Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A 48-year-old woman comes to the physician because of progressively worsening dyspnea on exertion and fatigue for the past 2 months. She had Hodgkin lymphoma as an adolescent, which was treated successfully with chemotherapy and radiation. Her father died from complications related to amyloidosis. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 124/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 98/60 mm Hg. Cardiac examination shows no murmurs. Coarse crackles are heard at the lung bases bilaterally. An ECG shows an irregularly irregular rhythm with absent P waves. An x-ray of the chest shows globular enlargement of the cardiac shadow with prominent hila and bilateral fluffy infiltrates. Transthoracic echocardiography shows a dilated left ventricle with an ejection fraction of 40%. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Postradiation fibrosis
- B. Coronary artery occlusion
- C. Amyloid deposition
- D. Acute psychological stress
- E. Chronic tachycardia (Correct Answer)
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Chronic tachycardia***
- The **irregularly irregular rhythm with absent P waves** on ECG is characteristic of **atrial fibrillation**, which can lead to **tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy** if sustained. The pulse of 124/min supports this.
- A sustained elevated heart rate like 124/min, especially in the context of atrial fibrillation, can cause **ventricular dilation** and reduced ejection fraction, leading to symptoms like dyspnea and fatigue observed in the patient.
*Postradiation fibrosis*
- While the patient has a history of radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma, **radiation-induced cardiac damage** typically manifests as perivascular **fibrosis**, leading to **restrictive cardiomyopathy** or pericardial disease, not primarily dilated cardiomyopathy with an irregularly irregular rhythm.
- This condition is often associated with a **reduced diastolic filling** and **normal systolic function** initially, which contradicts the dilated left ventricle and reduced ejection fraction described.
*Amyloid deposition*
- The family history of amyloidosis is a red herring in this clinical picture. While **cardiac amyloidosis** can cause heart failure, it typically presents as **restrictive cardiomyopathy** with **thickened ventricular walls** and normal or reduced ventricular cavity size, not a dilated left ventricle.
- ECG findings in amyloidosis often include **low voltage QRS complexes** despite thickened walls, which is not described.
*Coronary artery occlusion*
- **Coronary artery occlusion** (e.g., myocardial infarction) can lead to dilated cardiomyopathy and reduced ejection fraction, but it usually presents with chest pain or specific ECG changes (e.g., ST elevation/depression, Q waves) that are not mentioned.
- The **irregularly irregular rhythm** (atrial fibrillation) and absence of murmurs make a primary ischemic event less likely as the sole explanation for the global cardiac changes.
*Acute psychological stress*
- **Acute psychological stress** can trigger **takotsubo cardiomyopathy** (stress-induced cardiomyopathy), which presents with left ventricular dysfunction and apical ballooning.
- However, this is typically an acute event with different ECG patterns (often ST elevation) and would not explain the chronic, sustained tachycardia and atrial fibrillation leading to dilated cardiomyopathy.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 2: A 26-year-old nursing home staff presents to the emergency room with complaints of palpitations and chest pain for the past 2 days. She was working at the nursing home for the last year but has been trying to get into modeling for the last 6 months and trying hard to lose weight. She is a non-smoker and occasionally drinks alcohol on weekends with friends. On examination, she appears well nourished and is in no distress. The blood pressure is 150/84 mm Hg and the pulse is 118/min. An ECG shows absent P waves. All other physical findings are normal. What is the probable diagnosis?
- A. Anorexia nervosa
- B. Graves' disease
- C. Hashimoto thyroiditis
- D. Toxic nodular goiter
- E. Factitious thyrotoxicosis (Correct Answer)
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Factitious thyrotoxicosis***
- The patient's profession as a nursing home staff member provides access to medications, and her attempts to lose weight for modeling suggest a motive for **self-administration of thyroid hormones**.
- **Absent P waves** on ECG along with **palpitations and tachycardia** are consistent with atrial arrhythmias often seen in thyrotoxicosis, but the overall presentation with a desire for weight loss points towards an exogenous source.
*Anorexia nervosa*
- While patients with anorexia nervosa do try to lose weight, their presentation is typically associated with **bradycardia**, not the tachycardia and elevated blood pressure seen here.
- ECG findings in anorexia nervosa would more likely show **QT prolongation** or other conduction abnormalities due to electrolyte imbalances, not specifically absent P waves caused by arrhythmia.
*Graves' disease*
- Graves' disease is an autoimmune condition causing hyperthyroidism, presenting with similar symptoms like **tachycardia and palpitations**. However, it is typically associated with other systemic findings such as **ophthalmopathy (exophthalmos)**, **pretibial myxedema**, or a palpable goiter, none of which are mentioned.
- Laboratory findings would show **high T3/T4** with **low TSH**, and often **positive TSH receptor antibodies**, differentiating it from factitious causes.
*Hashimoto thyroiditis*
- Hashimoto thyroiditis is an **autoimmune cause of hypothyroidism**, characterized by fatigue, weight gain, and bradycardia, which are opposite to the patient's symptoms of palpitations, tachycardia, and weight loss efforts.
- While it can initially present with transient hyperthyroidism (hashitoxicosis), the chronic state is hypothyroidism, and the ECG would not typically show absent P waves.
*Toxic nodular goiter*
- A toxic nodular goiter causes hyperthyroidism due to **autonomous thyroid nodules**, leading to symptoms similar to Graves' disease (palpitations, weight loss).
- However, the physical examination would usually reveal a **palpable nodular goiter**, which is not mentioned in this case, making it a less likely diagnosis compared to factitious thyrotoxicosis given the context.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 3: A 39-year-old female with poorly controlled systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) presents to the emergency room with a cough and pleuritic chest pain. She states that she developed these symptoms 2 days prior. The pain appears to improve when the patient leans forward. She currently takes hydroxychloroquine for her systemic lupus erythematosus but has missed several doses recently. Her temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 135/80 mmHg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination reveals a rise in jugular venous pressure during inspiration. In addition to tachycardia, which of the following EKG patterns is most likely to be seen in this patient?
- A. Peaked T waves with flattened P waves
- B. Irregularly irregular QRS complexes with no P waves
- C. PR depressions and diffuse ST elevations (Correct Answer)
- D. ST segment depressions in leads II, III, and aVF
- E. Prolonged PR interval with normal QRS complexes
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***PR depressions and diffuse ST elevations***
- The patient's symptoms of **pleuritic chest pain** that improves with **leaning forward**, along with a history of **poorly controlled SLE**, are classic for **acute pericarditis**.
- **Elevated JVP during inspiration (Kussmaul's sign)** suggests pericardial involvement with possible early effusion, though this sign is more classically associated with constrictive pericarditis or tamponade. However, the **characteristic ECG findings in acute pericarditis** are diffuse **ST segment elevations** (concave upward) and **PR segment depressions**, typically seen in leads II, III, aVF, and V2-V6.
- These ECG changes reflect the inflammatory process affecting the pericardium and are the hallmark of acute pericarditis, regardless of whether early effusion is present.
*Peaked T waves with flattened P waves*
- This pattern is characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, which presents with muscle weakness, fatigue, and cardiac arrhythmias, none of which are present in this case.
- The patient's presentation with pleuritic chest pain relieved by leaning forward is not consistent with hyperkalemia.
*Irregularly irregular QRS complexes with no P waves*
- This EKG pattern is indicative of **atrial fibrillation**, which presents with palpitations and may cause shortness of breath.
- While tachycardia is present, the irregular rhythm and absence of P waves characteristic of atrial fibrillation are not typical findings in acute pericarditis.
*ST segment depressions in leads II, III, and aVF*
- **ST segment depressions** in these leads typically suggest **inferior myocardial ischemia** or infarction, which would cause chest pain that is usually substernal, pressure-like, and not improved by positional changes.
- The pleuritic nature of the pain and its relief with leaning forward point away from ischemia.
*Prolonged PR interval with normal QRS complexes*
- A prolonged PR interval indicates **first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block**, which is usually asymptomatic and not associated with pleuritic chest pain.
- While SLE can be associated with conduction abnormalities, first-degree AV block would not explain the acute presentation or the characteristic pericarditis symptoms.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A 36-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with chest discomfort and fatigue. She reports that her symptoms began approximately 1 week ago and are associated with shortness of breath, swelling of her legs, and worsening weakness. She’s been having transitory fevers for about 1 month and denies having similar symptoms in the past. Medical history is significant for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated with hydroxychloroquine. She had a SLE flare approximately 2 weeks prior to presentation, requiring a short course of prednisone. Physical exam was significant for a pericardial friction rub. An electrocardiogram showed widespread ST-segment elevation and PR depression. After extensive work-up, she was admitted for further evaluation, treatment, and observation. Approximately 2 days after admission she became unresponsive. Her temperature is 100°F (37.8°C), blood pressure is 75/52 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 22/min. Heart sounds are muffled. Which of the following is a clinical finding that will most likely be found in this patient?
- A. Warm extremities
- B. Pericardial knock
- C. Decreased systolic blood pressure by 8 mmHg with inspiration
- D. Jugular venous distension (Correct Answer)
- E. Unequal blood pressure measurements between both arms
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Jugular venous distension***
- The patient's presentation with **muffled heart sounds**, **hypotension**, and a **pericardial friction rub** points towards **cardiac tamponade**, a medical emergency caused by fluid accumulation in the pericardial sac.
- **Jugular venous distension** is a key component of **Beck's triad** (along with muffled heart sounds and hypotension) and indicates increased right atrial pressure due to restricted ventricular filling.
*Warm extremities*
- **Warm extremities** are more characteristic of **vasodilatory shock** (e.g., septic shock), where peripheral vasodilation leads to increased skin temperature.
- In **cardiac tamponade**, reduced cardiac output typically results in **cool and clammy extremities** due to compensatory peripheral vasoconstriction.
*Pericardial knock*
- A **pericardial knock** is an early diastolic sound often heard in **constrictive pericarditis**, caused by the sudden cessation of ventricular filling.
- While the patient has pericardial involvement, the acute presentation with signs of shock is more consistent with **cardiac tamponade**, rather than chronic constriction.
*Decreased systolic blood pressure by 8 mmHg with inspiration*
- **Pulsus paradoxus** (a decrease in systolic blood pressure of **>10 mmHg with inspiration**) is a hallmark sign of **cardiac tamponade**.
- While this patient likely has pulsus paradoxus, the value of **8 mmHg falls below the diagnostic threshold** of 10 mmHg and would not be considered pathological pulsus paradoxus.
- **Jugular venous distension** is a more reliable and clinically obvious finding in cardiac tamponade.
*Unequal blood pressure measurements between both arms*
- **Unequal blood pressure measurements between the arms** (>10-15 mmHg difference) are characteristic of conditions like **aortic dissection** or **subclavian artery stenosis**.
- This finding is not typically associated with **cardiac tamponade**, which affects global cardiac function.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 5: A 19-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by ambulance 30 minutes after her neighbor found her unconscious on a running trail. Her neighbor reports that she has been training for a marathon since the beginning of the summer. She is alert and oriented but becomes irritable when realizing that she is at a hospital and refuses to answer questions. She appears tired. She is 174 cm (5 ft 7 in) tall and weighs 51 kg (112 lb). Her temperature is 35.5°C (96°F), pulse is 44/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 84/48 mm Hg. Examination shows dry, scaly skin and dry mucous membranes. Cardiopulmonary examination shows a high-frequency, mid-to-late systolic murmur that is heard best at the apex. Her hemoglobin concentration is 11.9 g/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Heat exhaustion
- B. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
- C. Hypothyroidism
- D. Amphetamine use
- E. Anorexia nervosa (Correct Answer)
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Anorexia nervosa***
- The patient's **low BMI** (16.9 kg/m^2), **bradycardia**, **hypotension**, **hypothermia**, and **dry, scaly skin** are classic signs of anorexia nervosa, exacerbated by intense exercise (marathon training).
- The **mid-to-late systolic murmur** heard best at the apex is likely due to **mitral valve prolapse**, a common cardiac finding in patients with severe anorexia nervosa due to decreased ventricular size and structural changes.
*Heat exhaustion*
- Although the patient was exercising, her **temperature is low (96°F)**, which contradicts the expected elevated temperature in heat exhaustion.
- Heat exhaustion typically presents with profuse sweating, not **dry mucous membranes** or **dry, scaly skin**.
*Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy*
- While it can cause a **systolic murmur** and exercise-induced syncope, it usually presents with a **loud S4**, and the patient's other symptoms like **hypothermia**, **bradycardia**, and severe **cachexia** are not typical.
- It would not explain the **low body weight**, **dry skin**, or **hypotension** as primary symptoms.
*Hypothyroidism*
- Hypothyroidism can cause **fatigue**, **bradycardia**, **hypothermia**, and **dry skin**, but it does not typically lead to such extreme **weight loss** or **hypotension** in a young, active individual.
- It doesn't explain the specific cardiac murmur described or the history of intense marathon training contributing to the presentation.
*Amphetamine use*
- Amphetamine use typically causes **tachycardia**, **hypertension**, **dilation of pupils**, and **hyperthermia**, which are opposite to this patient's presentation of bradycardia, hypotension, and hypothermia.
- The patient's **cachectic appearance** could be associated with stimulant use, but the vital signs and overall clinical picture strongly contradict it.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 68-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and muscle cramps for the past 4 weeks. He has also noticed several episodes of tingling in both hands. He has not had fever or nausea. He has had a chronic cough for 10 years. He has chronic bronchitis, hypertension, and osteoarthritis of both knees. His father died from lung cancer. Current medications include salbutamol, ibuprofen, and ramipril. He has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for 45 years. He is 175 cm (5 ft 9 in) tall and weighs 68 kg (163 lb); BMI is 22 kg/m2. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 60/min, and blood pressure is 115/76 mm Hg. While measuring the patient's blood pressure, the physician observes carpopedal spasm. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. His hematocrit is 41%, leukocyte count is 5,800/mm3, and platelet count is 195,000/mm3. Serum alkaline phosphatase activity is 55 U/L. An ECG shows sinus rhythm with a prolonged QT interval. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Multiple endocrine neoplasia
- B. Ectopic hormone production
- C. Medication side effect
- D. Destruction of parathyroid glands
- E. Vitamin D deficiency (Correct Answer)
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Vitamin D deficiency***
- The patient's symptoms of **fatigue**, **muscle cramps**, **paresthesias** (tingling in hands), and **carpopedal spasm** (Trousseau's sign) are classic manifestations of **hypocalcemia**.
- The **prolonged QT interval** on ECG further confirms hypocalcemia.
- **Vitamin D deficiency** is the most common cause of hypocalcemia in elderly patients, especially those with:
- **Chronic disease** (chronic bronchitis)
- **Limited sun exposure** (likely given chronic illness)
- **Poor nutrition** or malabsorption
- **Normal alkaline phosphatase** (55 U/L) helps rule out severe bone disease
- This is the most likely diagnosis given the clinical presentation and demographic factors.
*Multiple endocrine neoplasia*
- **MEN syndromes** (MEN1, MEN2a) typically cause **primary hyperparathyroidism** with **hypercalcemia**, not hypocalcemia.
- There is no evidence of other endocrine tumors or family history to suggest MEN.
*Ectopic hormone production*
- **Ectopic PTHrP production** (e.g., from squamous cell lung carcinoma) causes **hypercalcemia**, not hypocalcemia.
- While the patient has smoking history and chronic cough, his presentation is clearly hypocalcemia.
*Medication side effect*
- The patient's current medications (**salbutamol**, **ibuprofen**, **ramipril**) are not commonly associated with symptomatic hypocalcemia.
- None of these medications typically cause carpopedal spasm or prolonged QT interval from calcium disturbances.
*Destruction of parathyroid glands*
- **Hypoparathyroidism** from parathyroid destruction (surgical, autoimmune, or infiltrative) would cause hypocalcemia.
- However, there is **no history** of neck surgery, radiation, or autoimmune disease.
- Without such history, this is less likely than vitamin D deficiency in an elderly patient with chronic disease.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 34-year-old Caucasian female presents at the ER with fever and sharp pain in her chest upon coughing and inhalation. Three weeks earlier she presented to her rheumatologist with a butterfly rash, joint pain and fatigue and was given a diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. A friction rub is present upon physical exam. Which of the following do you most suspect in this patient?
- A. Pericardial tamponade
- B. Pericarditis (Correct Answer)
- C. Acute myocardial infarction
- D. Pulmonary hypertension
- E. Interstitial lung disease
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Pericarditis***
- The patient's symptoms of **sharp chest pain** worsened by coughing and inhalation, along with a **friction rub** upon examination, are classic signs of pericarditis.
- Her recent diagnosis of **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)** makes pericarditis a highly suspect complication, as SLE can affect the pericardium.
*Pericardial tamponade*
- While pericarditis can lead to tamponade, the clinical presentation here (chest pain, friction rub) more strongly points to **inflammation of the pericardium** rather than the signs of **hemodynamic compromise** seen in tamponade (e.g., muffled heart sounds, hypotension, jugular venous distention).
- There are no specific signs of **Beck's triad** (hypotension, muffled heart sounds, JVD) which would indicate tamponade.
*Acute myocardial infarction*
- The described **sharp chest pain worsened by inspiration and coughing** is atypical for myocardial infarction, which usually involves crushing or pressure-like pain.
- The presence of a **friction rub** is highly characteristic of pericarditis, not an MI.
*Pulmonary hypertension*
- Pulmonary hypertension typically presents with **dyspnea, fatigue, and signs of right-sided heart failure**, none of which are highlighted in this patient's acute presentation.
- **Chest pain** in pulmonary hypertension is usually exertion-related or due to right ventricular ischemia, not pleuritic.
*Interstitial lung disease*
- Interstitial lung disease primarily causes **progressive dyspnea and cough**, often with crackles on auscultation.
- The acute, pleuritic chest pain and **friction rub** are not characteristic findings of interstitial lung disease.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 23-year-old Sicilian male presents to his primary care physician complaining of lethargy, joint pain, and urinary frequency. Vitals signs include T 98.7 F, HR 96 bpm, BP 135/71 mm/Hg, RR 18 breaths/minute, O2 99%. Laboratory findings include: random glucose 326 mg/dL, Hemoglobin 7.1, and elevated reticulocyte count and transferrin saturation. The patient is not surprised that his "blood level is low" and suggests that he might need another transfusion. An echocardiogram demonstrates restrictive cardiomyopathy. The disorder with which this patient presents can be characterized by which of the following?
- A. Mutations resulting in copper accumulation
- B. Presence of the fetal hemoglobin
- C. Absence of the hemoglobin alpha-chain
- D. Mutation resulting in increased iron absorption
- E. Absence of the hemoglobin beta-chain (Correct Answer)
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Absence of the hemoglobin beta-chain***
- The patient's symptoms (lethargy, joint pain, elevated glucose, restrictive cardiomyopathy, high transferrin saturation, and need for transfusions) in a **Sicilian male** are highly suggestive of **beta-thalassemia major**, which involves a reduced or absent production of hemoglobin beta-chains.
- This leads to ineffective erythropoiesis, **chronic anemia**, and subsequent **iron overload** due to frequent transfusions and increased intestinal iron absorption.
*Mutation resulting in increased iron absorption*
- This describes **hereditary hemochromatosis**, which can present with increased iron absorption, joint pain, and diabetes, but typically does not involve the severe, transfusion-dependent anemia and high reticulocyte count seen in this patient.
- While iron overload is present in this patient, it's primarily secondary to the underlying anemia and transfusions, not a primary mutation in iron absorption regulation.
*Absence of the hemoglobin alpha-chain*
- This describes **alpha-thalassemia**. The most severe form, **hydrops fetalis**, is incompatible with life, and milder forms present differently, often without the severe, transfusion-dependent anemia and systemic iron overload from transfusions seen here.
- Beta-thalassemia is more common in Mediterranean populations and aligns better with the clinical picture of profound anemia, extramedullary hematopoiesis, and resultant iron overload.
*Presence of the fetal hemoglobin*
- While patients with thalassemia may have **increased fetal hemoglobin (HbF)** as a compensatory mechanism, its *presence* is not the primary characteristic of the disease itself, but rather a response to the deficient or absent adult hemoglobin chain production.
- The fundamental genetic defect lies in the reduced or absent synthesis of adult hemoglobin chains (alpha or beta).
*Mutations resulting in copper accumulation*
- This describes **Wilson's disease**, which involves copper accumulation and can affect the liver, brain, and other organs, but does not present with severe anemia requiring transfusions or the specific type of iron overload-related cardiomyopathy and diabetes seen here.
- The laboratory findings of high reticulocytes, low hemoglobin, and high transferrin saturation specifically point to a primary hematological disorder with secondary iron loading rather than a copper metabolism disorder.
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with joint pain and a notable rash. She has had joint pain for the past 12 months but noticed the rash recently as well as generalized malaise. She states her joint pain is symmetric, in her upper extremities, and is worse in the morning. Her temperature is 97.6°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 111/74 mmHg, pulse is 83/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Laboratory studies are ordered as seen below.
Hemoglobin: 10 g/dL
Hematocrit: 30%
Leukocyte count: 6,800/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 207,000/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 140 mEq/L
Cl-: 101 mEq/L
K+: 4.9 mEq/L
HCO3-: 21 mEq/L
BUN: 30 mg/dL
Glucose: 120 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.8 mg/dL
The patient is ultimately admitted to the hospital. Which of the following is the most appropriate test to monitor her disease progression?
- A. Rheumatoid factor
- B. Anti-topoisomerase
- C. Anti-dsDNA (Correct Answer)
- D. Anti-CCP
- E. Anti-nuclear antibody
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***Anti-dsDNA***
- The patient's presentation with **symmetric polyarthritis**, a **rash**, and **renal involvement** (elevated BUN and creatinine) is highly suggestive of **Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)**.
- **Anti-dsDNA antibodies** correlate well with disease activity, especially **lupus nephritis**, making them an excellent marker for monitoring disease progression and response to therapy in SLE.
*Rheumatoid factor*
- **Rheumatoid factor** is primarily associated with **Rheumatoid Arthritis** and is generally not used for monitoring SLE activity.
- While some SLE patients may test positive for RF, it is not a specific marker for SLE.
*Anti-topoisomerase*
- **Anti-topoisomerase I (Scl-70) antibodies** are characteristic of **systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)**, particularly the diffuse cutaneous form.
- This antibody is not typically seen in SLE and does not help monitor its progression.
*Anti-CCP*
- **Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies** are highly specific for **Rheumatoid Arthritis**.
- They are useful for diagnosis and prognosis in RA but have no role in monitoring SLE.
*Anti-nuclear antibody*
- **Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)** are present in almost all patients with SLE and are essential for diagnosis, but they do not correlate with disease activity.
- A positive ANA test is a screening tool but cannot be used to monitor disease progression or response to treatment.
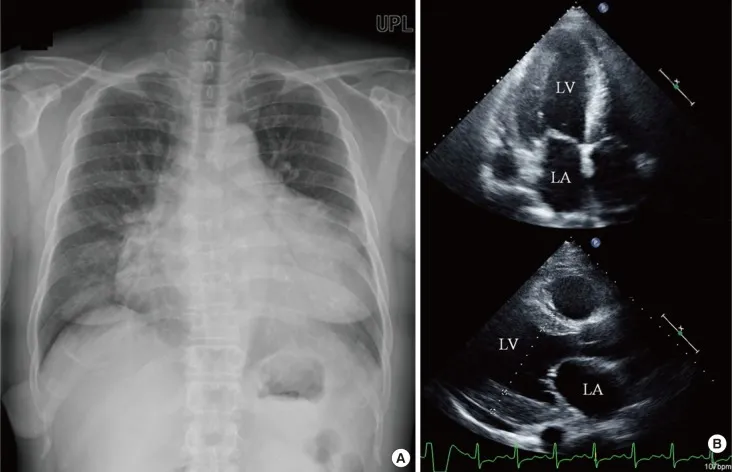
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of palpitations, dry cough, and shortness of breath for 1 week. She immigrated to the United States from Korea at the age of 20. She says that her heart is racing and she has never felt these symptoms before. Her cough is dry and is associated with shortness of breath that occurs with minimal exertion. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. She has no allergies and is not currently taking any medications. She is a nonsmoker and an occasional drinker. She denies illicit drug use. Her blood pressure is 100/65 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, respiratory rate is 23/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F). Her physical examination is significant for bibasilar lung crackles and a non-radiating, low-pitched, mid-diastolic rumbling murmur best heard at the apical region. In addition, she has jugular vein distention and bilateral pitting edema in her lower extremities. Which of the following best describes the infectious agent that led to this patient’s condition?
- A. A bacterium that induces partial lysis of red cells with hydrogen peroxide
- B. A bacterium that requires an anaerobic environment to grow properly
- C. A bacterium that does not lyse red cells
- D. A bacterium that induces heme degradation of the red cells of a blood agar plate
- E. A bacterium that induces complete lysis of the red cells of a blood agar plate with an oxygen-sensitive cytotoxin (Correct Answer)
Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases Explanation: ***A bacterium that induces complete lysis of the red cells of a blood agar plate with an oxygen-sensitive cytotoxin***
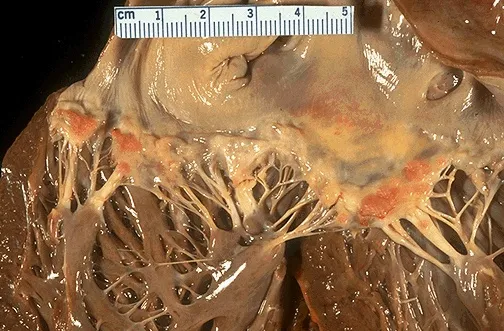
- This describes **Group A Streptococcus (GAS)**, specifically *Streptococcus pyogenes*, which causes **rheumatic fever** leading to **mitral stenosis**. Mitral stenosis is characterized by a **mid-diastolic rumbling murmur** at the apex, left atrial enlargement causing **palpitations**, and **pulmonary congestion** leading to dyspnea, cough, and bibasilar crackles.
- The delayed onset of symptoms (immigrated at 20, symptoms at 43) is typical for **rheumatic heart disease**, where repeated GAS infections in childhood/adolescence lead to valve damage that manifests years later. GAS produces **streptolysin O**, an **oxygen-labile cytotoxin** responsible for **beta-hemolysis** (complete lysis) on blood agar.
*A bacterium that induces partial lysis of red cells with hydrogen peroxide*
- This describes **alpha-hemolytic** bacteria like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* or *Viridans streptococci*, which cause **partial hemolysis** (greenish discoloration) on blood agar due to **hydrogen peroxide** production.
- While *Viridans streptococci* can cause **infective endocarditis**, the clinical picture of **rheumatic mitral stenosis** is more consistent with a history of recurrent streptococcal pharyngitis (GAS).
*A bacterium that requires an anaerobic environment to grow properly*
- This description typically refers to **anaerobic bacteria**, such as *Clostridium* or *Bacteroides* species.
- These bacteria are generally not associated with the primary cause of acute rheumatic fever or the subsequent development of chronic valvular heart disease like mitral stenosis.
*A bacterium that does not lyse red cells*
- This describes **gamma-hemolytic** (non-hemolytic) bacteria, such as *Enterococcus faecalis* or some *Staphylococcus* species.
- These organisms do not cause the characteristic hemolysis seen with the streptococci responsible for rheumatic fever.
*A bacterium that induces heme degradation of the red cells of a blood agar plate*
- This description is **too vague** and does not specifically identify the organism. While heme degradation occurs with various types of hemolysis, the key distinguishing feature of **Group A Streptococcus** is **complete lysis (beta-hemolysis)** combined with production of the **oxygen-sensitive toxin streptolysin O**.
- This option lacks the specificity needed to identify GAS as the causative agent of rheumatic fever. Both alpha- and beta-hemolytic organisms can degrade heme, but only beta-hemolytic GAS causes rheumatic heart disease.
More Cardiac manifestations of systemic diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.