Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
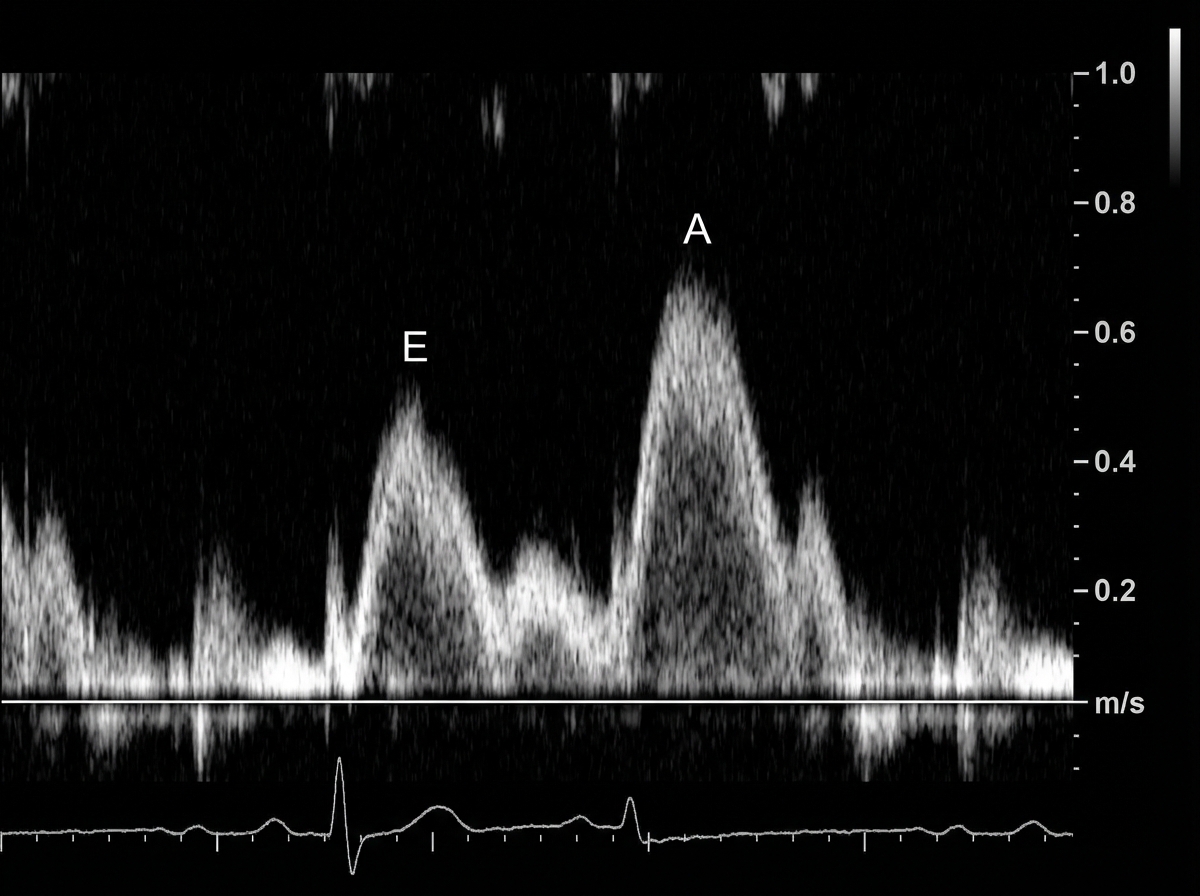
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 1: A 49-year-old man presents to his physician complaining of weakness and fatigue. On exam, you note significant peripheral edema. Transthoracic echocardiogram is performed and reveals a preserved ejection fraction with impaired diastolic relaxation. A representative still image is shown in Image A. Which of the following is likely the cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Hemochromatosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Heavy, long-term alcohol consumption
- C. History of myocardial infarction
- D. History of a recent viral infection
- E. Previous treatment with doxorubicin
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Hemochromatosis***
- **Hemochromatosis** can lead to **restrictive cardiomyopathy** due to iron deposition in the myocardium, causing **diastolic dysfunction** with a **preserved ejection fraction**.
- The symptoms of **weakness**, **fatigue**, and **peripheral edema** are consistent with **heart failure** secondary to this cardiac impairment.
*Heavy, long-term alcohol consumption*
- **Alcoholic cardiomyopathy** typically presents as **dilated cardiomyopathy**, characterized by **systolic dysfunction** and a **reduced ejection fraction**, which contradicts the preserved ejection fraction seen in this patient.
- While chronic alcohol use can cause heart failure symptoms, the specific echocardiographic findings do not align with this etiology.
*History of myocardial infarction*
- A **myocardial infarction** commonly leads to **systolic dysfunction** or **ischemic cardiomyopathy**, resulting in a **reduced ejection fraction** due to scar tissue formation and impaired contractility.
- The patient's preserved ejection fraction and primary diastolic relaxation abnormality make this diagnosis less likely.
*History of a recent viral infection*
- A recent viral infection can cause **viral myocarditis**, which typically leads to **dilated cardiomyopathy** and **systolic dysfunction** with a **reduced ejection fraction**.
- The observed preserved ejection fraction and isolated diastolic relaxation impairment are not characteristic features of acute viral myocarditis.
*Previous treatment with doxorubicin*
- **Doxorubicin** (an anthracycline) is a well-known cardiotoxic agent that causes **dilated cardiomyopathy** with a **reduced ejection fraction**, primarily affecting **systolic function**.
- The patient's preserved ejection fraction makes doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity an unlikely cause of his current presentation.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 2: A 76-year-old woman seeks evaluation at a medical office for chest pain and shortness of breath on exertion of 3 months' duration. Physical examination shows bilateral pitting edema on the legs. On auscultation, diffuse crackles are heard over the lower lung fields. Cardiac examination shows jugular venous distention and an S3 gallop. Troponin is undetectable. A chest film shows cardiomegaly and pulmonary edema. Which of the following medications would be effective in lowering her risk of mortality?
- A. Propranolol
- B. Digoxin
- C. Lisinopril (Correct Answer)
- D. Furosemide
- E. Verapamil
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Lisinopril***
- The patient presents with classic signs and symptoms of **heart failure**, including dyspnea on exertion, bilateral pitting edema, jugular venous distention, S3 gallop, cardiomegaly, and pulmonary edema. **ACE inhibitors** like lisinopril are cornerstone therapy for **heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)** and significantly reduce mortality.
- They work by blocking the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)**, leading to **vasodilation**, reduced preload and afterload, and prevention of cardiac remodeling.
*Propranolol*
- While beta-blockers are used in heart failure, **non-selective beta-blockers** like propranolol are generally not preferred due to potential for exacerbating symptoms in acutely decompensated heart failure and lack of evidence for mortality benefit in this context.
- **Cardioselective beta-blockers** (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol succinate) are used in stable heart failure, but propranolol's broad effects make it less suitable for this specific indication, especially when there are signs of decompensation.
*Digoxin*
- Digoxin can improve symptoms and reduce hospitalizations in heart failure, but it **does not demonstrate a mortality benefit** in patients with heart failure.
- It is primarily used for **symptom control** in patients with HFrEF, especially those with coexisting **atrial fibrillation**.
*Furosemide*
- Furosemide is a **loop diuretic** that is highly effective at reducing fluid overload and improving symptoms like pulmonary edema and peripheral edema in heart failure.
- However, while it improves symptoms and quality of life, furosemide **does not independently reduce mortality** in heart failure.
*Verapamil*
- Verapamil, a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker**, is generally **contraindicated** in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) because it can worsen cardiac function and increase mortality.
- It has **negative inotropic effects**, which can further impair the already weakened pumping ability of the heart.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 3: A 64-year-old man presents to his physician for a scheduled follow-up visit. He has chronic left-sided heart failure with systolic dysfunction. His current regular medications include captopril and digoxin, which were started after his last episode of symptomatic heart failure approximately 3 months ago. His last episode of heart failure was accompanied by atrial fibrillation, which followed an alcohol binge over a weekend. Since then he stopped drinking. He reports that he has no current symptoms at rest and is able to perform regular physical exercise without limitation. On physical examination, mild bipedal edema is noted. The physician suggested to him that he should discontinue digoxin and continue captopril and scheduled him for the next follow-up visit. Which of the following statements best justifies the suggestion made by the physician?
- A. Long-term digoxin therapy produces significant survival benefits in patients with heart failure, but at the cost of increased heart failure-related admissions.
- B. Both captopril and digoxin are likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, but digoxin has more severe side effects.
- C. Captopril is likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, unlike digoxin.
- D. Digoxin does not benefit patients with left-sided heart failure in the absence of atrial fibrillation.
- E. Digoxin is useful to treat atrial fibrillation, but does not benefit patients with systolic dysfunction who are in sinus rhythm. (Correct Answer)
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Digoxin is useful to treat atrial fibrillation, but does not benefit patients with systolic dysfunction who are in sinus rhythm.***
- The patient's **atrial fibrillation** was likely triggered by the alcohol binge and has since resolved, suggesting he is now in **sinus rhythm**.
- Digoxin's primary benefit in heart failure with **systolic dysfunction** (HFrEF) is to control ventricular rate in patients with **atrial fibrillation**, but it does not offer survival benefit in HFrEF patients who are in **sinus rhythm** and well-managed with other therapies.
*Long-term digoxin therapy produces significant survival benefits in patients with heart failure, but at the cost of increased heart failure-related admissions.*
- This statement is incorrect; digoxin has been shown to **reduce hospital admissions** for heart failure, but it does **not provide a significant survival benefit** in patients with HFrEF in sinus rhythm.
- The main benefit of digoxin in HFrEF is to improve symptoms and quality of life, alongside reducing hospitalizations, but not prolonging life.
*Both captopril and digoxin are likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, but digoxin has more severe side effects.*
- **Captopril (an ACE inhibitor)** does improve **long-term survival** in heart failure, but **digoxin does not** demonstrably improve survival.
- While digoxin can have side effects, its lack of survival benefit for HFrEF in sinus rhythm is the primary reason for discontinuation, not just side effect severity.
*Captopril is likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, unlike digoxin.*
- This statement is partially correct that **captopril improves survival**, but it does not fully explain the physician's decision to discontinue digoxin.
- The key missing piece is the patient's current **sinus rhythm** and the lack of benefit of digoxin in that specific context for HFrEF.
*Digoxin does not benefit patients with left-sided heart failure in the absence of atrial fibrillation.*
- This statement is nearly correct, but "left-sided heart failure" is broad. It is specifically in patients with **systolic dysfunction (HFrEF)** who are in **sinus rhythm** that digoxin lacks significant benefit beyond symptom control, and does not provide survival benefit.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 4: The serum brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-BNP are elevated. A diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is made. In addition to supplemental oxygen therapy, which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Intravenous dobutamine
- B. Intravenous furosemide therapy (Correct Answer)
- C. Intravenous morphine therapy
- D. Thoracentesis
- E. Intermittent hemodialysis
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Intravenous furosemide therapy***
- Heart failure with **preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)** often presents with **pulmonary congestion** due to elevated filling pressures.
- **Furosemide**, a loop diuretic, effectively reduces fluid overload and associated symptoms by increasing renal excretion of sodium and water.
*Intravenous dobutamine*
- **Dobutamine** is an inotropic agent that increases myocardial contractility and heart rate.
- It is typically used for **acute decompensated heart failure with low cardiac output** and is generally avoided in HFpEF unless there is significant hypoperfusion, as it can worsen myocardial oxygen demand and diastolic dysfunction.
*Intravenous morphine therapy*
- **Morphine** can be used in acute heart failure to reduce preload and anxiety, but it is not a primary treatment for the underlying fluid overload.
- It can cause respiratory depression and hypotension, and its use is typically reserved for patients with severe pain or dyspnea not adequately managed by other therapies.
*Thoracentesis*
- **Thoracentesis** is indicated for symptomatic **pleural effusions** causing respiratory distress.
- While pleural effusions can occur in heart failure, initial management of generalized fluid overload typically involves diuretics, making thoracentesis a secondary intervention if diuretic therapy is insufficient.
*Intermittent hemodialysis*
- **Intermittent hemodialysis** is an invasive procedure primarily used for severe renal failure or refractory fluid overload that has not responded to maximal diuretic therapy.
- It is not the initial step in managing heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and would only be considered in highly selected cases with **acute kidney injury** or diuretic resistance.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 5: On cardiology service rounds, your team sees a patient admitted with an acute congestive heart failure exacerbation. In congestive heart failure, decreased cardiac function leads to decreased renal perfusion, which eventually leads to excess volume retention. To test your knowledge of physiology, your attending asks you which segment of the nephron is responsible for the majority of water absorption. Which of the following is a correct pairing of the segment of the nephron that reabsorbs the majority of all filtered water with the means by which that segment absorbs water?
- A. Distal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption
- B. Distal convoluted tubule via aquaporin channels
- C. Thick ascending loop of Henle via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption
- D. Proximal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption (Correct Answer)
- E. Collecting duct via aquaporin channels
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Proximal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption***
- The **proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)** is responsible for reabsorbing approximately **65-70% of filtered water**, making it the primary site of water reabsorption in the nephron.
- This water reabsorption primarily occurs **passively**, following the active reabsorption of solutes (especially **sodium ions**), which creates an osmotic gradient.
*Distal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption*
- The **distal convoluted tubule (DCT)** reabsorbs a much smaller percentage of filtered water (around 5-10%) and its water reabsorption is largely **regulated by ADH**, not primarily simple passive diffusion following bulk ion reabsorption.
- While some passive water movement occurs, it is not the main mechanism or location for the majority of water reabsorption.
*Distal convoluted tubule via aquaporin channels*
- While aquaporin channels do play a role in water reabsorption in the DCT, particularly under the influence of **ADH**, the DCT is not the segment responsible for the **majority of all filtered water absorption**.
- The bulk of water reabsorption occurs earlier in the nephron, independently of ADH for the most part.
*Thick ascending loop of Henle via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption*
- The **thick ascending loop of Henle** is primarily involved in reabsorbing ions like Na+, K+, and Cl- but is largely **impermeable to water**.
- Its impermeability to water is crucial for creating the **osmotic gradient** in the renal medulla, which is necessary for later water reabsorption.
*Collecting duct via aquaporin channels*
- The **collecting duct** is critically important for **regulated water reabsorption** via **aquaporin-2 channels** under the influence of **ADH**, allowing for fine-tuning of urine concentration.
- However, it reabsorbs only a variable portion (typically 5-19%) of the remaining filtered water, not the **majority of all filtered water**.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 6: A 60-year-old male engineer who complains of shortness of breath when walking a few blocks undergoes a cardiac stress test because of concern for coronary artery disease. During the test he asks his cardiologist about what variables are usually used to quantify the functioning of the heart. He learns that one of these variables is stroke volume. Which of the following scenarios would be most likely to lead to a decrease in stroke volume?
- A. Anxiety
- B. Heart failure (Correct Answer)
- C. Exercise
- D. Pregnancy
- E. Digitalis
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Heart failure***
- In **heart failure**, the heart's pumping ability is impaired, leading to a reduced **ejection fraction** and thus a decreased **stroke volume**.
- The weakened myocardium cannot effectively contract to expel the normal volume of blood, resulting in lower blood output per beat.
*Anxiety*
- **Anxiety** typically causes an increase in **sympathetic nervous system** activity, leading to increased heart rate and myocardial contractility.
- This often results in a temporary **increase in stroke volume** due to enhanced cardiac performance, not a decrease.
*Exercise*
- During **exercise**, there is a significant **increase in venous return** and sympathetic stimulation, leading to increased **end-diastolic volume** and contractility.
- This physiological response causes a substantial **increase in stroke volume** to meet the body's higher oxygen demands.
*Pregnancy*
- **Pregnancy** leads to significant **physiological adaptations** to accommodate the growing fetus, including a substantial increase in **blood volume**.
- This increased blood volume and cardiac output result in an **increase in stroke volume** to maintain adequate perfusion for both mother and fetus.
*Digitalis*
- **Digitalis** is a cardiac glycoside that **increases intracellular calcium** in myocardial cells, enhancing the **force of contraction**.
- This positive inotropic effect leads to an **increased stroke volume** by improving the heart's pumping efficiency.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 7: A 64-year-old male with a history of coronary artery disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type II diabetes presents to his primary care physician with increasing shortness of breath and ankle swelling over the past month. Which of the following findings is more likely to be seen in left-sided heart failure and less likely to be seen in right-sided heart failure?
- A. Abdominal fullness
- B. Basilar crackles on pulmonary auscultation (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatojugular reflex
- D. Increased ejection fraction on echocardiogram
- E. Lower extremity edema
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Basilar crackles on pulmonary auscultation***
- **Left-sided heart failure** leads to increased pressure in the pulmonary veins, causing fluid to leak into the **pulmonary interstitium and alveoli**, manifesting as **basilar crackles** on auscultation.
- This symptom is a direct result of **pulmonary congestion** and edema, which is not characteristic of isolated right-sided heart failure.
*Abdominal fullness*
- **Abdominal fullness** is typically a symptom of **right-sided heart failure**, due to **venous congestion** in the splanchnic circulation, leading to hepatomegaly and ascites.
- While it can occur in severe biventricular failure, it is not a primary or earlier sign of isolated left-sided heart failure.
*Hepatojugular reflex*
- The **hepatojugular reflex** is a sign of **right ventricular dysfunction** and **elevated right atrial pressure**, indicating systemic venous congestion.
- It is elicited by applying pressure to the liver, which causes a temporary increase in jugular venous distention.
*Increased ejection fraction on echocardiogram*
- **Heart failure**, whether left- or right-sided, is characterized by a **reduced (or preserved but not increased)** ejection fraction, reflecting impaired pumping ability.
- An **increased ejection fraction** would indicate supra-normal cardiac function and is not associated with heart failure.
*Lower extremity edema*
- **Lower extremity edema** is a hallmark symptom of **right-sided heart failure**, as venous congestion leads to fluid accumulation in the peripheral tissues.
- While present in biventricular failure, it is not a primary or early symptom of isolated left-sided heart failure.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 8: A 71-year-old woman with a past medical history of type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension was admitted to the hospital 8 hours ago with substernal chest pain for management of acute non-ST-elevated myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). The ECG findings noted by ST-depressions and T-wave inversions on anterolateral leads, which is also accompanied by elevated cardiac enzymes. Upon diagnosis, management with inhaled oxygen therapy, beta-blockers and aspirin, and low-molecular-weight heparin therapy were initiated, and she was placed on bed rest with continuous electrocardiographic monitoring. Since admission, she required 2 doses of sublingual nitroglycerin for recurrent angina, and the repeat troponin levels continued to rise. Given her risk factors, plans were made for early coronary angiography. The telemetry nurse calls the on-call physician because of her concern with the patient's mild confusion and increasing need for supplemental oxygen. At bedside evaluation, The vital signs include: heart rate 122/min, blood pressure 89/40 mm Hg, and the pulse oximetry is 91% on 6L of oxygen by nasal cannula. The telemetry and a repeat ECG show sinus tachycardia. She is breathing rapidly, appears confused, and complains of shortness of breath. On physical exam, the skin is cool and clammy and appears pale and dull. She has diffuse bilateral pulmonary crackles, and an S3 gallop is noted on chest auscultation with no new murmurs. She has jugular venous distention to the jaw-line, rapid and faint radial pulses, and 1+ dependent edema. She is immediately transferred to the intensive care unit for respiratory support and precautions for airway security. The bedside sonography shows abnormal hypodynamic anterior wall movement and an ejection fraction of 20%, but no evidence of mitral regurgitation or ventricular shunt. The chest X-ray demonstrates cephalization of pulmonary veins and pulmonary edema. What is the most appropriate next step in the stabilization of this patient?
- A. Obtain blood cultures and start preliminary broad-spectrum antibiotics
- B. Start intravenous fluids and epinephrine therapy
- C. Intubate the patient and perform an emergency cardiocentesis
- D. Initiate dopamine therapy and diuresis (Correct Answer)
- E. Insert two large-bore intravenous catheters and start rapid fluid resuscitation
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Initiate dopamine therapy and diuresis***
- This patient is presenting with **cardiogenic shock** secondary to extensive NSTEMI, characterized by **hypotension**, signs of **end-organ hypoperfusion** (confusion, cool clammy skin), **pulmonary edema** (crackles, dyspnea, elevated jugular venous pressure), and **severely reduced ejection fraction**. Dopamine is a vasopressor that can increase cardiac output and blood pressure.
- **Diuresis** with loop diuretics such as furosemide is crucial to reduce the fluid overload contributing to the pulmonary edema and jugular venous distention.
*Obtain blood cultures and start preliminary broad-spectrum antibiotics*
- While infection is a concern in critically ill patients, there are **no signs of infection** in this clinical presentation. The patient's symptoms are clearly attributable to acute cardiac decompensation.
- A delay in treating cardiogenic shock to investigate for infection would be detrimental and potentially fatal.
*Start intravenous fluids and epinephrine therapy*
- Intravenous fluids would **worsen the existing pulmonary edema and fluid overload** in a patient with an ejection fraction of 20% and clinical signs of volume overload (crackles, JVD, S3 gallop).
- Epinephrine is a potent vasopressor but is generally reserved for more severe shock refractory to other inotropes, or in cases of **cardiac arrest**, not typically first-line for cardiogenic shock with significant pulmonary congestion.
*Intubate the patient and perform an emergency cardiocentesis*
- While the patient is confused and has respiratory distress, **intubation** should be considered after hemodynamic stabilization, if respiratory failure persists or worsens.
- **Cardiocentesis** is indicated for **cardiac tamponade**, which is not supported by the absence of an effusion on bedside sonography and the finding of hypodynamic anterior wall movement, which points to pump failure.
*Insert two large-bore intravenous catheters and start rapid fluid resuscitation*
- This patient is in **cardiogenic shock with clear evidence of fluid overload**, including pulmonary edema and elevated jugular venous pressure.
- **Rapid fluid resuscitation would exacerbate heart failure** and worsen respiratory compromise due to increased preload.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 9: A 72-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 2-week history of worsening shortness of breath, lower extremity swelling, and a 3-kg (6.6-lb) weight gain. Crackles are heard on auscultation of the chest. Cardiac examination shows a dull, low-pitched early diastolic sound at the 5th left intercostal space that becomes louder in the left lateral decubitus position at end-expiration. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these auscultation findings?
- A. Increased ventricular contractility
- B. Increased capacity of the pulmonary circulation
- C. Decreased left-ventricular filling pressure
- D. Increased left ventricular end-systolic volume
- E. Decreased left myocardial compliance (Correct Answer)
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Decreased left myocardial compliance***
- A dull, low-pitched early **diastolic sound (S3 gallop)**, heard best in the left lateral decubitus position at end-expiration, indicates **rapid ventricular filling** into a ventricle with altered diastolic properties. This finding, along with worsening shortness of breath, lower extremity swelling, and weight gain, suggests **heart failure with impaired ventricular filling**.
- Decreased left myocardial compliance (increased stiffness) means the left ventricle cannot **relax and fill properly** during diastole. The S3 occurs when blood rapidly decelerates as it enters the stiff, non-compliant ventricle, creating the characteristic sound.
- This represents **diastolic dysfunction** (heart failure with preserved ejection fraction - HFpEF), which is common in elderly patients with hypertension and is characterized by a stiff ventricle with increased filling pressures.
*Increased ventricular contractility*
- Increased ventricular contractility would lead to a more forceful ejection of blood during systole, not an early diastolic filling sound.
- This would not explain the S3 gallop or the signs of heart failure with fluid retention.
*Increased capacity of the pulmonary circulation*
- Increased pulmonary circulation capacity would help accommodate fluid and prevent pulmonary congestion, which contradicts the symptoms of crackles and shortness of breath.
- The patient has **decreased** capacity to handle the fluid volume, leading to pulmonary edema.
*Decreased left-ventricular filling pressure*
- Decreased LV filling pressure would imply less fluid overload and better cardiac function, contrary to the clinical presentation.
- An S3 gallop and signs of heart failure (crackles, edema, weight gain) indicate **increased** filling pressures from impaired ventricular function.
*Increased left ventricular end-systolic volume*
- Increased end-systolic volume indicates **systolic dysfunction** (reduced ejection fraction), where the ventricle cannot adequately eject blood, leaving residual volume after contraction.
- While systolic dysfunction can also produce an S3 gallop due to volume overload, the specific clinical description emphasizes a **diastolic filling abnormality** (sound during early diastole in a specific position that optimizes detection of ventricular filling).
- The S3 in systolic dysfunction is primarily due to **volume overload**, whereas the S3 here is attributed to blood entering a **stiff ventricle** with impaired compliance, which is the primary pathophysiologic mechanism being tested.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG Question 10: Background: Beta-blockers reduce mortality in patients who have chronic heart failure, systolic dysfunction, and are on background treatment with diuretics and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. We aimed to compare the effects of carvedilol and metoprolol on clinical outcome.
Methods: In a multicenter, double-blind, randomized parallel group trial, we assigned 1511 patients with chronic heart failure to treatment with carvedilol (target dose, 25 mg twice daily) and 1518 to metoprolol (target dose, 50 mg twice daily). The patients were required to have chronic heart failure (NYHA II-IV), the previous admission for a cardiovascular indication, an ejection fraction of < 0.35, and to have been treated optimally with diuretics and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors unless not tolerated. The primary endpoints were all-cause mortality and the composite endpoint of all-cause mortality or all-cause admission. The analysis was done by intention-to-treat.
Findings: The mean study duration was 58 months (SD, 6). The mean ejection fraction was 0.26 (SD, 0.07) and the mean age was 62 years (SD, 11). The all-cause mortality was 34% (512 of 1511) for carvedilol and 40% (600 of 1518) for metoprolol (hazard ratio, 0.83 [95% CI 0.74-0.93], p = 0.0017). The reduction in all-cause mortality was consistent across pre-defined subgroups. The incidence of side effects and drug withdrawals did not differ significantly between the 2 study groups.
Based on the best interpretation of the results of this clinical trial, which of the following statements is most accurate?
- A. The study was underpowered and unable to arrive at a statistically significant conclusion.
- B. Metoprolol demonstrated a significant improvement in all-cause mortality in patients with heart failure compared to carvedilol.
- C. The results are likely biased due to trial design, and therefore non-generalizable.
- D. Carvedilol demonstrated a significant improvement in all-cause mortality in patients with heart failure as compared to metoprolol. (Correct Answer)
- E. There is no appreciable, statistically significant difference in overall mortality between the 2 treatment arms.
Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) Explanation: ***Carvedilol demonstrated a significant improvement in all-cause mortality in patients with heart failure as compared to metoprolol.***
- The study explicitly states that the all-cause mortality for carvedilol was 34% compared to 40% for metoprolol, with a **hazard ratio of 0.83** and a **p-value of 0.0017**.
- A p-value of < 0.05 indicates statistical significance, and a hazard ratio less than 1 favors the intervention (carvedilol), showing a **20% relative risk reduction** in mortality.
*The study was underpowered and unable to arrive at a statistically significant conclusion.*
- The p-value of 0.0017 for all-cause mortality is well below the conventional significance level of 0.05, indicating a **statistically significant result**.
- With **over 1500 patients in each arm** and mean follow-up of 58 months, the study was sufficiently powered to detect a difference, as evidenced by the significant findings.
*Metoprolol demonstrated a significant improvement in all-cause mortality in patients with heart failure compared to carvedilol.*
- The data shows that **metoprolol had a higher all-cause mortality (40%)** compared to carvedilol (34%), meaning metoprolol was associated with worse outcomes.
- The hazard ratio of 0.83, favoring carvedilol, clearly refutes any claim of metoprolol providing a significant improvement over carvedilol.
*There is no appreciable, statistically significant difference in overall mortality between the two treatment arms.*
- The **p-value of 0.0017** is statistically significant, indicating that the observed difference in mortality is unlikely due to chance.
- The **6% absolute difference** in mortality (40% vs. 34%) is both statistically and clinically appreciable in a chronic condition like heart failure.
*The results are likely biased due to trial design, and therefore non-generalizable.*
- The study was a **multicenter, double-blind, randomized parallel group trial**, which is a robust design aimed at minimizing bias.
- The "intention-to-treat" analysis further strengthens the generalizability by reflecting real-world clinical practice where patients may not always adhere to assigned treatments.
More Classification of heart failure (HFrEF vs HFpEF) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.