Rheumatology (autoimmune diseases, arthritis)

On this page
🎯 Rheumatologic Mastery: The Autoimmune Arsenal
Rheumatology demands you recognize the body turning against itself-where immune precision becomes pathologic chaos, joints swell with inflammatory mediators, and autoantibodies leave serologic signatures that unlock diagnoses. You'll master the cytokine networks driving disease, decode clinical patterns from rash to synovitis, and navigate treatment algorithms that balance immunosuppression with infection risk. This lesson builds your framework for connecting autoimmune mechanisms to multi-system manifestations, transforming complex rheumatologic presentations into confident, systematic clinical decisions.

Rheumatology represents the intersection of immunology, internal medicine, and musculoskeletal medicine, where autoimmune dysregulation creates diverse clinical presentations affecting multiple organ systems. Understanding the fundamental principles of autoimmune disease pathophysiology provides the foundation for recognizing patterns across 20+ major rheumatologic conditions.
📌 Remember: AIMS for Autoimmune Disease Features - Autoantibodies (specific markers), Inflammation (systemic), Molecular mimicry (trigger mechanisms), Systemic involvement (multi-organ)
The autoimmune spectrum encompasses Type II and Type III hypersensitivity reactions, with >80% of rheumatologic conditions involving autoantibody production and immune complex formation. HLA associations occur in >70% of autoimmune rheumatologic diseases, with HLA-B27 present in >90% of ankylosing spondylitis cases and HLA-DR4 in 70% of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
| Disease Category | Prevalence | Primary Mechanism | Key Autoantibodies | HLA Association | Organ Systems |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA | 1% population | Synovial inflammation | RF (80%), Anti-CCP (95% specific) | HLA-DR4 (70%) | Joints, lungs, heart |
| SLE | 0.1% population | Immune complexes | ANA (95%), Anti-dsDNA (60%) | HLA-DR2/DR3 | Multi-system |
| Spondyloarthritis | 0.5% population | Enthesitis | Seronegative | HLA-B27 (90%) | Spine, joints, eyes |
| Vasculitis | 0.05% population | Vessel inflammation | ANCA (80% small vessel) | Variable | Vascular beds |
| Myositis | 0.01% population | Muscle inflammation | Anti-Jo1 (30%), Anti-Mi2 | HLA-DR3 | Muscle, skin |
The complement system plays crucial roles in autoimmune disease, with low C3/C4 levels indicating active immune complex consumption in >60% of SLE flares. Inflammatory markers including ESR >30 mm/hr and CRP >10 mg/L suggest active inflammation, though normal values don't exclude autoimmune disease in 20% of cases.
💡 Master This: Autoimmune rheumatologic diseases follow predictable patterns of molecular mimicry → autoantibody production → immune complex formation → tissue inflammation → organ damage. Understanding this sequence enables early intervention before irreversible damage occurs.
Genetic susceptibility accounts for 40-60% of autoimmune disease risk, with environmental triggers including infections (>50% of cases), smoking (increases RA risk 2-fold), and UV exposure (triggers SLE in 70% of photosensitive patients) providing the additional stimulus for disease development.
Connect autoimmune fundamentals through inflammatory pathway mastery to understand how cytokine networks orchestrate the diverse clinical presentations across rheumatologic conditions.
🎯 Rheumatologic Mastery: The Autoimmune Arsenal
🔥 Inflammatory Cascade Command: The Cytokine Symphony
📌 Remember: FIRE Cytokine Cascade - Fibroblasts activated by TNF-α, IL-1β destroys cartilage, Reactive oxygen species damage, Endothelial activation spreads inflammation
TNF-α concentrations in synovial fluid reach >1000 pg/mL (normal <50 pg/mL) during active inflammation, explaining why TNF-α inhibitors achieve ACR20 responses in >70% of RA patients. IL-17 drives neutrophil recruitment and bone erosion, with IL-17 inhibitors showing >80% efficacy in psoriatic arthritis.
| Cytokine | Normal Level | Inflammatory Level | Primary Function | Clinical Target | Response Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | <50 pg/mL | >1000 pg/mL | Synovial activation | Anti-TNF agents | 70-80% |
| IL-1β | <10 pg/mL | >500 pg/mL | Cartilage destruction | IL-1 inhibitors | 60-70% |
| IL-6 | <7 pg/mL | >100 pg/mL | Acute phase response | Tocilizumab | 65-75% |
| IL-17 | <15 pg/mL | >200 pg/mL | Neutrophil recruitment | Secukinumab | 75-85% |
| IFN-γ | <20 pg/mL | >300 pg/mL | Macrophage activation | JAK inhibitors | 55-65% |
The JAK-STAT pathway mediates >15 cytokine signals including IL-6, IL-12, IL-23, and interferons. JAK inhibitors block multiple inflammatory pathways simultaneously, explaining their broad efficacy across RA, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis with ACR20 responses in 60-70% of patients.
-
Type 1 Immunity (Th1/IFN-γ dominant)
- Drives macrophage activation and granuloma formation
- Predominant in giant cell arteritis and Takayasu arteritis
- IFN-γ levels >300 pg/mL predict vascular inflammation
- Corticosteroid response: >80% initial improvement
- Relapse rate: 50% within 2 years of tapering
-
Type 17 Immunity (Th17/IL-17 dominant)
- Promotes neutrophil recruitment and bone erosion
- Central to psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis
- IL-17 levels >200 pg/mL correlate with radiographic progression
- Anti-IL-17 efficacy: 75-85% in spondyloarthritis
- Bone formation inhibition: 60% reduction in syndesmophyte growth

💡 Master This: Cytokine redundancy explains why single-target therapies may fail - IL-1β and TNF-α can compensate for each other, requiring combination therapy or broader pathway inhibition through JAK inhibitors in refractory cases.
Complement activation amplifies cytokine responses, with C5a levels >50 ng/mL driving neutrophil degranulation and tissue damage. Low complement (C3 <90 mg/dL, C4 <16 mg/dL) indicates immune complex consumption in >80% of active SLE cases.
Bridge inflammatory mechanisms through autoantibody recognition patterns to understand how specific antibodies create distinct clinical phenotypes across rheumatologic diseases.
🔥 Inflammatory Cascade Command: The Cytokine Symphony
🎯 Autoantibody Decoder: The Serologic Fingerprint
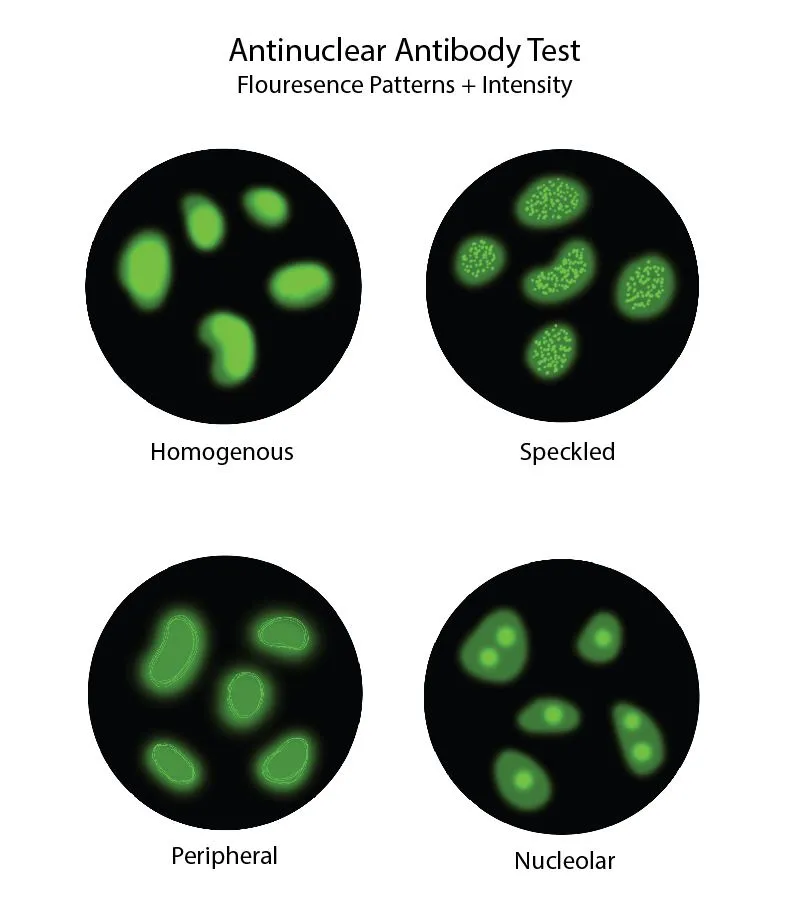
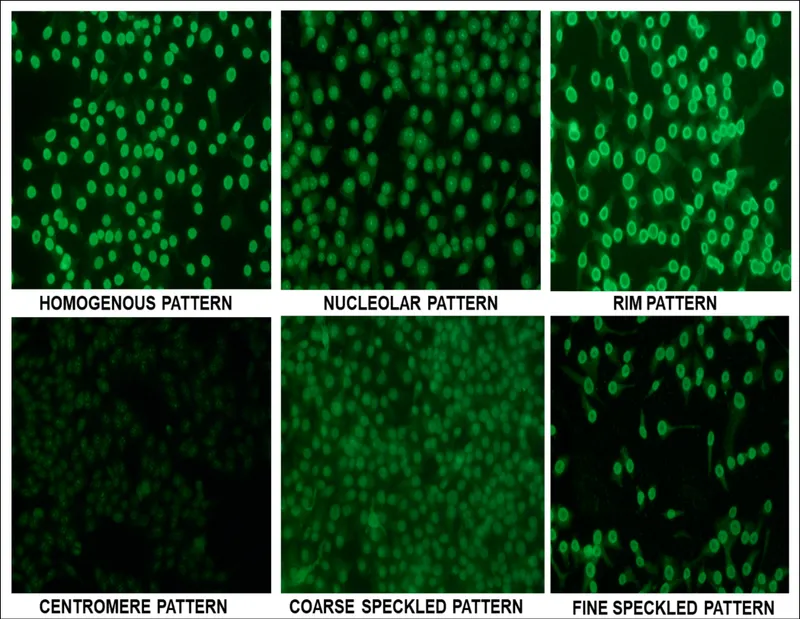
Autoantibody specificity creates distinct clinical phenotypes, where anti-CCP antibodies predict erosive RA in >90% of positive patients, while anti-centromere antibodies identify limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis with >95% accuracy. Understanding antibody-disease associations enables precision diagnosis and prognostic stratification.
📌 Remember: SPECIFIC Autoantibody Patterns - Systemic (ANA), Prognostic (Anti-CCP), Erosive (RF), Cardiac (Anti-Ro/SSA), Interstitial lung (Anti-Scl70), Fibrosing (Anti-centromere), Inflammatory muscle (Anti-Jo1), Cerebral (Anti-dsDNA)
| Autoantibody | Disease Association | Specificity | Clinical Significance | Prognostic Value | Monitoring Utility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-CCP | Rheumatoid Arthritis | 95% | Erosive disease predictor | 90% develop erosions | Disease activity |
| Anti-dsDNA | SLE | 90% | Nephritis risk | 60% develop LN | Flare prediction |
| Anti-Scl70 | Systemic Sclerosis | 95% | Diffuse cutaneous | 80% ILD risk | Pulmonary monitoring |
| Anti-centromere | Limited SSc | 95% | Pulmonary hypertension | 20% PAH risk | Echo screening |
| Anti-Jo1 | Myositis | 90% | Antisynthetase syndrome | 70% ILD risk | Muscle/lung monitoring |
-
High-Specificity Antibodies (>90% disease-specific)
- Anti-CCP: RA diagnosis and erosive prognosis
- Anti-dsDNA: SLE nephritis risk stratification
- Anti-Scl70: Diffuse SSc with ILD risk
- Positive predictive value: >95% for respective diseases
- Therapeutic implications: Guide aggressive treatment decisions
-
Moderate-Specificity Antibodies (70-90% disease-specific)
- Rheumatoid Factor: RA but also other autoimmune diseases
- Anti-Ro/SSA: Sjögren's, SLE, neonatal lupus
- Anti-La/SSB: Sjögren's syndrome with severe glandular dysfunction
- Cross-reactivity: Requires clinical correlation for diagnosis
- Monitoring value: Track disease activity in established cases
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Anti-CCP antibodies can appear 5-10 years before clinical RA symptoms, enabling pre-clinical intervention with methotrexate to delay disease onset by 2-3 years in high-risk individuals.
ANCA patterns distinguish vasculitis subtypes with c-ANCA/PR3 associated with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (>95% specificity) and p-ANCA/MPO linked to microscopic polyangiitis and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (>90% specificity).
- Vasculitis-Associated Antibodies
- c-ANCA (PR3): Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Sensitivity: 85% in active generalized disease
- Relapse correlation: Rising titers predict flare in 70%
- p-ANCA (MPO): Microscopic polyangiitis
- Renal involvement: >90% of MPO-positive patients
- Treatment response: Titer reduction correlates with remission
- c-ANCA (PR3): Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
💡 Master This: Autoantibody evolution occurs during disease progression - epitope spreading in SLE leads to new antibody development, while affinity maturation in RA increases anti-CCP pathogenicity over time.
Complement-fixing antibodies including anti-dsDNA and anti-Sm drive immune complex formation with low C3/C4 levels indicating active consumption in >80% of SLE flares. Non-complement-fixing antibodies like anti-Ro/SSA cause direct cellular damage without complement depletion.
Bridge autoantibody patterns through clinical phenotype recognition to understand how serologic profiles translate into specific disease manifestations and treatment responses.
🎯 Autoantibody Decoder: The Serologic Fingerprint
🔍 Clinical Pattern Recognition: The Phenotype Matrix
Clinical phenotypes in rheumatology follow predictable patterns based on target organ involvement and autoimmune mechanisms. Synovial-predominant diseases (RA, PsA) cause joint destruction, vascular-predominant diseases (vasculitis) create organ ischemia, and connective tissue diseases (SLE, SSc) produce multi-system inflammation.
📌 Remember: JOINTS Clinical Assessment Framework - Joint swelling/tenderness, Organ system involvement, Inflammatory markers, Neurologic symptoms, Tissue changes (skin/muscle), Serologic markers
| Disease Pattern | Joint Involvement | Skin Manifestations | Organ Systems | Diagnostic Markers | Treatment Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory Arthritis | Synovial swelling | Minimal | Joints primarily | RF/Anti-CCP | DMARD responsive |
| Connective Tissue | Arthralgia > arthritis | Prominent rashes | Multi-system | ANA positive | Steroid responsive |
| Spondyloarthritis | Axial + peripheral | Psoriasis/uveitis | Spine/entheses | HLA-B27 | Anti-TNF responsive |
| Vasculitis | Secondary arthritis | Purpura/ulcers | Vascular beds | ANCA/biopsy | Immunosuppressive |
| Crystal Arthropathy | Acute monoarthritis | Tophi (gout) | Joints/kidneys | Crystal analysis | Anti-inflammatory |
- Inflammatory Arthritis Patterns
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symmetric MCP/PIP involvement
- Morning stiffness: >60 minutes in 85% of patients
- Progression pattern: Small → large joints over months
- Extra-articular: Rheumatoid nodules in 25%, ILD in 10%
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Asymmetric oligoarthritis or DIP involvement
- Nail changes: 80% have psoriatic nail disease
- Dactylitis: Sausage digits in 40% of patients
- Axial involvement: Asymmetric sacroiliitis in 30%
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symmetric MCP/PIP involvement
⭐ Clinical Pearl: DIP joint involvement occurs in <5% of RA patients but >40% of psoriatic arthritis patients, making DIP arthritis a key distinguishing feature between these inflammatory arthritides.
Systemic manifestations provide diagnostic clues with malar rash in >50% of SLE patients, Raynaud's phenomenon in >90% of systemic sclerosis, and dry eyes/mouth in >95% of Sjögren's syndrome. Constitutional symptoms including fatigue, fever, and weight loss occur in >70% of active autoimmune diseases.
- Skin Pattern Recognition
- SLE: Malar rash (spares nasolabial folds), discoid lesions
- Photosensitivity: >60% of patients
- Oral ulcers: Painless in 40% of cases
- Systemic Sclerosis: Skin thickening, digital ulcers
- Raynaud's: >90% of patients, often first symptom
- Telangiectasias: Face/hands in limited cutaneous disease
- Dermatomyositis: Heliotrope rash, Gottron's papules
- Mechanic's hands: Hyperkeratotic fissures
- Shawl sign: V-neck/shoulder distribution
- SLE: Malar rash (spares nasolabial folds), discoid lesions
💡 Master This: Organ system clustering helps distinguish diseases - SLE affects kidneys + CNS + hematologic, SSc targets skin + lungs + GI, while RA primarily involves joints + lungs with minimal other organ involvement.
Laboratory pattern recognition combines inflammatory markers (ESR >30, CRP >10), autoantibodies, and organ-specific tests. Normal inflammatory markers don't exclude autoimmune disease in 20% of cases, particularly early disease or organ-specific involvement.
Bridge clinical patterns through therapeutic algorithm mastery to understand how pattern recognition guides treatment selection and monitoring strategies across rheumatologic diseases.
🔍 Clinical Pattern Recognition: The Phenotype Matrix
⚖️ Therapeutic Algorithm Mastery: The Treatment Decision Tree
Treatment algorithms in rheumatology follow evidence-based pathways where disease activity measures (DAS28, CDAI, SLEDAI) guide therapeutic escalation. Treat-to-target strategies achieve remission (DAS28 <2.6) in >60% of RA patients within 6 months when algorithms are followed systematically.
📌 Remember: TARGET Treatment Algorithm - Treat to remission, Assess disease activity, Risk stratification, Guided escalation, Evaluate response, Time-bound decisions
Methotrexate remains first-line therapy for >80% of inflammatory arthritis cases, achieving ACR20 responses in 65% of RA patients at 15-25 mg weekly. Folic acid supplementation (5 mg weekly) reduces MTX toxicity by >50% without compromising efficacy.
| Treatment Class | First-Line Use | Response Rate | Time to Effect | Monitoring Requirements | Major Toxicities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methotrexate | RA/PsA | 65% ACR20 | 6-12 weeks | CBC/LFTs q8-12 weeks | Hepatotoxicity/pneumonitis |
| Anti-TNF | MTX failure | 70-80% ACR20 | 4-8 weeks | Infection screening | Serious infections |
| JAK Inhibitors | Biologic failure | 60-70% ACR20 | 2-4 weeks | CBC/lipids q12 weeks | VTE/malignancy |
| Rituximab | RA (RF+) | 75% ACR20 | 8-16 weeks | Immunoglobulin levels | Hypogammaglobulinemia |
| Tocilizumab | Systemic symptoms | 65-75% ACR20 | 4-8 weeks | Neutrophils/platelets | GI perforation |
-
Anti-TNF Selection Criteria
- First-line biologic for most inflammatory arthritis
- Contraindications: Active infection, heart failure (Class III/IV)
- Screening requirements: TB, hepatitis B/C, CBC
- Latent TB reactivation: <1% with proper screening
- Serious infection rate: 3-5% annually
- Malignancy risk: No increased risk in meta-analyses
-
JAK Inhibitor Considerations
- Oral administration advantage over injectable biologics
- Rapid onset: Clinical improvement within 2-4 weeks
- Black box warnings: VTE, malignancy, serious infections
- VTE risk: Increased in patients >65 with CV risk factors
- Monitoring: CBC q4 weeks × 3, then q12 weeks

⭐ Clinical Pearl: Combination therapy (MTX + biologic) achieves remission rates of >50% compared to <30% with monotherapy, but triple DMARD therapy (MTX + SSZ + HCQ) shows equivalent efficacy to MTX + anti-TNF in early RA.
Disease-specific algorithms optimize outcomes through targeted approaches. SLE treatment prioritizes organ involvement with hydroxychloroquine for mild disease, methotrexate for arthritis, and mycophenolate or cyclophosphamide for nephritis.
- SLE Treatment Algorithm
- Mild disease (skin/joints): HCQ 400 mg daily
- Retinal toxicity screening: Annual after 5 years
- Response rate: >80% for cutaneous/articular symptoms
- Moderate disease: MTX 15-25 mg weekly + HCQ
- Steroid-sparing effect: >60% reduction in prednisone use
- Severe disease (nephritis/CNS): MMF or CYC + steroids
- Remission rates: >70% with appropriate immunosuppression
- Mild disease (skin/joints): HCQ 400 mg daily
💡 Master This: Therapeutic drug monitoring optimizes outcomes - MTX polyglutamate levels predict response and toxicity, while anti-drug antibodies explain secondary loss of efficacy in 20-30% of biologic-treated patients.
Monitoring algorithms ensure safety and efficacy with standardized intervals for laboratory assessment and clinical evaluation. Disease activity scores guide treatment adjustments every 3 months until remission, then every 6 months for maintenance.
Bridge therapeutic algorithms through advanced integration concepts to understand how multi-system involvement and comorbidity management create complex treatment scenarios requiring individualized approaches.
⚖️ Therapeutic Algorithm Mastery: The Treatment Decision Tree
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Autoimmune Connectome
Autoimmune diseases create systemic inflammation affecting multiple organ systems through shared inflammatory pathways. Cardiovascular risk increases 2-3 fold in RA and SLE patients, with accelerated atherosclerosis driven by chronic inflammation rather than traditional risk factors alone.
📌 Remember: SYSTEMS Integration Framework - Systemic inflammation, Yearly CV screening, Steroid complications, Thrombotic risk, Endocrine effects, Malignancy surveillance, Secondary infections
Cardiovascular complications represent the leading cause of death in RA (40% of mortality) and SLE (35% of mortality). Inflammatory burden measured by CRP >3 mg/L increases MI risk by >2-fold, while disease activity (DAS28 >3.2) correlates with endothelial dysfunction in >70% of patients.
| Organ System | RA Impact | SLE Impact | Monitoring Strategy | Intervention Threshold | Outcome Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | 2-3x MI risk | 5-10x stroke risk | Annual lipids/BP | LDL >70 mg/dL | 30% risk reduction |
| Pulmonary | ILD in 10% | Pleuritis in 50% | Annual PFTs | DLCO <80% | Slow progression |
| Renal | Rare | Nephritis in 60% | q3 month UA/Cr | Proteinuria >0.5g | Preserve function |
| Bone | 2x fracture risk | Steroid osteoporosis | DEXA q2 years | T-score <-2.5 | 50% fracture reduction |
| Infection | 2x serious infections | 3x opportunistic | Vaccination status | Live vaccine avoid | Prevention focus |
- Pulmonary Autoimmune Patterns
- RA-ILD: UIP pattern in 60%, NSIP in 30%
- Risk factors: Male sex, smoking, RF/anti-CCP positive
- Prognosis: 5-year survival 60-70% for UIP pattern
- Treatment: MTX contraindicated, rituximab or MMF preferred
- SSc-ILD: NSIP pattern predominant (>80%)
- Screening: Annual HRCT and PFTs
- Progression markers: DLCO decline >10% annually
- Therapy: Cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate first-line
- RA-ILD: UIP pattern in 60%, NSIP in 30%
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Methotrexate-induced pneumonitis occurs in <1% of patients but carries >20% mortality. Risk factors include age >60, diabetes, hypoalbuminemia, and previous lung disease. Immediate MTX discontinuation and high-dose steroids are life-saving.
Renal involvement varies dramatically by disease with lupus nephritis affecting >60% of SLE patients, while RA rarely causes primary renal disease (<5%). ANCA-associated vasculitis causes rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in >80% of cases, requiring urgent immunosuppression.
- Lupus Nephritis Classification (ISN/RPS)
- Class I/II: Minimal/mesangial - Conservative management
- Class III/IV: Focal/diffuse endocapillary - Aggressive immunosuppression
- Induction therapy: MMF or CYC × 6 months
- Complete remission: 50-60% with optimal therapy
- Renal survival: >90% at 10 years with early treatment
- Class V: Membranous - Anti-proteinuric therapy
- Class VI: Sclerotic - Supportive care

💡 Master This: Autoimmune disease clustering occurs in >30% of patients - RA + Sjögren's, SLE + APS, SSc + myositis. Overlapping autoantibodies and shared HLA alleles explain these syndrome combinations and guide comprehensive screening.
Endocrine complications include steroid-induced diabetes in >20% of patients on chronic prednisone, thyroid dysfunction in >15% of autoimmune disease patients, and adrenal insufficiency with rapid steroid withdrawal. Bone health deteriorates through inflammatory cytokines and steroid effects.
Malignancy surveillance becomes critical with lymphoma risk increased 2-5 fold in RA and Sjögren's syndrome, while immunosuppressive therapy increases skin cancer risk by >3-fold. HPV-related cancers occur more frequently in SLE patients (>2-fold increase).
Bridge multi-system integration through clinical mastery frameworks to develop rapid assessment tools and decision-making algorithms for complex autoimmune presentations.
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Autoimmune Connectome
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Rheumatologic Rapid Response
Rapid assessment frameworks enable systematic evaluation of complex presentations through structured approaches that minimize diagnostic errors and optimize treatment selection. Time-sensitive decisions in vasculitis (<24 hours), lupus nephritis (<48 hours), and septic arthritis (<6 hours) require immediate pattern recognition and algorithmic responses.
📌 Remember: MASTER Clinical Framework - Multi-system assessment, Autoantibody interpretation, Systemic inflammation markers, Treatment algorithm selection, Emergency recognition, Risk stratification
| Clinical Scenario | Recognition Time | Key Discriminators | Immediate Actions | Treatment Timeline | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Giant Cell Arteritis | <30 minutes | Age >50, ESR >50, temporal symptoms | High-dose steroids | Within 24 hours | Vision preservation |
| Lupus Nephritis | <60 minutes | ANA+, anti-dsDNA+, proteinuria | Renal biopsy, immunosuppression | Within 48 hours | Renal function preservation |
| Septic Arthritis | <15 minutes | Fever, monoarthritis, WBC >50K | Joint aspiration, antibiotics | Within 6 hours | Joint preservation |
| ANCA Vasculitis | <45 minutes | Multi-organ, ANCA+, biopsy | Pulse steroids, CYC | Within 24 hours | Organ preservation |
| Myositis Crisis | <30 minutes | CK >1000, weakness, dysphagia | High-dose steroids, IVIG | Within 12 hours | Respiratory function |
-
Red Flag Recognition (Immediate Action Required)
- Visual symptoms + temporal headache = GCA → Prednisone 1 mg/kg
- Acute kidney injury + ANCA+ = Vasculitis → Pulse methylprednisolone
- Fever + monoarthritis = Septic joint → Emergent aspiration
- Time to treatment: <6 hours for joint preservation
- Diagnostic accuracy: >95% with systematic approach
-
Urgent Assessment (Within 24-48 hours)
- New proteinuria + ANA+ = Lupus nephritis → Renal biopsy
- Proximal weakness + CK elevation = Myositis → MRI/EMG
- Multi-organ involvement + constitutional symptoms = Systemic vasculitis
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Steroid responsiveness within 48-72 hours helps distinguish autoimmune inflammation from infection or malignancy. >50% symptom improvement with prednisone 0.5-1 mg/kg strongly suggests autoimmune etiology.
Diagnostic efficiency improves through targeted testing strategies based on clinical phenotypes. Symmetric polyarthritis + morning stiffness triggers RF/anti-CCP testing, while asymmetric oligoarthritis + psoriasis suggests HLA-B27 and imaging for spondyloarthritis.
- Essential Clinical Arsenal (Memorize These Numbers)
- ESR >100: Think GCA, infection, malignancy
- CRP >100: Bacterial infection until proven otherwise
- CK >1000: Myositis, rhabdomyolysis, drug-induced
- Proteinuria >3g: Nephrotic syndrome, lupus nephritis
- Platelet <100K: SLE, APS, drug-induced
- ANA >1:320: Significant - pursue ENA panel
- Anti-CCP >20: RA diagnosis - start DMARD therapy
💡 Master This: Treatment response patterns guide diagnosis refinement - Anti-TNF response supports inflammatory arthritis, steroid dependence suggests autoimmune disease, while lack of anti-inflammatory response raises suspicion for non-inflammatory conditions.
Monitoring mastery ensures optimal outcomes through systematic follow-up with disease-specific intervals and safety parameters. Treat-to-target approaches achieve remission in >70% of patients when algorithms are consistently applied.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Rheumatologic Rapid Response
Practice Questions: Rheumatology (autoimmune diseases, arthritis)
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of body aches for the past 9 months. She also has stiffness of the shoulders and knees that is worse in the morning and tingling in the upper extremities. Examination shows marked tenderness over the posterior neck, bilateral mid trapezius, and medial aspect of the left knee. A complete blood count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are within the reference ranges. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?













