Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Thyroid nodules and cancer. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 1: A 36-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up visit after she had a PET scan that showed a nodule on the thyroid gland. She has no difficulty or pain while swallowing. She was treated for non-Hodgkin lymphoma at the age of 28 years, which included external beam radiation to the head and neck and 4 cycles of chemotherapy. She appears healthy. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Serum studies show:
Glucose 82 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.7 mg/dL
Thyroid-stimulating hormone 3 μU/mL
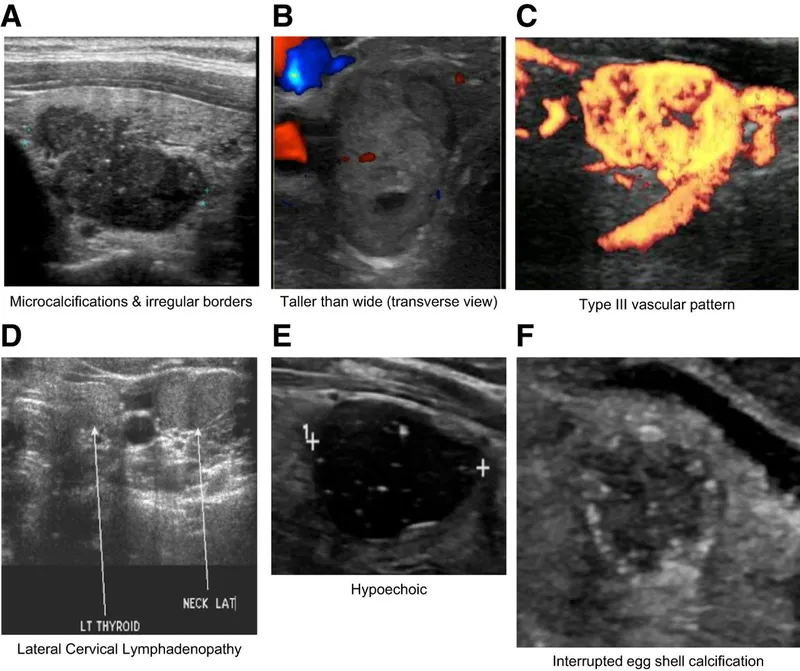
Ultrasound of the neck shows a 1.2-cm (0.5-in) nodule on the left lobe of the thyroid with irregular margins and microcalcifications. A fine-needle aspiration biopsy shows Psammoma bodies and cells with clear, ground-glass, empty nuclei. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Thyroid scintigraphy
- B. Observation and follow-up in 3 months
- C. Radioiodine therapy
- D. Total thyroidectomy (Correct Answer)
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Total thyroidectomy***
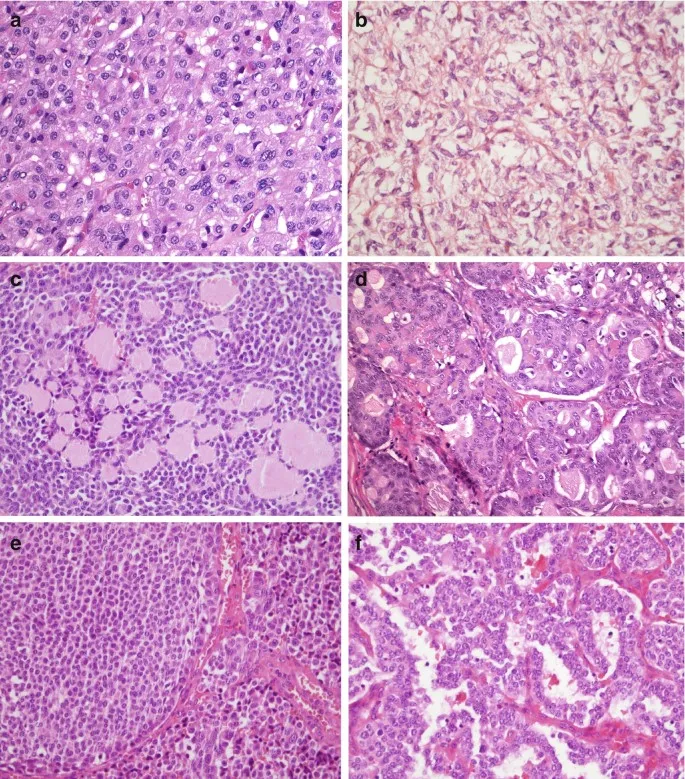
- The fine-needle aspiration biopsy findings of **Psammoma bodies** and **clear, ground-glass, empty nuclei** are classic for **papillary thyroid carcinoma**, which is the most common type of thyroid cancer.
- Given the patient's history of **neck radiation** for lymphoma (a risk factor for thyroid cancer), the concerning ultrasound features (irregular margins, microcalcifications), and the confirmed diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma, **total thyroidectomy** is the definitive treatment.
*Thyroid scintigraphy*
- **Thyroid scintigraphy** is primarily used to assess the functional status of thyroid nodules (hot vs. cold) and is helpful if the TSH is suppressed or if the FNA is indeterminate.
- In this case, the **fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy** has already provided a definitive diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer, making scintigraphy unnecessary for initial management.
*Observation and follow-up in 3 months*
- **Observation** is not appropriate given the definitive diagnosis of **papillary thyroid carcinoma** confirmed by biopsy and the patient's history of neck radiation.
- Papillary thyroid cancer, although often slow-growing, requires active management, especially with adverse features on ultrasound and a clear diagnosis.
*Radioiodine therapy*
- **Radioiodine therapy** is typically used as **adjuvant treatment** *after* thyroidectomy to ablate residual thyroid tissue or treat metastatic disease, particularly in higher-risk cases.
- It is not the primary treatment for localized papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 2: A 54-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by a nurse 30 minutes after receiving scheduled radiation therapy for papillary thyroid cancer. After the radioisotope was ingested, the physician realized that a much larger fixed dose was given instead of the appropriate dose based on radiation dosimetry. Which of the following pharmacotherapies should be administered immediately to prevent complications from this exposure?
- A. Dexrazoxane
- B. Methimazole
- C. Propylthiouracil
- D. Potassium iodide (Correct Answer)
- E. Mercaptoethanesulfonate
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Potassium iodide***
- **Potassium iodide (KI)** is the immediate treatment for **radioactive iodine exposure** and works by saturating the thyroid gland with stable, non-radioactive iodine.
- This **competitive inhibition** prevents the uptake of radioactive iodine-131 by the thyroid, thereby reducing the risk of radiation-induced thyroid damage and cancer.
- **Timing is critical**: KI is most effective when given immediately (within hours) after exposure to radioactive iodine.
- The patient received an overdose of **radioactive iodine-131** (commonly used for papillary thyroid cancer treatment), making immediate KI administration the definitive thyroid protective measure.
*Dexrazoxane*
- **Dexrazoxane** is a **cardioprotective agent** used to reduce cardiotoxicity associated with **anthracycline chemotherapy** (e.g., doxorubicin).
- It chelates iron and prevents formation of anthracycline-iron complexes that generate free radicals.
- It has no role in preventing complications from radioactive iodine exposure.
*Methimazole*
- **Methimazole** is an **antithyroid drug** that inhibits thyroid peroxidase, thereby blocking the **iodination and coupling of tyrosyl residues** in thyroid hormone synthesis.
- While it reduces thyroid hormone production, it does **not prevent uptake** of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland.
- It is ineffective for acute radiation protection in this scenario.
*Propylthiouracil*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)** is another **antithyroid drug** that inhibits thyroid peroxidase and also blocks peripheral conversion of **T4 to T3**.
- Like methimazole, PTU does **not prevent radioactive iodine uptake** by the thyroid.
- It is not indicated for acute radioactive iodine exposure management.
*Mercaptoethanesulfonate*
- **Mercaptoethanesulfonate (MESNA)** is a **uroprotective agent** used to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis caused by **oxazaphosphorine chemotherapy agents** (cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide).
- MESNA binds to and detoxifies acrolein, the toxic metabolite responsible for bladder toxicity.
- It has no role in managing radioactive iodine exposure.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 3: A 74-year-old retired female teacher is referred to the endocrinology clinic. She is very concerned about a large mass in her neck that has progressively enlarged over the past 2 weeks. She also reports a 15 pound weight loss over the last 3 months. She now has hoarseness and difficulty swallowing her food, giving her a sensation that food gets stuck in her windpipe when she swallows. There is no pain associated with swallowing. Her speech is monotonous. No other gait or language articulation problems are noted. Testing for cranial nerve lesions is unremarkable. On palpation, a large, fixed and non-tender mass in the thyroid is noted. Cervical lymph nodes are palpable bilaterally. The patient is urgently scheduled for an ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration to guide management. Which of the following is the most likely gene mutation to be found in this mass?
- A. Activating mutation of the Ras protooncogene
- B. Inactivating mutation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene (Correct Answer)
- C. RET/PTC rearrangement
- D. BRAF mutation
- E. RET gene mutation
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Inactivating mutation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene***
- The patient's presentation with a **rapidly enlarging, fixed, non-tender thyroid mass**, *hoarseness*, *dysphagia*, *weight loss*, and *palpable cervical lymph nodes* is highly suggestive of **anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC)**, an aggressive malignancy.
- Inactivating mutations of the **p53 tumor suppressor gene** are frequently associated with the development and progression of ATC, contributing to its uncontrolled growth and poor prognosis.
*Activating mutation of the Ras protooncogene*
- **Ras mutations** are more commonly found in *follicular thyroid carcinoma* and *follicular variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma*.
- While they can indicate malignancy, they are not typically the primary genetic driver for the highly aggressive features seen in anaplastic carcinoma.
*RET/PTC rearrangement*
- **RET/PTC rearrangements** are characteristic genetic alterations found in **papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC)**.
- PTC typically presents with a *slower growth rate* and *less aggressive features* compared to the rapid progression described in the patient.
*BRAF mutation*
- The **BRAF V600E mutation** is the most common genetic alteration in **papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC)**, especially the conventional and tall-cell variants.
- While it indicates a more aggressive subset of PTC, it is generally not the primary mutation associated with the extremely aggressive and rapidly progressing features of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.
*RET gene mutation*
- **Germline RET mutations** are primarily associated with **medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC)**, often occurring as part of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN2).
- The clinical presentation with a *rapidly growing, fixed mass* and *compressive symptoms* is less typical for MTC, which can also be aggressive but usually presents differently.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 4: A 19-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician because she has been feeling increasingly lethargic over the last 6 months. Specifically, she says that she feels tired easily and has been cold even though she is wearing lots of layers. Her medical history is significant for seasonal allergies but is otherwise unremarkable. When prompted, she also says that she has a hard time swallowing food though she has no difficulty drinking liquids. Physical exam reveals a midline mass in her neck. Which of the following structures would most likely be seen if this patient's mass was biopsied?
- A. Lymphatic ducts
- B. Neutrophilic invasion
- C. Blood vessels
- D. Follicles with colloid (Correct Answer)
- E. Hollow epithelial duct
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Follicles with colloid***
- The patient's symptoms (lethargy, cold intolerance, difficulty swallowing solids, midline neck mass) are highly suggestive of **hypothyroidism** due to a **goiter**, which often arises from an enlarged thyroid gland.
- The **thyroid gland** is composed of follicles filled with **colloid**, which is the storage form of thyroid hormones. A biopsy of an enlarged thyroid gland would therefore show these structures.
*Lymphatic ducts*
- **Lymphatic ducts** are part of the lymphatic system, which is involved in immune function and fluid balance, not typically found in a thyroid biopsy under these circumstances.
- While neck masses can sometimes be enlarged lymph nodes, the symptoms point specifically to thyroid dysfunction rather than a lymphatic issue.
*Neutrophilic invasion*
- **Neutrophilic invasion** indicates an acute inflammatory or infectious process, which is not suggested by the chronic and systemic symptoms presented here.
- This finding would be more typical of an abscess or acute thyroiditis, which usually presents with pain and fever.
*Blood vessels*
- While **blood vessels** are present in all tissues, including the thyroid, they are not the *most characteristic* or defining structure seen during a biopsy of a mass suspected to be an enlarged thyroid gland.
- The question asks for the structure *most likely* to be seen, implying a unique and diagnostic histological feature.
*Hollow epithelial duct*
- **Hollow epithelial ducts** are characteristic of structures like salivary glands or cysts formed from developmental remnants (e.g., thyroglossal duct cyst), but less likely to be the primary finding in an enlarged thyroid gland causing systemic symptoms of hypothyroidism.
- A thyroglossal duct cyst would typically present as a midline neck mass that moves with tongue protrusion, and while it could cause dysphagia, it typically doesn't cause symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 5: A 44-year-old woman comes to the physician for the evaluation of a 1-month history of fatigue and difficulty swallowing. During this period, she has also had dry skin, thinning hair, and rounding of her face. She has type 1 diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis. Her father had a thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid cancer. The patient had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years but quit 3 years ago. She drinks 2–3 glasses of wine daily. Her current medications include insulin, omeprazole, and daily ibuprofen. She appears well. Her temperature is 36.3°C (97.3°F), pulse is 62/min, and blood pressure is 102/76 mm Hg. Examination of the neck shows a painless, diffusely enlarged thyroid gland. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Positive thyroid peroxidase antibodies and thyroglobulin antibodies in serum (Correct Answer)
- B. Diffusely increased uptake on a radioactive iodine scan
- C. Increased uptake on radioactive iodine scan in discrete 1-cm area
- D. Large irregular nuclei, nuclear grooves, and Psammoma bodies on thyroid biopsy
- E. Positive immunohistochemical stain for calcitonin on thyroid biopsy
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Positive thyroid peroxidase antibodies and thyroglobulin antibodies in serum***
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, dry skin, thinning hair, rounded face, bradycardia) are classic for **hypothyroidism**.
- The presence of **Type 1 diabetes mellitus** and **rheumatoid arthritis** suggests an underlying autoimmune diathesis, making **Hashimoto thyroiditis** (autoimmune hypothyroidism) highly likely, which is characterized by positive thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and thyroglobulin antibodies.
*Diffusely increased uptake on a radioactive iodine scan*
- **Diffusely increased uptake** on a radioactive iodine scan is characteristic of **hyperthyroidism**, such as in **Graves' disease**, which contradicts the patient's hypothyroid symptoms.
- In Hashimoto thyroiditis, especially in the hypothyroid phase, uptake is typically **reduced or normal**, not diffusely increased.
*Increased uptake on radioactive iodine scan in discrete 1-cm area*
- **Increased uptake in a discrete area** (a 'hot nodule') suggests a **toxic adenoma** or a multinodular goiter, which are causes of hyperthyroidism, not hypothyroidism.
- This finding would also contradict the patient's clinical presentation of hypothyroidism.
*Large irregular nuclei, nuclear grooves, and Psammoma bodies on thyroid biopsy*
- These are classic cytologic features seen in **papillary thyroid carcinoma**, not Hashimoto thyroiditis.
- While the patient's father had papillary thyroid cancer, her clinical presentation is strongly indicative of hypothyroidism, and her diffusely enlarged, painless gland is more consistent with Hashimoto's than a focal malignant lesion showing these specific cytological features.
*Positive immunohistochemical stain for calcitonin on thyroid biopsy*
- A positive immunohistochemical stain for **calcitonin** is diagnostic for **medullary thyroid carcinoma**.
- This is a neuroendocrine tumor and does not typically present with the generalized hypothyroid symptoms described in the patient.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 6: A 40-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of a lump on her neck. The lump is mildly painful. She appears healthy. Examination shows a swelling on the left side of her neck that moves on swallowing. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Her TSH is 3.6 μU/mL. Ultrasound shows a 4.0-cm (1.6-in) hypoechoic mass in the left thyroid lobe. Fine-needle aspiration of the mass shows neoplastic follicular cells. Molecular analysis of the aspirate shows a mutation in the RAS gene. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Radioiodine therapy
- B. External beam radiation
- C. Total thyroidectomy
- D. Thyroid lobectomy (Correct Answer)
- E. Watchful waiting
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Thyroid lobectomy***
- A **thyroid lobectomy** is appropriate for a **solitary thyroid nodule** with suspicious features (hypoechoic, neoplastic follicular cells, **RAS mutation**) and a size of 4.0 cm, as it allows for pathological diagnosis and treatment while preserving the other lobe.
- The **RAS mutation** indicates a moderate risk of malignancy, and for a unilateral tumor of this size, lobectomy is often preferred over total thyroidectomy as it minimizes the risk of **hypoparathyroidism** and the need for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
*Radioiodine therapy*
- This therapy is primarily used as an **adjunctive treatment** after surgical removal of thyroid cancer, especially for **metastatic disease** or **large residual tumors**, not as a primary treatment for a localized tumor before surgery.
- It is also typically reserved for **differentiated thyroid cancers** (papillary, follicular) that have demonstrated uptake, and surgical removal is the initial step for diagnosis and treatment.
*External beam radiation*
- **External beam radiation** is generally reserved for **advanced, inoperable thyroid cancers** or for cases with **extracapsular invasion** or **distant metastases** that are not amenable to radioiodine therapy.
- It carries significant side effects and is not a first-line treatment for an early-stage, localized thyroid nodule.
*Total thyroidectomy*
- **Total thyroidectomy** is indicated for larger thyroid cancers (>4 cm), bilateral disease, or aggressive histological subtypes.
- Given the patient's **unilateral tumor** with a **RAS mutation** (which signifies moderate risk), a thyroid lobectomy is appropriate as the initial surgical approach, with total thyroidectomy reserved if final pathology shows aggressive features.
*Watchful waiting*
- **Watchful waiting** is inappropriate given the presence of **neoplastic follicular cells** and a **RAS mutation**, as these findings indicate a significant risk of malignancy.
- The nodule size of 4.0 cm and molecular findings warrant surgical intervention for definitive diagnosis and treatment rather than observation.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 7: A previously healthy 39-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a slowly enlarging, painless neck mass that she first noticed 3 months ago. During this period, she has also experienced intermittent palpitations, hair loss, and a weight loss of 4.5 kg (10 lb). There is no personal or family history of serious illness. She appears anxious and fidgety. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 101/min and irregular, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Physical examination shows a firm, nontender left anterior cervical nodule that moves with swallowing. Laboratory studies show:
TSH 0.4 μU/mL
T4 13.2 μg/dL
T3 196 ng/dL
Ultrasonography confirms the presence of a 3-cm solid left thyroid nodule. A thyroid 123I radionuclide scintigraphy scan shows increased uptake in a nodule in the left lobe of the thyroid gland with suppression of the remainder of the thyroid tissue. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's condition?
- A. Gain-of-function mutations of the TSH receptor (Correct Answer)
- B. Thyroglobulin antibody production
- C. Activation of oncogenes promoting cell division
- D. Persistent TSH stimulation and heterogeneous thyroid tissue hyperplasia
- E. Thyroid peroxidase autoantibody-mediated destruction of thyroid tissue
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Gain-of-function mutations of the TSH receptor***
- The patient's symptoms (palpitations, weight loss, anxiety, irregular pulse) and lab results (low TSH, high T3/T4) indicate **hyperthyroidism**. The **hot nodule** on scintigraphy with suppressed surrounding tissue points to a **toxic adenoma**.
- **Gain-of-function mutations** in the TSH receptor gene (e.g., *TSHR* gene) cause constitutive activation of the receptor, leading to autonomous thyroid hormone production independent of TSH.
*Thyroglobulin antibody production*
- **Antithyroglobulin antibodies** are typically associated with autoimmune thyroid diseases like **Hashimoto's thyroiditis** (hypothyroidism) or occasionally Graves' disease (hyperthyroidism), but the specific presentation here points to a functional nodule.
- While they can be present in Graves' disease, the scintigraphy showing a **single hot nodule** with suppressed surrounding tissue is not characteristic of Graves' disease, which typically shows diffuse uptake.
*Activation of oncogenes promoting cell division*
- While thyroid nodules can be malignant and involve **oncogene activation** (e.g., *BRAF, RET/PTC*), this mechanism primarily relates to uncontrolled cell growth and **cancer**, not necessarily hyperfunction and excessive hormone production (toxic nodule).
- Malignant nodules are typically "cold" on scintigraphy, meaning they do not take up iodine, unlike the **"hot" nodule** described in this patient.
*Persistent TSH stimulation and heterogeneous thyroid tissue hyperplasia*
- This description is characteristic of a **multinodular goiter** or **diffuse hyperplasia**, often seen in conditions of **chronic TSH stimulation** (e.g., iodine deficiency leading to hypothyroidism and compensatory TSH rise).
- The patient has **suppressed TSH** and a **single hyperfunctioning nodule**, not diffuse hyperplasia or chronic TSH stimulation.
*Thyroid peroxidase autoantibody-mediated destruction of thyroid tissue*
- **Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibodies** are involved in **Hashimoto's thyroiditis**, an autoimmune condition leading to gradual **destruction of thyroid tissue** and **hypothyroidism**.
- This patient presents with **hyperthyroidism** and a hyperfunctioning nodule, which is the opposite of the clinical picture seen with TPO antibody-mediated destruction.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 8: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of a lump on her neck and a 1-week history of hoarseness. Examination shows a 3-cm, firm, non-tender nodule on the anterior neck. Further evaluation confirms a thyroid malignancy, and she undergoes thyroidectomy. Histopathologic examination of the surgical specimen shows lymphatic invasion. Genetic analysis shows an activating mutation in the RET/PTC genes. Microscopic examination of the surgical specimen is most likely to also show which of the following?
- A. Pleomorphic giant cells with numerous atypical mitotic figures
- B. Cuboidal cells arranged spherically around colloid lakes
- C. Hyperplastic epithelium with colloid scalloping
- D. Calcified spherules and large oval cells with empty-appearing nuclei (Correct Answer)
- E. Sheets of polygonal cells surrounding amyloid deposition
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Calcified spherules and large oval cells with empty-appearing nuclei***
- The presence of an **activating mutation in RET/PTC genes**, **lymphatic invasion**, and a new neck lump with hoarseness (suggesting nerve involvement) are highly characteristic of **papillary thyroid carcinoma**.
- Microscopic features of papillary thyroid carcinoma include **Psammoma bodies (calcified spherules)**, **Orphan Annie eye nuclei (large oval cells with empty-appearing nuclei)**, and nuclear grooves.
*Pleomorphic giant cells with numerous atypical mitotic figures*
- This description typically refers to **anaplastic thyroid carcinoma**, a highly aggressive and undifferentiated tumor.
- While anaplastic carcinoma can present with rapid growth and hoarseness, it is less commonly associated with a **RET/PTC mutation** (BRAF mutations are more common) and typically has a much poorer prognosis, often presenting with a rapidly enlarging mass rather than a 2-month history suggestive of a more indolent tumor.
*Cuboidal cells arranged spherically around colloid lakes*
- This morphology is characteristic of **follicular thyroid carcinoma** or **follicular adenoma**.
- While follicular tumors can have RET/PTC mutations in some variants, the classic features described (empty-appearing nuclei and psammoma bodies) are absent here.
*Hyperplastic epithelium with colloid scalloping*
- This describes the histologic features seen in **Graves' disease** or **diffuse toxic goiter**, a benign condition.
- It is not indicative of malignancy, and the patient's presentation with a solitary nodule and hoarseness points to a malignant process.
*Sheets of polygonal cells surrounding amyloid deposition*
- This is the classic microscopic appearance of **medullary thyroid carcinoma**.
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma is also associated with **RET mutations**, but these are typically **germline or somatic RET point mutations** (e.g., RET M918T), not RET/PTC rearrangements, and it arises from parafollicular C cells, producing calcitonin, not thyroid hormones.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 9: A 47-year-old woman presents to the clinic complaining of difficulty swallowing that started 1 month ago. The patient also reports a weight loss of 10 lbs during this time, without a change in her appetite. She denies fatigue, cough, hoarseness, pain, or hemoptysis. The patient has a history of childhood lymphoma, which was treated with radiation. She takes no medications. She has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes per day since she was 25 years old. Her physical exam is notable for a palpable nodule on the right side of the thyroid. An ultrasound is performed, which confirms a 1.2 cm hyperechoic nodule in the right lobe. Thyroid function labs are drawn and shown below:
Serum TSH: 0.2 mU/L
Serum thyroxine (T4): 187 nmol/L
Serum triiodothyronine (T3): 3.3 nmol/L
Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. Radioactive iodine
- B. Partial thyroidectomy
- C. Fine needle aspiration (Correct Answer)
- D. Levothyroxine
- E. Thyroid scintigraphy
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***Fine needle aspiration***
- This patient has several risk factors for **thyroid malignancy**, including a history of **radiation exposure** to the neck (for childhood lymphoma) and a palpable thyroid nodule associated with **dysphagia** and unexplained **weight loss**. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is the best next step to evaluate for malignancy.
- The patient also presents with **hyperthyroidism** (low TSH, elevated T4), but the primary concern given the clinical picture is to rule out thyroid cancer.
- Per American Thyroid Association guidelines, FNA is indicated for any nodule in a patient with a history of head/neck radiation exposure.
*Radioactive iodine*
- Radioactive iodine ablation is used to treat **hyperthyroidism**, especially in cases of **Graves' disease** or toxic nodular goiter. While the patient has hyperthyroidism, the presence of a suspicious nodule warrants investigation for malignancy first.
- Administering radioactive iodine without first ruling out malignancy in a suspicious nodule could delay definitive treatment for cancer or complicate its management.
*Partial thyroidectomy*
- **Partial thyroidectomy** would be considered if the FNA results indicate malignancy or a highly suspicious follicular neoplasm.
- Performing surgery without a prior FNA would be premature, as many thyroid nodules are benign and do not require surgical intervention unless causing compressive symptoms or confirmed malignancy.
*Levothyroxine*
- **Levothyroxine** is used to treat **hypothyroidism** or to suppress TSH in cases of benign thyroid nodules or after thyroid cancer surgery.
- This patient is **hyperthyroid**, making exogenous levothyroxine inappropriate.
*Thyroid scintigraphy*
- **Thyroid scintigraphy** (radioactive iodine uptake scan) is useful in characterizing thyroid nodules as "hot" (functioning) or "cold" (non-functioning) in the context of hyperthyroidism.
- "Hot" nodules are rarely malignant, while "cold" nodules have a higher (though still relatively low) risk of malignancy. However, given the patient's strong risk factors for thyroid cancer and compressive symptoms, an FNA is more direct and informative for assessing malignancy than scintigraphy at this stage.
Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG Question 10: A 10-year-old boy is brought by his mother to his pediatrician for "skin growths." His mother reports that she started noticing small lumps arising from the patient's lips and eyelids several months ago. She also notes that he seems to suffer from frequent constipation and appears "weaker" than many of his peers. The boy's past medical history is unremarkable. His father and paternal grandmother have a history of medullary thyroid carcinoma. His height and weight are in the 85th and 45th percentiles, respectively. His temperature is 99°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 18/min. On examination, he has an elongated face with protruding lips. There are numerous sessile painless nodules on the patient's lips, tongue, and eyelids. This patient's condition is most strongly associated with a mutation in which of the following genes?
- A. NF1
- B. MEN1
- C. RET (Correct Answer)
- D. NF2
- E. c-KIT
Thyroid nodules and cancer Explanation: ***RET***
- The constellation of **skin growths** on the lips and eyelids (neuromas), **constipation** (ganglioneuromatosis), and a family history of **medullary thyroid carcinoma** (MTC) strongly suggests **Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2B (MEN2B)**.
- MEN2B is caused by a germline mutation in the **RET proto-oncogene**, which is a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in cell growth and differentiation.
*NF1*
- Mutations in the **NF1 gene** cause **Neurofibromatosis type 1**, characterized by **café-au-lait spots**, neurofibromas (subcutaneous, not typically mucosal), iris Lisch nodules, and optic pathway gliomas.
- While it involves skin growths (neurofibromas), the specific mucosal neuromas, elongated facies, and family history of MTC are not typical features.
*MEN1*
- **MEN1 syndrome** is caused by mutations in the **MEN1 gene** and is associated with tumors of the **parathyroid**, **anterior pituitary**, and **pancreatic islet cells** (the 3 Ps).
- This patient's presentation of mucosal neuromas and medullary thyroid carcinoma is not characteristic of MEN1.
*NF2*
- Mutations in the **NF2 gene** cause **Neurofibromatosis type 2**, classically characterized by **bilateral vestibular schwannomas**, meningiomas, and ependymomas.
- Skin manifestations are less prominent and different from what is described, and MTC is not associated.
*c-KIT*
- Mutations in the **c-KIT gene** are primarily associated with **gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST)** and certain types of mastocytosis.
- It is not linked to the constellation of mucosal neuromas, elongated facies, or medullary thyroid carcinoma seen in this patient.
More Thyroid nodules and cancer US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.