Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Preventive cardiology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
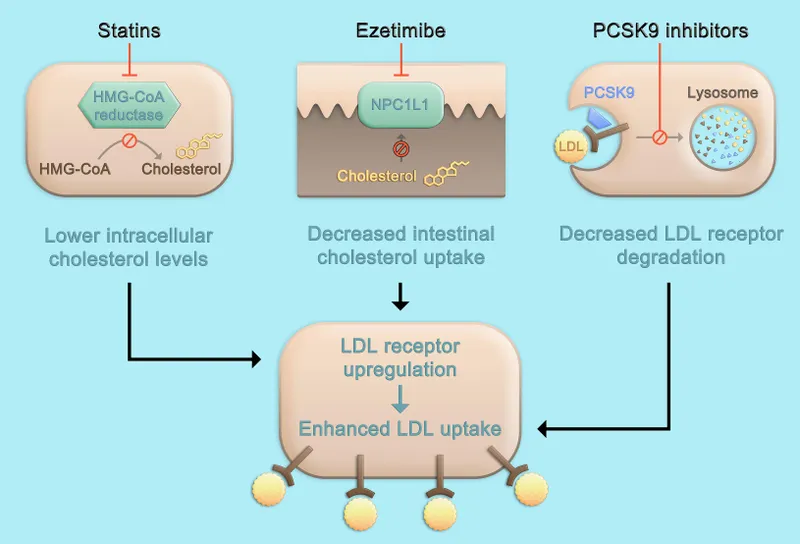
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 1: A 53-year old man presents for a well physical examination. He reports his diet is suboptimal, but otherwise reports a healthy lifestyle. He has no past medical history and only takes a multivitamin. He has a blood pressure of 116/74 mm Hg and a pulse of 76/min. On physical examination, he is in no acute distress, has no cardiac murmurs, and his lung sounds are clear to auscultation bilaterally. You order a lipid panel that returns as follows: LDL 203, HDL 37, TG 292. Of the following, which medication should be initiated?
- A. Ezetimibe 10 mg daily
- B. Colesevelam 3.75 grams daily
- C. Atorvastatin 40 mg daily (Correct Answer)
- D. Fenofibrate 145 mg daily
- E. Simvastatin 10 mg daily
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Atorvastatin 40 mg***
- This patient has a **very high LDL level of 203 mg/dL** and is over 40 years old, placing him in a high-risk group that warrants initiation of a **high-intensity statin** for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.
- **Atorvastatin 40 mg** is a high-intensity statin known to reduce LDL cholesterol by 50% or more, which is appropriate for this patient's elevated risk.
*Ezetimibe 10 mg daily*
- **Ezetimibe** works by inhibiting cholesterol absorption in the small intestine and is typically used as an add-on therapy for patients who do not achieve their LDL goals with statins alone, or for those who are statin-intolerant.
- It is not a first-line monotherapy for a patient with such significantly elevated LDL cholesterol.
*Colesevelam 3.75 grams daily*
- **Colesevelam** is a bile acid sequestrant that lowers LDL by increasing its fecal excretion; however, it has a more modest LDL-lowering effect compared to statins and can sometimes increase triglycerides.
- It is not the most effective or appropriate first-line agent, especially given the patient's existing elevated triglyceride levels.
*Fenofibrate 145 mg daily*
- **Fenofibrate** is primarily used to lower **triglycerides** and can mildly raise HDL, but it has minimal effect on LDL cholesterol.
- While the patient has elevated triglycerides, his primary and most significant lipid abnormality requiring immediate intervention for cardiovascular risk reduction is his severely elevated LDL.
*Simvastatin 10 mg daily*
- **Simvastatin 10 mg** is a **low-intensity statin** dose (typical range: 10-20 mg), which is not sufficient for a patient with an LDL of 203 mg/dL and high cardiovascular risk.
- Guidelines recommend a **high-intensity statin** like atorvastatin 40-80 mg or rosuvastatin 20-40 mg for such elevated LDL levels.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 2: A previously healthy 61-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of morning headaches. He also has fatigue and trouble concentrating on his daily tasks at work. He sleeps for 8 hours every night; his wife reports that he sometimes stops breathing for a few seconds while sleeping. His pulse is 71/min and blood pressure is 158/96 mm Hg. He is 178 cm (5 ft 10 in) tall and weighs 100 kg (220 lb); BMI is 31.6 kg/m2 . Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's hypertension?
- A. Proliferation of adrenal chromaffin cells
- B. Overproduction of cortisol
- C. Hypophyseal neoplasm
- D. Nocturnal upper airway obstruction (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypersecretion of aldosterone
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Nocturnal upper airway obstruction***
- The patient's **obesity (BMI 31.6)**, **morning headaches**, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and spousal report of **witnessed apneic episodes during sleep** are classic signs of **obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)**.
- OSA causes **intermittent hypoxia and hypercapnia** during sleep, leading to **sympathetic nervous system activation**, increased catecholamine release, and **sustained hypertension** even during waking hours.
- OSA is one of the most common **secondary causes of hypertension**, especially in obese patients.
*Proliferation of adrenal chromaffin cells*
- This describes a **pheochromocytoma**, which typically presents with **paroxysmal hypertension**, severe episodic headaches, palpitations, and diaphoresis (the classic "triad").
- While headaches are present, the **sleep-related breathing disturbances** and obesity are not consistent with pheochromocytoma.
*Overproduction of cortisol*
- This suggests **Cushing's syndrome**, which includes symptoms like central obesity, **moon facies, buffalo hump, purple striae**, muscle weakness, and easy bruising, along with hypertension.
- The patient lacks the classic cushingoid features, and the symptoms are more consistent with sleep-disordered breathing.
*Hypophyseal neoplasm*
- A pituitary tumor could cause hypertension if it leads to conditions like **Cushing's disease** (ACTH-secreting) or **acromegaly** (growth hormone excess).
- However, there are no specific symptoms pointing towards a pituitary tumor (no visual field defects, acromegalic features, or cushingoid appearance), and the prominent **witnessed apneas** fit OSA much better.
*Hypersecretion of aldosterone*
- This is characteristic of **primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn's syndrome)**, which commonly presents with hypertension, often accompanied by **hypokalemia**, muscle weakness, and polyuria.
- The patient's symptoms do not suggest electrolyte abnormalities or other classic signs of mineralocorticoid excess.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 3: A peripheral artery is found to have 50% stenosis (50% reduction in cross-sectional area). Therefore, compared to a normal artery with no stenosis, by what factor has the flow of blood been decreased?
- A. 8
- B. 2
- C. 32
- D. 16
- E. 4 (Correct Answer)
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***4***
- According to **Poiseuille's Law**, blood flow is proportional to the fourth power of the radius (Flow ∝ r⁴).
- If the cross-sectional area is reduced by 50%, the new area is 0.5 times the original. Since Area = πr², we have: πr_new² = 0.5πr_original², which gives r_new = √0.5 × r_original ≈ 0.707 × r_original.
- The new flow becomes: Flow_new ∝ (0.707r)⁴ = (0.707)⁴ × r⁴ = 0.25 × r⁴.
- Therefore, the flow is reduced to **1/4 of the original**, meaning it has decreased by a factor of **4**.
*8*
- This would only be correct if flow were proportional to r³ (the cube of radius), which does not apply to laminar blood flow.
- Poiseuille's Law establishes a **fourth-power relationship** between radius and flow, not a cubic relationship.
*2*
- A factor of 2 would imply either a linear relationship between flow and radius, or only a minimal stenosis (~16% area reduction).
- This significantly **underestimates** the impact of a 50% area reduction on blood flow through the vessel.
*32*
- This represents an excessive reduction that would only occur if flow were proportional to r⁵ or higher.
- With 50% area stenosis and the r⁴ relationship, the mathematical result is a factor of **4**, not 32.
*16*
- This would be the correct answer if "50% stenosis" referred to a **50% reduction in diameter** (radius) rather than area.
- With 50% diameter reduction: r_new = 0.5r, so Flow_new ∝ (0.5r)⁴ = 0.0625r⁴, giving a decrease by factor of 16.
- However, the question specifies **area reduction**, making this option incorrect.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 4: A popular news outlet recently published an article that discussed the size of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol particles: type A and type B. Type B is thought to be more harmful to arterial walls. A group of researchers wants to determine whether patients who have an elevated level of type B LDL cholesterol are more likely to develop cardiovascular events. A study is designed with 3418 adult participants. Initial levels of type B LDL are obtained and participants are separated into normal and elevated levels of type B LDL. Socio-demographics including age, gender, education level, and smoking status are also recorded. The primary outcome is incidence of cardiovascular events over 10 years. Secondary outcomes include all-cause death, death by cardiovascular events, stroke, and hospitalizations. For this study, which of the following analyses would be the most appropriate measure to determine the association between type B LDL and cardiovascular events?
- A. Analysis of covariance
- B. Fisher’s exact test
- C. Likelihood ratios
- D. Relative risk (Correct Answer)
- E. Odds ratio
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Relative risk***
- **Relative risk** is the most appropriate measure for **cohort studies** to determine the likelihood of an event in an exposed group compared to an unexposed group.
- This study prospectively follows participants with and without elevated type B LDL to observe the **incidence of cardiovascular events** over 10 years, which perfectly aligns with the calculation and interpretation of relative risk.
*Analysis of covariance*
- **ANCOVA** is used to compare means across groups while statistically controlling for the effects of one or more **covariates**.
- While covariates like age and smoking status are collected, ANCOVA is not the primary measure for assessing the association between an exposure (Type B LDL) and the incidence of an outcome (cardiovascular events) in this **cohort study design**.
*Fisher’s exact test*
- This test is used for analyzing **categorical data** in **small sample sizes** or when expected cell counts are low, typically in 2x2 contingency tables.
- Given the large sample size (3418 participants) and the prospective nature of the study, it would not be the most appropriate primary analytical tool for determining the risk association.
*Likelihood ratios*
- **Likelihood ratios** are used to assess the **diagnostic accuracy of a test**, indicating how much a positive or negative test result changes the probability of a disease.
- This study is focused on the **prognostic association** between an exposure and an outcome, not the diagnostic performance of a test.
*Odds ratio*
- The **odds ratio** is primarily used in **case-control studies** or cross-sectional studies where the incidence of the outcome cannot be directly calculated.
- While it can approximate relative risk when the outcome is rare, this is a **cohort study** where the **incidence** of cardiovascular events can be directly measured, making relative risk more suitable.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 5: A 56-year-old woman comes to the physician for follow-up after a measurement of elevated blood pressure at her last visit three months ago. She works as a high school teacher at a local school. She says that she mostly eats cafeteria food and take-out. She denies any regular physical activity. She does not smoke or use any recreational drugs. She drinks 2 to 3 glasses of wine per day. She has hypercholesterolemia for which she takes atorvastatin. Her height is 165 cm (5 ft 5 in), weight is 82 kg (181 lb), and BMI is 30.1 kg/m2. Her pulse is 67/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 152/87 mm Hg on the right arm and 155/92 mm Hg on the left arm. She would like to try lifestyle modifications to improve her blood pressure before considering pharmacologic therapy. Which of the following lifestyle modifications is most likely to result in the greatest reduction of this patient's systolic blood pressure?
- A. Walking for 30 minutes, 5 days per week
- B. Reducing sodium intake to less than 2.4 g per day
- C. Losing 15 kg (33 lb) of body weight (Correct Answer)
- D. Adopting a DASH diet
- E. Decreasing alcohol consumption to maximum of one drink per day
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Losing 15 kg (33 lb) of body weight***
- **Weight reduction** is the most effective lifestyle modification for lowering blood pressure, correlating directly with the amount of weight lost.
- A loss of 15 kg (33 lb) in this patient, who is **obese (BMI 30.1)**, could significantly reduce her systolic blood pressure, potentially by 5-20 mmHg per 10 kg weight loss.
*Walking for 30 minutes, 5 days per week*
- Regular **aerobic physical activity** is beneficial for blood pressure reduction, typically resulting in a 4-9 mmHg decrease in systolic pressure.
- While helpful, the magnitude of reduction from exercise alone is generally less than that achieved with significant weight loss in an obese individual.
*Reducing sodium intake to less than 2.4 g per day*
- **Sodium restriction** is an effective strategy, often leading to a 2-8 mmHg reduction in systolic blood pressure.
- Given the patient's diet of cafeteria and take-out food, high sodium intake is likely, making this a relevant intervention, but typically less impactful than substantial weight loss.
*Adopting a DASH diet*
- The **Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet** emphasizes fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy, and can significantly lower blood pressure, by 8-14 mmHg.
- This diet is highly effective, but for an obese individual, the blood pressure reduction from achieving a healthy weight is often greater.
*Decreasing alcohol consumption to maximum of one drink per day*
- Reducing **excessive alcohol intake** can decrease systolic blood pressure by 2-4 mmHg, as the patient reports 2-3 glasses of wine daily.
- While beneficial, this reduction is likely to be less substantial compared to major weight loss or other dietary changes.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 6: A 68-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up visit for elevated blood pressure. Two weeks ago, her blood pressure was 154/78 mm Hg at a routine visit. Subsequent home blood pressure measurements at days 5, 10, and 14 have been: 156/76 mm Hg, 158/80 mm Hg, and 160/80 mm Hg. She has trouble falling asleep but otherwise feels well. She had a cold that resolved with over-the-counter medication 2 weeks ago. She has a history of primary hypothyroidism and a cyst in the right kidney, which was found incidentally 20 years ago. She takes levothyroxine. She is 178 cm (5 ft 10 in) tall and weighs 67 kg (148 lb); BMI is 21.3 kg/m2. Her pulse is 82/min, and blood pressure is 162/79 mm Hg. Examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies, including thyroid function studies, serum electrolytes, and serum creatinine, are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's blood pressure findings?
- A. Medication-induced vasoconstriction
- B. Decrease in baroreceptor sensitivity
- C. Increase in kidney size
- D. Increase in aldosterone production
- E. Decrease in arterial compliance (Correct Answer)
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Decrease in arterial compliance***
- As individuals **age**, the large elastic arteries become stiffer and less compliant due to changes in **collagen and elastin**, leading to an increase in **systolic blood pressure** and pulse pressure. This patient's blood pressure readings consistently show elevated systolic pressure without other identifiable causes.
- The patient's age (68 years old) and the absence of other specific causes for secondary hypertension, combined with an isolated **systolic hypertension**, strongly suggest age-related decrease in arterial compliance as the underlying mechanism.
*Medication-induced vasoconstriction*
- While certain over-the-counter medications like **decongestants (e.g., pseudoephedrine)** can cause vasoconstriction and elevate blood pressure, the patient's cold resolved two weeks ago, making it unlikely to be a persistent cause of her current blood pressure readings.
- There is no mention of her currently taking any medications known to cause vasoconstriction beyond the short-term use for her cold, which should have resolved.
*Decrease in baroreceptor sensitivity*
- **Baroreceptor sensitivity** can decrease with age, leading to impaired short-term blood pressure regulation and an increased risk of orthostatic hypotension, but it does not directly cause sustained **essential hypertension** or primarily elevated systolic pressure in this manner.
- While decreased baroreflex sensitivity is common in the elderly, it is not the primary mechanism behind the patient's sustained high systolic blood pressure; rather, it relates more to blood pressure variability and postural changes.
*Increase in kidney size*
- An **increase in kidney size** is not typically associated with hypertension; rather, conditions like polycystic kidney disease, which causes renal enlargement, can cause hypertension through **renal ischemia** and **RAAS activation**, but the patient has a single simple cyst and normal renal function.
- The patient's history of a simple renal cyst and normal renal function tests do not suggest any kidney-related pathology causing hypertension.
*Increase in aldosterone production*
- An **increase in aldosterone production** (primary hyperaldosteronism) typically causes **hypertension** along with **hypokalemia**, which is not present in this patient as her serum electrolytes are normal.
- Primary hyperaldosteronism would likely present with **resistant hypertension** and often **metabolic alkalosis**, none of which are indicated by the patient's symptoms or laboratory findings.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 7: A 66-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with lower extremity pain. She reports that she has had worsening pain in her left calf over the past year while walking. The pain improves with rest, but the patient notes that she now has to stop walking more frequently than in the past to relieve the pain. The patient’s past medical history is otherwise notable for hypertension and coronary artery disease. Her home medications include hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril. Her family history is significant for diabetes mellitus in her father. On physical exam, her left lower extremity is slightly cool to the touch with palpable distal pulses. The skin of the left lower extremity appears smooth and shiny below the mid-calf. Laboratory testing is performed and reveals the following:
Serum:
High-density lipoprotein (HDL): 60 mg/dL
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): 96 mg/dL
Triglycerides: 140 mg/dL
This patient should be started on which of the following medication regimens?
- A. Aspirin and cilostazol
- B. Aspirin only
- C. Aspirin and atorvastatin (Correct Answer)
- D. Atorvastatin and cilostazol
- E. Atorvastatin only
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Aspirin and atorvastatin***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms and signs of **peripheral artery disease (PAD)**, including **intermittent claudication** (pain with walking, relieved by rest), **cool extremity**, and **trophic skin changes** (smooth, shiny skin).
- Both **aspirin** (for antiplatelet activity to reduce thrombotic events) and a **statin** like atorvastatin (for lipid lowering and plaque stabilization) are crucial for managing PAD and reducing cardiovascular risk due to her history of hypertension and coronary artery disease.
*Aspirin and cilostazol*
- **Aspirin** is appropriate for its antiplatelet effects, but **cilostazol** is primarily used to improve claudication symptoms and does not address the underlying lipid abnormalities or the need for cardiovascular risk reduction as comprehensively as a statin.
- While cilostazol can alleviate symptoms, it's not a first-line agent for overall cardiovascular risk reduction in PAD when dyslipidemia is also a concern.
*Aspirin only*
- **Aspirin** is essential for secondary prevention of cardiovascular events in PAD, but it does not address the patient's **lipid profile** which, while within "normal" limits by some metrics, warrants statin therapy given her high-risk cardiovascular history (hypertension, CAD, PAD).
- Optimal management of PAD involves both antiplatelet therapy and intensive lipid lowering.
*Atorvastatin and cilostazol*
- **Atorvastatin** is appropriate for lipid lowering and cardiovascular risk reduction in PAD. However, omitting **aspirin** means missing a crucial component of antiplatelet therapy for PAD, which significantly reduces the risk of serious thrombotic events.
- **Cilostazol** helps with symptoms but does not replace aspirin's role in preventing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
*Atorvastatin only*
- **Atorvastatin** is vital for its pleiotropic effects, including plaque stabilization and lipid lowering, in a patient with PAD and other cardiovascular risk factors.
- However, managing PAD optimally requires concurrent **antiplatelet therapy** (e.g., aspirin) to reduce the risk of thrombotic events, which is not included in this regimen.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 8: A prospective cohort study was conducted to assess the relationship between LDL and the incidence of heart disease. The patients were selected at random. Results showed a 10-year relative risk of 2.3 for people with elevated LDL levels compared to individuals with normal LDL levels. The 95% confidence interval was 1.05-3.50. This study is most likely to have which of the following p values?
- A. 0.20
- B. 0.06
- C. 0.08
- D. 0.04 (Correct Answer)
- E. 0.10
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***0.04***
- A 95% confidence interval that **does not include 1 (one)** suggests a **statistically significant** association, meaning the p-value is likely to be **less than 0.05**.
- The given CI of 1.05-3.50 for the relative risk (RR) is entirely above 1, indicating a significant positive association, and therefore, a p-value less than 0.05.
*0.20*
- A p-value of 0.20 is **greater than 0.05**, which would imply the finding is **not statistically significant**.
- If the p-value were 0.20, the 95% confidence interval would likely **include 1**, suggesting no significant difference in risk.
*0.06*
- A p-value of 0.06 is **greater than 0.05**, indicating that the association is **not statistically significant at the conventional alpha level**.
- If the p-value were 0.06, the 95% confidence interval would likely **include 1**, or be very close to including it, contradicting the given CI of 1.05-3.50.
*0.08*
- A p-value of 0.08 is **greater than 0.05**, indicating that the finding is **not statistically significant**.
- If the p-value were 0.08, the 95% confidence interval would almost certainly **include 1**, which is inconsistent with the provided interval.
*0.10*
- A p-value of 0.10 is **greater than 0.05**, which signifies that the finding is **not statistically significant**.
- If the p-value were 0.10, the 95% confidence interval for the relative risk would typically **include 1**, contradicting the given confidence interval.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 9: A 65-year-old man with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after the onset of severe anterior chest pain and shortness of breath. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years. He appears distressed. His pulse is 116/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 156/88 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 98%. A grade 3/6, high-pitched, blowing, diastolic murmur is heard over the right upper sternal border. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Rupture of a bulla in the lung
- B. Perforation of the esophageal wall
- C. Obstruction of the pulmonary arteries
- D. Fibrofatty plaque in the aortic wall
- E. Tear in the tunica intima (Correct Answer)
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Tear in the tunica intima***
- The sudden onset of **severe anterior chest pain**, hypertension, and a **diastolic murmur** consistent with **aortic insufficiency** points strongly to an **aortic dissection**, which begins with a tear in the tunica intima.
- Risk factors like **hypertension**, **smoking**, and **advanced age** increase the likelihood of aortic dissection.
*Rupture of a bulla in the lung*
- This would typically cause **pneumothorax**, leading to **sharp, pleuritic chest pain** and **dyspnea**, often with diminished breath sounds on the affected side.
- A **cardiac murmur** and severe distress in the context of vascular risk factors are not characteristic of a ruptured bulla.
*Perforation of the esophageal wall*
- Esophageal perforation (Boerhaave syndrome) presents with **severe chest pain**, **vomiting**, and often **subcutaneous emphysema** or **pleural effusion**.
- While it causes severe chest pain, the described **diastolic murmur** and absence of vomiting or other specific signs make this less likely.
*Obstruction of the pulmonary arteries*
- **Pulmonary embolism** (obstruction of pulmonary arteries) typically causes **sudden onset dyspnea**, **pleuritic chest pain**, **tachycardia**, and **hypoxia**, often without a significant cardiac murmur of this nature.
- The oxygen saturation of 98% makes a large pulmonary embolism less probable.
*Fibrofatty plaque in the aortic wall*
- While common in patients with hypertension and smoking history, an **atherosclerotic plaque** in the aortic wall itself rarely causes acute, severe chest pain and a new diastolic murmur unless it leads to an **aortic dissection** or **rupture**.
- This option describes a precursor to diseases like aortic dissection but not the acute event itself.
Preventive cardiology US Medical PG Question 10: A 59-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a sudden onset of severe pain (10/10 in severity) between the shoulder blades. He describes the pain as tearing in nature. Medical history is positive for essential hypertension for 11 years. The patient has smoked 10–15 cigarettes daily for the past 30 years. His temperature is 36.6°C (97.8°F), the heart rate is 107/min, and the blood pressure is 179/86 mm Hg in the right arm and 157/72 mm Hg in the left arm. CT scan of the chest shows an intimal flap limited to the descending thoracic aorta. Which of the following best describes the most likely predisposing factor for this condition?
- A. Coronary atherosclerosis
- B. Aortic coarctation
- C. Hypertensive urgency
- D. Aortic atherosclerosis
- E. Abnormal elastic properties of the aorta (Correct Answer)
Preventive cardiology Explanation: ***Abnormal elastic properties of the aorta***
- Chronic **hypertension** (11 years) is the #1 risk factor for aortic dissection, causing **cystic medial degeneration** (breakdown of elastic fibers and smooth muscle in the tunica media).
- This degenerative process results in **abnormal elastic properties** and weakening of the aortic wall, predisposing to dissection.
- The tearing pain, blood pressure differential between arms, and CT findings of intimal flap are classic for **Type B aortic dissection**.
- While often associated with connective tissue disorders in younger patients, cystic medial degeneration is also the pathophysiologic result of chronic hypertension in older patients.
*Aortic atherosclerosis*
- Atherosclerosis primarily affects the **intima** layer, while aortic dissection occurs in the **media** layer.
- Though hypertension and smoking contribute to atherosclerosis, this is not the primary predisposing mechanism for dissection.
- The underlying pathology is medial degeneration with abnormal elastic properties, not atherosclerotic plaque.
*Coronary atherosclerosis*
- This affects the coronary arteries supplying the heart, not the aortic wall structure.
- Does not explain the anatomical location of dissection or the tearing interscapular pain.
- Not a predisposing factor for aortic dissection.
*Hypertensive urgency*
- This refers to elevated blood pressure without acute end-organ damage.
- The patient has **aortic dissection**, which represents acute end-organ damage (hypertensive emergency, not urgency).
- While hypertension can precipitate dissection, the underlying **predisposing factor** is the chronic medial wall changes (abnormal elastic properties), not the acute blood pressure elevation itself.
*Aortic coarctation*
- This is a **congenital** narrowing of the aorta, typically diagnosed in childhood or young adulthood.
- Classic finding is upper extremity hypertension with **lower extremity hypotension** (opposite pattern from arm-to-arm differential seen in dissection).
- The patient's age, presentation, and 11-year history of essential hypertension make this unlikely.
More Preventive cardiology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.