Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 1: A 55-year-old male is hospitalized for acute heart failure. The patient has a 20-year history of alcoholism and was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2) 5 years ago. Physical examination reveals ascites and engorged paraumbilical veins as well as 3+ pitting edema around both ankles. Liver function tests show elevations in gamma glutamyl transferase and aspartate transaminase (AST). Of the following medication, which most likely contributed to this patient's presentation?
- A. Glargine
- B. Pramlintide
- C. Pioglitazone (Correct Answer)
- D. Glipizide
- E. Metformin
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Pioglitazone***
- **Pioglitazone**, a thiazolidinedione, is known to cause **fluid retention** and can exacerbate or precipitate **congestive heart failure**.
- The patient's presentation with **ascites**, **pitting edema**, and **acute heart failure** is consistent with the adverse effects of this medication, especially in a patient with risk factors like alcoholism.
*Glargine*
- **Glargine** is a **long-acting insulin** analog primarily used to control blood glucose levels in diabetes.
- It does not typically cause **fluid retention** or worsen **heart failure** directly, making it an unlikely contributor to these specific symptoms.
*Pramlintide*
- **Pramlintide** is an **amylin analog** used to improve glycemic control by slowing gastric emptying and suppressing glucagon secretion.
- It is not associated with **fluid retention** or the exacerbation of **heart failure**.
*Glipizide*
- **Glipizide** is a **sulfonylurea** that stimulates insulin release from pancreatic beta cells.
- While it can cause hypoglycemia, it does not typically contribute to **fluid retention** or worsen **heart failure**.
*Metformin*
- **Metformin** is a **biguanide** that reduces hepatic glucose production and increases insulin sensitivity.
- It is generally considered **cardioprotective** and does not cause **fluid retention** or exacerbate **heart failure**.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 2: An endocrinologist is working with a pharmaceutical research company on a new drug for diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2). In their experimental studies, they isolated a component from Gila monster saliva, which was found to have > 50% homology with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP1). During the animal studies, the experimental drug was found to have no GLP1 agonist effect. Instead, it irreversibly binds DPP-IV with a higher affinity than GLP1. Which of the following drugs has a similar mechanism of action to this new experimental drug?
- A. Metformin
- B. Sitagliptin (Correct Answer)
- C. Canagliflozin
- D. Pramlintide
- E. Exenatide
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Sitagliptin***
- This drug is a **dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor**, which works by preventing the breakdown of **endogenous GLP-1** and other incretin hormones.
- By inhibiting DPP-4, sitagliptin increases the availability of GLP-1, leading to **glucose-dependent insulin secretion** and reduced glucagon secretion.
- **Note:** While sitagliptin is a **reversible** DPP-4 inhibitor and the experimental drug is described as irreversible, sitagliptin shares the same **target enzyme (DPP-4)** and overall therapeutic mechanism, making it the closest match among the options provided.
*Metformin*
- Metformin is a **biguanide** that primarily reduces **hepatic glucose production** and improves insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
- Its mechanism does not involve direct interaction with DPP-4 or GLP-1 pathways, unlike the experimental drug.
*Canagliflozin*
- Canagliflozin is a **sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor** that blocks glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to **increased urinary glucose excretion**.
- Its action is independent of insulin and does not involve the incretin system or DPP-4 inhibition.
*Pramlintide*
- Pramlintide is an **amylin analog** that works by slowing gastric emptying, suppressing glucagon secretion, and promoting satiety.
- It is administered via injection and acts synergistically with insulin, but does not affect DPP-4 enzyme activity.
*Exenatide*
- Exenatide is a **glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist** that directly mimics the action of GLP-1, stimulating insulin release and suppressing glucagon.
- Notably, exenatide is also derived from Gila monster saliva (similar to the experimental drug's origin), but it acts as a GLP-1 agonist rather than a DPP-4 inhibitor, which is the opposite mechanism described for the experimental drug.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 3: A 52-year-old man is seen by his endocrinologist for routine followup of his type 2 diabetes. Although he has previously been on a number of medication regimens, his A1C has remained significantly elevated. In order to try to better control his glucose level, the endocrinologist prescribes a new medication. He explains that this new medication works by blocking the ability of his kidneys to reabsorb glucose and therefore causes glucose wasting in the urine. Which of the following medications has this mechanism of action?
- A. Canagliflozin (Correct Answer)
- B. Acarbose
- C. Metformin
- D. Glyburide
- E. Exenatide
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Canagliflozin***
- **Canagliflozin** is an **SGLT2 inhibitor** that works by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the renal tubules, leading to glucose excretion in the urine.
- This mechanism of action directly matches the description provided: "blocking the ability of his kidneys to reabsorb glucose and therefore causes glucose wasting in the urine."
*Acarbose*
- **Acarbose** is an **alpha-glucosidase inhibitor** that delays the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine.
- Its primary action is in the gastrointestinal tract, not by directly affecting renal glucose reabsorption.
*Metformin*
- **Metformin** is a **biguanide** that primarily works by decreasing hepatic glucose production and improving insulin sensitivity.
- It does not directly affect the kidney's ability to reabsorb glucose.
*Glyburide*
- **Glyburide** is a **sulfonylurea** that stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells.
- Its mechanism involves increasing insulin release, independent of renal glucose handling.
*Exenatide*
- **Exenatide** is a **GLP-1 receptor agonist** that enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppresses glucagon secretion, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety.
- Its actions are mainly related to insulin and glucagon regulation, not direct renal glucose filtration.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 4: A 56-year-old man presents for a follow-up regarding his management for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). He was diagnosed with type 2 DM about 7 years ago and was recently started on insulin therapy because oral agents were insufficient to control his glucose levels. He is currently following a regimen combining insulin lispro and neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin. He is taking insulin lispro 3 times a day before meals and NPH insulin once in the morning. He has been on this regimen for about 2 months. He says that his glucose reading at night averages around 200 mg/dL and remains close to 180 mg/dL before his shot of NPH in the morning. The readings during the rest of the day range between 100–120 mg/dL. The patient denies any changes in vision or tingling or numbness in his hands or feet. His latest HbA1C level was 6.2%. Which of the following adjustments to his insulin regimen would be most effective in helping this patient achieve better glycemic control?
- A. Add another dose of insulin lispro in the evening.
- B. Reduce a dose of insulin lispro.
- C. Replace lispro with insulin aspart.
- D. Add insulin glargine to the current regimen.
- E. Add another dose of NPH in the evening. (Correct Answer)
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Add another dose of NPH in the evening.***
- The patient has persistently elevated **nighttime** and **pre-morning glucose levels** (200 mg/dL and 180 mg/dL, respectively), while daytime levels are well-controlled. This indicates insufficient **basal insulin coverage** overnight.
- Adding a dose of **intermediate-acting NPH insulin** in the evening would provide longer-acting basal insulin to cover the overnight period and address the high morning fasting glucose.
*Add another dose of insulin lispro in the evening.*
- Insulin lispro is a **rapid-acting insulin** primarily used to cover post-prandial glucose spikes. Adding another dose would primarily affect post-dinner glucose, not the sustained overnight hyperglycemia.
- While it might slightly lower evening glucose, its short duration of action would not adequately address the **pre-morning hyperglycemia**.
*Reduce a dose of insulin lispro.*
- The patient's **daytime glucose levels (100–120 mg/dL)** are well-controlled, suggesting that the current lispro doses are appropriate for meal coverage.
- Reducing lispro could lead to **post-prandial hyperglycemia** during the day, worsening overall control.
*Replace lispro with insulin aspart.*
- Both insulin lispro and insulin aspart are **rapid-acting insulins** with very similar pharmacokinetics and duration of action.
- Replacing one with the other would likely not significantly alter the glycemic profile, as the problem lies with **basal insulin coverage**, not rapid-acting insulin.
*Add insulin glargine to the current regimen.*
- While **insulin glargine** is a **long-acting basal insulin** and could address the overnight hyperglycemia, the patient is already on NPH as his basal insulin.
- The simpler and more direct adjustment would be to optimize the **existing NPH regimen** by adding an evening dose, rather than introducing a new type of basal insulin, which might complicate the regimen further or be less cost-effective.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 5: A 56-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He reports that he has been compliant with his current antidiabetic medication regimen. His hemoglobin A1c concentration is 8.5%. The physician prescribes a drug that reversibly inhibits a membrane-bound enzyme that hydrolyzes carbohydrate bonds. Which of the following drugs was most likely added to this patient's medication regimen?
- A. Canagliflozin
- B. Miglitol (Correct Answer)
- C. Linagliptin
- D. Pramlintide
- E. Rosiglitazone
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Miglitol***
- Miglitol is an **alpha-glucosidase inhibitor** that reversibly inhibits enzymes like sucrase and maltase in the brush border of the small intestine.
- This action **delays carbohydrate digestion and absorption**, reducing postprandial glucose excursions, which fits the description of inhibiting a "membrane-bound enzyme that hydrolyzes carbohydrate bonds."
*Canagliflozin*
- Canagliflozin is a **sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor** that acts in the kidney to reduce glucose reabsorption, leading to increased glucose excretion in the urine.
- It does not inhibit carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract.
*Linagliptin*
- Linagliptin is a **dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor** that increases the levels of incretin hormones (GLP-1 and GIP), thereby enhancing glucose-dependent insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon secretion.
- This mechanism is distinct from inhibiting carbohydrate hydrolysis.
*Pramlintide*
- Pramlintide is an **amylin analog** that slows gastric emptying, suppresses postprandial glucagon secretion, and promotes satiety.
- It works by mimicking the action of amylin, not by inhibiting enzymes that break down carbohydrates.
*Rosiglitazone*
- Rosiglitazone is a **thiazolidinedione (TZD)** that acts as an agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ) to improve insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
- Its mechanism of action is related to gene transcription and insulin sensitization rather than direct inhibition of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 6: A 58-year-old male presents to the clinic for a follow-up visit. He takes metformin every day and says that he is compliant with his medication but can not control his diet. Three months prior, his HbA1c was 8.2% when he was started on metformin. He does not have any complaints on this visit. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), respirations are 15/min, pulse is 67/min and blood pressure is 122/88 mm Hg. His BMI is 33. Physical examination is within normal limits. Blood is drawn for laboratory tests and the results are given below:
Fasting blood glucose 150 mg/dL
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) 7.2 %
Serum Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
BUN 12 mg/dL
The physician wants to initiate another medication for his blood glucose control, specifically one that does not carry a risk of weight gain. Addition of which of the following drugs would be most suitable for this patient?
- A. Sitagliptin (Correct Answer)
- B. Glimepiride
- C. Rosiglitazone
- D. Glyburide
- E. Pioglitazone
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Sitagliptin***
- This is a **dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor** that enhances incretin effects, leading to glucose-dependent insulin secretion and suppressed glucagon.
- DPP-4 inhibitors like sitagliptin are **weight-neutral** and pose a low risk of hypoglycemia, making them suitable additions for patients who need further glycemic control without weight gain, especially with their current BMI.
*Glimepiride*
- This is a **sulfonylurea** that stimulates insulin release from pancreatic beta cells independently of glucose levels.
- Sulfonylureas are associated with a **risk of weight gain** and hypoglycemia, which is an undesirable effect for this patient.
*Rosiglitazone*
- This is a **thiazolidinedione (TZD)** that improves insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues and the liver.
- TZDs, including rosiglitazone, are associated with **weight gain** due to fluid retention and increased adipogenesis, and can also cause congestive heart failure.
*Glyburide*
- This is also a **sulfonylurea**, similar to glimepiride, that stimulates insulin secretion.
- Like other sulfonylureas, glyburide carries a significant risk of **weight gain** and hypoglycemia, making it less ideal for this patient.
*Pioglitazone*
- This is another **thiazolidinedione (TZD)** that improves insulin sensitivity.
- Pioglitazone is known to cause **weight gain** and fluid retention, and it has a black box warning for exacerbating heart failure.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 7: A 14-year-old boy is rushed to the emergency room after he became disoriented at home. His parents say that the boy was doing well until 2 days ago when he got sick and vomited several times. They thought he was recovering but today he appeared to be disoriented since the morning. His vitals are normal except shallow rapid breathing at a rate of 33/min. His blood sugar level is 654 mg/dL and urine is positive for ketone bodies. He is diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis and is managed with fluids and insulin. He responds well to the therapy. His parents are told that their son has type 1 diabetes and insulin therapy options are being discussed. Which of the following types of insulin can be used in this patient for the rapid action required during mealtimes?
- A. Insulin detemir
- B. Insulin degludec
- C. NPH insulin
- D. Insulin glargine
- E. Insulin lispro (Correct Answer)
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Insulin lispro***
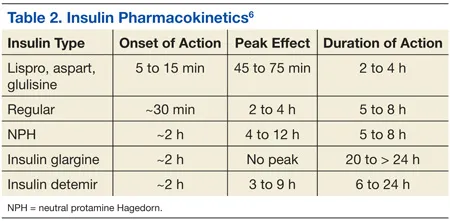
- **Insulin lispro** is a **rapid-acting insulin analog** designed to be taken immediately before or with a meal, offering quick onset (5-15 minutes) and short duration of action.
- Its rapid action helps to control **postprandial glucose spikes**, closely mimicking the physiological insulin response to food, which is crucial for mealtime coverage in **Type 1 diabetes**.
*Insulin detemir*
- **Insulin detemir** is a **long-acting insulin analog** used for basal insulin coverage, providing a relatively constant insulin level over an extended period (12-24 hours).
- It is not suitable for **mealtime insulin coverage** due to its slow onset of action and prolonged duration, which would not effectively manage postprandial glucose excursions.
*Insulin degludec*
- **Insulin degludec** is an **ultra-long-acting basal insulin analog** with a duration of action exceeding 42 hours, providing stable basal coverage.
- Its extremely slow onset and prolonged duration make it unsuitable for **prandial (mealtime) insulin**, as it cannot address the rapid rise in blood glucose following a meal.
*NPH insulin*
- **NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insulin** is an **intermediate-acting insulin** that provides basal insulin coverage, with an onset of 2-4 hours and a peak effect around 6-10 hours.
- Its slow onset and prolonged action make it unsuitable for **mealtime insulin coverage**, as it would not adequately prevent the rapid rise in blood sugar immediately after eating.
*Insulin glargine*
- **Insulin glargine** is a **long-acting insulin analog** used for **basal insulin coverage**, providing a relatively flat and peakless insulin profile over 24 hours.
- It is not used for **prandial (mealtime) insulin** because its slow onset and sustained action would not effectively counteract the rapid rise in blood glucose following a meal.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 8: A 37-year-old woman accompanied by her husband presents to the emergency department after loss of consciousness 30 minutes ago. The husband reports that she was sitting in a chair at home and began having sustained rhythmic contractions of all 4 extremities for approximately 1 minute. During transport via ambulance she appeared confused but arousable. Her husband reports she has no medical conditions, but for the past 2 months she has occasionally complained of episodes of sweating, palpitations, and anxiety. Her brother has epilepsy and her mother has type 1 diabetes mellitus. Laboratory studies obtained in the emergency department demonstrate the following:
Serum:
Na+: 136 mEq/L
K+: 3.8 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
HCO3-: 19 mEq/L
BUN: 16 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL
Glucose: 54 mg/dL
C-peptide: Low
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Beta cell tumor
- B. Surreptitious insulin use (Correct Answer)
- C. Diabetic ketoacidosis
- D. Surreptitious sulfonylurea use
- E. Alpha cell tumor
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Surreptitious insulin use***
- The patient presents with **hypoglycemia** (glucose 54 mg/dL) and symptoms consistent with **neuroglycopenia** (loss of consciousness, confusion, sustained rhythmic contractions similar to seizures). The **low C-peptide** in the presence of hypoglycemia strongly indicates exogenous insulin administration, as C-peptide is co-secreted with endogenous insulin.
- The reported past episodes of **sweating, palpitations, and anxiety** are classic symptoms of **adrenergic response to hypoglycemia**, further supporting a diagnosis of recurrent hypoglycemic events.
*Beta cell tumor*
- A beta cell tumor (insulinoma) would also cause **hypoglycemia** (neuroglycopenia) and symptoms like sweating, palpitations, and anxiety.
- However, an insulinoma would typically result in inappropriately **high C-peptide** levels during hypoglycemia, as the tumor produces both insulin and C-peptide endogenously.
*Diabetic ketoacidosis*
- **Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** is characterized by **hyperglycemia**, **ketonemia**, and **metabolic acidosis**, which is the exact opposite of the patient's presentation of hypoglycemia.
- While the patient's mother has type 1 diabetes, this patient does not exhibit any signs of DKA.
*Surreptitious sulfonylurea use*
- Sulfonylurea use would lead to **hypoglycemia** by stimulating insulin release from pancreatic beta cells.
- This would result in **high C-peptide** levels during hypoglycemia, similar to an insulinoma, differentiating it from exogenous insulin use.
*Alpha cell tumor*
- **Alpha cell tumors (glucagonomas)** produce **excess glucagon**, which would lead to **hyperglycemia**, not hypoglycemia.
- Symptoms typically associated with glucagonomas include necrolytic migratory erythema, diabetes, weight loss, and diarrhea, which are not present in this case.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 9: A 44-year-old female is brought to the emergency room after losing consciousness at a shopping mall. Her husband states that they were shopping when the patient appeared sweaty and tremulous, became confused, then collapsed. She was unconscious for 5 minutes until a paramedic arrived. Fingerstick glucose at that time was 31 mg/dL and intramuscular glucagon was administered. The patient regained consciousness as she was being transported to the ambulance. On arrival in the emergency room, she is conscious but sleepy. She is able to report that her last meal prior to the mall was 5 hours ago. Her husband notes that over the last 3 months, she has complained of headaches and a milky discharge from both breasts, as well as nausea if she goes too long without eating. She works as an inpatient nurse and was exposed to tuberculosis 10 years ago but adequately treated. Because she was adopted as an infant, family history is unknown. Temperature is 98.4 deg F (36.9 deg C), blood pressure is 101/59 mmHg, pulse is 88/min, and respiration is 14/min. Preliminary lab values are shown below:
Plasma glucose: 54 mg/dL
Plasma insulin: 29 pmol/L (normal < 19 pmol/L)
Plasma C-peptide: 272 pmol/L (normal < 200 pmol/L)
Plasma proinsulin: 8 pmol/L (normal < 5 pmol/L)
Plasma ß-hydroxybutyrate: 1.2 mmol/L (normal > 2.7 mmol/L after fasting)
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s hypoglycemic episode?
- A. Noninsulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome (NIPHS)
- B. Primary adrenal insufficiency
- C. Insulinoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Sulfonylurea use
- E. Exogenous insulin use
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: ***Insulinoma***
- The patient's presentation with **recurrent hypoglycemic episodes** (sweaty, tremulous, confused, collapsed) that resolve with glucose administration (intramuscular glucagon) is highly suggestive of an insulinoma.
- The laboratory findings of **elevated insulin, C-peptide, and proinsulin levels** during hypoglycemia, coupled with suppressed beta-hydroxybutyrate, confirm endogenous hyperinsulinism, characteristic of an insulin-producing tumor. The **galactorrhea** and **headaches** suggest a possible co-occurring **pituitary adenoma** as part of **MEN1**, which is often associated with insulinomas.
*Noninsulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome (NIPHS)*
- NIPHS typically presents with **postprandial hypoglycemia** and is more common after gastric bypass surgery, which is not mentioned in this patient's history.
- While it also involves endogenous hyperinsulinism, the patient's symptoms are more consistent with **fasting hypoglycemia**, a hallmark of insulinoma.
*Primary adrenal insufficiency*
- Adrenal insufficiency can cause hypoglycemia due to **cortisol deficiency**, which impairs gluconeogenesis.
- However, the lab results show **elevated insulin and C-peptide**, indicating hyperinsulinism, which is not characteristic of primary adrenal insufficiency.
*Sulfonylurea use*
- Sulfonylureas stimulate insulin release from pancreatic beta cells, leading to **elevated insulin and C-peptide** levels during hypoglycemia.
- However, the patient's history does not mention diabetes or sulfonylurea use, and her persistent symptoms over months without a diagnosis of diabetes make this less likely. A **sulfonylurea screen** would distinguish this.
*Exogenous insulin use*
- Exogenous insulin administration would result in **high insulin levels** but **suppressed C-peptide levels**, as C-peptide is co-secreted with endogenous insulin.
- The patient's lab results show **elevated C-peptide**, ruling out exogenous insulin as the sole cause of hyperinsulinism.
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG Question 10: A 60-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of recurrent episodes of fatigue, palpitations, nausea, and diaphoresis over the past 6 months. The episodes have become more frequent in the last 2 weeks and he has missed work several times because of them. His symptoms usually improve after he drinks some juice and rests. He has had a 2-kg (4.5-lb) weight gain in the past 6 months. He has a history of bipolar disorder, hypertension, and asthma. His sister has type 2 diabetes mellitus and his mother has a history of medullary thyroid carcinoma. His medications include lithium, hydrochlorothiazide, aspirin, and a budesonide inhaler. His temperature is 36.3°C (97.3°F), pulse is 92/min and regular, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 118/65 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows no abnormalities. Serum studies show:
Na+ 145 mEq/L
K+ 3.9 mEq/L
Cl- 103 mEq/L
Calcium 9.2 mg/dL
Glucose 88 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Corticotropin stimulation test
- B. Water deprivation test
- C. Oral glucose tolerance test
- D. 24-hour urine catecholamine test
- E. 72-hour fasting test (Correct Answer)
Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents Explanation: **72-hour fasting test**
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, palpitations, nausea, diaphoresis) that improve with eating (drinking juice) are highly suggestive of **hypoglycemia**, fitting **Whipple's triad**.
- A 72-hour fasting test is the gold standard for diagnosing **insulinoma**, a neuroendocrine tumor that causes endogenous hyperinsulinism and recurrent hypoglycemia.
*Corticotropin stimulation test*
- This test is used to diagnose **adrenal insufficiency** by evaluating the adrenal glands' response to ACTH.
- The patient's symptoms are inconsistent with adrenal insufficiency, and his blood pressure is stable, arguing against a hypotensive crisis.
*Water deprivation test*
- This test is used to diagnose **diabetes insipidus** by assessing the kidney's ability to concentrate urine.
- The patient's symptoms do not align with polyuria and polydipsia characteristic of diabetes insipidus.
*Oral glucose tolerance test*
- This test is primarily used to diagnose **diabetes mellitus** or impaired glucose tolerance.
- While helpful for assessing glucose metabolism, it is not the initial test for recurrent symptomatic hypoglycemia that improves with sugar intake.
*24-hour urine catecholamine test*
- This test is used to diagnose **pheochromocytoma**, a tumor that causes excessive catecholamine release.
- While palpitations and diaphoresis can occur, the improvement with glucose and lack of sustained hypertension make pheochromocytoma less likely.
More Insulin and oral antidiabetic agents US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.