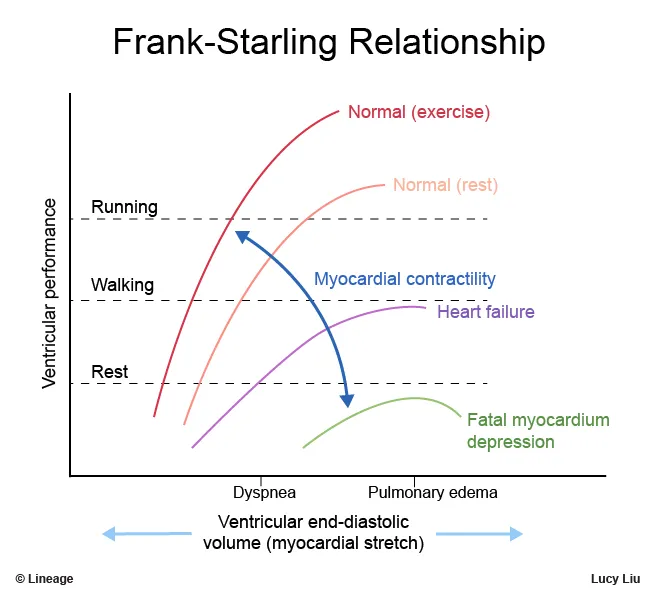
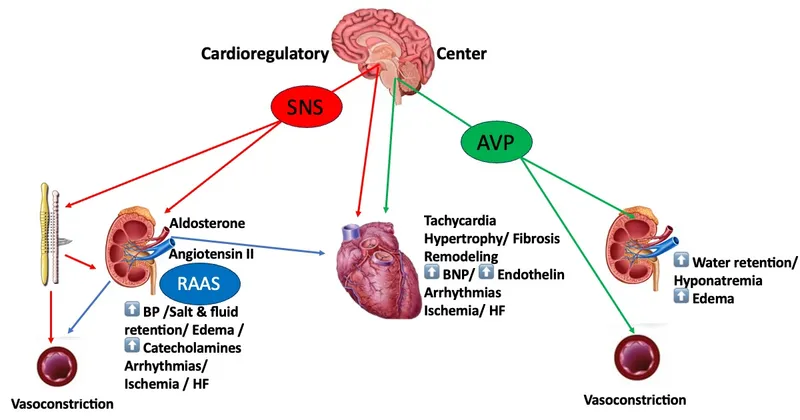
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Heart failure pathophysiology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old female volunteers for an invasive study to measure her cardiac function. She has no previous cardiovascular history and takes no medications. With the test subject at rest, the following data is collected using blood tests, intravascular probes, and a closed rebreathing circuit:
Blood hemoglobin concentration 14 g/dL
Arterial oxygen content 0.22 mL O2/mL
Arterial oxygen saturation 98%
Venous oxygen content 0.17 mL O2/mL
Venous oxygen saturation 78%
Oxygen consumption 250 mL/min
The patient's pulse is 75/min, respiratory rate is 14/ min, and blood pressure is 125/70 mm Hg. What is the cardiac output of this volunteer?
- A. Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.
- B. Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.
- C. 250 mL/min
- D. 5.0 L/min (Correct Answer)
- E. 50 L/min
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***5.0 L/min***
- Cardiac output can be calculated using the **Fick principle**: Cardiac Output $(\text{CO}) = \frac{{\text{Oxygen Consumption}}}{{\text{Arterial } \text{O}_2 \text{ Content} - \text{Venous O}_2 \text{ Content}}}$.
- Given Oxygen Consumption = 250 mL/min, Arterial O$_2$ Content = 0.22 mL/mL, and Venous O$_2$ Content = 0.17 mL/mL. Thus, CO = $\frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{(0.22 - 0.17) \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = \frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{0.05 \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = 5000 \text{ mL/min } = 5.0 \text{ L/min}$.
*Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- **Body surface area (BSA)** is used to calculate **cardiac index**, which is cardiac output normalized to body size, but not cardiac output directly.
- While a normal cardiac output might be compared to a patient's BSA for context, it is not a necessary component for calculating the absolute cardiac output.
*Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- Cardiac output can be calculated as **Stroke Volume (SV) x Heart Rate (HR)**. However, stroke volume is not provided directly in this question.
- The Fick principle allows for the calculation of cardiac output **without explicit knowledge of stroke volume** or heart rate, using oxygen consumption and arteriovenous oxygen difference.
*250 mL/min*
- 250 mL/min represents the **oxygen consumption**, not the cardiac output.
- Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute, which is influenced by both oxygen consumption and the difference in oxygen content between arterial and venous blood.
*50 L/min*
- A cardiac output of 50 L/min is an **extremely high and physiologically impossible** value for a resting individual.
- This value is 10 times higher than the calculated cardiac output and typically represents a calculation error.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is studying patients with acute decompensated congestive heart failure. He takes measurements of a hormone released from atrial myocytes, as well as serial measurements of left atrial and left ventricular pressures. The investigator observes a positive correlation between left atrial pressures and the serum level of this hormone. Which of the following is most likely the mechanism of action of this hormone?
- A. Increases potassium excretion at the collecting ducts
- B. Constricts afferent renal arteriole
- C. Decreases sodium reabsorption at the collecting tubules (Correct Answer)
- D. Decreases reabsorption of bicarbonate in the proximal convoluted tubules
- E. Increases free water reabsorption from the distal tubules
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Decreases sodium reabsorption at the collecting tubules***
- The hormone described, exhibiting a positive correlation with left atrial pressure and released from atrial myocytes, is **Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)**.
- ANP promotes **natriuresis** (sodium excretion) and **diuresis** by directly inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubules, thereby reducing blood volume and cardiac preload.
*Increases potassium excretion at the collecting ducts*
- While ANP does promote fluid and electrolyte excretion, its primary effect is on sodium and water, not a direct increase in **potassium excretion**. **Aldosterone**, not ANP, primarily increases potassium secretion in the collecting ducts.
- This option describes a mechanism more consistent with **mineralocorticoid activity**, which is counteracted by ANP.
*Constricts afferent renal arteriole*
- ANP generally causes **vasodilation** of the afferent arteriole and constriction of the efferent arteriole, increasing glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- **Angiotensin II** is a primary constrictor of the afferent and efferent renal arterioles, which is the opposite effect of ANP.
*Decreases reabsorption of bicarbonate in the proximal convoluted tubules*
- This mechanism is primarily involved in **acid-base balance** and is influenced by factors like parathyroid hormone or respiratory/metabolic acidosis/alkalosis.
- ANP's main action is on **sodium and water balance**, not directly on bicarbonate reabsorption.
*Increases free water reabsorption from the distal tubules*
- **Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone, ADH)** is responsible for increasing free water reabsorption in the distal tubules and collecting ducts.
- ANP's action is to *increase* water excretion, working in opposition to ADH to reduce circulating fluid volume.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 3: A 59-year-old man with a history of congestive heart failure presents to his cardiologist for a follow-up visit. His past medical history is notable for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obesity. He takes metformin, glyburide, aspirin, lisinopril, and metoprolol. He has a 40 pack-year smoking history and drinks alcohol socially. His temperature is 99.1°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 150/65 mmHg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination reveals bilateral rales at the lung bases and 1+ edema in the bilateral legs. The physician decides to start the patient on an additional diuretic but warns the patient about an increased risk of breast enlargement. Which of the following is the most immediate physiologic effect of the medication in question?
- A. Decreased sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule
- B. Decreased bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule
- C. Decreased sodium reabsorption in the thick ascending limb
- D. Decreased renin enzyme activity
- E. Decreased sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct (Correct Answer)
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Decreased sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct***
- The physician is initiating **spironolactone**, an **aldosterone antagonist**, due to its known side effect of **gynecomastia** (breast enlargement).
- Spironolactone acts on the **collecting duct** to inhibit aldosterone's effects, leading to decreased sodium reabsorption and **decreased potassium excretion** (potassium-sparing effect).
- This makes it useful in heart failure but requires monitoring for **hyperkalemia**, especially in patients on ACE inhibitors like lisinopril.
*Decreased sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule*
- This is the primary site of action for **thiazide diuretics**, such as **hydrochlorothiazide** or **chlorthalidone**.
- While effective for heart failure, thiazides are not associated with breast enlargement.
*Decreased bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule*
- This is the main action of **carbonic anhydrase inhibitors**, such as **acetazolamide**.
- These diuretics are typically used for conditions like glaucoma or metabolic alkalosis, not first-line for heart failure and do not cause breast enlargement.
*Decreased sodium reabsorption in the thick ascending limb*
- This is the mechanism of action for **loop diuretics**, such as **furosemide** or **bumetanide**.
- Loop diuretics are potent and frequently used in heart failure, but they do not cause breast enlargement.
*Decreased renin enzyme activity*
- This effect is primarily seen with **beta-blockers** or **direct renin inhibitors**.
- While beta-blockers (like metoprolol, which the patient is already taking) are used in heart failure, they do not cause breast enlargement.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old male with a history of CHF presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath, lower leg edema, and fatigue. He is diagnosed with acute decompensated congestive heart failure, was admitted to the CCU, and treated with a medication that targets beta-1 adrenergic receptors preferentially over beta-2 adrenergic receptors. The prescribing physician explained that this medication would only be used temporarily as its efficacy decreases within 2-3 days due to receptor downregulation. Which of the following was prescribed?
- A. Epinephrine
- B. Norepinephrine
- C. Milrinone
- D. Isoproterenol
- E. Dobutamine (Correct Answer)
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Dobutamine***
- **Dobutamine** is a beta-1 adrenergic agonist preferentially acting on beta-1 receptors in the heart, increasing contractility and heart rate during acute decompensated heart failure.
- Its efficacy reduces over time due to **receptor downregulation**, making it effective for only short-term use, typically less than 72 hours.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is a non-selective adrenergic agonist acting on both alpha and beta receptors, causing vasoconstriction and bronchodilation in addition to cardiac stimulation.
- It is typically used in emergency situations like **cardiac arrest** and **anaphylaxis**, not primarily for acute CHF exacerbation in this manner.
*Norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** primarily acts on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing significant vasoconstriction, and has some beta-1 agonistic effects.
- It is mainly used as a **vasopressor** in septic shock or severe hypotension to increase systemic vascular resistance, rather than directly improving cardiac output in decompensated CHF.
*Milrinone*
- **Milrinone** is a phosphodiesterase-3 inhibitor, increasing intracellular cAMP levels and leading to positive inotropy and vasodilation.
- While used in acute heart failure, its mechanism is distinct from adrenergic agonists, and its efficacy is not limited by a rapid receptor downregulation mechanism as described.
*Isoproterenol*
- **Isoproterenol** is a non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist, stimulating both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, leading to increased heart rate and contractility, as well as bronchodilation and vasodilation.
- Due to its strong chronotropic effects and potential for severe arrhythmias and hypotension, it is rarely used in CHF and is primarily reserved for conditions like **bradycardia** or **torsades de pointes**.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 5: A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department with shortness of breath and weakness. Past medical history includes coronary artery disease, arterial hypertension, and chronic heart failure. He reports that the symptoms started around 2 weeks ago and have been gradually worsening. His temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F), blood pressure is 135/90 mm Hg, heart rate is 95/min, respiratory rate is 24/min, and oxygen saturation is 94% on room air. On examination, mild jugular venous distention is noted. Auscultation reveals bilateral loud crackles. Pitting edema of the lower extremities is noted symmetrically. His plasma brain natriuretic peptide level on rapid bedside assay is 500 pg/mL (reference range < 125 pg/mL). A chest X-ray shows enlarged cardiac silhouette. He is diagnosed with acute on chronic left heart failure with pulmonary edema and receives immediate care with furosemide. The physician proposes a drug trial with a new BNP stabilizing agent. Which of the following changes below are expected to happen if the patient is enrolled in this trial?
- A. Increased potassium release from cardiomyocytes
- B. Increased water reabsorption by the renal collecting ducts
- C. Increased blood pressure
- D. Inhibition of funny sodium channels
- E. Restricted aldosterone release (Correct Answer)
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Restricted aldosterone release***
- **BNP** acts to counter the **RAAS** system. By stabilizing BNP, there will be increased **natriuresis** and reduced levels of aldosterone due to its inhibitory effect on **renin secretion**.
- This **aldosterone** restriction contributes to **diuresis** and vasodilation, which ultimately helps to reduce cardiac preload and afterload.
*Increased potassium release from cardiomyocytes*
- An increase in **potassium release** from cardiomyocytes is not a direct or expected effect of a **BNP stabilizing agent**.
- BNP primarily influences **sodium** and **water balance** through renal and vascular effects, not direct cardiomyocyte potassium regulation.
*Increased water reabsorption by the renal collecting ducts*
- **BNP** promotes **natriuresis** and **diuresis**, leading to decreased water reabsorption in the renal collecting ducts.
- A BNP stabilizing agent would therefore **decrease water reabsorption**, working against the action of **ADH**.
*Increased blood pressure*
- **BNP** acts as a **vasodilator** and promotes fluid excretion, which typically leads to a **reduction** in blood pressure.
- Stabilizing BNP would therefore be expected to maintain or reduce **blood pressure**, not increase it.
*Inhibition of funny sodium channels*
- **Funny channels** (If channels) are primarily found in the **pacemaker cells** of the heart and are involved in controlling heart rate.
- While BNP can influence heart rate indirectly, its primary mechanism of action does not involve direct **inhibition of funny sodium channels**.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 6: A 71-year-old man presents to his cardiologist with a 1-month history of increasing shortness of breath. He says that he is finding it very difficult to walk up the flight of stairs to his bedroom and he is no longer able to sleep flat on his bed because he wakes up choking for breath. His past medical history is significant for a myocardial infarction 3 years ago. On physical exam, he is found to have diffuse, moist crackles bilaterally on pulmonary auscultation and pitting edema in his lower extremities. Serum tests reveal an increased abundance of a product produced by cardiac myocytes. Which of the following most likely describes the function of this product?
- A. Increases water reabsorption in the kidney
- B. Stimulates parasympathetic nerves
- C. Increases conversion of angiotensin
- D. Inhibits release of renin (Correct Answer)
- E. Binds to intracellular receptors in the collecting duct
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Inhibits release of renin***
- The patient's symptoms (shortness of breath, orthopnea, crackles, edema) and history of MI are consistent with **heart failure**, leading to increased natriuretic peptide production from cardiac myocytes due to ventricular stretch.
- **Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)**, released in heart failure, counteracts fluid retention by inhibiting renin release, thereby reducing aldosterone and angiotensin II, and promoting diuresis and natriuresis.
*Increases water reabsorption in the kidney*
- This is the primary function of **Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)**, which acts on the collecting ducts to increase water reabsorption.
- Natriuretic peptides, in contrast, promote water excretion rather than retention.
*Stimulates parasympathetic nerves*
- The **parasympathetic nervous system** primarily slows heart rate and promotes digestion through the vagus nerve.
- Natriuretic peptides primarily exert their effects on the cardiovascular and renal systems to regulate blood volume and pressure, not through direct nervous system stimulation.
*Increases conversion of angiotensin*
- The conversion of angiotensin I to **angiotensin II** is mediated by **angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)**, primarily in the lungs.
- The product described (natriuretic peptide) works to *inhibit* the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), thus indirectly reducing angiotensin II levels.
*Binds to intracellular receptors in the collecting duct*
- Hormones that bind to **intracellular receptors** are typically steroid hormones (e.g., aldosterone, cortisol) that regulate gene expression.
- Natriuretic peptides bind to **cell-surface receptors** (guanylyl cyclase receptors) on target cells, activating second messenger systems like cGMP.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 7: A 72-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and systolic heart failure comes to the physician because of a 5-day history of progressively worsening shortness of breath at rest. Physical examination shows jugular venous distention, diffuse crackles over the lower lung fields, and bilateral lower extremity edema. As a part of treatment, he is given a derivative of a hormone that acts by altering guanylate cyclase activity. This drug has been found to reduce pulmonary capillary wedge pressure and causes systemic hypotension as an adverse effect. The drug is most likely a derivative of which of the following hormones?
- A. Prostacyclin
- B. Aldosterone
- C. Somatostatin
- D. Brain natriuretic peptide (Correct Answer)
- E. Angiotensin II
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Brain natriuretic peptide***
- **Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)** derivatives, like nesiritide, activate **guanylate cyclase**, leading to increased cGMP, vasodilation, and reduced preload/afterload, alleviating heart failure symptoms.
- The patient's symptoms (shortness of breath, jugular venous distention, crackles, edema) are classic for **acute decompensated heart failure**, making a BNP derivative an appropriate treatment.
*Prostacyclin*
- **Prostacyclin** analogs (e.g., epoprostenol) are primarily used for **pulmonary hypertension** due to their potent vasodilatory effects in the pulmonary circulation.
- They activate **adenylyl cyclase** (increasing cAMP), not guanylate cyclase (which increases cGMP), representing a different mechanism of action.
*Aldosterone*
- **Aldosterone** is a mineralocorticoid that promotes **sodium and water retention** and potassium excretion, exacerbating heart failure symptoms.
- Its antagonists (e.g., spironolactone) are used in chronic heart failure but do not directly act via guanylate cyclase for acute symptom relief.
*Somatostatin*
- **Somatostatin** is a peptide hormone that **inhibits the secretion of various hormones**, including growth hormone, insulin, and glucagon.
- It is used in conditions like acromegaly or variceal bleeding and has no direct role in heart failure management via guanylate cyclase.
*Angiotensin II*
- **Angiotensin II** is a potent vasoconstrictor and a key component of the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)**, contributing to hypertension and heart failure progression.
- Drugs targeting angiotensin II (ACE inhibitors, ARBs) reduce its effects but do not act by directly altering guanylate cyclase activity; instead, they block its receptors or synthesis.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 9: You are interested in studying the etiology of heart failure reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and attempt to construct an appropriate design study. Specifically, you wish to look for potential causality between dietary glucose consumption and HFrEF. Which of the following study designs would allow you to assess for and determine this causality?
- A. Cross-sectional study
- B. Case series
- C. Cohort study (Correct Answer)
- D. Case-control study
- E. Randomized controlled trial
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Cohort study***
- A **cohort study** observes a group of individuals over time to identify risk factors and outcomes, allowing for the assessment of **temporal relationships** between exposure (dietary glucose) and outcome (HFrEF).
- This design is suitable for establishing a potential **causal link** as it tracks participants from exposure to outcome, enabling the calculation of incidence rates and relative risks.
*Cross-sectional study*
- A **cross-sectional study** measures exposure and outcome simultaneously at a single point in time, making it impossible to determine the **temporal sequence** of events.
- This design can only identify **associations** or correlations, not causation, as it cannot establish whether high glucose consumption preceded HFrEF.
*Case series*
- A **case series** describes characteristics of a group of patients with a particular disease or exposure, often to highlight unusual clinical features, but it lacks a **comparison group**.
- It cannot assess causality because it does not provide information on the frequency of exposure in healthy individuals or the incidence of the disease in unexposed individuals.
*Case-control study*
- A **case-control study** compares individuals with the outcome (cases) to those without the outcome (controls) to determine past exposures, which makes it prone to **recall bias**.
- While it can suggest associations, it cannot definitively establish a temporal relationship or causation as the outcome is already known when exposure is assessed.
*Randomized controlled trial*
- A **randomized controlled trial (RCT)** is the gold standard for establishing causation by randomly assigning participants to an intervention or control group, but it may not be ethical or feasible for studying long-term dietary exposures and chronic diseases like HFrEF due to the long follow-up period and complexity of diet.
- While ideal for causality, directly controlling and randomizing dietary glucose intake over decades to observe HFrEF development might be practically challenging or unethical.
Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG Question 10: A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician because of 2 episodes of loss of consciousness over the past week. She recovered immediately and was not confused following the episodes. During the past 5 months, she has also had increased shortness of breath and palpitations. She has been unable to carry out her daily activities. She also reports some chest tightness that resolves with rest. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. She immigrated with her family from India 10 years ago. Her temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 115/min and irregular, and blood pressure is 108/70 mm Hg. Examination shows jugular venous distention and pitting edema below the knees. Bilateral crackles are heard at the lung bases. Cardiac examination shows an accentuated and split S2. There is an opening snap followed by a low-pitched diastolic murmur in the fifth left intercostal space at the midclavicular line. An ECG shows atrial fibrillation and right axis deviation. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of these findings?
- A. Increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure
- B. Increased left to right shunting
- C. Increased systemic arterial resistance
- D. Increased left atrial pressure (Correct Answer)
- E. Decreased left ventricular contractility
Heart failure pathophysiology Explanation: ***Increased left atrial pressure***
- The patient's symptoms (dyspnea, palpitations, chest tightness, volume overload signs like JVD, edema, crackles) and cardiac findings (**accentuated S2, opening snap, diastolic murmur**) are highly suggestive of **mitral stenosis**.
- **Mitral stenosis** causes obstruction of blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, leading to a significant increase in **left atrial pressure** to maintain cardiac output, which can then cause atrial fibrillation and pulmonary hypertension.
*Increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure*
- This is typically seen in conditions like **aortic stenosis**, **aortic regurgitation**, or **decompensated heart failure** where the left ventricle is distended or failing.
- The patient's presentation with an **opening snap** and **diastolic murmur** points away from primary left ventricular pathology causing elevated LVEDP, and more towards a valvular issue upstream.
*Increased left to right shunting*
- This typically occurs in **septal defects** (e.g., VSD, ASD, PDA) and would lead to symptoms of pulmonary hypertension and right heart strain, but the specific murmur and opening snap are not characteristic of a shunt.
- While it can cause right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary hypertension, the classic auscultatory findings are distinct from those described here.
*Increased systemic arterial resistance*
- This is characteristic of **hypertension** or conditions causing systemic vasoconstriction, which primarily affect afterload on the left ventricle.
- While it can lead to left ventricular hypertrophy over time, it does not explain the specific findings of an **opening snap** and **diastolic murmur**, or the symptoms of pulmonary congestion in this context.
*Decreased left ventricular contractility*
- This would lead to **systolic heart failure** with reduced ejection fraction, causing symptoms like fatigue and dyspnea, and often a **S3 gallop** with a systolic murmur if mitral regurgitation develops.
- However, it does not explain the specific auscultatory findings of an **opening snap** and **diastolic murmur** that are pathognomonic for mitral stenosis.
More Heart failure pathophysiology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.