HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for HIV/AIDS. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 1: For which of the following patients would you recommend prophylaxis against mycobacterium avium-intracellulare?
- A. 30-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 20 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL (Correct Answer)
- B. 22-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 750 cells/microliter and a viral load of 500,000 copies/mL
- C. 45-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 250 cells/microliter and a viral load of 100,000 copies/mL
- D. 50-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 150 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL
- E. 36-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 75 cells/microliter and an undetectable viral load
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***30-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 20 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL***
- Prophylaxis against **Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)** is recommended for HIV-positive individuals with a **CD4 count below 50 cells/µL** to prevent disseminated MAC infection.
- While an undetectable viral load suggests effective antiretroviral therapy (ART) in general, the extremely low CD4 count indicates severe immunosuppression, making prophylaxis crucial.
*36-year old HIV positive male with CD4 count of 75 cells/microliter and an undetectable viral load*
- The **CD4 count of 75 cells/µL** is above the threshold of 50 cells/µL for MAC prophylaxis, even though it's still low.
- An **undetectable viral load** indicates successful ART, which generally helps improve immune function over time, albeit slowly in this CD4 range.
*22-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 750 cells/microliter and a viral load of 500,000 copies/mL*
- A **CD4 count of 750 cells/µL** is well above the threshold for MAC prophylaxis, indicating relatively preserved immune function.
- Although the **viral load is very high**, suggesting uncontrolled HIV replication, the immune system is currently strong enough to ward off MAC.
*45-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 250 cells/microliter and a viral load of 100,000 copies/mL*
- A **CD4 count of 250 cells/µL** is above the threshold for MAC prophylaxis, which is 50 cells/µL.
- While the **high viral load** implies an increased risk for opportunistic infections over time, other specific prophylaxes (e.g., PCP if <200) would be considered earlier.
*50-year old HIV positive female with CD4 count of 150 cells/microliter and a viral load of < 50 copies/mL*
- A **CD4 count of 150 cells/µL** is above the threshold for MAC prophylaxis (50 cells/µL).
- An **undetectable viral load** is a positive sign of ART efficacy, but this patient would still require prophylaxis for **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP)**, as her CD4 count is below 200 cells/µL.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 2: A 60-year-old man comes to the physician’s office with jaundice. Liver ultrasound reveals a shrunken liver and biopsy reveals cirrhosis. Hepatitis serologies are below:
Anti-HAV: negative
HBsAg: negative
HBsAb: positive
HBeAg: negative
Anti-HBe: negative
Anti-HBc: negative
Anti-HCV: positive
The hepatitis C viral load is 1,000,000 copies/mL. The patient is started on an antiviral regimen including sofosbuvir. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibits reverse transcriptase
- B. Inhibits integrase
- C. Inhibits synthesis of DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- D. Inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibits hepatitis C protease
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***Inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase***
- Sofosbuvir is a **nucleotide analog** that targets the **HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (NS5B)**, essential for viral replication.
- By inhibiting NS5B, it acts as a **chain terminator**, preventing the synthesis of new viral RNA strands.
*Inhibits reverse transcriptase*
- This mechanism is characteristic of drugs used to treat **HIV infection**, as reverse transcriptase is an enzyme found in retroviruses.
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is an **RNA virus** that replicates via an RNA intermediate, not DNA, and thus does not utilize reverse transcriptase.
*Inhibits integrase*
- Integrase inhibitors are a class of drugs primarily used in the treatment of **HIV infection**, preventing the viral DNA from integrating into the host genome.
- HCV replication does not involve an integration step into the host DNA, making this mechanism irrelevant for HCV treatment.
*Inhibits synthesis of DNA-dependent DNA polymerase*
- Inhibition of DNA-dependent DNA polymerase primarily targets organisms that replicate their DNA, such as **herpesviruses** or host cell processes.
- HCV is an RNA virus and does not synthesize or rely on a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase for its replication cycle.
*Inhibits hepatitis C protease*
- While **protease inhibitors (e.g., -previr drugs)** are an important class of anti-HCV drugs, sofosbuvir specifically targets the viral **RNA polymerase (NS5B)**.
- Protease inhibitors block the **NS3/4A protease**, which is responsible for cleaving the large HCV polyprotein into functional proteins.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old HIV-positive male is seen in clinic for follow-up care. When asked if he has been adhering to his HIV medications, the patient exclaims that he has been depressed, thus causing him to not take his medication for six months. His CD4+ count is now 33 cells/mm3. What medication(s) should he take in addition to his anti-retroviral therapy?
- A. Azithromycin and fluconazole
- B. Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole
- C. Dapsone
- D. Fluconazole
- E. Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Correct Answer)
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole***
- With a **CD4+ count of 33 cells/mm3**, this patient is at high risk for **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)** and **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis**, for which **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is the prophylaxis of choice.
- He is also at very high risk for **Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection**, for which **azithromycin** is the recommended preventative treatment when the CD4 count is below 50 cells/mm3.
*Azithromycin and fluconazole*
- While **azithromycin** is indicated for MAC prophylaxis, **fluconazole** is typically used for **cryptococcal meningitis** or **candidiasis**, which are not the primary, immediate prophylactic concerns at this specific CD4 count unless there's evidence of these infections.
- The most critical opportunistic infections to prevent at a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3 are PJP, Toxoplasmosis, and MAC.
*Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole*
- **Dapsone** can be used as an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** if TMP-SMX is contraindicated, but it is not the first-line choice and does not cover toxoplasmosis as effectively as TMP-SMX alone.
- **Fluconazole** again is not a primary prophylactic agent at this CD4 count in the absence of specific indications.
*Dapsone*
- **Dapsone** is an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** and can also prevent **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis** when combined with pyrimethamine, but it is not the first-line recommendation.
- It does not provide coverage against **MAC infection**, which is a significant risk at this CD4 count.
*Fluconazole*
- **Fluconazole** is primarily used for **fungal infections** like **candidiasis** or **cryptococcosis**.
- It does not prevent **PJP, Toxoplasmosis, or MAC**, which are the most critical prophylactic concerns for a patient with a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 4: A 49-year-old homeless man comes to the emergency department because of fatigue, cough, and worsening shortness of breath for 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with HIV-infection 25 years ago but has never had any symptoms. He has always refused to take antiretroviral medication. Pulmonary examination shows diffuse crackles over bilateral lower lung fields. An x-ray of the chest shows diffuse, symmetrical interstitial infiltrates. His serum level of beta-d-glucan is elevated. Further testing shows a heterozygous mutation that prevents entry of HIV into macrophages. Which of the following proteins is most likely affected by the mutation in this patient?
- A. ICAM-1
- B. Gp120
- C. CD4
- D. P antigen
- E. CCR5 (Correct Answer)
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***CCR5***
- The mutation preventing HIV entry into **macrophages** points to an issue with a coreceptor, most commonly **CCR5**, which is crucial for macrophage-tropic HIV strains.
- A **heterozygous mutation** in CCR5 (CCR5-Δ32) can confer partial resistance to HIV-1 infection, explaining why the patient has been asymptomatic for 25 years despite refusing antiretroviral therapy.
- This is a well-documented host genetic factor that slows HIV disease progression.
*ICAM-1*
- **ICAM-1 (Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1)** is involved in cell adhesion and immune cell trafficking, but not directly in HIV entry into macrophages.
- Mutations in ICAM-1 would not specifically prevent HIV entry, nor would it explain the long-term asymptomatic status in an HIV-positive individual.
*Gp120*
- **Gp120** is an HIV envelope glycoprotein that binds to the **CD4 receptor** and a coreceptor (CCR5 or CXCR4) on host cells.
- While gp120 is essential for HIV entry, it is a **viral protein**; the question asks about a mutation in a **host protein** that prevents viral entry.
*CD4*
- **CD4** is the primary receptor for HIV on T cells and macrophages, essential for viral entry.
- However, a **heterozygous CD4 mutation** would not provide meaningful protection against HIV, as one functional copy would be sufficient for viral entry.
- In contrast, heterozygous **CCR5-Δ32** mutation provides documented partial resistance, making CCR5 the better answer given this patient's 25-year asymptomatic course.
*P antigen*
- **P antigen** typically refers to a red blood cell antigen and is not involved in HIV entry into macrophages.
- There is no known direct association between P antigen and HIV susceptibility or disease progression.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old pregnant woman presents to an obstetrician at 35 weeks gestation reporting that she noted the presence of a mucus plug in her vaginal discharge this morning. The obstetrician performs an examination and confirms that she is in labor. She was diagnosed with HIV infection 1 year ago. Her current antiretroviral therapy includes abacavir, lamivudine, and nevirapine. Her last HIV RNA level was 2,000 copies/mL 3 weeks ago. Which of the following anti-retroviral drugs should be administered intravenously to the woman during labor?
- A. Enfuvirtide
- B. Nevirapine
- C. Abacavir
- D. Rilpivirine
- E. Zidovudine (Correct Answer)
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***Zidovudine***
- Intravenous **zidovudine** is recommended during labor for HIV-positive pregnant women, especially when the viral load is **>1000 copies/mL**, to reduce the risk of **mother-to-child transmission (MTCT)**.
- This intervention significantly lowers the viral load in the maternal blood and reduces fetal exposure to the virus during delivery.
*Enfuvirtide*
- **Enfuvirtide** is a **fusion inhibitor** administered subcutaneously, not intravenously, and is reserved for treatment-experienced patients with multi-drug resistant HIV.
- It is not a standard recommendation for intrapartum prophylaxis against MTCT.
*Nevirapine*
- **Nevirapine** is an **NNRTI** that is typically given orally, and while it has been used for MTCT prophylaxis, intravenous administration is not standard for intrapartum use.
- The woman is already on oral nevirapine as part of her ART regimen.
*Abacavir*
- **Abacavir** is an **NRTI** given orally and is part of the patient's current ART regimen.
- It is not administered intravenously for intrapartum MTCT prophylaxis.
*Rilpivirine*
- **Rilpivirine** is an **NNRTI** that is taken orally and is not indicated for intravenous administration during labor to prevent MTCT.
- Its use is limited by potential drug interactions and efficacy in patients with high viral loads.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old man interested in pre-exposure therapy for HIV (PrEP) is being evaluated to qualify for a PrEP study. In order to qualify, patients must be HIV- and hepatitis B- and C-negative. Any other sexually transmitted infections require treatment prior to initiation of PrEP. The medical history is positive for a prior syphilis infection and bipolar affective disorder, for which he takes lithium. On his next visit, the liver and renal enzymes are within normal ranges. HIV and hepatitis B and C tests are negative. Which of the following about the HIV test is true?
- A. It is a quantitative test used for screening purposes.
- B. It is a qualitative test used for screening purposes. (Correct Answer)
- C. A secondary reagent is needed to interpret the results.
- D. A known antigen binds directly to the patient's serum.
- E. An unknown antigen binds to the known serum.
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***It is a qualitative test used for screening purposes.***
- **HIV screening tests** (e.g., 4th generation antibody/antigen combination assays) are typically **qualitative**, meaning they detect the presence or absence of HIV markers, not their exact amount.
- These tests are primarily used for broad **screening** of populations to identify potential cases of HIV infection.
*It is a quantitative test used for screening purposes.*
- **Quantitative tests** for HIV, such as viral load tests, measure the amount of virus in the blood and are typically used for monitoring disease progression or treatment effectiveness, not for initial screening.
- Screening tests are designed for high sensitivity to detect infection, even with low viral loads or early antibody responses, making a quantitative measurement less relevant for initial screening.
*A secondary reagent is needed to interpret the results.*
- While some complex immunoassays might involve multiple steps, modern **HIV screening tests** often use advanced technologies that directly yield results, making a separate secondary reagent for interpretation generally unnecessary.
- The results are typically indicated by a color change or a signal detected by an instrument, without requiring an additional interpretive reagent.
*A known antigen binds directly to the patient's serum.*
- **HIV antibody tests** detect **antibodies** produced by the patient's immune system in response to HIV infection.
- In such tests, **known HIV antigens** (from the test kit) bind to **HIV-specific antibodies present in the patient's serum**, not to serum components directly.
- This option is incorrect because it omits the critical role of antibodies as the target molecules being detected.
*An unknown antigen binds to the known serum.*
- This statement describes a different type of immunological assay where an unknown antigen is being identified using a known antibody, which is contrary to how **HIV screening tests** for infection are typically structured.
- **HIV screening tests** use known components (e.g., HIV antigens or antibodies) in the test kit to detect unknown components (e.g., HIV antibodies or viral antigens) in the patient's sample.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 7: A 31-year-old man with untreated HIV infection is admitted to the hospital because of a 3-day history of blurred vision and flashing lights in his left eye. Indirect ophthalmoscopy shows retinal hemorrhages of the left eye. Treatment with a drug that directly inhibits viral DNA polymerases by binding to pyrophosphate-binding sites is initiated. Two days later, the patient has a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. This patient's seizure was most likely caused by which of the following?
- A. Hypoglycemia
- B. Demyelination
- C. Encephalitis
- D. Hypocalcemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Lactic acidosis
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***Hypocalcemia***
- The drug described is **foscarnet**, which inhibits viral DNA polymerase by binding to **pyrophosphate-binding sites** and is used to treat CMV retinitis, common in HIV patients.
- A known side effect of foscarnet is **electrolyte abnormalities**, including **hypocalcemia** and **hypomagnesemia**, which can precipitate seizures.
*Hypoglycemia*
- While hypoglycemia can cause seizures, it is not a direct known side effect of foscarnet or typically associated with the treatment of CMV retinitis.
- The clinical presentation does not suggest **low blood sugar** as the primary cause for the seizure.
*Demyelination*
- Demyelination can be seen in HIV infection (e.g., **PML**), but it's a slower process and less likely to cause an acute, sudden seizure following initiation of an antiviral drug for CMV retinitis.
- There is no direct link between foscarnet administration and acute demyelination leading to seizures.
*Encephalitis*
- Encephalitis can cause seizures, but the primary clinical picture describes **CMV retinitis** and a subsequent seizure after starting a specific antiviral medication.
- While HIV patients are susceptible to various CNS infections, the acute onset seizure directly linked to the initiation of foscarnet therapy points to a drug-related adverse effect rather than a new infection.
*Lactic acidosis*
- Lactic acidosis can occur in HIV patients, particularly with certain antiretroviral therapies (**NRTIs**), but it is not a direct or common side effect of foscarnet.
- While severe lactic acidosis can cause neurological symptoms, it primarily manifests with other systemic signs (e.g., nausea, vomiting, tachypnea) not described here.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 8: A 44-year-old man with HIV comes to the physician for a routine follow-up examination. He has been noncompliant with his antiretroviral medication regimen for several years. He appears chronically ill and fatigued. CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 180/mm³ (N ≥ 500). Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Multifocal demyelination on brain MRI
- B. Violaceous lesions on skin exam (Correct Answer)
- C. Ring-enhancing lesions on brain MRI
- D. Cotton-wool spots on fundoscopy
- E. Ground-glass opacities on chest CT
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***Violaceous lesions on skin exam***
- A CD4 count of 180/mm³ indicates severe **immunosuppression**, making the patient highly susceptible to **opportunistic infections** and cancers, such as Kaposi sarcoma.
- **Kaposi sarcoma** typically presents with violaceous (purple-blue) cutaneous lesions, which are often the initial manifestation of the disease in HIV-positive patients.
*Multifocal demyelination on brain MRI*
- This finding is characteristic of **progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)**, caused by the **JC virus**.
- PML typically occurs at **CD4 counts below 100/mm³**, lower than the patient's current count, although still possible with severe immunosuppression.
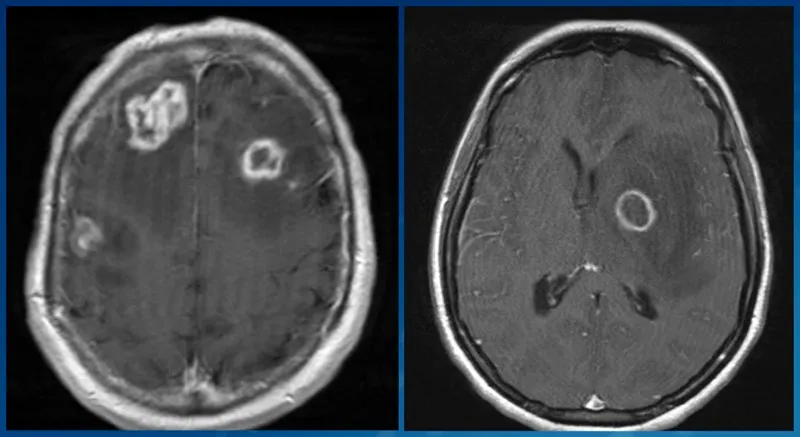
*Ring-enhancing lesions on brain MRI*
- **Ring-enhancing lesions** on brain MRI are often seen in cerebral **toxoplasmosis** or CNS **lymphoma** in HIV patients.
- Toxoplasmosis usually presents with focal neurological deficits and seizures, and is more common with CD4 counts below 100/mm³.
*Cotton-wool spots on fundoscopy*
- **Cotton-wool spots** are a common finding in **HIV retinopathy** due to retinal ischemia.
- While possible, they are non-specific and are usually asymptomatic, whereas the patient's presentation suggests a more prominent and diagnosable condition.
*Ground-glass opacities on chest CT*
- **Ground-glass opacities** on chest CT are characteristic of **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)**, a common opportunistic infection in HIV patients.
- While PJP is a strong possibility with a CD4 count <200/mm³, the question asks for a finding that is *most likely* given the patient's general appearance and the option of Kaposi sarcoma, which manifests directly on examination.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old G1P0 woman at 16 weeks estimated gestational age presents for prenatal care. Routine prenatal screening tests are performed and reveal a positive HIV antibody test. The patient is extremely concerned about the possible transmission of HIV to her baby and wants to have the baby tested as soon as possible after delivery. Which of the following would be the most appropriate diagnostic test to address this patient’s concern?
- A. CD4+ T cell count
- B. Viral culture
- C. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for HIV RNA (Correct Answer)
- D. Antigen assay for p24
- E. EIA for HIV antibody
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for HIV RNA***
- **PCR for HIV RNA** directly detects the viral genetic material, providing a definitive diagnosis of HIV infection in an infant.
- Unlike antibody tests, PCR can distinguish between passively acquired maternal antibodies and actual infant infection, making it suitable for newborns.
*CD4+ T cell count*
- **CD4+ T cell count** is used to monitor the progression of HIV infection and immunosuppression, not for initial diagnosis, especially in neonates.
- While it's an important marker for HIV disease, it does not confirm the presence of the virus itself in a newborn.
*Viral culture*
- **Viral culture** is a highly specific method for detecting HIV, but it is expensive, time-consuming, and technically demanding.
- It is not routinely used for rapid early diagnosis in neonates due to its practical limitations and the availability of faster, reliable alternatives like PCR.
*Antigen assay for p24*
- The **p24 antigen test** can detect early HIV infection in adults, but its sensitivity is lower in neonates compared to PCR, especially immediately after birth.
- It may not reliably detect infection in newborns due to low viral loads or the presence of maternal antibodies that complex the antigen.
*EIA for HIV antibody*
- An **EIA for HIV antibody** will detect maternal antibodies that have crossed the placenta, meaning it will be positive in nearly all infants born to HIV-positive mothers, regardless of the infant's infection status.
- This test cannot distinguish between passive maternal antibody transfer and true infant infection.
HIV/AIDS US Medical PG Question 10: A 34-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He was diagnosed with HIV 8 years ago. He is currently receiving triple antiretroviral therapy. He is sexually active and uses condoms consistently. He is planning a trip to Thailand with his partner to celebrate his 35th birthday in 6 weeks. His last tetanus and diphtheria booster was given 4 years ago. He received three vaccinations against hepatitis B 5 years ago. He had chickenpox as a child. Other immunization records are unknown. Vital signs are within normal limits. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Leukocyte count shows 8,700/mm3, and CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 480 cells/mm3 (Normal ≥ 500); anti-HBs is 150 mIU/mL. Which of the following recommendations is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Yellow fever vaccine
- B. Hepatitis B vaccine
- C. Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis vaccine (Tdap)
- D. Measles, mumps, rubella vaccine
- E. No vaccination (Correct Answer)
HIV/AIDS Explanation: ***Correct: No vaccination***
- Given the patient's current immunization status and clinical scenario, **none of the listed vaccines are indicated at this time**.
- His CD4+ count of 480 cells/mm³ indicates relatively preserved immune function on effective antiretroviral therapy.
- His **anti-HBs level of 150 mIU/mL** demonstrates **adequate hepatitis B immunity** (protective level ≥10 mIU/mL).
- His **tetanus-diphtheria booster was given 4 years ago**, and routine boosters are recommended every **10 years**, so he is not due for another 6 years.
*Incorrect: Yellow fever vaccine*
- **Thailand is not a yellow fever endemic country**, so yellow fever vaccination is **not required or recommended** for travel there.
- Yellow fever vaccine is a **live attenuated vaccine** that can be given to HIV-positive patients with **CD4+ counts ≥200 cells/mm³** when travel to endemic areas (parts of Africa and South America) is necessary.
- Since the patient has a CD4+ count of 480 and Thailand doesn't require this vaccine, this is not applicable.
*Incorrect: Hepatitis B vaccine*
- The patient's **anti-HBs level of 150 mIU/mL** indicates **adequate protective immunity** against hepatitis B.
- A level ≥10 mIU/mL is considered protective, so **no booster is needed**.
*Incorrect: Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis vaccine (Tdap)*
- **Tetanus-diphtheria boosters are recommended every 10 years**.
- The patient received his last booster **4 years ago**, so he is **not due** for another booster at this time.
- There is no specific indication for **pertussis vaccination** (e.g., pregnancy, close contact with infants).
*Incorrect: Measles, mumps, rubella vaccine*
- **MMR is a live attenuated vaccine** that is **contraindicated** in HIV-positive individuals with **CD4+ counts <200 cells/mm³**.
- While this patient's CD4+ count is 480, MMR should only be given to HIV patients if they lack immunity and have CD4 ≥200.
- There is **no documented need** for MMR based on the clinical scenario provided, and his immunity status to these infections is unknown.
- Without evidence of susceptibility or specific exposure risk, vaccination is not indicated.
More HIV/AIDS US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.