysis is pathognomonic for **gout**, caused by monosodium urate crystal deposition.
- Intermittent pain in the **first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint** (podagra) and medial soft tissue swelling are classic clinical findings associated with gout.
*Tuberculosis*
- Tuberculosis of a joint typically presents with **chronic pain and swelling**, often with osteolytic lesions, but not with characteristic crystal findings.
- Joint fluid analysis would show **acid-fast bacilli** or granulomatous inflammation, not birefringent crystals.
*Calcium pyrophosphate deposition*
- This condition (pseudogout) involves **rhomboid-shaped crystals** that are **weakly positively birefringent**, not needle-shaped and strongly negatively birefringent.
- Pseudogout more commonly affects larger joints like the knee and wrist, not typically the great toe MTP joint as the primary site.
*Rheumatoid arthritis*
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an **inflammatory polyarthritis** primarily affecting small joints of the hands and feet symmetrically, and does not involve crystal deposition.
- Joint fluid analysis would show inflammatory changes but not specific crystals, and serology for **rheumatoid factor** and **anti-CCP antibodies** would be positive.
*Septic arthritis*
- Septic arthritis presents with acute onset of severe joint pain, swelling, warmth, and restricted range of motion, often with **fever** and elevated inflammatory markers.
- Joint fluid analysis would show **markedly elevated white blood cell count** (typically >50,000 cells/μL with neutrophil predominance) and positive Gram stain or culture, not birefringent crystals.
- The **intermittent nature** over 2 years and crystal findings rule out acute infection.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 2: A 62-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-day history of dull pain and stiffness of the right knee. He takes chlorthalidone for hypertension. Physical examination of the right knee shows a large effusion and mild erythema; range of motion is limited by pain. Arthrocentesis of right knee yields a cloudy aspirate. Gram stain is negative. Analysis of the synovial fluid shows a leukocyte count of 15,000/mm3 and 55% neutrophils. Microscopic examination of the synovial fluid under polarized light shows positively birefringent rhomboid crystals. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Chalky nodules on the external ear
- B. Expression of human leukocyte antigen-B27
- C. Thickening of the synovia at the metacarpophalangeal joints
- D. Calcification of the meniscal cartilage (Correct Answer)
- E. Elevation of serum uric acid concentration
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Calcification of the meniscal cartilage***
- The presence of **positively birefringent rods and rhomboid crystals** in synovial fluid is pathognomonic for **calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD)**, also known as pseudogout.
- **Calcification of articular cartilage (chondrocalcinosis)**, particularly in the meniscal cartilage of the knee, is a characteristic radiographic finding in CPPD and would be expected on further evaluation.
*Chalky nodules on the external ear*
- **Chalky nodules (tophi)**, often found on the external ear, are characteristic of **gout**, which is caused by monosodium urate crystal deposition.
- The synovial fluid crystals described (**positively birefringent rods and rhomboid crystals**) are indicative of CPPD, not gout.
*Expression of human leukocyte antigen-B27*
- **HLA-B27** is strongly associated with **spondyloarthropathies** such as ankylosing spondylitis and reactive arthritis.
- This patient's symptoms and synovial fluid analysis are not consistent with a spondyloarthropathy.
*Thickening of the synovia at the metacarpophalangeal joints*
- **Synovial thickening and swelling** in the **metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints** are characteristic features of **rheumatoid arthritis**.
- This patient presents with an acute monoarticular arthritis of the knee and synovial fluid findings consistent with CPPD, not rheumatoid arthritis.
*Elevation of serum uric acid concentration*
- **Elevated serum uric acid** is typically associated with **gout**, indicating hyperuricemia.
- While chlorothalidone can increase uric acid, the synovial fluid findings of **positively birefringent rods and rhomboid crystals** specifically point to CPPD, not gout.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 3: A 65-year-old man with chronic myelogenous leukemia comes to the physician because of severe pain and swelling in both knees for the past day. He finished a cycle of chemotherapy 1 week ago. His temperature is 37.4°C (99.4°F). Physical examination shows swelling and erythema of both knees and the base of his left big toe. Laboratory studies show:
Leukocyte count 13,000/mm3
Serum
Creatinine 2.2 mg/dL
Calcium 8.2 mg/dL
Phosphorus 7.2 mg/dL
Arthrocentesis of the involved joints is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Calcium phosphate crystals
- B. Monosodium urate crystals (Correct Answer)
- C. Gram-negative diplococci
- D. Gram-positive cocci in clusters
- E. Calcium pyrophosphate crystals
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: **Correct Answer: Monosodium urate crystals**
- The patient has a history of **chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)** and recently underwent **chemotherapy**, increasing the risk of **tumor lysis syndrome** and subsequent hyperuricemia.
- The presentation of acute, severe joint pain and swelling in multiple joints, including the **left big toe** (podagra), with elevated creatinine, phosphorus, and mildly low calcium, is highly suggestive of **gout**.
- Laboratory findings of **hyperphosphatemia (7.2 mg/dL)** and **acute kidney injury (Cr 2.2 mg/dL)** with **hypocalcemia (8.2 mg/dL)** are classic for **tumor lysis syndrome**, which causes massive purine breakdown and hyperuricemia.
*Incorrect: Calcium phosphate crystals*
- These are associated with **hydroxyapatite deposition disease**, which typically presents with periarticular calcification and inflammation, often involving the shoulder, but not typically with the **biochemical abnormalities** seen here (hyperphosphatemia, elevated creatinine).
- The clinical picture of **podagra** and the context of chemotherapy-induced **hyperuricemia** strongly point away from calcium phosphate crystals.
*Incorrect: Gram-negative diplococci*
- This would indicate **gonococcal arthritis**, which typically occurs in younger, sexually active individuals and presents with fever, skin lesions (pustules), and tenosynovitis, which are absent here.
- The patient's age (65), lack of significant fever, and specific presentation of podagra with relevant **chemotherapy history** do not support infectious arthritis, especially gonococcal.
*Incorrect: Gram-positive cocci in clusters*
- This suggests **Staphylococcal septic arthritis**, which would often present with a higher fever, chills, and typically affects a single joint, although multiple joints can be involved.
- While chemotherapy can lead to immunocompromise, the elevated **uric acid precursors** (due to tumor lysis) and the characteristic **podagra** in the big toe make gout a much more likely diagnosis than septic arthritis.
*Incorrect: Calcium pyrophosphate crystals*
- These cause **pseudogout**, also known as calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), which can affect knees and mimic gout, but it is not directly associated with leukemia or chemotherapy-induced **tumor lysis syndrome**.
- The laboratory findings of **hyperphosphatemia** and history of chemotherapy, leading to high cell turnover, are more consistent with **hyperuricemia** from tumor lysis than with pseudogout.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 4: A 30-year-old man with a BMI of 33.7 kg/m2 presents with severe pain in his right great toe that began this morning. He had a few beers last night at a friend's party but otherwise has had no recent dietary changes. On examination, the right great toe appears swollen, warm, red, and tender to touch. Joint aspiration is performed. What will examination of the fluid most likely reveal?
- A. Anti-CCP antibodies
- B. Needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals on polarized light (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased glucose
- D. Rhomboid-shaped, positively birefringent crystals on polarized light
- E. Gram-negative diplococci
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals on polarized light***
- The clinical presentation, including the patient's **BMI**, **alcohol consumption**, rapid onset of severe pain, and classic signs of inflammation in the **first metatarsophalangeal joint** (**podagra**), is highly indicative of **gout**.
- **Urate crystals** are characteristically **needle-shaped** and display **negative birefringence** under polarized light microscopy.
*Anti-CCP antibodies*
- **Anti-CCP antibodies** are a serological marker for **rheumatoid arthritis**, which typically presents with chronic, symmetric polyarthritis, not acute monoarticular pain.
- The acute, severe inflammation in a single joint, especially the toe, makes rheumatoid arthritis unlikely.
*Increased glucose*
- Synovial fluid glucose levels are **not diagnostically useful** for gout or most inflammatory arthritides.
- Synovial fluid glucose is typically **decreased** in septic arthritis due to bacterial metabolism, not increased.
*Rhomboid-shaped, positively birefringent crystals on polarized light*
- **Rhomboid-shaped**, **positively birefringent crystals** are characteristic of **calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD)**, also known as **pseudogout**.
- While pseudogout can cause acute arthritis, the typical presentation of **podagra** and the specific historical context (obesity, alcohol consumption) point more strongly to gout.
*Gram-negative diplococci*
- The presence of **Gram-negative diplococci** in joint fluid would indicate **septic arthritis** due to **Neisseria gonorrhoeae**.
- While septic arthritis can cause acute, severe joint pain, the classic features of gout are more prominent in this case, and there's no mention of risk factors for gonococcal infection (e.g., sexually active young adult, disseminated infection).
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 5: A 69-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for pain when he walks. He states that the pain is the worst in his left great toe but is also present in his hips and knees. He says that his symptoms are worse with activity and tend to improve with rest. His symptoms have progressively worsened over the past several years. He has a past medical history of obesity, type II diabetes mellitus, smoking, and hypertension. He drinks roughly ten beers per day. His current medications include metformin, insulin, lisinopril, and hydrochlorothiazide. The patient has a recent travel history to Bangkok where he admits to having unprotected sex. On physical exam, examination of the lower extremity results in pain. There is crepitus of the patient's hip when his thigh is flexed and extended. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pseudogout
- B. Gout
- C. Rheumatoid arthritis
- D. Infectious arthritis
- E. Osteoarthritis (Correct Answer)
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Osteoarthritis***
- The patient presents with classic features of **osteoarthritis (OA)**: **progressive worsening over several years**, pain that is **worse with activity and improves with rest** (mechanical pain pattern), and **crepitus of the hip** on examination.
- **Crepitus** is a hallmark physical finding in OA, indicating cartilage degradation and bone-on-bone contact.
- The patient has major risk factors including **age (69 years)**, **obesity**, and involvement of **weight-bearing joints** (hips and knees).
- While the great toe is also affected, polyarticular OA commonly involves multiple joints including the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
*Gout*
- Although the patient has risk factors for gout (**alcohol consumption** and **thiazide diuretic use**), gout typically presents with **acute, severe attacks** of monoarticular arthritis, not chronic progressive pain over several years.
- Acute gout would present with sudden onset of severe pain, erythema, warmth, and swelling, which are not described in this case.
- The **mechanical pain pattern** (worse with activity, better with rest) and **crepitus** are inconsistent with gout.
*Pseudogout*
- Pseudogout (calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease) typically causes **acute attacks** affecting larger joints like the knees, similar to gout.
- The **chronic progressive nature** of this patient's symptoms over several years, along with crepitus, is not consistent with pseudogout.
- Pseudogout does not explain the mechanical pain pattern or the hip crepitus.
*Infectious arthritis*
- While the patient's recent travel and unprotected sex raise concern for sexually transmitted infections, **septic arthritis** would present with **acute onset**, severe pain, fever, warmth, erythema, and systemic signs of infection.
- The **chronic progressive course over several years** is completely inconsistent with infectious arthritis.
- Gonococcal arthritis can cause migratory polyarthritis but would be acute, not chronic.
*Rheumatoid arthritis*
- Rheumatoid arthritis typically presents with **symmetric polyarthritis** affecting small joints of the hands and feet, with **prolonged morning stiffness** (>30-60 minutes).
- The pain pattern in RA is **inflammatory** (worse with rest, improves with activity), which is the **opposite** of this patient's presentation.
- **Crepitus** and mechanical pain pattern point to a degenerative process (OA), not an inflammatory arthropathy like RA.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 6: A 45-year-old woman presents to the clinic for a routine examination. She has a chronic history of systemic lupus erythematosus, diagnosed at age 27. Medications include hydroxychloroquine and low-dose prednisone. She has had no recent flare-ups and is compliant with her medication. Anticardiolipin and anti-beta-2 glycoprotein-1 antibodies are negative, and she has had no history of thrombi or emboli. Physical examination is normal except for mild bilateral tenderness and swelling of the knees. Creatinine and GFR are normal. Which of the following is the next best step in management to monitor disease activity?
- A. Anti-Smith antibody levels
- B. Anti-dsDNA antibody levels (Correct Answer)
- C. Urinalysis and renal biopsy
- D. Reduce dosage and taper off hydroxychloroquine
- E. Arthrocentesis and synovial fluid analysis
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Anti-dsDNA antibody levels***
- **Anti-dsDNA antibodies** correlate well with **disease activity** in SLE, especially with **lupus nephritis**, making them a useful marker for monitoring.
- While her GFR is normal now, monitoring these antibodies can help detect early changes or increased risk of renal involvement.
*Anti-Smith antibody levels*
- **Anti-Smith antibodies** are highly specific for SLE but do not typically fluctuate with disease activity, so they are not useful for monitoring.
- They are primarily used for diagnosis rather than follow-up.
*Urinalysis and renal biopsy*
- A **renal biopsy** is an invasive procedure and is not indicated at this time given her normal creatinine and GFR, and reported absence of recent flare-ups.
- While **urinalysis** is important for monitoring, it is not the *next best step* to broadly assess systemic disease activity, and the question asks for monitoring disease activity, not just kidney function.
*Reduce dosage and taper off hydroxychloroquine*
- **Hydroxychloroquine** is a cornerstone of SLE management, even in quiescent disease, to prevent flares and organ damage.
- Reducing its dosage without evidence of sustained remission or adverse effects is generally not recommended and could lead to a flare.
*Arthrocentesis and synovial fluid analysis*
- **Arthrocentesis** is a diagnostic procedure to identify the cause of joint effusion but is not a routine measure to monitor overall SLE disease activity.
- Her mild knee tenderness and swelling could be part of her chronic SLE and does not automatically warrant an invasive joint procedure as the primary next step for overall disease monitoring.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 7: A 53-year-old man comes to the emergency department for severe left knee pain for the past 8 hours. He describes it as an unbearable, burning pain that woke him up from his sleep. He has been unable to walk since. He has not had any trauma to the knee. Ten months ago, he had an episode of acute pain and swelling of the right great toe that subsided after treatment with indomethacin. He has hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, psoriasis, and hyperlipidemia. Current medications include topical betamethasone, metformin, glipizide, losartan, and simvastatin. Two weeks ago, hydrochlorothiazide was added to his medication regimen to improve blood pressure control. He drinks 1–2 beers daily. He is 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) tall and weighs 110 kg (242 lb); BMI is 38.1 kg/m2. His temperature is 38.4°C (101.1°F). Examination shows multiple scaly plaques over his palms and soles. The left knee is erythematous, swollen, and tender; range of motion is limited by pain. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Arthrocentesis (Correct Answer)
- B. Serum uric acid level
- C. Oral methotrexate
- D. Intra-articular triamcinolone
- E. Oral colchicine
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: **Arthrocentesis**
- **Arthrocentesis** is crucial to confirm the diagnosis of **gout** by identifying **negatively birefringent needle-shaped crystals** in the joint fluid, while also ruling out **septic arthritis**.
- Given the patient's **acute monoarticular pain**, fever, and predisposing risk factors (obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diuretics, alcohol), **septic arthritis** is a critical consideration requiring immediate differentiation.
*Serum uric acid level*
- A **serum uric acid level** should be checked, but it is not the most appropriate immediate next step given the acute presentation.
- Serum uric acid can be **normal or even low during an acute gout flare** due to increased renal excretion in response to inflammation.
*Oral methotrexate*
- **Methotrexate** is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) used for long-term management of **psoriatic arthritis** or severe chronic gout, not for acute flares.
- It works by suppressing the immune system and takes weeks to months to show effect, making it unsuitable for immediate pain relief.
*Intra-articular triamcinolone*
- **Intra-articular corticosteroids** like triamcinolone could be considered for acute gout management but only after **septic arthritis has been definitively ruled out by arthrocentesis**.
- Administering corticosteroids into an infected joint can worsen the infection and lead to severe joint damage.
*Oral colchicine*
- **Oral colchicine** is an effective treatment for acute gout flares, but it is not the most appropriate *next step* because **septic arthritis must first be excluded**.
- Without arthrocentesis, treating a potentially infected joint with anti-inflammatory medication alone would be a critical omission.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 8: A 29-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a sharp pain in the center of his chest. The pain is knife-like and constant. Sitting alleviates the pain and lying supine aggravates it. He denies the use of nicotine, alcohol or illicit drugs. Vital signs include: temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 135/92 mm Hg, and pulse 97/min. On examination, a friction rub is heard at the left sternal border while the patient is leaning forward. His ECG is shown in the image. Which of the following can prevent recurrence of this patient’s condition?
- A. Ibuprofen
- B. Aspirin
- C. Colchicine (Correct Answer)
- D. Glucocorticoids
- E. Systemic antibiotics
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Colchicine***
- Colchicine is an **anti-inflammatory agent** that is highly effective in preventing recurrences of pericarditis, especially when used in conjunction with NSAIDs.
- It is recommended for initial treatment and for several months to reduce the risk of future episodes in cases of acute and recurrent pericarditis.
*Ibuprofen*
- Ibuprofen, a **NSAID**, is a first-line treatment for acute pericarditis to manage pain and inflammation.
- While effective for acute symptom relief, it is not primarily used for long-term prevention of recurrent pericarditis without an additional agent like colchicine.
*Aspirin*
- Aspirin, like other **NSAIDs**, is used to treat the acute inflammation and pain of pericarditis, particularly in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
- It does not offer superior anti-recurrent properties compared to other NSAIDs or colchicine for pericarditis.
*Glucocorticoids*
- Glucocorticoids are generally **reserved for refractory cases** of pericarditis or when NSAIDs and colchicine are contraindicated due to potential side effects and an increased risk of recurrence.
- Their use as a primary agent can actually **increase the risk of recurrence** once tapered, making them a less desirable option for prevention.
*Systemic antibiotics*
- Pericarditis is most commonly **viral or idiopathic**; therefore, systemic antibiotics are not indicated unless there is clear evidence of a bacterial infection.
- The presented symptoms and ECG findings are not suggestive of bacterial pericarditis, which is rare.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 9: A 33-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for gradually worsening pain in both wrists that began several months ago. The pain originally did not bother her, but it has recently begun to affect her daily functioning. She states that the early morning stiffness in her hands is severe and has made it difficult to tend to her rose garden. She occasionally takes ibuprofen for the pain, but she says this does not really help. Her medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus and major depressive disorder. She is currently taking insulin, sertraline, and a daily multivitamin. The vital signs include: blood pressure 126/84 mm Hg, heart rate 82/min, and temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F). On physical exam, her wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints are swollen, tender, erythematous, and warm to the touch. There are no nodules or vasculitic lesions. Which of the following antibodies would be most specific to this patient’s condition?
- A. c-ANCA
- B. Anti-Ro
- C. Anti-Scl-70
- D. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (Correct Answer)
- E. Rheumatoid factor
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide***
- **Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)** antibodies are highly specific for **rheumatoid arthritis (RA)** and are often present early in the disease course.
- The patient's presentation with **symmetric polyarthritis**, particularly affecting the **wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints**, with severe **morning stiffness**, is classic for RA.
*c-ANCA*
- **c-ANCA (cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies)** are primarily associated with **granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's)**, a systemic vasculitis.
- This condition typically presents with symptoms such as **upper and lower respiratory tract involvement**, **renal disease**, and constitutional symptoms, which are not described here.
*Anti-Ro*
- **Anti-Ro (SS-A)** antibodies are strongly associated with **Sjögren's syndrome**, a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by dry eyes and mouth, and also with **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**.
- While Sjögren's can present with arthritis, the prominent joint inflammation and morning stiffness described are more characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis.
*Anti-Scl-70*
- **Anti-Scl-70 (anti-topoisomerase I)** antibodies are highly specific for **systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)**, particularly the diffuse cutaneous form.
- Scleroderma presents with **skin thickening**, **Raynaud's phenomenon**, and potential involvement of internal organs like the lungs and esophagus, which are absent in this patient's presentation.
*Rheumatoid factor*
- **Rheumatoid factor (RF)** is often positive in **rheumatoid arthritis**, but it is less specific than anti-CCP antibodies.
- RF can also be elevated in other autoimmune diseases, chronic infections, and even in healthy individuals, making it a less specific diagnostic marker.
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG Question 10: A 26-year-old woman presents with 8 weeks of symmetric polyarthritis affecting hands, wrists, and feet with 90 minutes of morning stiffness. RF negative, anti-CCP negative, ANA 1:160 (homogeneous), ESR 45 mm/hr. She has no rash, oral ulcers, or systemic symptoms. Radiographs show soft tissue swelling without erosions. She desires pregnancy within the year. Apply the most appropriate initial management considering her reproductive plans.
- A. Defer DMARD therapy until after pregnancy to avoid any fetal risk
- B. Initiate sulfasalazine given safety profile in pregnancy
- C. Start combination hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine for adequate disease control (Correct Answer)
- D. Begin hydroxychloroquine as pregnancy-compatible DMARD
- E. Start methotrexate with strict contraception counseling; switch when ready to conceive
Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) Explanation: ***Start combination hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine for adequate disease control***
- This patient presents with **symmetric polyarthritis** and an elevated **ANA**, suggesting an early connective tissue disease or seronegative RA; the combination of **hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine** is the best choice for achieving remission while ensuring safety for **future pregnancy**.
- Both medications are considered **Category B/C** but are standard of care in pregnancy-compatible DMARD regimens to prevent joint damage and systemic flares.
*Start methotrexate with strict contraception counseling; switch when ready to conceive*
- **Methotrexate** is absolutely **teratogenic** and must be discontinued at least 3 months prior to conception, making it suboptimal for someone wanting to conceive within the year.
- Starting a known teratogen when a patient has active pregnancy plans within a short window increases the risk of **accidental fetal exposure**.
*Begin hydroxychloroquine as pregnancy-compatible DMARD*
- While **hydroxychloroquine** is safe in pregnancy, monotherapy may be insufficient to control **symmetric polyarthritis** with significant inflammatory markers (**ESR 45**).
- A more robust initial approach with **combination therapy** is often preferred to quickly suppress inflammation before the patient conceives.
*Initiate sulfasalazine given safety profile in pregnancy*
- **Sulfasalazine** is safe in pregnancy (with folic acid supplementation), but as monotherapy, it may not provide adequate control for **ANA-positive** inflammatory arthritis.
- Utilizing a single agent risks **persistent disease activity**, which itself is associated with poorer pregnancy outcomes compared to well-controlled disease.
*Defer DMARD therapy until after pregnancy to avoid any fetal risk*
- Deferring treatment is inappropriate as active **maternal inflammation** increases the risk of **preterm birth** and low birth weight.
- Non-erosive arthritis can progress to **irreversible joint damage** if left untreated for the duration of a pregnancy and postpartum period.
More Crystal arthropathies (gout, pseudogout) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.