Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Supraventricular tachycardias. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 1: A 51-year-old woman with a history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation comes to the physician for a follow-up visit. She feels well and wants to discuss pausing her only current medication, flecainide. Her pulse is 75/min and regular, blood pressure is 125/75 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. An ECG shows a PR interval of 180 ms, QRS time of 120 ms, and corrected QT interval of 440 ms. Which of the following ECG changes is most likely to be seen on cardiac stress testing in this patient?
- A. Decreased maximal heart rate
- B. Prolonged QRS complex (Correct Answer)
- C. Shortened PR interval
- D. False-positive ST-segment depression
- E. Prolonged QTc interval
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Prolonged QRS complex***
- **Flecainide** is a class Ic antiarrhythmic that **blocks fast sodium channels** in myocardial cells, slowing conduction in the atria, ventricles, and His-Purkinje system.
- Its effects are **use-dependent**, meaning the drug binds more effectively to channels that are frequently activated (i.e., at higher heart rates), leading to a **further widening of the QRS complex** during exercise.
*Decreased maximal heart rate*
- While some class II antiarrhythmics (beta-blockers) can decrease maximal heart rate, **flecainide** primarily affects cardiac conduction and does not significantly impact heart rate response to stress.
- The ECG does not suggest sinus node dysfunction that would limit heart rate increase with activity.
*Shortened PR interval*
- Flecainide typically **prolongs the PR interval** by slowing conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node.
- Exercise would likely exacerbate this effect rather than shorten the PR interval.
*False-positive ST-segment depression*
- While wide QRS complexes (as may occur with flecainide-induced conduction slowing) can cause abnormal ST-segment morphology, the **most prominent and characteristic effect** of flecainide during stress testing is **progressive QRS widening** due to use-dependent sodium channel blockade.
- False-positive ST changes are a nonspecific finding and not the hallmark ECG change expected with flecainide during exercise.
*Prolonged QTc interval*
- Flecainide is generally known to **not significantly prolong the QT interval**; in some cases, it may even shorten it due to its effect on action potential duration.
- Other antiarrhythmics like Class III agents (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) are more commonly associated with QTc prolongation.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 2: A researcher is studying how electrical activity propagates across the heart. In order to do this, he decides to measure the rate at which an action potential moves within various groups of cardiac muscle tissue. In particular, he isolates fibers from areas of the heart with the following characteristics:
A) Dysfunction leads to fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
B) Dysfunction leads to increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
C) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex
D) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram
Which of the following is the proper order of these tissues from fastest action potential propagation to slowest action potential propagation.
- A. B > D > C > A
- B. D > C > A > B
- C. B > C > D > A
- D. A > D > C > B (Correct Answer)
- E. A > C > D > B
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***A > D > C > B***
* **Purkinje fibers (A)** have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart to ensure rapid and synchronous ventricular depolarization. The description of "fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" in **Mobitz type II second-degree AV block** indicates an issue with conduction distal to the AV node, often in the His-Purkinje system, while still maintaining typical conduction through the atria and AV node for conducted beats.
* **Atrial muscle (D)** has a faster conduction velocity than the AV node but slower than Purkinje fibers. The "sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram" unequivocally points to **atrial flutter**, which is characterized by rapid, regular depolarization of the atria.
* **Ventricular muscle (C)** has a conduction velocity slower than Purkinje fibers but faster than the AV node. "Tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex" is characteristic of **ventricular tachycardia (VT)**, which arises from abnormal electrical activity within the ventricles.
* **AV node (B)** has the slowest conduction velocity in the heart, which allows for proper ventricular filling. "Increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" describes **Mobitz type I second-degree AV block (Wenckebach phenomenon)**, which is due to progressive prolongation of conduction delay within the AV node itself.
*B > D > C > A*
* This order incorrectly places the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest, which is contrary to the known conduction velocities in the heart.
* The AV node is critical for delaying the impulse, making it the slowest, while Purkinje fibers are designed for rapid spread, making them the fastest.
*D > C > A > B*
* This option incorrectly places **atrial muscle (D)** as faster than **Purkinje fibers (A)**. Purkinje fibers have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart, considerably faster than atrial muscle.
*B > C > D > A*
* This arrangement incorrectly lists the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest. The AV node is the slowest for its physiological role of delaying ventricular contraction, while Purkinje fibers are optimized for rapid conduction.
*A > C > D > B*
* While placing **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the fastest and the **AV node (B)** as the slowest is correct, this order incorrectly places **ventricular muscle (C)** as faster than **atrial muscle (D)**. Atrial muscle generally conducts faster than ventricular muscle in normal physiology.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 3: A cardiologist is studying how a new virus that infects the heart affects the electrical conduction system of the cardiac myocytes. He decides to obtain electrocardiograms on patients with this disease in order to see how the wave patterns and durations change over time. While studying these records, he asks a medical student who is working with him to interpret the traces. Specifically, he asks her to identify the part that represents initial ventricular depolarization. Which of the following characteristics is most consistent with this feature of the electrocardiogram?
- A. Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart
- B. Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia
- C. Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia
- D. Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds (Correct Answer)
- E. Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds***
- The question asks for the representation of **initial ventricular depolarization**, which corresponds to the **QRS complex** on an ECG.
- The normal duration of the **QRS complex** is typically less than **0.12 seconds (120 milliseconds)**, reflecting efficient ventricular depolarization.
*Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart*
- This description refers to the **ST segment elevation** seen in **ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)**, which represents myocardial injury, not initial ventricular depolarization.
- While related to cardiac electrical activity, **ST segment elevation** is a consequence of injury and refers to repolarization abnormalities, not the QRS complex itself.
*Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia*
- **Peaked T waves** are characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, indicating altered ventricular repolarization, not ventricular depolarization.
- The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, and its morphology changes significantly with potassium imbalances.
*Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia*
- A **prominent U wave** is sometimes observed in **hypokalemia**, which follows the T wave and is thought to represent repolarization of Purkinje fibers.
- The U wave is distinct from the QRS complex and does not represent initial ventricular depolarization.
*Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds*
- A duration of less than 200 milliseconds (0.20 seconds) typically refers to the normal duration of the **PR interval**, which represents atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node.
- The **QRS complex** (initial ventricular depolarization) has a shorter normal duration, typically less than 120 milliseconds.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 4: A 50-year-old man with a history of atrial fibrillation presents to his cardiologist’s office for a follow-up visit. He recently started treatment with an anti-arrhythmic drug to prevent future recurrences and reports that he has been feeling well and has no complaints. The physical examination shows that the arrhythmia appears to have resolved; however, there is now mild bradycardia. In addition, the electrocardiogram recording shows a slight prolongation of the PR and QT intervals. Which of the following drugs was most likely used to treat this patient?
- A. Metoprolol
- B. Sotalol (Correct Answer)
- C. Propranolol
- D. Verapamil
- E. Carvedilol
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Sotalol***
- **Sotalol** is a **beta-blocker** and a **Class III antiarrhythmic** drug, meaning it blocks potassium channels.
- This dual action explains the **bradycardia** (beta-blockade) and the **prolongation of the PR and QT intervals** (potassium channel blockade), which are characteristic side effects.
*Metoprolol*
- **Metoprolol** is a **selective beta-1 blocker** (Class II antiarrhythmic) that would cause **bradycardia** and **PR prolongation**, but it does not typically prolong the **QT interval**.
- It primarily affects the heart rate and AV nodal conduction without significant potassium channel blocking properties.
*Propranolol*
- **Propranolol** is a **non-selective beta-blocker** (Class II antiarrhythmic) that would cause **bradycardia** and **PR prolongation**.
- Similar to metoprolol, it does not typically prolong the **QT interval**.
*Verapamil*
- **Verapamil** is a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** (Class IV antiarrhythmic) that causes **bradycardia** and **PR prolongation**.
- However, it does not prolong the **QT interval**; instead, it can sometimes shorten it.
*Carvedilol*
- **Carvedilol** is a **non-selective beta-blocker** with **alpha-1 blocking properties** (Class II antiarrhythmic), leading to **bradycardia** and **PR prolongation**.
- It does not have effects on potassium channels that would lead to **QT prolongation**.
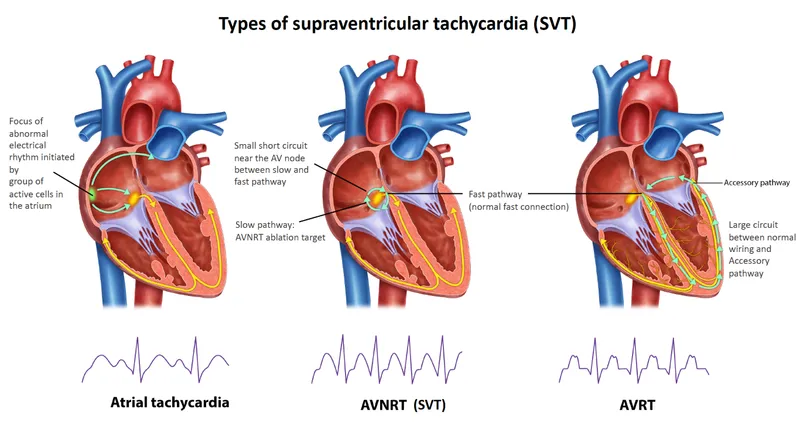
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 5: A 40-year-old woman comes to the physician for a 6-month history of recurrent episodes of chest pain, racing pulse, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. The episodes last up to several minutes. She also reports urinary urgency and two episodes of loss of consciousness followed by spontaneous recovery. There is no personal or family history of serious illness. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Vitals signs are within normal limits. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Holter monitoring is performed. ECG recordings during episodes of tachycardia show a QRS duration of 100 ms, regular RR-interval, and absent P waves. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's condition?
- A. AV node with slow and fast pathway (Correct Answer)
- B. Pre-excitation of the ventricles
- C. Mutations in genes that code for myocyte ion channels
- D. Macroreentrant rhythm in the right atria through cavotricuspid isthmus
- E. Fibrosis of the sinoatrial node and surrounding myocardium
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***AV node with slow and fast pathway***
- This describes **AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)**, a common cause of **paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)**. The ECG findings of **narrow QRS (100 ms)**, regular RR-interval, and **absent P waves** (often hidden within the QRS complex) are characteristic of AVNRT.
- The patient's symptoms of recurrent chest pain, racing pulse, dizziness, and spontaneous recovery from loss of consciousness fit the episodic nature of **AVNRT**. The presence of two pathways (slow and fast) within the AV node facilitates the reentrant circuit.
*Pre-excitation of the ventricles*
- **Pre-excitation syndromes** (e.g., Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome) involve an accessory pathway that bypasses the AV node, leading to a **delta wave** and **short PR interval** on the baseline ECG.
- While they can cause SVT, the ECG during tachycardia would typically show a **wide QRS complex** if the accessory pathway is part of the reentrant circuit (antidromic), or a narrow QRS with a visible P wave if orthodromic and the accessory pathway is used for retrograde conduction, which doesn't fully align with the absent P waves and typically *normal* QRS during tachycardia as described.
*Mutations in genes that code for myocyte ion channels*
- This refers to **channelopathies** (e.g., long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome), which predispose to **ventricular arrhythmias** like **polymorphic ventricular tachycardia** and **ventricular fibrillation**.
- These conditions typically cause **wide QRS tachycardias** and have distinct ECG patterns (e.g., prolonged QT interval, Brugada pattern) not described here. The narrow QRS and regular rhythm point away from primary ventricular channelopathies as the cause of this specific tachycardia.
*Macroreentrant rhythm in the right atria through cavotricuspid isthmus*
- This describes **atrial flutter**, which typically presents with characteristic **"sawtooth" F waves** on ECG, representing atrial activity.
- While atrial flutter can cause recurrent episodes of rapid heart rate, the ECG description of **absent P waves** and a **narrow QRS complex** without F waves makes atrial flutter less likely.
*Fibrosis of the sinoatrial node and surrounding myocardium*
- **Sinoatrial node dysfunction (sick sinus syndrome)** can lead to bradycardia, sinus pauses, or alternating bradycardia and tachycardia (tachy-brady syndrome).
- It does not primarily cause the described paroxysmal narrow-complex tachycardia with absent P waves. The patient's symptoms are more consistent with an abrupt-onset, regular supraventricular tachycardia.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 6: The rapid response team is called for a 74-year-old woman on an inpatient surgical floor for supraventricular tachycardia. The patient had surgery earlier in the day for operative management of a femur fracture. The patient has a history of hypertension, atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, and uterine cancer status post total abdominal hysterectomy 20 years prior. With carotid massage, valsalva maneuvers, and metoprolol, the patient breaks out of her supraventricular tachycardia. Thirty minutes later, the nurse notices a decline in the patient’s status. On exam, the patient has a temperature of 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure of 102/74 mmHg, pulse of 86/min, and respirations are 14/min. The patient is now dysarthric with noticeable right upper extremity weakness of 2/5 in elbow flexion and extension. All other extremities demonstrate normal strength and sensation. Which of the following most likely contributed to this decline?
- A. Long bone fracture
- B. Diabetes
- C. Hypertension
- D. Malignancy
- E. Atherosclerosis (Correct Answer)
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Atherosclerosis***
- The sudden onset of **right upper extremity weakness** and **dysarthria** after an episode of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) strongly suggests an **ischemic stroke**. Atherosclerosis is the primary underlying condition that made this patient vulnerable to stroke.
- **Carotid massage** in patients with **carotid atherosclerosis** carries a risk of **dislodging atherosclerotic plaques**, leading to embolic stroke. The temporal relationship between the carotid massage and the onset of focal neurological deficits 30 minutes later is highly suspicious for an atheroembolic event.
- The patient's history of **hypertension** and **type 2 diabetes** are significant risk factors that accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, increasing plaque burden and the likelihood of **atheroembolic events**.
*Long bone fracture*
- While a long bone fracture can lead to complications, such as **fat emboli**, these typically cause a triad of respiratory distress, neurological symptoms (altered mental status, not localized weakness), and a petechial rash.
- The neurological symptoms of a fat embolism are usually more global and diffuse, unlike the focal deficits observed here (dysarthria, right upper extremity weakness).
- Fat embolism syndrome typically develops **24-72 hours post-fracture**, not immediately after carotid massage.
*Diabetes*
- Diabetes is a significant risk factor for **atherosclerosis** and stroke, but it is not the direct cause of the acute neurological decline; rather, it contributes to the underlying vascular disease.
- While diabetes can cause neurological complications like **neuropathy**, it does not typically present as acute focal weakness and dysarthria in this manner.
*Hypertension*
- Hypertension is a major modifiable risk factor for both **atherosclerosis** and **ischemic stroke**, contributing to vascular damage and plaque formation over time.
- However, hypertension itself is not the immediate cause of the focal neurological deficits in this scenario; it primarily exacerbates the underlying atherosclerotic process that enables embolic events.
*Malignancy*
- Malignancy can increase the risk of prothrombotic states (**Trousseau's syndrome**) and lead to embolic events, potentially causing a stroke.
- However, the patient's uterine cancer was treated 20 years prior, and there is no indication of active malignancy or a hypercoagulable state specifically linked to cancer in this acute presentation.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 7: A 58-year-old man is diagnosed with right lower lobe pneumonia and has been admitted to a tertiary care hospital. His laboratory investigations suggest that he acquired an infection from the hospital where he underwent an elective abdominal surgery 3 weeks ago. His past medical records reveal a history of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism one year prior. After a steady clinical improvement over 5 days of inpatient treatment, he develops a cough, breathlessness, and hemoptysis on the 6th day. His temperature is 38.6°C (101.5°F), the pulse is 112/min, the blood pressure is 130/84 mm Hg, and the respiratory rate is 28/min. A general examination shows the presence of edema over the right leg and tenderness over the right calf region. Auscultation of the chest reveals localized crackles over the left mammary region and right infrascapular region. However, his heart sounds are normal, except for the presence of tachycardia, and there are no murmurs. Which of the following is the investigation of choice as the immediate next step in this patient’s management?
- A. Ventilation-perfusion scanning
- B. Echocardiography
- C. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) of chest (Correct Answer)
- D. Serum brain natriuretic peptide
- E. Plasma D-dimer
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) of chest***
- This patient presents with an acute onset of **cough, breathlessness, and hemoptysis** along with signs of **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**, including leg edema and calf tenderness. This clinical picture, especially with a history of DVT and pulmonary embolism, is highly suggestive of a **pulmonary embolism (PE)**.
- **CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA)**, performed as a contrast-enhanced CT of the chest, is the **gold standard** for diagnosing PE, as it directly visualizes thrombi within the pulmonary arteries and provides detailed anatomical information.
- Given the **high pre-test probability** (prior DVT/PE, clinical signs of DVT, recent surgery, hemoptysis, tachycardia), immediate imaging with CTPA is indicated without need for D-dimer testing.
*Ventilation-perfusion scanning*
- **Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scanning** is an alternative for diagnosing PE, but it is less sensitive and specific than CTPA, especially in the presence of **pre-existing lung disease** (like the pneumonia this patient has), which can lead to indeterminate results.
- It is usually reserved for patients with **renal insufficiency** or **contrast allergy** who cannot undergo CTPA.
*Echocardiography*
- **Echocardiography** can show signs of **right heart strain** in massive PE, but it is not diagnostic for PE itself, as it cannot directly visualize the emboli in the pulmonary arteries.
- It is more useful in assessing **cardiac function** and ruling out other cardiac causes of breathlessness, or for risk stratification in confirmed PE.
*Serum brain natriuretic peptide*
- **Serum brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)** levels can be elevated in patients with **right heart strain** due to PE, but it is a **non-specific marker** and cannot confirm the diagnosis of PE.
- Elevated BNP can also indicate other cardiac conditions, such as **heart failure**.
*Plasma D-dimer*
- **Plasma D-dimer** is a useful test to **exclude PE** in patients with a **low or intermediate pre-test probability**, but a **positive D-dimer** is non-specific and can be elevated in many conditions, including infection, surgery, and inflammation.
- Given the patient's **high clinical probability** for PE (prior DVT/PE, current DVT signs, recent surgery, hemoptysis) and active pneumonia, D-dimer testing is **not indicated** as it would not change management—imaging with CTPA is already warranted regardless of D-dimer result.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 8: A previously healthy 33-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because she could feel her heart racing intermittently for the last 2 hours. Each episode lasts about 10 minutes. She does not have any chest pain. Her mother died of a heart attack and her father had an angioplasty 3 years ago. She has smoked a half pack of cigarettes daily for 14 years. She drinks one to two beers daily. She appears anxious. Her temperature is 37.6°C (98.1°F), pulse is 160/min, and blood pressure is 104/76 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination shows no murmurs, rubs, or gallops. An ECG is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Intravenous adenosine
- B. Aspirin
- C. Intravenous procainamide
- D. Vagal maneuvers (Correct Answer)
- E. Coronary angioplasty
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Vagal maneuvers***
- The ECG shows a **narrow complex tachycardia** at a rate of 160/min. Given the patient's stable hemodynamics (BP 104/76 mm Hg), **vagal maneuvers** are the most appropriate initial step to attempt to terminate the re-entrant rhythm, such as Valsalva maneuver or carotid sinus massage.
- Vagal maneuvers increase **parasympathetic tone** to the heart, which can slow conduction through the AV node and potentially break the re-entrant circuit causing the supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
*Intravenous adenosine*
- **Adenosine** is a treatment for **narrow complex tachycardia** if vagal maneuvers fail, but it is not the *initial* step in a hemodynamically stable patient.
- It works by transiently blocking the **AV node**, interrupting re-entrant pathways.
*Intravenous procainamide*
- **Procainamide** is an antiarrhythmic typically used for **wide complex tachycardia** or for narrow complex tachycardias that are refractory to vagal maneuvers and adenosine, or when there is evidence of pre-excitation.
- It is not the first-line treatment for a stable **narrow complex tachycardia**.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is an **antiplatelet agent** used in the management of acute coronary syndromes or for cardiovascular disease prevention.
- It has no role in the immediate termination of a **tachyarrhythmia** like the one presented.
*Coronary angioplasty*
- **Coronary angioplasty** is a procedure used to open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, usually for **acute coronary syndromes** or chronic stable angina.
- The patient presents with a **tachyarrhythmia** and no signs of acute ischemia (no chest pain, although risk factors are present), making angioplasty an inappropriate initial management step.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man with a past medical history of obesity and hyperlipidemia suddenly develops left-sided chest pain and shortness of breath while at work. He relays to coworkers that the pain is intense and has spread to his upper left arm over the past 10 minutes. He reports it feels a lot like the “heart attack” he had a year ago. He suddenly collapses and is unresponsive. Coworkers perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation for 18 minutes until emergency medical services arrives. Paramedics pronounce him dead at the scene. Which of the following is the most likely cause of death in this man?
- A. Pericarditis
- B. Aortic dissection
- C. Atrial fibrillation
- D. Ventricular tachycardia (Correct Answer)
- E. Free wall rupture
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Ventricular tachycardia***
- The patient's history of MI **1 year ago** creates a substrate of **scarred myocardium** that predisposes to life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
- The current presentation of sudden chest pain radiating to the arm suggests **acute re-infarction**, which triggers electrical instability in already compromised myocardium.
- **Ventricular tachycardia (VT)** degenerating to **ventricular fibrillation (VF)** is the **most common cause of sudden cardiac death** in patients with prior MI, especially during acute ischemic events.
- The rapid collapse and death within minutes, despite CPR, is classic for fatal ventricular arrhythmia.
*Free wall rupture*
- Free wall rupture is a **mechanical complication** that occurs **3-14 days** (typically days 3-7) after an **acute MI**, not 1 year later.
- By 1 year post-MI, the ventricular wall has either healed with fibrous scar tissue or formed a chronic ventricular aneurysm.
- While this would cause sudden death via cardiac tamponade, the **timing makes this unlikely** in this scenario.
*Pericarditis*
- Pericarditis causes **pleuritic chest pain** that is sharp, positional, and typically relieved by leaning forward.
- It is **not an immediate cause of sudden cardiac death** and would not explain the rapid collapse and unresponsiveness.
- While post-MI (Dressler) pericarditis can occur weeks after MI, it doesn't cause this presentation.
*Aortic dissection*
- Aortic dissection presents with **sudden, severe, tearing chest pain** often radiating to the back.
- While potentially fatal, the patient's description of pain "a lot like the heart attack he had a year ago" and his cardiac risk factors make **recurrent MI with fatal arrhythmia more likely**.
- No mention of blood pressure differential or pulse deficits that would suggest dissection.
*Atrial fibrillation*
- Atrial fibrillation is a **supraventricular arrhythmia** that causes palpitations, dyspnea, and irregular pulse.
- It is **not typically immediately fatal** in isolation and does not cause sudden collapse and death within minutes.
- While AF can lead to stroke or heart failure over time, it doesn't explain this acute sudden cardiac death.
Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG Question 10: An 18-year-old male reports to his physician that he is having repeated episodes of a "racing heart beat". He believes these episodes are occurring completely at random. He is experiencing approximately 2 episodes each week, each lasting for only a few minutes. During the episodes he feels palpitations and shortness of breath, then nervous and uncomfortable, but these feelings resolve in a matter of minutes. He is otherwise well. Vital signs are as follows: T 98.8F, HR 60 bpm, BP 110/80 mmHg, RR 12. His resting EKG shows a short PR interval and a delta wave. What is the likely diagnosis?
- A. Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (Correct Answer)
- B. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- C. Ventricular tachycardia
- D. Panic attacks
- E. Atrioventricular block, Mobitz Type II
Supraventricular tachycardias Explanation: ***Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia***
- The patient's presentation with sudden onset, paroxysmal episodes of "racing heartbeat," shortness of breath, and nervousness in an otherwise healthy young male is highly suggestive of **supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)**.
- The **short PR interval and delta wave** on resting EKG are pathognomonic for **Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome**, which involves an accessory pathway (bundle of Kent) between the atria and ventricles.
- **Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT)** is the most common arrhythmia associated with WPW syndrome, where the reentrant circuit involves the accessory pathway, causing paroxysmal tachycardia episodes.
*Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation*
- While paroxysmal atrial fibrillation can cause a "racing heartbeat," it typically presents with an **irregularly irregular rhythm**, which is not suggested by the consistent episodes described.
- The presence of **delta waves on EKG** points specifically to an accessory pathway (WPW), not atrial fibrillation as the primary diagnosis.
- Note: Patients with WPW can develop atrial fibrillation, but it would conduct irregularly, not as the regular paroxysmal episodes described.
*Ventricular tachycardia*
- **Ventricular tachycardia (VT)** is a more serious arrhythmia, generally associated with structural heart disease or channelopathies, and typically presents with more severe symptoms like syncope or hemodynamic compromise.
- The **delta wave and short PR interval** indicate a supraventricular accessory pathway, not a ventricular origin of the arrhythmia.
- In a young, otherwise healthy individual with normal vital signs between episodes, VT is much less likely than AVRT.
*Panic attacks*
- While panic attacks can cause symptoms like palpitations and shortness of breath, they would not produce **EKG findings of delta waves and short PR interval**.
- The specific EKG findings indicate a **structural cardiac accessory pathway** rather than a purely psychological etiology.
- The description of consistent "racing heart beat" episodes with characteristic EKG changes confirms a primary cardiac arrhythmia (AVRT) rather than panic disorder.
*Atrioventricular block, Mobitz Type II*
- **Mobitz Type II AV block** is a bradyarrhythmia characterized by intermittent dropped QRS complexes following P waves, leading to a slow heart rate.
- This condition would cause **bradycardia and possible syncope**, not a "racing heart beat" or palpitations associated with tachycardia.
- The EKG findings of **short PR interval (not prolonged) and delta wave** are completely inconsistent with AV block.
More Supraventricular tachycardias US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.