Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Alcoholic liver disease. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old G1P0010 presents to the clinic with nausea and vomiting 8 weeks after a spontaneous abortion at 10 weeks gestation. She admits to heavy drinking (7–8 glasses of wine per day) for the last 20 years; however, after the pregnancy loss, she increased her drinking to 8–9 glasses per day. Hepatomegaly, right upper quadrant pain, and jaundice are noted on abdominal examination. The lungs are clear to auscultation with no abnormalities on chest X-ray. Liver function tests are obtained and a biopsy is performed. Which of the following findings is most likely to be true in her condition?
- A. ↑ NADH/NAD+; ALT:AST ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↓; β-hydroxybutyrate ↓; lactic acid ↓
- B. ↑ NAD+/NADH; AST:ALT ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↑; β-hydroxybutyrate ↓; lactic acid ↓
- C. ↑ NADH/NAD+; AST:ALT ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↓; β-hydroxybutyrate ↑; lactic acid ↑ (Correct Answer)
- D. ↑ NADH/NAD+; ALT:AST ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↓; β-hydroxybutyrate ↓; lactic acid ↑
- E. ↑ NAD+/NADH; ALT:AST ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↑; β-hydroxybutyrate, no change; lactic acid ↓
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***↑ NADH/NAD+; AST:ALT ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↓; β-hydroxybutyrate ↑; lactic acid ↑***
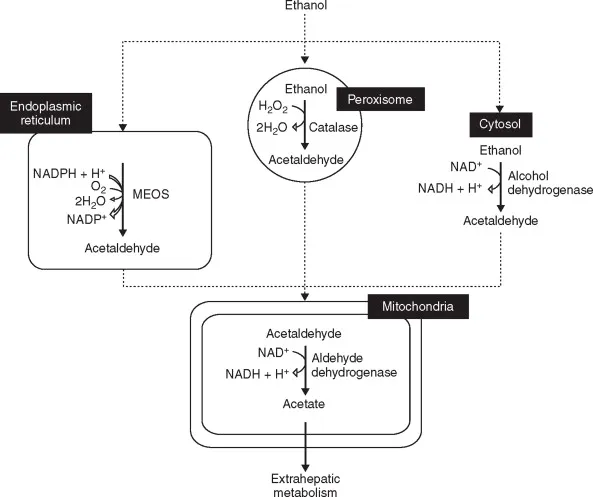
- **Alcohol metabolism** increases the **NADH/NAD+ ratio**, diverting substrates to lipid synthesis (leading to fatty liver) and inhibiting **β-oxidation**.
- The elevated NADH also promotes **lactic acid** and **β-hydroxybutyrate** formation, while the **AST:ALT ratio ≥ 2:1** is characteristic of **alcoholic liver disease**, often due to mitochondrial damage and pyridoxal phosphate deficiency.
*↑ NADH/NAD+; ALT:AST ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↓; β-hydroxybutyrate ↓; lactic acid ↑*
- While a high **NADH/NAD+ ratio** and **lactic acid ↑** are consistent with alcohol metabolism, the **ALT:AST ≥ 2:1** ratio is more commonly seen in **non-alcoholic liver diseases**, and **β-hydroxybutyrate ↓** is incorrect as it should be elevated.
- **β-hydroxybutyrate** is increased in alcoholic ketoacidosis due to altered redox state, not decreased.
*↑ NAD+/NADH; AST:ALT ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↑; β-hydroxybutyrate ↓; lactic acid ↓*
- This option incorrectly states an **↑ NAD+/NADH ratio**, when alcohol metabolism actually increases **NADH**.
- **β-oxidation** is inhibited, not increased, and both **β-hydroxybutyrate** and **lactic acid** would be elevated.
*↑ NADH/NAD+; ALT:AST ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↓; β-hydroxybutyrate ↓; lactic acid ↓*
- While **↑ NADH/NAD+** and **β-oxidation ↓** are correct, the **ALT:AST ≥ 2:1** ratio is atypical for alcoholic liver disease where AST is usually higher.
- Both **β-hydroxybutyrate** and **lactic acid** should be elevated due to the increased NADH, not decreased.
*↑ NAD+/NADH; ALT:AST ≥ 2:1; β-oxidation ↑; β-hydroxybutyrate, no change; lactic acid ↓*
- This option is incorrect as **alcohol metabolism** increases **NADH**, not NAD+, and inhibits **β-oxidation**.
- **β-hydroxybutyrate** and **lactic acid** are typically elevated, not unchanged or decreased.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 2: A 59-year-old woman comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. She feels well. She has systemic lupus erythematosus and hypertension. She does not drink alcohol. Her current medications include lisinopril and hydroxychloroquine. She appears malnourished. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a soft, nontender abdomen. There is no ascites or hepatosplenomegaly. Serum studies show:
Total bilirubin 1.2 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 60 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase 456 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase 145 U/L
Hepatitis A IgM antibody negative
Hepatitis A IgG antibody positive
Hepatitis B surface antigen positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody negative
Hepatitis B envelope antigen positive
Hepatitis B envelope antibody negative
Hepatitis B core antigen IgM antibody negative
Hepatitis B core antigen IgG antibody positive
Hepatitis C antibody negative
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
- A. Pegylated interferon alpha therapy
- B. Tenofovir therapy (Correct Answer)
- C. Referral to a liver transplantation center
- D. Reassurance and follow-up
- E. Lamivudine therapy
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***Tenofovir therapy***
- This patient has **chronic hepatitis B** with evidence of **active viral replication** (positive HBsAg, HBeAg, and elevated liver enzymes), indicating a need for antiviral treatment.
- **Tenofovir** is a highly effective and well-tolerated oral antiviral agent for chronic hepatitis B, suitable for initial therapy.
*Pegylated interferon alpha therapy*
- While an option for chronic hepatitis B, **pegylated interferon alpha** has more significant side effects and is generally avoided in patients with **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)** due to the risk of exacerbating the autoimmune condition.
- It also requires subcutaneous injections and has a lower rate of HBeAg seroconversion compared to nucleos(t)ide analogs in many patient populations.
*Referral to a liver transplantation center*
- This patient currently shows **elevated liver enzymes** but no immediate signs of **decompensated liver disease** (e.g., ascites, encephalopathy, variceal bleeding) or severe liver failure that would warrant urgent transplantation.
- Treatment with antiviral medication is the first step to prevent progression to end-stage liver disease.
*Reassurance and follow-up*
- The patient has **elevated transaminases** and markers of **active viral replication** (positive HBeAg), indicating ongoing liver injury and potential progression to cirrhosis.
- Simply observing the patient without treatment would be inappropriate and could lead to irreversible liver damage.
*Lamivudine therapy*
- **Lamivudine** is an older nucleos(t)ide analog for hepatitis B that has a significantly **higher rate of drug resistance** compared to newer agents like tenofovir.
- It is generally not recommended as a first-line treatment due to its resistance profile.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 3: A 45-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He feels well. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus. There is no family history of serious illness. He works as an engineer at a local company. He does not smoke. He drinks one glass of red wine every other day. He does not use illicit drugs. His only medication is metformin. He is 180 cm (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 100 kg (220 lb); BMI is 31 kg/m2. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a soft, nontender abdomen. The liver is palpated 2 to 3 cm below the right costal margin. Laboratory studies show an aspartate aminotransferase concentration of 100 U/L and an alanine aminotransferase concentration of 130 U/L. Liver biopsy shows hepatocyte ballooning degeneration, as well as inflammatory infiltrates with scattered lymphocytes, neutrophils, and Kupffer cells. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Autoimmune hepatitis
- C. Viral hepatitis
- D. Primary biliary cholangitis
- E. Alcoholic fatty liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis***
- The patient's **obesity (BMI 31)**, **type 2 diabetes mellitus**, and elevated liver enzymes (ALT > AST) in the absence of significant alcohol intake or other causes of liver disease are highly suggestive of **nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)**, with the biopsy findings of **hepatocyte ballooning degeneration** and **inflammatory infiltrates** confirming progression to **nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)**.
- **NASH** is a severe form of NAFLD characterized by **steatosis**, **inflammation**, and hepatocyte injury (ballooning degeneration), which can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure.
*Autoimmune hepatitis*
- This condition is typically characterized by high levels of **autoantibodies** (e.g., ANA, anti-smooth muscle antibodies), which are not mentioned and would be an important diagnostic clue.
- Although it can cause elevated transaminases and inflammatory infiltrates, the biopsy typically shows **interface hepatitis** and prominent plasma cell infiltrates, rather than significant steatosis and ballooning degeneration.
*Viral hepatitis*
- While viral hepatitis (e.g., hepatitis B or C) causes elevated transaminases and inflammatory changes, the biopsy findings of **hepatocyte ballooning** are not characteristic.
- The patient's presentation does not include risk factors or symptoms typically associated with acute or chronic viral hepatitis, and serological markers would be required for diagnosis.
*Primary biliary cholangitis*
- This is a chronic autoimmune cholestatic liver disease primarily affecting **interlobular bile ducts**, usually seen in middle-aged women.
- It is characterized by elevated **alkaline phosphatase** levels and positive **antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA)**, which are not described in this patient, and the biopsy would show granulomatous destruction of bile ducts.
*Alcoholic fatty liver disease*
- Although the biopsy findings of **steatosis**, **hepatocyte ballooning**, and **inflammation** can be seen in alcoholic liver disease, the patient's reported alcohol consumption of "one glass of red wine every other day" is well below the threshold for causing significant alcoholic liver damage.
- **Alcoholic hepatitis** typically involves an AST:ALT ratio of >2 and a history of heavy, prolonged alcohol use.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 4: A 43-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of severe epigastric pain and vomiting for 6 hours. The pain radiates to his back and he describes it as 9 out of 10 in intensity. He has had 3–4 episodes of vomiting during this period. He admits to consuming over 13 alcoholic beverages the previous night. There is no personal or family history of serious illness and he takes no medications. He is 177 cm (5 ft 10 in) tall and weighs 55 kg (121 lb); BMI is 17.6 kg/m2. He appears uncomfortable. His temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 97/min, and blood pressure is 128/78 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows severe epigastric tenderness to palpation. Bowel sounds are hypoactive. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.5 g/dL
Hematocrit 62%
Leukocyte count 13,800/mm3
Serum
Na+ 134 mEq/L
K+ 3.6 mEq/L
Cl- 98 mEq/L
Calcium 8.3 mg/dL
Glucose 180 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
Amylase 150 U/L
Lipase 347 U/L (N = 14–280)
Total bilirubin 0.8 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 66 U/L
AST 19 U/L
ALT 18 U/L
LDH 360 U/L
Which of the following laboratory studies is the best prognostic indicator for this patient's condition?
- A. AST/ALT ratio
- B. Alkaline phosphatase
- C. Total bilirubin
- D. Lipase
- E. Hematocrit (Correct Answer)
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***Hematocrit***
- A rising **hematocrit** (due to **hemoconcentration**) or one that fails to fall after initial fluid resuscitation is an important indicator of volume depletion and a **poor prognostic sign** in **acute pancreatitis**.
- This patient's hematocrit is elevated at **62%**, suggesting significant hemoconcentration and a higher risk for complications like **pancreatic necrosis**.
*AST/ALT ratio*
- While an elevated AST/ALT ratio can suggest **alcoholic liver disease**, it is not a direct **prognostic indicator** for the severity or outcome of **acute pancreatitis**.
- In pancreatitis, liver enzymes are typically elevated secondarily to inflammation or biliary obstruction, but their ratio does not directly predict the course of the pancreatitis itself.
*Alkaline phosphatase*
- **Alkaline phosphatase** is an indicator of **biliary obstruction** or **cholestasis**, which can be a cause of pancreatitis (e.g., gallstone pancreatitis).
- Its value does not directly predict the **severity** or **prognosis** of acute pancreatitis once it has developed, especially in a case of alcoholic pancreatitis.
*Total bilirubin*
- **Total bilirubin** levels primarily reflect **biliary obstruction** or **liver dysfunction**.
- While gallstone pancreatitis can increase bilirubin, it is not a primary prognostic marker for the development of severe complications in **acute pancreatitis**, nor is it significantly elevated in this patient.
*Lipase*
- **Elevated lipase** is highly specific and sensitive for the **diagnosis of acute pancreatitis**, confirming the diagnosis in this case.
- However, the absolute level of lipase does **not correlate** with the **severity** or **prognosis** of acute pancreatitis; even mild pancreatitis can have very high lipase levels.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 5: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. During the past month, he has had mild itching. He has alcoholic cirrhosis, hypertension, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. He used to drink a pint of vodka and multiple beers daily but quit 4 months ago. Current medications include ramipril, esomeprazole, and vitamin B supplements. He appears thin. His temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), pulse is 68/min, and blood pressure is 115/72 mm Hg. Examination shows reddening of the palms bilaterally and several telangiectasias over the chest, abdomen, and back. There is symmetrical enlargement of the breast tissue bilaterally. His testes are small and firm on palpation. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.1 g/dL
Leukocyte count 4300/mm3
Platelet count 89,000/mm3
Prothrombin time 11 sec (INR = 1)
Serum
Albumin 3 g/dL
Bilirubin
Total 2.0 mg/dL
Direct 0.2 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 43 U/L
AST 55 U/L
ALT 40 U/L
α-Fetoprotein 8 ng/mL (N < 10)
Anti-HAV IgG antibody positive
Anti-HBs antibody negative
Abdominal ultrasonography shows a nodular liver surface with atrophy of the right lobe of the liver. An upper endoscopy shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Perform liver biopsy now
- B. Obtain CT scan of the abdomen now
- C. Repeat abdominal ultrasound in 6 months (Correct Answer)
- D. Measure serum α-fetoprotein levels in 3 months
- E. Administer hepatitis A vaccine now
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***Repeat abdominal ultrasound in 6 months***
- This patient has **alcoholic cirrhosis** and is at high risk for developing **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**
- **Current AASLD/ACR guidelines** recommend surveillance with **ultrasound (with or without AFP) every 6 months** for all cirrhotic patients
- The patient just had an ultrasound showing cirrhotic changes but **no focal lesions**, and AFP is normal (8 ng/mL)
- The **most appropriate next step** is to continue routine HCC surveillance with **ultrasound in 6 months**
- Ultrasound is the **primary surveillance modality** due to its non-invasive nature, wide availability, and reasonable sensitivity for detecting early HCC
*Measure serum α-fetoprotein levels in 3 months*
- AFP alone is **not recommended** as a standalone surveillance tool for HCC
- The surveillance interval for cirrhotic patients is **6 months, not 3 months**
- While AFP can be checked alongside ultrasound during surveillance, it has **limited sensitivity** (approximately 60%) and is not sufficient by itself
- Checking AFP in 3 months without imaging does not follow standard surveillance protocols
*Perform liver biopsy now*
- Liver biopsy is indicated when there is a **discrete liver lesion** that needs tissue diagnosis for staging or treatment planning
- The current ultrasound shows only **diffuse cirrhotic changes** with no focal lesion identified
- Biopsy is **not indicated** for routine HCC surveillance in the absence of a suspicious mass
*Administer hepatitis A vaccine now*
- The patient has a **positive anti-HAV IgG antibody**, indicating **prior exposure and immunity** to Hepatitis A
- Vaccination is **not needed** as the patient is already immune
- Hepatitis A vaccine would only be indicated in cirrhotic patients who are **anti-HAV IgG negative**
*Obtain CT scan of the abdomen now*
- CT or MRI is indicated when ultrasound identifies a **suspicious lesion** requiring further characterization
- CT would also be considered if ultrasound quality is inadequate or if there is high clinical suspicion for HCC despite negative ultrasound
- In this case, the ultrasound was adequate and showed **no focal lesions**, so advanced imaging is not currently indicated
- Routine surveillance uses ultrasound, not CT, due to cost-effectiveness and lack of radiation exposure
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 6: A 53-year-old homeless woman is brought to the emergency department by the police after she was found in the park lying unconscious on the ground. Both of her pupils are normal in size and reactive to light. There are no signs of head trauma. Finger prick test shows a blood glucose level of 20 mg/dL. She has been brought to the emergency department for acute alcohol intoxication several times before. Her vitals signs include: blood pressure 100/70 mm Hg, heart rate 90/min, respiratory rate 22/min, and temperature 35.0℃ (95.0℉). On general examination, she looks pale, but there is no sign of icterus noted. On physical examination, the abdomen is soft and non-tender and no hepatosplenomegaly noted. She spontaneously opens her eyes after the administration of a bolus of intravenous dextrose, thiamine, and naloxone. Blood and urine samples are drawn for toxicology screening. Finally, the blood alcohol level turns out to be 300 mg/dL. What will be the most likely laboratory findings in this patient?
- A. Decreased MCV
- B. AST > ALT, increased gamma-glutamyl transferase (Correct Answer)
- C. Decreased ALP
- D. ALT > AST, increased gamma-glutamyl transferase
- E. AST > ALT, normal gamma-glutamyl transferase
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***AST > ALT, increased gamma-glutamyl transferase***
- Chronic **alcohol abuse** typically leads to an elevation of **aspartate aminotransferase (AST)** that is greater than alanine aminotransferase (ALT), with an AST/ALT ratio commonly greater than 2:1.
- **Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)** is a mitochondrial enzyme that is induced by alcohol, making its elevation a sensitive indicator of alcohol consumption and hepatotoxicity.
*AST > ALT, normal gamma-glutamyl transferase*
- While an AST/ALT ratio greater than 2:1 is consistent with alcoholic liver injury, a **normal GGT** would be highly unusual in a patient with chronic alcohol abuse and liver involvement, as GGT is notoriously sensitive to alcohol.
- A normal GGT would suggest a different etiology for the AST > ALT pattern, such as **muscle damage** or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in some cases, which is less likely here given the history.
*Decreased MCV*
- Chronic alcohol abuse more commonly leads to **macrocytosis** (increased MCV) due to direct toxic effects of alcohol on bone marrow and interference with folate metabolism, rather than decreased MCV.
- **Microcytosis** (decreased MCV) is typically indicative of iron deficiency anemia or thalassemia, which are not suggested by the patient's presentation.
*Decreased ALP*
- **Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)** is unlikely to be decreased in chronic alcohol abuse; it is more often **elevated** due to cholestasis or effects on bone.
- Decreased ALP can be seen in rare conditions like hypophosphatasia or severe malnutrition, but it is not a characteristic finding of alcoholic liver disease.
*ALT > AST, increase gamma glutamyl transferase*
- An **ALT > AST** ratio is more typical of non-alcoholic liver diseases such as viral hepatitis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Although increased GGT is consistent with alcohol abuse, the **AST > ALT** pattern is the hallmark of alcoholic liver injury, contrasting with this option.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 7: A 67-year-old man presents with fatigue, progressive abdominal distention and yellow skin coloration for the past 2 weeks. He denies fever, chills, or other symptoms. Past medical history is unremarkable. He reports heavy alcohol consumption for the past several years but says he quit recently. On physical examination, the patient appears jaundiced and is ill-appearing. There is shifting dullness present on abdominal percussion with a positive fluid wave. Sclera are icteric. Bilateral gynecomastia is present. Laboratory findings are significant for the following:
Hgb 13 g/dL
Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3
Platelets 86,000/mm3
Aspartate transaminase (AST) 108 U/L
Alanine transaminase (ALT) 55 U/L
GGT 185 U/L
Urea 23 mg/dL
Iron 120 μg/dL
Ferritin 180 μg/dL
Transferrin saturation 40%
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Alcoholic liver disease (Correct Answer)
- B. Hepatic adenoma
- C. Hemochromatosis
- D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- E. Chronic viral hepatitis
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***Alcoholic liver disease***
- The patient's history of **heavy alcohol consumption**, coupled with symptoms like **jaundice**, **ascites** (abdominal distension with shifting dullness and fluid wave), and signs of **chronic liver disease** such as **gynecomastia** and **thrombocytopenia**, strongly points toward alcoholic liver disease.
- The laboratory findings show an **AST:ALT ratio of approximately 2:1** (108:55), which is characteristic of alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis, along with elevated **GGT**, further supporting this diagnosis.
*Hepatic adenoma*
- Hepatic adenomas are **benign liver tumors** often associated with oral contraceptive use and typically present as an abdominal mass or pain, with rupture being a serious complication.
- They are not typically associated with the widespread signs of **liver failure** like jaundice, ascites, or gynecomastia seen in this patient.
*Hemochromatosis*
- Hemochromatosis is characterized by **iron overload** and would typically show significantly **elevated ferritin** and **transferrin saturation**, often above 60-90%.
- While this patient has normal iron studies, his symptoms are primarily indicative of **liver dysfunction due to alcohol**, not iron accumulation.
*Non alcoholic fatty liver disease*
- NAFLD is common in individuals with **metabolic syndrome**, obesity, and diabetes, none of which are mentioned in the patient's history.
- While it can progress to cirrhosis, the striking history of **heavy alcohol consumption** makes alcoholic liver disease a far more probable diagnosis.
*Chronic viral hepatitis*
- Chronic viral hepatitis (e.g., Hepatitis B or C) can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure, presenting with similar symptoms like jaundice and ascites.
- However, the patient's **heavy alcohol abuse** for several years provides a direct and strong etiology for his liver disease, making viral hepatitis less likely in the absence of specific risk factors or positive serology.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine examination. He does not take any medications. He drinks 6 to 7 bottles of beer every night, and says he often has a shot of whiskey in the morning “for my headache.” He was recently fired from his job for arriving late. He says there is nothing wrong with his drinking but expresses frustration at his best friend no longer returning his calls. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial response by the physician?
- A. I'm sorry that your friend no longer returns your calls. What do you think your friend is worried about? (Correct Answer)
- B. I'm sorry to hear you lost your job. I am concerned about the amount of alcohol you are drinking.
- C. I'm sorry to hear you lost your job. Drinking the amount of alcohol that you do can have very negative effects on your health.
- D. I'm sorry that your friend no longer returns your calls. It seems like your drinking is affecting your close relationships.
- E. I'm sorry that your friend no longer returns your calls. Do you feel that your drinking has affected your relationship with your friend?
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***"I'm sorry that your friend no longer returns your calls. What do you think your friend is worried about?"***
- This response acknowledges the patient's expressed **frustration** about his friend, which is a point of **distress** he has brought up.
- By asking what the friend is worried about, the physician invites the patient to reflect on the potential impact of his drinking from an external perspective, fostering **insight** without being confrontational.
*"I'm sorry to hear you lost your job. I am concerned about the amount of alcohol you are drinking."*
- While addressing the job loss is empathetic, immediately stating concern about his drinking can be confrontational and may lead the patient to become **defensive**, especially since he denies a problem.
- This approach might **shut down** further discussion rather than encourage it, as the patient has already stated "there is nothing wrong with his drinking."
*"I'm sorry to hear you lost your job. Drinking the amount of alcohol that you do can have very negative effects on your health."*
- This response is **judgmental** and directly highlights the negative consequences of his drinking, which the patient has already dismissed.
- Presenting medical facts about health effects at this stage, before establishing rapport and insight, is likely to be met with **resistance** and make the patient less receptive to further conversation.
*"I'm sorry that your friend no longer returns your calls. It seems like your drinking is affecting your close relationships."*
- This statement is a direct accusation, implying the physician knows the cause of the friend's actions and directly links it to the patient's drinking.
- Such a direct link is likely to be perceived as **judgmental** and can make the patient feel attacked, leading to defensiveness and a breakdown in communication.
*"I'm sorry that your friend no longer returns your calls. Do you feel that your drinking has affected your relationship with your friend?"*
- While this question is good, asking directly if his drinking has affected the relationship may elicit a **denial**, as the patient has already shown **lack of insight** regarding his drinking problem.
- A more open-ended question about what the friend is "worried about" is less threatening and more likely to encourage the patient to consider the connection himself.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 9: A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of moderate abdominal pain that is unresponsive to medication. She has a history of two spontaneous abortions at 11 and 12 weeks' gestation. Ultrasound examination of the abdomen shows normal liver parenchyma, a dilated portal vein, and splenic enlargement. Upper endoscopy shows dilated submucosal veins in the lower esophagus. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Increased serum bilirubin levels
- B. Increased prothrombin time
- C. Thrombocytopenia (Correct Answer)
- D. Hepatic venous congestion
- E. Councilman bodies
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***Thrombocytopenia***
- The patient's **recurrent spontaneous abortions** suggest **antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)**, a hypercoagulable state that predisposes to both arterial and venous thrombosis.
- APS likely caused **portal vein thrombosis**, leading to **prehepatic portal hypertension** (dilated portal vein, esophageal varices, and splenomegaly) with **normal liver parenchyma**.
- The **splenomegaly** causes **hypersplenism**, resulting in **thrombocytopenia** due to splenic sequestration and increased destruction of platelets.
- While APS can also cause immune-mediated thrombocytopenia directly, the primary mechanism here is hypersplenism secondary to portal hypertension.
*Increased serum bilirubin levels*
- Elevated bilirubin indicates **hepatocellular dysfunction** or **biliary obstruction**.
- The ultrasound shows **normal liver parenchyma**, making significant hepatocellular damage unlikely.
- Portal vein thrombosis without liver parenchymal disease does not typically cause hyperbilirubinemia.
*Increased prothrombin time*
- Prolonged PT reflects impaired **hepatic synthesis of coagulation factors** (II, VII, IX, X).
- With **normal liver parenchyma** on imaging, synthetic liver function should be preserved.
- Portal vein thrombosis alone does not impair hepatocyte function or coagulation factor synthesis.
*Hepatic venous congestion*
- This finding is characteristic of **Budd-Chiari syndrome** (hepatic vein thrombosis), which presents with hepatomegaly, ascites, and signs of hepatic outflow obstruction.
- The patient's findings (dilated **portal vein**, normal liver parenchyma) indicate **portal vein thrombosis** causing **prehepatic portal hypertension**, not posthepatic venous congestion.
*Councilman bodies*
- These are **eosinophilic apoptotic hepatocytes** seen in acute liver injury (viral hepatitis, yellow fever, toxic injury).
- **Normal liver parenchyma** on ultrasound excludes significant hepatocellular necrosis.
- This finding is unrelated to thrombotic disorders or portal hypertension.
Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG Question 10: A 72-year-old man comes to the emergency department for progressively worsening abdominal pain. The pain began 2 weeks ago and is localized to the right upper quadrant. He feels sick and fatigued. He also reports breathlessness when climbing the stairs to his first-floor apartment. He is a retired painter. He has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He is sexually active with one female partner and does not use condoms consistently. He began having sexual relations with his most recent partner 2 months ago. He smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years but quit 10 years ago. He does not drink alcohol. Current medications include insulin and enalapril. He is 181 cm (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 110 kg (264 lb); BMI is 33.5 kg/m2. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows jaundice, a distended abdomen, and tender hepatomegaly. There is no jugular venous distention. A grade 2/6 systolic ejection murmur is heard along the right upper sternal border. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 18.9 g/dL
Aspartate aminotransferase 450 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase 335 U/L
Total bilirubin 2.1 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
- A. Hepatotropic viral infection
- B. Increased iron absorption
- C. Hepatic steatosis
- D. Hepatic vein obstruction (Correct Answer)
- E. Thickened pericardium
Alcoholic liver disease Explanation: ***Hepatic vein obstruction***
- The patient's **acute liver injury** (elevated AST, ALT, bilirubin) with **right upper quadrant pain**, **tender hepatomegaly**, and **distended abdomen** are classic signs of hepatic vein obstruction (Budd-Chiari syndrome).
- The elevated **hemoglobin (18.9 g/dL)** suggests **polycythemia**, a common predisposing factor for thrombotic events, including hepatic vein thrombosis.
*Hepatotropic viral infection*
- While **hepatotropic viral infections** can cause acute liver injury, the patient's **polycythemia** and the specific presentation of **tender hepatomegaly** and **abdominal distention** are less indicative of this cause alone.
- Though he reports unprotected sex, acute viral hepatitis would generally present with more pronounced acute symptoms and specific markers on serology, which are not provided.
*Increased iron absorption*
- **Hemochromatosis**, due to increased iron absorption, causes liver damage but typically presents with **bronze skin**, diabetes, and joint pain, and the liver injury is usually insidious rather than acute with marked abdominal symptoms.
- The extremely high hemoglobin level in this acute setting is not characteristic of iron overload alone as a primary etiology for acute liver injury mimicking Budd-Chiari.
*Hepatic steatosis*
- **Hepatic steatosis** (fatty liver) is common in patients with **diabetes** and **obesity**; however, it usually presents as asymptomatic elevation of liver enzymes or chronic liver disease, not acute, severe right upper quadrant pain, marked tender hepatomegaly, and abdominal distension, especially with concurrent polycythemia.
- The degree of liver enzyme elevation and bilirubin is more pronounced than typically seen in uncomplicated hepatic steatosis.
*Thickened pericardium*
- A **thickened pericardium** (constrictive pericarditis) can cause **hepatomegaly** and **abdominal distension** due to right-sided heart failure. However, this is characteristically associated with **jugular venous distention** and often **ascites**, which are not noted here.
- The prominent **acute right upper quadrant pain** and **marked liver enzyme elevation** are less typical of cardiac causes of liver congestion compared to thrombotic occlusion.
More Alcoholic liver disease US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.