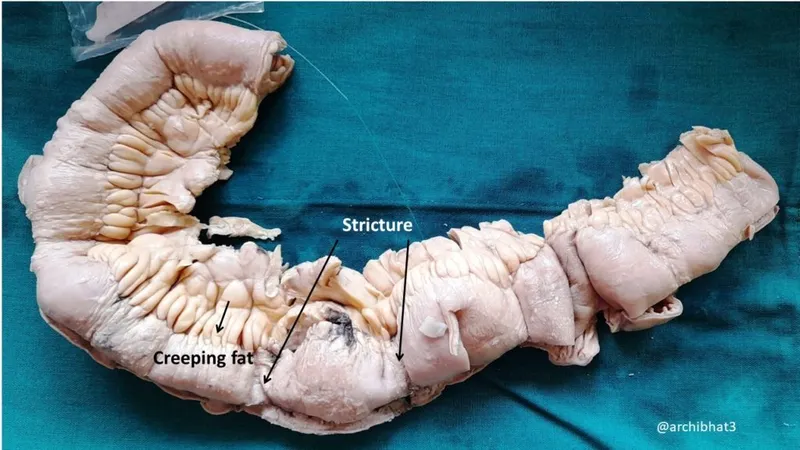
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Crohn's disease pathophysiology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 1: A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician because of progressively worsening episodes of severe, crampy abdominal pain and nonbloody diarrhea for the past 3 years. Examination of the abdomen shows mild distension and generalized tenderness. There is a fistula draining stool in the perianal region. Immunohistochemistry shows dysfunction of the nucleotide oligomerization binding domain 2 (NOD2) protein. This dysfunction most likely causes overactivity of which of the following immunological proteins in this patient?
- A. Interferon-γ
- B. β-catenin
- C. IL-1β
- D. IL-10
- E. NF-κB (Correct Answer)
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***NF-κB***
- **NOD2** is a pattern recognition receptor that normally detects bacterial products and regulates inflammatory responses. In **Crohn's disease**, loss-of-function **NOD2 mutations** lead to impaired bacterial sensing and clearance.
- This defective NOD2 function results in **compensatory overactivation of NF-κB** through alternative inflammatory pathways (particularly TLR signaling), causing excessive **pro-inflammatory cytokine** production.
- This **NF-κB hyperactivation** is a key driver of chronic inflammation in **Crohn's disease**, contributing to symptoms like fistulas, strictures, and transmural inflammation.
*Interferon-γ*
- **Interferon-γ** is an important pro-inflammatory cytokine in Crohn's disease and is part of the Th1-mediated immune response.
- However, its production is downstream of **NF-κB** activation and other inflammatory cascades. **NOD2 dysfunction** does not directly cause **IFN-γ** overactivity through the primary molecular pathway.
*β-catenin*
- **β-catenin** is a key component of the **Wnt signaling pathway** involved in cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation.
- It is not directly affected by **NOD2 dysfunction**. Dysregulation of **β-catenin** is more commonly associated with colorectal adenomas and cancer, not the inflammatory mechanisms of Crohn's disease.
*IL-1β*
- **IL-1β** is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine that is indeed elevated in **Crohn's disease**.
- However, **IL-1β** is produced **downstream** of **NF-κB** activation. The primary molecular consequence of **NOD2 dysfunction** is the overactivity of **NF-κB**, which then drives production of various cytokines including **IL-1β**.
*IL-10*
- **IL-10** is an **anti-inflammatory cytokine** essential for maintaining intestinal immune homeostasis and suppressing excessive inflammatory responses.
- In Crohn's disease, **IL-10** signaling is often **impaired or deficient** rather than overactive. The question asks about overactivity, making this the opposite of what occurs in the disease.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 2: A 27-year-old female has a history of periodic bloody diarrhea over several years. Colonoscopy shows sigmoid colon inflammation, and the patient complains of joint pain in her knees and ankles. You suspect inflammatory bowel disease. Which of the following would suggest a diagnosis of Crohn disease:
- A. Jaundice
- B. Mucosal and submucosal ulcerations
- C. Perianal fistula (Correct Answer)
- D. Loss of large bowel haustra
- E. Left lower quadrant pain
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Perianal fistula***
- The presence of a **perianal fistula** is highly characteristic of **Crohn disease** due to its **transmural inflammation**, which can extend through the bowel wall and form tracts to the skin.
- While other inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) symptoms like bloody diarrhea and joint pain are present, a fistula specifically points towards Crohn disease rather than ulcerative colitis.
*Jaundice*
- **Jaundice** is not a typical manifestation of Crohn disease itself, though it can occur as a complication if there is associated **primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)**, which is more commonly linked with **ulcerative colitis**.
- It would suggest a primary liver issue or biliary obstruction, rather than directly supporting a diagnosis of Crohn disease.
*Mucosal and submucosal ulcerations*
- While **ulcerations** are a feature of both ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease, the description of **mucosal and submucosal ulcerations** is not specific enough to differentiate between them.
- In Crohn disease, ulcers tend to be **scattered** and **deep ("cobblestoning")**, potentially extending transmurally, whereas in ulcerative colitis, they are typically more **superficial** and **continuous**.
*Loss of large bowel haustra*
- **Loss of haustra**, also known as **"lead pipe" appearance**, is a characteristic finding in chronic **ulcerative colitis** due to continuous inflammation and fibrosis, leading to a straightened appearance of the colon.
- This finding is less typical for Crohn disease, which often has **skip lesions** and can involve any part of the gastrointestinal tract.
*Left lower quadrant pain*
- **Left lower quadrant pain** can be associated with inflammation in the **descending or sigmoid colon**, which can occur in both Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Therefore, this symptom is **non-specific** and does not help to differentiate between the two conditions.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old man has a history of intermittent bloody diarrhea, tenesmus, fever, fatigue, and lower abdominal cramps for the past 2 weeks. On physical examination, he is lethargic and appears lean and pale. He has aphthous stomatitis, red congested conjunctiva, and tender swollen joints. At the doctor’s office, his pulse is 114/min, blood pressure is 102/76 mm Hg, respirations are 20/min, and his temperature is 39.4°C (102.9°F). There is vague lower abdominal tenderness and frank blood on rectal examination. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 7.6 g/dL
Hematocrit 33%
Total leucocyte count 22,000/mm3
Stool assay for C.difficile is negative
Abdominal X-ray shows no significant abnormality
He is symptomatically managed and referred to a gastroenterologist, who suggests a colonoscopy and contrast (barium) study for the diagnosis. Which of the following is the most likely combination of findings in his colonoscopy and barium study?
- A. Colonoscopy: Multiple vascular malformations that resemble telangiectasias on the colon wall, Barium study: Normal
- B. Colonoscopy: Patches of mucosal erosions with pseudomembrane formation, Barium study: Cobblestone appearance with strictures
- C. Colonoscopy: Discontinuous transmural ‘skip lesions’ with aphthoid linear ulcers and transverse fissures, non-caseating granulomas, and strictures, Barium study: Cobblestone appearance with strictures
- D. Colonoscopy: Normal, Barium study: Lead pipe colon appearance
- E. Colonoscopy: Continuous ulcerated lesions involving the mucosa and submucosa, granular mucosa, crypt abscess, and pseudopolyps, Barium study: Lead pipe colon appearance (Correct Answer)
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Colonoscopy: Continuous ulcerated lesions involving the mucosa and submucosa granular mucosa, crypt abscess, and pseudopolyps, Barium study: Lead pipe colon appearance***
- The patient's symptoms (bloody diarrhea, tenesmus, fever, fatigue, weight loss, aphthous stomatitis, red congested conjunctiva, tender swollen joints, anemia, high WBC count) are highly suggestive of **Ulcerative Colitis (UC)**.
- **UC** on colonoscopy is characterized by **continuous mucosal and submucosal inflammation**, granular mucosa, crypt abscesses, and **pseudopolyps**. The barium study finding of a **"lead pipe" colon** is classic for long-standing UC due to loss of haustrations.
*Colonoscopy: Multiple vascular malformations that resemble telangiectasias on the colon wall, Barium study: Normal*
- **Angiodysplasia** presents with vascular malformations, but it typically causes painless lower GI bleeding, not the inflammatory symptoms described.
- The patient's severe systemic symptoms (fever, weight loss, anemia, high WBC) are inconsistent with angiodysplasia.
*Colonoscopy: Patches of mucosal erosions with pseudomembrane formation, Barium study: Cobblestone appearance with strictures*
- **Pseudomembrane formation** is characteristic of **_Clostridioides difficile_ infection**, which has been ruled out by the stool assay.
- While "cobblestone appearance" and strictures can be seen in inflammatory bowel disease, the pseudomembranes point away from UC or Crohn's.
*Colonoscopy: Discontinuous transmural ‘skip lesions’ with aphthoid linear ulcers and transverse fissures, non-caseating granulomas, and strictures, Barium study: Cobblestone appearance with strictures*
- This description is characteristic of **Crohn's disease**, which involves **discontinuous**, **transmural inflammation** with **skip lesions**, aphthoid ulcers, and non-caseating granulomas.
- While some symptoms overlap with UC, the involvement of mucocutaneous lesions and generalized systemic symptoms fits better with the continuous inflammation of UC than the patchy disease of Crohn's.
*Colonoscopy: Normal, Barium study: Lead pipe colon appearance*
- A **normal colonoscopy** would be inconsistent with the patient's severe symptoms of bloody diarrhea, anemia, and elevated inflammatory markers.
- A "lead pipe" colon indicates chronic inflammatory changes, which would undoubtedly be visible on colonoscopy.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 4: A 22-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of abdominal pain, loose, non-bloody stools, and intermittent nausea. He also reports intermittent fever. He has not had vomiting, tenesmus, or rectal pain. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. His vital signs are within normal limits. Rectal exam is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 15,200/mm3 and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 44 mm/h. Test of the stool for occult blood and stool studies for infection are negative. A CT scan of the abdomen shows mural thickening and surrounding fat stranding of discrete regions of the terminal ileum and transverse colon. A colonoscopy is performed and biopsy specimens of the affected areas of the colon are taken. Which of the following findings is most specific for this patient's most likely diagnosis?
- A. Intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusion bodies
- B. Neutrophil-rich pseudomembranes
- C. Non-caseating granulomas (Correct Answer)
- D. Neutrophilic inflammation of the crypts
- E. Inflammation of the terminal ileum
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: **Non-caseating granulomas**
- The clinical presentation (abdominal pain, loose stools, fever, elevated white blood cells and ESR), imaging findings (mural thickening, fat stranding in terminal ileum and transverse colon), and negative stool cultures strongly suggest **Crohn's disease**.
- **Non-caseating granulomas** are a hallmark histological feature found in approximately 50-70% of Crohn's disease cases and are highly specific for the diagnosis, distinguishing it from ulcerative colitis and other causes of colitis.
*Intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusion bodies*
- These are characteristic histological findings in **cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection** of the gastrointestinal tract.
- While CMV colitis can cause similar symptoms, the presence of distinct inclusion bodies would be the primary diagnostic microscopic feature, which is not what we are looking for as the *most specific* for the suspected diagnosis.
*Neutrophil-rich pseudomembranes*
- These are characteristic of **Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI)**, also known as pseudomembranous colitis.
- The patient's negative stool studies for infection and absence of specific risk factors for CDI make this diagnosis less likely.
*Neutrophilic inflammation of the crypts*
- This describes **cryptitis** and **crypt abscesses**, which are common findings in various forms of colitis, including both **ulcerative colitis** and **Crohn's disease**, as well as infectious colitides.
- While present in Crohn's disease, it is not specific enough to definitively differentiate it from ulcerative colitis or other inflammatory conditions of the colon.
*Inflammation of the terminal ileum*
- While inflammation of the terminal ileum (ileitis) is a common and characteristic site of involvement in **Crohn's disease** and is consistent with the CT findings, it is a gross and macroscopic description of involvement rather than a specific microscopic finding on biopsy used for definitive diagnosis.
- Other conditions, such as **tuberculosis** or **Yersinia infection**, can also cause terminal ileitis, making it less specific as a *biopsy finding* for Crohn's disease compared to non-caseating granulomas.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 5: A 22-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 3-day history of fever and abdominal pain. She says that the pain is located in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen and feels crampy in nature. The pain has been associated with bloody diarrhea and joint tenderness. She has no past medical history but says that she returned 2 weeks ago from vacation in Asia where she tried many new foods. Her family history is significant for multiple cancers in close relatives. Physical exam reveals swollen ulcers on her legs, and colonoscopy reveals contiguous ulcerations from the rectum through the descending colon. Which of the following is associated with the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Noncaseating granulomas
- B. Severe aortic stenosis
- C. Gram-negative rod
- D. HLA-DQ2 positivity
- E. Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (Correct Answer)
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies***
- The patient's presentation with **bloody diarrhea**, low-grade fever, **crampy abdominal pain**, joint tenderness, and contiguous ulcerations in the colon is highly suggestive of **ulcerative colitis**.
- **Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (p-ANCA)** are found in 50-70% of patients with ulcerative colitis and are associated with a more extensive disease.
*Noncaseating granulomas*
- **Noncaseating granulomas** are a characteristic histological finding in **Crohn's disease**, not ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn's disease typically presents with **skip lesions**, **transmural inflammation**, and affects any part of the GI tract, often with perianal disease.
*Severe aortic stenosis*
- **Severe aortic stenosis** is a condition of the heart valves that can lead to symptoms like chest pain, syncope, and heart failure, and is not directly associated with the patient's gastrointestinal and systemic symptoms.
- While inflammatory conditions can rarely have cardiac manifestations, there's no direct link between aortic stenosis and inflammatory bowel disease in this context.
*Gram-negative rod*
- While infections, especially from **Gram-negative rods** like *Shigella* or *Salmonella*, can cause acute bloody diarrhea, the 3-day history with joint tenderness and contiguous ulcers on colonoscopy points more towards an inflammatory bowel disease.
- The chronicity and systemic involvement are less typical for an acute bacterial enteritis, although such infections might trigger IBD.
*HLA-DQ2 positivity*
- **HLA-DQ2 positivity** is strongly associated with **celiac disease**, an immune-mediated enteropathy triggered by gluten.
- Celiac disease typically presents with malabsorption symptoms like fatty stools, weight loss, and iron deficiency, rather than bloody diarrhea and contiguous colonic ulcerations.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of multiple right inframammary lumps. They are tender and have a foul-smelling odor. She has had previous episodes of painful swellings in the axillae 12 months ago that resolved with antibiotic therapy, leaving some scarring. She has Crohn disease. Menses occur at irregular 18- to 40-day intervals and last 1–5 days. The patient's only medication is mesalamine. She appears anxious. She is 162 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 87 kg (192 lb); BMI is 33 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination of the right inframammary fold shows multiple tender, erythematous nodules and fistulas with purulent discharge. Hirsutism is present. Her fasting glucose concentration is 136 mg/dL. Which of the following areas is most likely to also be affected by this patient's condition?
- A. Forehead
- B. Back
- C. Shin
- D. Central face
- E. Groin (Correct Answer)
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Groin***
- The patient's presentation with recurrent tender, foul-smelling lumps in the **inframammary fold** and past episodes in the **axillae**, along with scarring, strongly suggests **hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)**. HS commonly affects areas with a high density of apocrine glands, including the **axillae, groin, inframammary folds**, and anogenital region.
- Her history of **Crohn disease**, obesity (BMI 33 kg/m²), and possible insulin resistance (fasting glucose 136 mg/dL) are all associated risk factors for HS. The groin is another typical site for lesions.
*Forehead*
- The forehead is generally considered part of the **T-zone of the face**, where sebaceous glands are abundant, but it is not a primary site for *hidradenitis suppurativa*.
- Lesions in this area are more commonly associated with **acne vulgaris** or other folliculitis, which typically present differently.
*Back*
- While the back can be affected by various follicular conditions like **acne inversa** or folliculitis, it is not a primary or highly characteristic site for the deep, painful, and recurring lesions of *hidradenitis suppurativa* in the way intertriginous areas are.
- The specific pattern of involvement in **skin folds** points away from the broader back area as an equally likely site.
*Shin*
- The shins are not typically affected by *hidradenitis suppurativa* as they lack the high concentration of **apocrine glands** found in the classic affected areas.
- Lesions on the shin are more characteristic of conditions like **erythema nodosum** or other forms of vasculitis, which have different presentations.
*Central face*
- The central face, like the forehead, is rich in **sebaceous glands** and is a common site for conditions like **acne vulgaris** or rosacea.
- However, it is not a typical anatomical location for the characteristic deep, recurrent abscesses and sinus tracts seen in *hidradenitis suppurativa*.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 7: A 22-year-old man presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain. The patient states that he has had right lower quadrant abdominal pain for "a while now". The pain comes and goes, and today it is particularly painful. The patient is a college student studying philosophy. He drinks alcohol occasionally and is currently sexually active. He states that sometimes he feels anxious about school. The patient's father died of colon cancer at the age of 55, and his mother died of breast cancer when she was 57. The patient has a past medical history of anxiety and depression which is not currently treated. Review of systems is positive for bloody diarrhea. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 100/58 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Cardiopulmonary exam is within normal limits. Abdominal exam reveals diffuse tenderness. A fecal occult blood test is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Irritable bowel syndrome
- B. Colon cancer
- C. Appendicitis
- D. Infectious colitis
- E. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (Correct Answer)
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)***
- The patient's presentation with **recurrent right lower quadrant pain**, **bloody diarrhea**, a **positive fecal occult blood test**, and a family history concerning for GI issues (colon cancer in father) in a young adult is highly suggestive of IBD, specifically **Crohn's disease** due to the RLQ pain location.
- His history of anxiety and depression is common in IBD patients, and the elevated pulse with mild hypotension suggests **volume depletion** from bloody diarrhea, a common complication.
*Irritable bowel syndrome*
- While IBS can cause recurrent abdominal pain, it is characterized by **functional bowel changes** and typically does not present with **bloody diarrhea** or a positive fecal occult blood test.
- IBS symptoms are often relieved by defecation and are not usually associated with significant systemic inflammation or blood loss.
*Colon cancer*
- Colon cancer is less likely in a **22-year-old** presenting with these acute symptoms, despite the family history, as it typically affects older individuals.
- While it can cause bloody stools and abdominal pain, the **recurrent nature** and acute presentation with bloody diarrhea are more classic for IBD in this age group.
*Appendicitis*
- Appendicitis presents with acute, **migratory right lower quadrant pain** that typically progresses and worsens over hours to a day, often with fever and leukocytosis.
- The given history of pain for "**a while now**" and bloody diarrhea makes appendicitis an unlikely primary diagnosis.
*Infectious colitis*
- Infectious colitis can cause abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea, but it's usually **acute in onset** without a long history of recurrent symptoms.
- While possible, the **recurrent nature** of the pain and bloody diarrhea for "**a while now**" makes a chronic condition like IBD more probable.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 8: A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department for severe abdominal pain. The patient states that for the past week he has felt fatigued and had a fever. He states that he has had crampy lower abdominal pain and has experienced several bouts of diarrhea. The patient states that his pain is somewhat relieved by defecation. The patient returned from a camping trip 2 weeks ago in the Rocky Mountains. He is concerned that consuming undercooked meats on his trip may have caused this. He admits to consuming beef and chicken cooked over a fire pit. The patient is started on IV fluids and morphine. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 130/77 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Laboratory studies are ordered and are seen below.
Hemoglobin: 10 g/dL
Hematocrit: 28%
Leukocyte count: 11,500 cells/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 445,000/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 140 mEq/L
Cl-: 102 mEq/L
K+: 4.1 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
BUN: 24 mg/dL
Glucose: 145 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL
Ca2+: 9.6 mg/dL
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): 75 mm/hour
Physical exam is notable for a patient who appears to be uncomfortable. Gastrointestinal (GI) exam is notable for abdominal pain upon palpation. Ear, nose, and throat exam is notable for multiple painful shallow ulcers in the patient's mouth. Inspection of the patient's lower extremities reveals a pruritic ring-like lesion. Cardiac and pulmonary exams are within normal limits. Which of the following best describes this patient's underlying condition?
- A. p-ANCA positive autoimmune bowel disease
- B. Transmural granulomas in the bowel (Correct Answer)
- C. Gram-negative microaerophilic organism
- D. Rectal mucosa outpouching
- E. Bowel wall spasticity
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Transmural granulomas in the bowel***
- This patient's symptoms, including **chronic diarrhea**, **abdominal pain relieved by defecation**, **oral ulcers**, **fatigue**, **fever**, and **elevated ESR**, along with a **pruritic ring-like lesion** (suggestive of erythema nodosum, a common extraintestinal manifestation), are highly indicative of **Crohn's disease**.
- **Crohn's disease** is characterized by **transmural inflammation** of any part of the GI tract, often with the formation of **non-caseating granulomas**.
*p-ANCA positive autoimmune bowel disease*
- This describes **ulcerative colitis**, which is typically associated with **p-ANCA positivity** in a subset of patients.
- Unlike the diffuse and continuous inflammation seen in ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease features **skip lesions** and **transmural inflammation**, which aligns better with the varied symptoms and extraintestinal manifestations presented.
*Gram-negative microaerophilic organism*
- This refers to bacterial infections such as those caused by **Campylobacter jejuni** or **Helicobacter pylori**, which can cause GI symptoms.
- While the patient's camping trip and consumption of undercooked meat might suggest an infectious etiology, the **chronic nature of symptoms** (week-long fatigue and fever), **oral ulcers**, **elevated ESR**, and **erythema nodosum-like lesion** point more strongly towards an autoimmune/inflammatory bowel disease rather than an acute bacterial infection.
*Rectal mucosa outpouching*
- **Diverticula** are outpouchings of the colon, commonly affecting the sigmoid colon, and are typically associated with **diverticulitis** when inflamed.
- This condition does not explain the widespread systemic symptoms, oral ulcers, or the chronic, crampy abdominal pain and diarrhea pattern seen in this patient.
*Bowel wall spasticity*
- **Bowel spasticity** is a feature of **irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)**.
- While IBS can cause crampy abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits, it is a **functional disorder** and does not cause **fever**, **oral ulcers**, **elevated ESR**, or significant **anemia** and **thrombocytosis** as seen in this patient.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 9: A 38-year-old woman with a history of Crohn’s disease presents with a 3-week history of weight gain. The patient also presents with a 1-month history of abdominal pain, cramping, and bloody diarrhea consistent with worsening of her inflammatory bowel disease. Past medical history is significant for Crohn’s disease diagnosed 2 years ago for which she currently takes an oral medication daily and intermittently receives intravenous medication she cannot recall the name of. Her temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 120/90 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical examination reveals significant truncal weight gain. The patient has excessive facial hair in addition to purplish striae on her abdomen. Which of the following laboratory findings would most likely be found in this patient?
- A. Hyperglycemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Hypoglycemia
- C. Metabolic acidosis
- D. Hyperkalemia
- E. Hypokalemia
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Hyperglycemia***
- The patient exhibits **Cushing's syndrome** due to chronic corticosteroid use for Crohn's disease, with classic features including truncal obesity, hirsutism, and purplish striae.
- **Hyperglycemia is the most common and expected metabolic abnormality** with chronic glucocorticoid therapy, occurring in 30-40% of patients.
- Glucocorticoids cause hyperglycemia by **increasing gluconeogenesis**, **promoting glycogenolysis**, and **inducing insulin resistance** in peripheral tissues.
- This is a direct and prominent effect of glucocorticoid excess, making it the most likely laboratory finding in this clinical scenario.
*Hypokalemia*
- While possible with high-dose corticosteroids, hypokalemia is **less common** with modern synthetic glucocorticoids (prednisone, methylprednisolone) which have minimal mineralocorticoid activity.
- Hypokalemia primarily occurs with corticosteroids having significant mineralocorticoid effects (hydrocortisone, cortisone) or at very high doses.
- Compared to hyperglycemia, this is not the "most likely" finding in typical glucocorticoid therapy.
*Hypoglycemia*
- Glucocorticoids cause **hyperglycemia**, not hypoglycemia, due to their counter-regulatory effects on glucose metabolism.
- This is the opposite of what occurs with steroid excess.
*Metabolic acidosis*
- **Metabolic alkalosis**, not acidosis, can occur with Cushing's syndrome due to mineralocorticoid effects promoting hydrogen ion excretion.
- The hypokalemia that may develop is typically accompanied by alkalosis, not acidosis.
*Hyperkalemia*
- Glucocorticoids promote **potassium excretion** through mineralocorticoid receptor activation, making hyperkalemia unlikely.
- This would contradict the known effects of corticosteroid excess.
Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for evaluation of involuntary weight loss and recurrent abdominal pain. She noticed blood in her stool several times. The medical history is significant for the polycystic ovarian syndrome. The vital signs are as follows: temperature, 38.0°C (100.4°F); heart rate, 78/min; respiratory rate, 14/min; and blood pressure, 110/80 mm Hg. The family history is notable for paternal colon cancer. A colonoscopy is performed and is presented in the picture. What findings are expected?
- A. Crypt abscess (Correct Answer)
- B. Dermatitis herpetiformis
- C. Blunting of villi and crypt hyperplasia
- D. Non-caseating granulomas
- E. Aphthous stomatitis
Crohn's disease pathophysiology Explanation: ***Crypt abscess***
- The image provided shows **neutrophils infiltrating and filling the crypt lumina**, which are characteristic findings of crypt abscesses seen in **ulcerative colitis**.
- This pathology, combined with the patient's symptoms of **bloody diarrhea**, involuntary weight loss, and recurrent abdominal pain, points towards an inflammatory bowel disease, most consistent with ulcerative colitis.
*Dermatitis herpetiformis*
- This is a **skin manifestation of celiac disease**, presenting as intensely pruritic papules and vesicles, typically on extensor surfaces.
- It is not directly associated with inflammatory bowel disease, especially ulcerative colitis, and is not a histological finding in the colon.
*Blunting of villi and crypt hyperplasia*
- These are characteristic histological findings of **celiac disease** in the **small intestine**.
- The patient's symptoms and the histological image are from the colon, ruling out celiac disease as the primary diagnosis.
*Aphthous stomatitis*
- While **aphthous ulcers** are common extraintestinal manifestations in both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, it is a clinical finding in the oral cavity, not a histological finding in the colon.
- The question asks for *other findings expected* in the context of the provided colonic histology.
*Non-caseating granulomas*
- **Non-caseating granulomas** are a hallmark histological feature of **Crohn's disease**, not ulcerative colitis.
- The image shown, with widespread crypt abscesses and diffuse inflammatory infiltrate, is more typical of ulcerative colitis rather than Crohn's disease.
More Crohn's disease pathophysiology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.