Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Extraintestinal manifestations. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 1: A 54-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a painful skin lesion on her right leg for 1 month. It initially started out as a small red spot but has rapidly increased in size during this period. She remembers an ant bite on her leg prior to the lesion occurring. She was treated for anterior uveitis 8 months ago with corticosteroids. She has Crohn's disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. Current medications include insulin, mesalamine, enalapril, and aspirin. She returned from Wisconsin after visiting her son 2 months ago. Her temperature is 37.6°C (98°F), pulse is 98/min, and blood pressure is 126/88 mm Hg. Examination shows pitting pedal edema of the lower extremities. There is a 4-cm tender ulcerative lesion on the anterior right leg with a central necrotic base and purplish irregular borders. There are dilated tortuous veins in both lower legs. Femoral and pedal pulses are palpated bilaterally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pyoderma gangrenosum (Correct Answer)
- B. Basal cell carcinoma
- C. Squamous cell carcinoma
- D. Ecthyma gangrenosum
- E. Blastomycosis
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Pyoderma gangrenosum***
- The patient's history of **Crohn's disease**, **anterior uveitis**, and a rapidly progressing, **tender ulcerative lesion** with a **necrotic base** and **purplish irregular borders** are highly characteristic of pyoderma gangrenosum.
- The phenomenon of **pathergy** (exacerbation of lesions after minor trauma like a bug bite) further supports this diagnosis.
*Basal cell carcinoma*
- Typically presents as a **slow-growing lesion** with **pearly borders** and **telangiectasias**, not a rapidly enlarging, tender ulcer with a necrotic base.
- It is often associated with sun exposure and rarely presents with the systemic associations seen in this case.
*Squamous cell carcinoma*
- Usually appears as a **scaly, erythematous patch** or an **indurated nodule** that may ulcerate, but it is generally a chronic lesion and less acutely painful or rapidly progressing.
- While it can be aggressive, the clinical presentation and rapid progression with a necrotic center and systemic associations point away from this diagnosis.
*Ecthyma gangrenosum*
- This condition is caused by **Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia** and is characterized by a central necrotic area surrounded by an erythematous halo, typically in immunocompromised patients.
- While there is some overlap in appearance, ecthyma gangrenosum is usually associated with **sepsis** and systemic signs of infection, which are not prominent here.
*Blastomycosis*
- A **fungal infection** endemic to the Great Lakes region (including Wisconsin), which can cause skin lesions that may be verrucous, ulcerative, or plaque-like.
- However, the description of a rapidly progressing, deeply ulcerative lesion with purplish, undermined borders and strong association with inflammatory bowel disease is more consistent with pyoderma gangrenosum.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 2: A 74-year-old man presents to the emergency room with abdominal pain. He reports acute onset of left lower quadrant abdominal pain and nausea three hours prior to presentation. The pain is severe, constant, and non-radiating. He has had two maroon-colored bowel movements since the pain started. His past medical history is notable for hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atrial fibrillation, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and rheumatoid arthritis. He takes lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, atorvastatin, dabigatran, methotrexate. He has a 60 pack-year smoking history and drinks 1-2 beers per day. He admits to missing some of his medications recently because he was on vacation in Hawaii. His last colonoscopy was 4 years ago which showed diverticular disease in the descending colon and multiple sessile polyps in the sigmoid colon which were removed. His temperature is 100.1°F (37.8°C), blood pressure is 145/85 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 20/min. On exam, he has notable abdominal distention and is exquisitely tender to palpation in all four abdominal quadrants. Bowel sounds are absent. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
- A. Cardiac thromboembolism
- B. Splanchnic vasoconstriction
- C. Perforated intestinal mucosal herniation (Correct Answer)
- D. Paradoxical thromboembolism
- E. Duodenal compression
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Perforated intestinal mucosal herniation***
- This patient's presentation with acute abdominal pain, maroon-colored bowel movements, fever, abdominal distention, diffuse tenderness, and absent bowel sounds, in the context of a history of **diverticular disease**, strongly suggests **perforated diverticulitis**. The "intestinal mucosal herniation" refers to a diverticulum, which can perforate.
- The history of **diverticular disease** and involvement of the **left lower quadrant pain** followed by generalized peritonitis and GI bleeding (maroon stools) makes this the most likely diagnosis.
*Cardiac thromboembolism*
- While the patient has **atrial fibrillation** and is on **dabigatran** (which he may have missed), a cardiac thromboembolism would typically lead to **ischemic enteritis** or **mesenteric ischemia**, presenting with severe pain out of proportion to exam findings, but diffuse peritonitis and perforation are less common primary presentations.
- The clinical picture strongly points towards a localized process that progressed to peritonitis rather than a primary embolic event causing perforation directly without prior significant ischemia symptoms.
*Splanchnic vasoconstriction*
- This mechanism is associated with **non-occlusive mesenteric ischemia**, often seen in critically ill patients, those on vasoconstrictors, or with **low cardiac output states**.
- While the patient has risk factors for vascular disease, the acute onset, localized pain progressing to diffuse peritonitis, and history of diverticula make a perforated diverticulum more probable than primary non-occlusive ischemia leading to perforation.
*Paradoxical thromboembolism*
- A paradoxical embolism involves a clot from the venous system bypassing the pulmonary circulation to enter the systemic circulation, typically through a **patent foramen ovale** or **atrial septal defect**.
- There is no clinical evidence in the patient's history to suggest such a defect or a venous thrombosis as the origin of the embolus, making it a less likely mechanism for the presenting symptoms.
*Duodenal compression*
- **Duodenal compression** (e.g., from superior mesenteric artery syndrome) typically causes **proximal bowel obstruction** symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, often worse postprandially.
- This patient's symptoms of left lower quadrant pain, diffuse peritonitis, and maroon-colored stools are not consistent with duodenal compression.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He has a 2-month history of increasing generalized fatigue and severe pruritus. He has hypertension and ulcerative colitis which was diagnosed via colonoscopy 5 years ago. Current medications include lisinopril and rectal mesalamine. He is sexually active with 2 female partners and uses condoms inconsistently. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 86/min, and blood pressure is 130/84 mm Hg. Examination shows scleral icterus and multiple scratch marks on the trunk and extremities. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is soft and nontender. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.5 g/dL
Leukocyte count 7500/mm3
Platelet count 280,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 138 mEq/L
Cl- 101 mEq/L
K+ 4.7 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 18 mg/dL
Glucose 91 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
Bilirubin
Total 1.5 mg/dL
Direct 0.9 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 460 U/L
AST 75 U/L
ALT 78 U/L
Anti-nuclear antibody negative
Antimitochondrial antibodies negative
Abdominal ultrasound shows thickening of the bile ducts and focal bile duct dilatation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Primary biliary cholangitis
- B. Hepatitis B infection
- C. Autoimmune hepatitis
- D. IgG4-associated cholangitis
- E. Primary sclerosing cholangitis (Correct Answer)
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Primary sclerosing cholangitis***
- This patient's history of **ulcerative colitis** combined with cholestatic liver injury (elevated alkaline phosphatase >> transaminases), **scleral icterus**, and **severe pruritus** strongly suggests primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC).
- The imaging findings of **bile duct thickening and focal dilatation** are characteristic of PSC, which causes chronic inflammation and fibrosis of intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts.
- PSC is strongly associated with inflammatory bowel disease, particularly **ulcerative colitis** (present in 60-80% of PSC patients), and typically affects men in their 30s-40s.
- Negative antimitochondrial antibodies help distinguish this from primary biliary cholangitis.
*Primary biliary cholangitis*
- Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) typically affects **middle-aged women** and is characterized by positive **antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs)**, which are negative in this patient.
- While PBC also causes cholestatic liver injury with pruritus, the male gender, younger age, strong association with ulcerative colitis, and bile duct changes on imaging point to PSC rather than PBC.
*Hepatitis B infection*
- Viral hepatitis B typically presents with a **hepatocellular pattern** of injury with AST and ALT elevated much higher than alkaline phosphatase (often >1000 U/L).
- This patient shows a **cholestatic pattern** (alkaline phosphatase 460 U/L with transaminases only mildly elevated at 75-78 U/L).
- Diagnosis would require positive hepatitis B serologies (HBsAg, anti-HBc), which are not present.
*Autoimmune hepatitis*
- Autoimmune hepatitis causes a **hepatocellular injury pattern** with very high transaminases (often >500-1000 U/L) and is associated with positive autoantibodies such as **ANA** or **anti-smooth muscle antibodies**, which are negative in this case.
- This patient's predominant cholestatic pattern and bile duct abnormalities are not consistent with autoimmune hepatitis.
*IgG4-associated cholangitis*
- IgG4-associated cholangitis can mimic PSC with bile duct stricturing and obstructive jaundice, but typically presents with **elevated serum IgG4 levels** and characteristic histopathology.
- It is **not associated with ulcerative colitis** and is much less common than PSC.
- This diagnosis would require tissue biopsy showing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with IgG4-positive plasma cells.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 4: A 26-year-old male presents to the emergency room with weight loss, abdominal pain, and bloody diarrhea. He reports having intermittent bloody stools and crampy left lower quadrant abdominal pain over the past several days. He is otherwise healthy, does not smoke, and takes no medications. His family history is notable for colon cancer in his father. He subsequently undergoes a colonoscopy which demonstrates a hyperemic friable mucosa with inflammation extending continuously from the rectum proximally through the colon. A biopsy of the rectal mucosa is notable for crypt abscesses and pseudopolyps. This patient’s condition is most commonly associated with what other condition?
- A. Primary sclerosing cholangitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Primary biliary cholangitis
- C. Intestinal strictures
- D. Perianal fistulae
- E. Aphthous ulcers
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: **Primary sclerosing cholangitis**
- The described clinical picture (weight loss, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, continuous inflammation from the rectum proximally, crypt abscesses, pseudopolyps) is highly characteristic of **ulcerative colitis (UC)**.
- **Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)** is a chronic cholestatic liver disease strongly associated with UC, occurring in 5-10% of UC patients.
*Primary biliary cholangitis*
- **Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)**, formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune liver disease primarily affecting small intrahepatic bile ducts, but it is typically associated with other autoimmune conditions like Sjögren's syndrome or rheumatoid arthritis, not inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- PBC is characterized by the presence of **antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA)** and predominantly affects middle-aged women.
*Intestinal strictures*
- While intestinal strictures can occur in inflammatory bowel disease, they are much more characteristic of **Crohn's disease**, which involves transmural inflammation and can lead to fibrosis and narrowing of the bowel lumen.
- Ulcerative colitis, with its mucosal inflammation, is less likely to cause strictures, though sometimes severe inflammation can lead to a toxic megacolon.
*Perianal fistulae*
- **Perianal fistulae** are a common complication of **Crohn's disease**, resulting from transmural inflammation and abscess formation penetrating the skin around the anus.
- They are extremely rare in ulcerative colitis, which primarily affects the colonic mucosa.
*Aphthous ulcers*
- **Aphthous ulcers** in the mouth can be an extraintestinal manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease, particularly **Crohn's disease**.
- While they can occur in UC, they are less specific and less commonly the most significant associated condition compared to PSC.
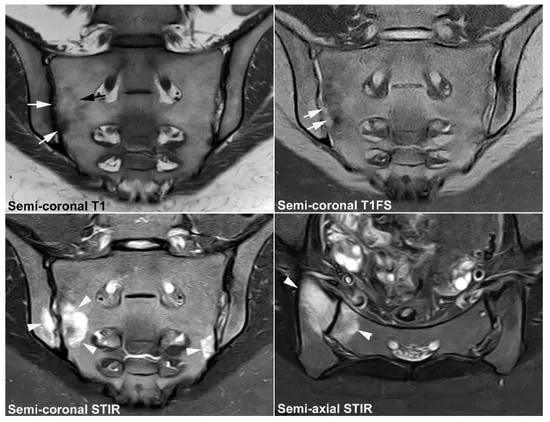
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 5: A 32-year-old man presents to the clinic with a dull low back pain radiating to the buttocks. He first noted it about 2 years ago and it has progressed since then. He notes that it is worse in the morning and improves later in the day after physical activity. The patient also reports morning stiffness lasting up to 30 minutes and blurred vision, which started about 7 months ago. The patient's vital signs include: blood pressure 130/80 mm Hg, heart rate 88/min, respiratory rate 16/min, and temperature 36.8°C (98.2°F). Physical examination reveals tenderness over the sacroiliac joints and limitation of the lumbar spine movements in the sagittal plane. The patient's X-ray is shown in the picture below. Which of the following HLA variants is associated with this patient's condition?
- A. HLA-B27 (Correct Answer)
- B. HLA-DQ2
- C. HLA-DR3
- D. HLA-B47
- E. HLA-DR4
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***HLA-B27***
- The clinical presentation of **dull low back pain**, morning stiffness improving with activity, and **blurred vision** (suggestive of uveitis) points to a spondyloarthropathy, most commonly **ankylosing spondylitis**.
- **HLA-B27** is a strong genetic risk factor and is present in a high percentage of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and other spondyloarthropathies, making it the most likely associated HLA variant.
*HLA-DQ2*
- **HLA-DQ2** is primarily associated with **celiac disease**, an autoimmune disorder affecting the small intestine, and has no direct linkage to spondyloarthropathies.
- The patient's symptoms are musculoskeletal and ocular, not gastrointestinal, which rules out celiac disease.
*HLA-DR3*
- **HLA-DR3** is associated with various autoimmune conditions such as **Type 1 Diabetes**, **Graves' disease**, and **Sjogren's syndrome**, none of which align with the patient's symptoms.
- There is no known direct association between HLA-DR3 and spondyloarthropathies or uveitis.
*HLA-B47*
- **HLA-B47** is primarily associated with **21-hydroxylase deficiency**, a form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and it has no relevance to the patient's musculoskeletal and ocular symptoms.
- This genetic marker is not linked to inflammatory joint diseases or uveitis.
*HLA-DR4*
- **HLA-DR4** is a significant genetic marker for **rheumatoid arthritis** and certain other autoimmune disorders.
- The patient's symptoms (back pain improving with activity, sacroiliac tenderness, uveitis) are not typical for rheumatoid arthritis, which usually affects peripheral joints and worsens with activity.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 6: A 37-year-old man presents to his gastroenterologist due to a transaminitis found by his primary care physician (PCP). He reports currently feeling well and has no acute concerns. Medical history is significant for ulcerative colitis treated with 5-aminosalicylate. He recently went on a trip to Mexico and experienced an episode of mild diarrhea. The patient is 5 ft 4 in and weighs 220 lbs (99.8 kg). His temperature is 98°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 138/88 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory testing demonstrates:
Leukocyte count: 7,200 /mm^3
Alkaline phosphatase: 205 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): 120 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): 115 U/L
Perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (pANCA): Positive
Antimitochondrial antibody: Negative
Which of the following is most likely the diagnosis?
- A. Choledocholithiasis
- B. Acute cholecystitis
- C. Acute viral hepatitis
- D. Primary sclerosing cholangitis (Correct Answer)
- E. Primary biliary cholangitis
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Primary sclerosing cholangitis***
- The patient's history of **ulcerative colitis**, elevated **alkaline phosphatase**, and positive **pANCA** are highly suggestive of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC).
- PSC often presents with **asymptomatic transaminitis** in early stages and is strongly associated with inflammatory bowel disease, particularly ulcerative colitis.
*Choledocholithiasis*
- This condition is characterized by **gallstones in the common bile duct**, usually presenting with **biliary colic**, jaundice, or cholangitis.
- While it can cause elevated liver enzymes, particularly alkaline phosphatase, the chronic, asymptomatic nature and strong association with ulcerative colitis and pANCA positivity point away from choledocholithiasis as the *most likely* diagnosis.
*Acute cholecystitis*
- **Acute cholecystitis** involves inflammation of the gallbladder, typically causing **right upper quadrant pain**, fever, and leukocytosis.
- The patient is asymptomatic, afebrile, and has an unremarkable physical exam, making acute cholecystitis unlikely.
*Acute viral hepatitis*
- **Acute viral hepatitis** usually presents with significantly higher **aminotransferase levels** (often in the thousands) and symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and jaundice.
- The patient's relatively mild transaminitis, asymptomatic status, and specific risk factors (ulcerative colitis, pANCA) do not fit the typical picture of acute viral hepatitis.
*Primary biliary cholangitis*
- **Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)** is characterized by destruction of small intrahepatic bile ducts, primarily affecting women, and is associated with **anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA)**.
- The patient is male, and his AMA is negative, making PBC an unlikely diagnosis, despite the elevated alkaline phosphatase.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 7: A 23-year-old female presents with a seven-day history of abdominal pain, and now bloody diarrhea that brings her to her primary care physician. Review of systems is notable for a 12-pound unintentional weight loss and intermittent loose stools. She has a family history notable for a father with CAD and a mother with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Upon further workup, she is found to have the following on colonoscopy and biopsy, Figures A and B respectively. Serum perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (P-ANCA) is positive. This patient's disease is likely to also include which of the following features?
- A. Worse disease severity near the ileocecal valve
- B. Cobblestoning and skip lesions
- C. Fistulae and stricture formation
- D. Perianal disease
- E. Continuous progression beginning in the rectum (Correct Answer)
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Continuous progression beginning in the rectum***
- The patient's presentation with abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, weight loss, and **positive P-ANCA** is highly suggestive of **ulcerative colitis**.
- **Ulcerative colitis** characteristically presents with **continuous inflammation** that begins in the **rectum** and extends proximally through the colon.
*Worse disease severity near the ileocecal valve*
- This feature is more characteristic of **Crohn's disease**, where the **ileocecal region** is a common site of severe involvement.
- In **ulcerative colitis**, inflammation is typically confined to the colon and does not disproportionately affect the ileocecal valve unless there is backwash ileitis.
*Cobblestoning and skip lesions*
- **Cobblestoning** and **skip lesions** are classic endoscopic findings in **Crohn's disease**, reflecting the patchy, transmural inflammation.
- **Ulcerative colitis** is characterized by diffuse, superficial inflammation without skip lesions.
*Fistulae and stricture formation*
- The formation of **fistulae** (abnormal connections between organs) and **strictures** (narrowing of the bowel lumen) are hallmarks of **Crohn's disease** due to its transmural inflammation.
- These complications are rare in **ulcerative colitis**, which primarily affects the mucosal layer.
*Perianal disease*
- **Perianal disease**, including **fissures**, **abscesses**, and **fistulae**, is a common extraintestinal manifestation and complication of **Crohn's disease**.
- While other extraintestinal manifestations like **primary sclerosing cholangitis** can occur in both, perianal disease itself is less typical for uncomplicated **ulcerative colitis**.
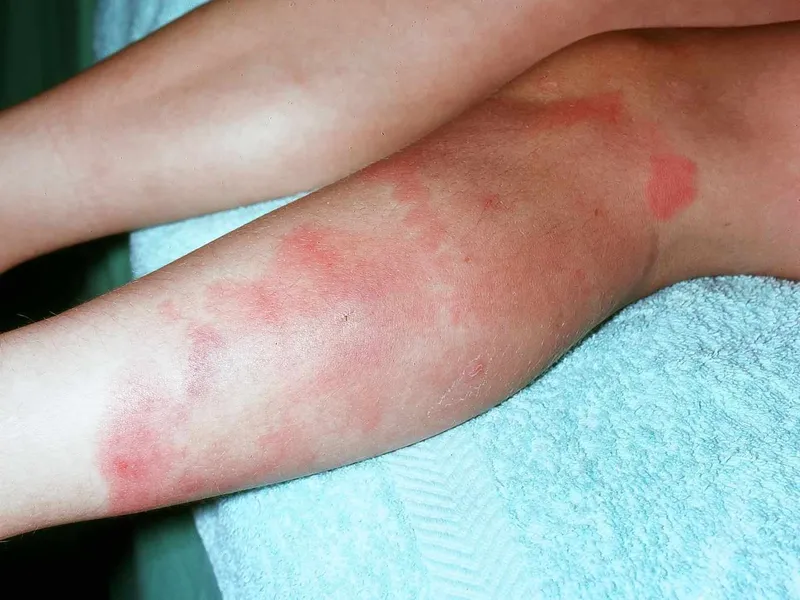
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 8: A 42-year-old man presents to the physician with a painful ulcer in the mouth for 1 week. He has had similar episodes of ulcers over the past year. Every episode lasts about a week and heals without leaving a scar. He has also had similar ulcers on the scrotum, but the ulcers have left scars. He takes no medications. His temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), and the rest of the vital signs are stable. On physical examination, a 1-cm yellowish ulcer with a necrotic base is seen on the right buccal mucosa. Also, there are several tender nodules of different sizes on both shins. An image of one of the nodules is shown. Which of the following is the most likely complication of this patient’s current condition?
- A. Uveitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Cerebral vein thrombosis
- C. Pulmonary embolism
- D. Gastrointestinal ulceration
- E. Deforming arthritis
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Uveitis***
- The constellation of **recurrent oral and genital ulcers**, **skin lesions** (erythema nodosum-like nodules on the shins), and positive pathergy test (implied by the "scars" from ulcers which may suggest an exaggerated skin response) is highly suggestive of **Behçet's disease**.
- **Uveitis** is a common and serious ocular complication of Behçet's disease, often leading to visual impairment or blindness if untreated.
*Cerebral vein thrombosis*
- While **central nervous system (CNS) involvement** can occur in Behçet's disease, leading to various neurological symptoms including **thrombosis**, it is less common than ocular complications like uveitis.
- **Cerebral vein thrombosis** is a severe but less frequent manifestation compared to the high prevalence of ocular involvement.
*Pulmonary embolism*
- **Vascular involvement**, including thrombophlebitis and arterial aneurysms, is a known feature of Behçet's disease, increasing the risk of **thrombosis**.
- However, **pulmonary embolism** specifically is a less frequent direct complication compared to other arterial or venous thromboses, and ocular issues are more prevalent.
*Gastrointestinal ulceration*
- Behçet's disease can affect the **gastrointestinal tract**, causing **ulcerations**, particularly in the ileocecal region.
- While a possible complication, gastrointestinal involvement is not as universally noted or as likely to be the *most likely* complication as uveitis, which affects a higher percentage of patients.
*Deforming arthritis*
- **Arthritis** is a common manifestation in Behçet's disease, typically presenting as **non-erosive and non-deforming** polyarthritis, predominantly affecting large joints like the knees and ankles.
- Unlike conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, Behçet's-associated arthritis rarely leads to **joint destruction or deformity**.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 9: A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department for severe abdominal pain. The patient states that for the past week he has felt fatigued and had a fever. He states that he has had crampy lower abdominal pain and has experienced several bouts of diarrhea. The patient states that his pain is somewhat relieved by defecation. The patient returned from a camping trip 2 weeks ago in the Rocky Mountains. He is concerned that consuming undercooked meats on his trip may have caused this. He admits to consuming beef and chicken cooked over a fire pit. The patient is started on IV fluids and morphine. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 130/77 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Laboratory studies are ordered and are seen below.
Hemoglobin: 10 g/dL
Hematocrit: 28%
Leukocyte count: 11,500 cells/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 445,000/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 140 mEq/L
Cl-: 102 mEq/L
K+: 4.1 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
BUN: 24 mg/dL
Glucose: 145 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL
Ca2+: 9.6 mg/dL
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): 75 mm/hour
Physical exam is notable for a patient who appears to be uncomfortable. Gastrointestinal (GI) exam is notable for abdominal pain upon palpation. Ear, nose, and throat exam is notable for multiple painful shallow ulcers in the patient's mouth. Inspection of the patient's lower extremities reveals a pruritic ring-like lesion. Cardiac and pulmonary exams are within normal limits. Which of the following best describes this patient's underlying condition?
- A. p-ANCA positive autoimmune bowel disease
- B. Transmural granulomas in the bowel (Correct Answer)
- C. Gram-negative microaerophilic organism
- D. Rectal mucosa outpouching
- E. Bowel wall spasticity
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Transmural granulomas in the bowel***
- This patient's symptoms, including **chronic diarrhea**, **abdominal pain relieved by defecation**, **oral ulcers**, **fatigue**, **fever**, and **elevated ESR**, along with a **pruritic ring-like lesion** (suggestive of erythema nodosum, a common extraintestinal manifestation), are highly indicative of **Crohn's disease**.
- **Crohn's disease** is characterized by **transmural inflammation** of any part of the GI tract, often with the formation of **non-caseating granulomas**.
*p-ANCA positive autoimmune bowel disease*
- This describes **ulcerative colitis**, which is typically associated with **p-ANCA positivity** in a subset of patients.
- Unlike the diffuse and continuous inflammation seen in ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease features **skip lesions** and **transmural inflammation**, which aligns better with the varied symptoms and extraintestinal manifestations presented.
*Gram-negative microaerophilic organism*
- This refers to bacterial infections such as those caused by **Campylobacter jejuni** or **Helicobacter pylori**, which can cause GI symptoms.
- While the patient's camping trip and consumption of undercooked meat might suggest an infectious etiology, the **chronic nature of symptoms** (week-long fatigue and fever), **oral ulcers**, **elevated ESR**, and **erythema nodosum-like lesion** point more strongly towards an autoimmune/inflammatory bowel disease rather than an acute bacterial infection.
*Rectal mucosa outpouching*
- **Diverticula** are outpouchings of the colon, commonly affecting the sigmoid colon, and are typically associated with **diverticulitis** when inflamed.
- This condition does not explain the widespread systemic symptoms, oral ulcers, or the chronic, crampy abdominal pain and diarrhea pattern seen in this patient.
*Bowel wall spasticity*
- **Bowel spasticity** is a feature of **irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)**.
- While IBS can cause crampy abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits, it is a **functional disorder** and does not cause **fever**, **oral ulcers**, **elevated ESR**, or significant **anemia** and **thrombocytosis** as seen in this patient.
Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG Question 10: A 33-year-old African-American female presents to her physician with complaints of a persistent, dry cough. She states that the cough has gone on for some time now. Three weeks ago, during her last general checkup, she was started on lisinopril and metformin for concerns regarding an elevated blood pressure and fasting blood glucose. Past medical history is notable for eczema, asthma, and seasonal allergies. At this visit the patient has other non-specific complaints such as fatigue and joint pain as well as a burning sensation in her sternum when she eats large meals. Her physical exam is only notable for painful bumps on her lower extremities (figure A) which the patient attributes to "bumping her shins," during exercise, and an obese habitus. Which of the following is most likely true for this patient's chief concern?
- A. Omeprazole is an appropriate next step in management
- B. Loratadine would best treat her chief complaint
- C. Serum levels of bradykinin will be elevated
- D. Non-caseating granulomas are found on biopsy of mediastinal lymph nodes (Correct Answer)
- E. Beta agonists would relieve this patient's symptoms
Extraintestinal manifestations Explanation: ***Non-caseating granulomas are found on biopsy of mediastinal lymph nodes***
- The patient's symptoms (persistent dry cough, fatigue, joint pain, painful shin bumps consistent with **erythema nodosum**) in an **African-American female** are highly suggestive of **sarcoidosis**.
- **Sarcoidosis** is characterized by the presence of **non-caseating granulomas** in affected organs, commonly the lungs and mediastinal lymph nodes.
*Omeprazole is an appropriate next step in management*
- While the patient has a "burning sensation in her sternum when she eats large meals," suggesting **gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)**, this is not her chief complaint.
- Treating GERD with **omeprazole** would address the burning sensation but not the persistent dry cough or other systemic symptoms.
*Loratadine would best treat her chief complaint*
- **Loratadine** is an antihistamine used to treat allergic reactions, including symptoms of seasonal allergies and eczema.
- Although the patient has a history of allergies and asthma, a persistent dry cough with systemic symptoms and erythema nodosum points away from an **allergic cough** as the primary cause.
*Serum levels of bradykinin will be elevated*
- High serum levels of **bradykinin** can cause an ACE inhibitor-induced dry cough, which should be considered given her recent initiation of **lisinopril**.
- However, the presence of **erythema nodosum**, joint pain, and fatigue, combined with a persistent dry cough, makes **sarcoidosis** a more comprehensive diagnosis that explains all her symptoms beyond just the cough.
*Beta agonists would relieve this patient's symptoms*
- **Beta-agonists** are bronchodilators used to relieve bronchospasm in conditions like asthma.
- While the patient has a history of asthma, her cough is described as persistent and dry, and combined with other systemic symptoms, it is less likely to be solely an asthma exacerbation treatable with **beta-agonists**.
More Extraintestinal manifestations US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.