Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 1: A 70-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a general checkup. He states that he has been doing well and taking his medications as prescribed. He recently started a new diet and supplement to improve his health and has started exercising. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes, a myocardial infarction, and hypertension. He denies any shortness of breath at rest or with exertion. An ECG is performed and is within normal limits. Laboratory values are ordered as seen below.
Serum:
Na+: 139 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 6.7 mEq/L
HCO3-: 25 mEq/L
Glucose: 133 mg/dL
Ca2+: 10.2 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's presentation?
- A. Medication (Correct Answer)
- B. Acute renal failure
- C. Hemolysis
- D. Dietary changes
- E. Rhabdomyolysis
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Medication***
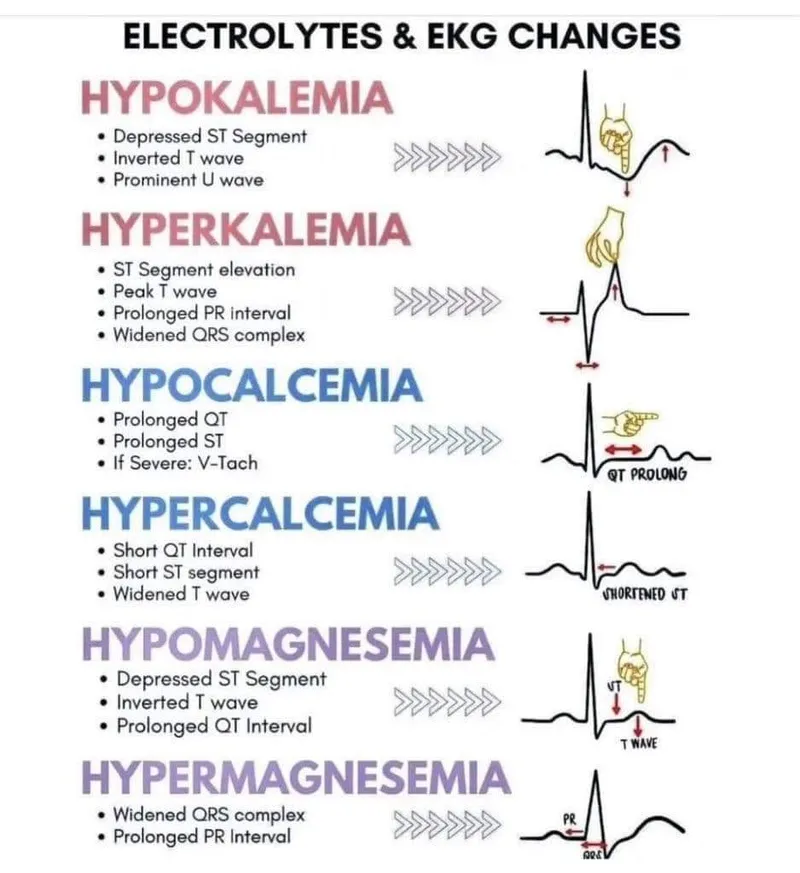
- The patient's **hyperkalemia** (K+ 6.7 mEq/L) despite feeling well, suggests a common side effect of medications, particularly those used for his pre-existing conditions like **hypertension** (**ACE inhibitors**, **ARBs**, **spironolactone**) and **diabetes**.
- Medications are a frequent cause of asymptomatic electrolyte abnormalities, and given his complex medical history and the absence of acute symptoms, this is the most likely culprit.
*Acute renal failure*
- While acute renal failure can cause **hyperkalemia**, it typically presents with other symptoms such as **oliguria**, **fluid retention**, or other signs of organ dysfunction, which are not described.
- The patient is reported to be "doing well" without **shortness of breath** or other acute complaints, making acute renal failure less likely as the primary cause of isolated hyperkalemia.
*Hemolysis*
- **Hemolysis** can release intracellular potassium, leading to **pseudohyperkalemia**, but it would typically be suspected in cases of **blood draw errors** or conditions causing red blood cell breakdown, none of which are indicated.
- The patient's presentation does not include any signs or symptoms suggestive of red cell destruction.
*Dietary changes*
- While an extremely **high-potassium diet** or certain **supplements** could contribute to hyperkalemia, it is less common for dietary changes alone to cause such a significant elevation in a patient with normal organ function.
- Given his medical history, medication-induced hyperkalemia is a more direct and common explanation.
*Rhabdomyolysis*
- **Rhabdomyolysis** involves the breakdown of muscle tissue, releasing potassium and other intracellular contents, but it is usually associated with significant **muscle pain**, **weakness**, and elevated **creatine kinase**.
- The patient denies these symptoms and has no other indicators pointing towards severe muscle injury.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 2: A 54-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of episodic palpitations for the past 12 hours. He has no chest pain. He has coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. His current medications include aspirin, insulin, and atorvastatin. His pulse is 155/min and blood pressure is 116/77 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. An ECG shows monomorphic ventricular tachycardia. An amiodarone bolus and infusion is given, and the ventricular tachycardia converts to normal sinus rhythm. He is discharged home with oral amiodarone. Which of the following is the most likely adverse effect associated with long-term use of this medication?
- A. Angle-closure glaucoma
- B. Hepatic adenoma
- C. Shortened QT interval on ECG
- D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- E. Chronic interstitial pneumonitis (Correct Answer)
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Chronic interstitial pneumonitis***
- **Amiodarone** is known to cause several dose-dependent adverse effects, including **pulmonary toxicity** in the form of **interstitial pneumonitis** or fibrosis.
- This adverse effect can manifest as progressive dyspnea, cough, and infiltrates on chest imaging, requiring careful monitoring during long-term use.
*Angle-closure glaucoma*
- While some medications can cause **angle-closure glaucoma**, it is **not a classic or common adverse effect of amiodarone**.
- **Topiramate** and **sulfonamides** are more commonly associated with acute angle-closure glaucoma.
*Hepatic adenoma*
- **Hepatic adenomas** are typically associated with **oral contraceptive use** and sometimes **anabolic steroid use**, not amiodarone.
- Amiodarone can cause **hepatic toxicity** (elevated transaminases, hepatitis), but not specifically hepatic adenoma.
*Shortened QT interval on ECG*
- **Amiodarone** is a Class III antiarrhythmic drug that **prolongs the QT interval** by blocking potassium channels, which is its mechanism of action for suppressing arrhythmias.
- Therefore, a shortened QT interval is the **opposite of what would be expected with amiodarone use**.
*Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy*
- **Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)** is a rare, severe opportunistic infection of the brain caused by the **JC virus**, typically seen in immunocompromised individuals.
- It is **not an adverse effect of amiodarone**; drugs like natalizumab or rituximab, which affect the immune system, are associated with PML.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 3: A 72-year-old man with congestive heart failure is brought to the emergency department because of chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, and palpitations for 30 minutes. An ECG shows a wide complex tachycardia with a P-wave rate of 105/min, an R-wave rate of 130/min, and no apparent relation between the two. Intravenous pharmacotherapy is initiated with a drug that prolongs the QRS and QT intervals. The patient was most likely treated with which of the following drugs?
- A. Carvedilol
- B. Verapamil
- C. Flecainide
- D. Quinidine (Correct Answer)
- E. Sotalol
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: **Quinidine**
- Quinidine is a **Class IA antiarrhythmic** that blocks fast sodium channels, prolonging both the **QRS complex** (due to slowed conduction) and the **QT interval** (due to prolonged repolarization).
- The ECG findings of **wide-complex tachycardia** and **AV dissociation** (P-wave rate different from R-wave rate without apparent relation) are consistent with ventricular tachycardia, which Class IA drugs can treat.
*Carvedilol*
- Carvedilol is a **beta-blocker** (Class II antiarrhythmic) that primarily slows heart rate and AV nodal conduction, generally **shortening the QT interval** or having no effect, and would not widen the QRS complex.
- Beta-blockers are typically contraindicated in **decompensated heart failure** and **wide-complex tachycardia** due to their negative inotropic effects and risk of worsening decompensation.
*Verapamil*
- Verapamil is a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** (Class IV antiarrhythmic) that mainly slows AV nodal conduction. It would not cause QRS widening and can shorten the QT interval.
- Verapamil is generally contraindicated in **wide-complex tachycardias** of unknown origin as it can precipitate cardiovascular collapse if the arrhythmia is ventricular.
*Flecainide*
- Flecainide is a **Class IC antiarrhythmic** that primarily blocks fast sodium channels, causing significant **QRS widening** but has **minimal effect on the QT interval**, which is contrary to the case description.
- Class IC agents are also generally avoided in patients with **structural heart disease** like congestive heart failure due to increased mortality risk.
*Sotalol*
- Sotalol is a **Class III antiarrhythmic** (beta-blocker with potassium channel blockade) that primarily prolongs the **QT interval** by blocking potassium channels. While it prolongs the QT, it does **not significantly widen the QRS complex**.
- Its beta-blocking effects could exacerbate **decompensated heart failure** in this patient, similar to carvedilol.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 4: A 53-year-old man with obesity and heart disease presents to your outpatient clinic with complaints of orthopnea, significant dyspnea on minimal exertion, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. He says that his old doctor gave him "some pills" that he takes in varying amounts every morning. Physical exam is significant for a severely displaced point of maximal impulse, bilateral rales in the lower lung fields, an S3 gallop, and hepatomegaly. You decide to perform an EKG (shown in figure A). Suddenly, his rhythm changes to ventricular tachycardia followed by ventricular fibrillation, and he syncopizes and expires despite resuscitative efforts. High levels of which medication are most likely responsible?
- A. Propranolol
- B. Amiodarone
- C. Lidocaine
- D. Verapamil
- E. Digoxin (Correct Answer)
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Digoxin***
- The patient's presentation with **heart failure** symptoms (dyspnea, orthopnea, rales, S3 gallop, hepatomegaly) and erratic self-dosing of "some pills" strongly suggests **digoxin toxicity**.
- **Gastrointestinal symptoms** (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) are common initial signs of digoxin toxicity, and the progression to **ventricular tachycardia** and **ventricular fibrillation** is consistent with severe digitalis-induced arrhythmia.
*Propranolol*
- This is a **beta-blocker** primarily used for hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias.
- While overdose can cause bradycardia, hypotension, and heart block, it typically does not lead to **ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation** as seen in this case.
*Amiodarone*
- This is a **Class III antiarrhythmic** medication with a long half-life, used for various tachyarrhythmias.
- Though it can cause many side effects, including proarrhythmia, it is less likely to present with the classic **GI symptoms** and rapid progression to fatal ventricular arrhythmias seen here, especially in the context of erratic self-dosing and underlying heart failure.
*Lidocaine*
- This is a **Class IB antiarrhythmic** primarily used for ventricular arrhythmias, especially post-myocardial infarction.
- Toxicity typically manifests as **neurological symptoms** (drowsiness, confusion, seizures) and sometimes hypotension or bradycardia, not the wide range of GI and lethal cardiac arrhythmias described.
*Verapamil*
- This is a **calcium channel blocker** used for hypertension, angina, and supraventricular tachycardias.
- Overdose primarily causes **bradycardia, hypotension, and atrioventricular block**, but it is generally not associated with the pronounced GI symptoms or directly triggering ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation like digoxin toxicity.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 5: A 64-year-old man presents to his physician for a scheduled follow-up visit. He has chronic left-sided heart failure with systolic dysfunction. His current regular medications include captopril and digoxin, which were started after his last episode of symptomatic heart failure approximately 3 months ago. His last episode of heart failure was accompanied by atrial fibrillation, which followed an alcohol binge over a weekend. Since then he stopped drinking. He reports that he has no current symptoms at rest and is able to perform regular physical exercise without limitation. On physical examination, mild bipedal edema is noted. The physician suggested to him that he should discontinue digoxin and continue captopril and scheduled him for the next follow-up visit. Which of the following statements best justifies the suggestion made by the physician?
- A. Long-term digoxin therapy produces significant survival benefits in patients with heart failure, but at the cost of increased heart failure-related admissions.
- B. Both captopril and digoxin are likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, but digoxin has more severe side effects.
- C. Captopril is likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, unlike digoxin.
- D. Digoxin does not benefit patients with left-sided heart failure in the absence of atrial fibrillation.
- E. Digoxin is useful to treat atrial fibrillation, but does not benefit patients with systolic dysfunction who are in sinus rhythm. (Correct Answer)
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Digoxin is useful to treat atrial fibrillation, but does not benefit patients with systolic dysfunction who are in sinus rhythm.***
- The patient's **atrial fibrillation** was likely triggered by the alcohol binge and has since resolved, suggesting he is now in **sinus rhythm**.
- Digoxin's primary benefit in heart failure with **systolic dysfunction** (HFrEF) is to control ventricular rate in patients with **atrial fibrillation**, but it does not offer survival benefit in HFrEF patients who are in **sinus rhythm** and well-managed with other therapies.
*Long-term digoxin therapy produces significant survival benefits in patients with heart failure, but at the cost of increased heart failure-related admissions.*
- This statement is incorrect; digoxin has been shown to **reduce hospital admissions** for heart failure, but it does **not provide a significant survival benefit** in patients with HFrEF in sinus rhythm.
- The main benefit of digoxin in HFrEF is to improve symptoms and quality of life, alongside reducing hospitalizations, but not prolonging life.
*Both captopril and digoxin are likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, but digoxin has more severe side effects.*
- **Captopril (an ACE inhibitor)** does improve **long-term survival** in heart failure, but **digoxin does not** demonstrably improve survival.
- While digoxin can have side effects, its lack of survival benefit for HFrEF in sinus rhythm is the primary reason for discontinuation, not just side effect severity.
*Captopril is likely to improve the long-term survival of the patient with heart failure, unlike digoxin.*
- This statement is partially correct that **captopril improves survival**, but it does not fully explain the physician's decision to discontinue digoxin.
- The key missing piece is the patient's current **sinus rhythm** and the lack of benefit of digoxin in that specific context for HFrEF.
*Digoxin does not benefit patients with left-sided heart failure in the absence of atrial fibrillation.*
- This statement is nearly correct, but "left-sided heart failure" is broad. It is specifically in patients with **systolic dysfunction (HFrEF)** who are in **sinus rhythm** that digoxin lacks significant benefit beyond symptom control, and does not provide survival benefit.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 6: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of vomiting, abdominal pain, and blurry vision for the past hour. The parents report that the boy developed these symptoms after he accidentally ingested 2 tablets of his grandfather’s heart failure medication. On physical examination, the child is drowsy, and his pulse is 120/min and irregular. Digoxin toxicity is suspected. A blood sample is immediately sent for analysis and shows a serum digoxin level of 4 ng/mL (therapeutic range: 0.8–2 ng/mL). Which of the following electrolyte abnormalities is most likely to be present in the boy?
- A. Hypermagnesemia
- B. Hypokalemia
- C. Hypercalcemia
- D. Hyperkalemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypocalcemia
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Hyperkalemia***
- **Digoxin** inhibits the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump**, leading to an increase in intracellular sodium and a decrease in intracellular potassium.
- The decreased function of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump results in reduced cellular uptake of potassium, causing **elevated extracellular potassium** levels.
*Hypermagnesemia*
- **Magnesium** is not directly affected by digoxin toxicity in a way that would lead to hypermagnesemia; in fact, hypomagnesemia can exacerbate digoxin toxicity.
- High magnesium levels are typically associated with renal failure or excessive intake of magnesium-containing antacids or laxatives.
*Hypokalemia*
- While hypokalemia can **predispose to digoxin toxicity** (by increasing digoxin binding to the Na+/K+-ATPase pump), acute digoxin overdose, as described here, often leads to **hyperkalemia** due to the direct inhibition of the pump's ability to drive potassium into cells.
- The classic association of hypokalemia with digoxin refers more to its role as a risk factor for toxicity, especially with diuretic use, rather than a direct consequence of acute overdose.
*Hypercalcemia*
- **Calcium** levels are not directly altered to hypercalcemia by digoxin toxicity.
- Digoxin's mechanism involves increasing intracellular calcium by promoting calcium influx and inhibiting its efflux via the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, but this typically does not manifest as measurable serum hypercalcemia.
*Hypocalcemia*
- Digoxin toxicity does not directly cause hypocalcemia.
- Digoxin actually leads to **increased intracellular calcium**, which is responsible for its positive inotropic effect, but this change is primarily intracellular and does not result in systemic hypocalcemia.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 7: A previously healthy 33-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because she could feel her heart racing intermittently for the last 2 hours. Each episode lasts about 10 minutes. She does not have any chest pain. Her mother died of a heart attack and her father had an angioplasty 3 years ago. She has smoked a half pack of cigarettes daily for 14 years. She drinks one to two beers daily. She appears anxious. Her temperature is 37.6°C (98.1°F), pulse is 160/min, and blood pressure is 104/76 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination shows no murmurs, rubs, or gallops. An ECG is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Intravenous adenosine
- B. Aspirin
- C. Intravenous procainamide
- D. Vagal maneuvers (Correct Answer)
- E. Coronary angioplasty
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Vagal maneuvers***
- The ECG shows a **narrow complex tachycardia** at a rate of 160/min. Given the patient's stable hemodynamics (BP 104/76 mm Hg), **vagal maneuvers** are the most appropriate initial step to attempt to terminate the re-entrant rhythm, such as Valsalva maneuver or carotid sinus massage.
- Vagal maneuvers increase **parasympathetic tone** to the heart, which can slow conduction through the AV node and potentially break the re-entrant circuit causing the supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
*Intravenous adenosine*
- **Adenosine** is a treatment for **narrow complex tachycardia** if vagal maneuvers fail, but it is not the *initial* step in a hemodynamically stable patient.
- It works by transiently blocking the **AV node**, interrupting re-entrant pathways.
*Intravenous procainamide*
- **Procainamide** is an antiarrhythmic typically used for **wide complex tachycardia** or for narrow complex tachycardias that are refractory to vagal maneuvers and adenosine, or when there is evidence of pre-excitation.
- It is not the first-line treatment for a stable **narrow complex tachycardia**.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is an **antiplatelet agent** used in the management of acute coronary syndromes or for cardiovascular disease prevention.
- It has no role in the immediate termination of a **tachyarrhythmia** like the one presented.
*Coronary angioplasty*
- **Coronary angioplasty** is a procedure used to open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, usually for **acute coronary syndromes** or chronic stable angina.
- The patient presents with a **tachyarrhythmia** and no signs of acute ischemia (no chest pain, although risk factors are present), making angioplasty an inappropriate initial management step.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 8: A 25-year-old male is brought into the emergency department by emergency medical services. The patient has a history of bipolar disease complicated by polysubstance use. He was found down in his apartment at the bottom of a staircase lying on his left arm. He was last seen several hours earlier by his roommate. He is disoriented and unable to answer any questions, but is breathing on his own. His vitals are HR 55, T 96.5, RR 18, BP 110/75. You decide to obtain an EKG as shown in Figure 1. What is the next best step in the treatment of this patient?
- A. Calcium gluconate (Correct Answer)
- B. Albuterol
- C. Intubation
- D. Insulin
- E. Epinephrine
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Calcium gluconate***
- The patient exhibits signs of **rhabdomyolysis** due to prolonged immobility and potential crush injury to the arm, leading to **hyperkalemia** suggested by the EKG changes (likely **peaked T waves**). **Calcium gluconate** stabilizes the cardiac membrane, preventing dangerous arrhythmias.
- While other measures are needed to reduce potassium levels, **calcium gluconate** provides immediate cardiac protection against the effects of hyperkalemia.
*Albuterol*
- **Albuterol** can temporarily shift potassium into cells, but it does not stabilize the cardiac membrane and is often used as an adjunct, not as a primary immediate treatment for severe hyperkalemia with EKG changes.
- Its effects are transient, and it does not directly counteract the cardiotoxic effects of high potassium.
*Intubation*
- The patient is **breathing on his own** and his respiratory rate is normal, indicating no immediate need for intubation for ventilatory support.
- While intubation may be needed for airway protection if his mental status deteriorates further, addressing the life-threatening hyperkalemia is the priority.
*Insulin*
- **Insulin** with glucose helps shift potassium into cells, thereby lowering serum potassium levels. However, it does not provide immediate cardiac membrane stabilization, which is crucial when EKG changes are present.
- Insulin's effect on potassium takes longer to manifest compared to the immediate action of calcium gluconate on the myocardium.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is a vasoconstrictor and cardiac stimulant typically used in cardiac arrest or severe bradycardia.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of **hyperkalemia-induced EKG changes** and would not prevent arrhythmia due to membrane instability.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of intermittent chest tightness that worsens with exercise. He has chronic atrial fibrillation treated with a drug that prolongs the QT interval. During cardiac stress testing, an ECG shows progressive shortening of the QT interval as the heart rate increases. Which of the following drugs is this patient most likely taking?
- A. Lidocaine
- B. Flecainide
- C. Carvedilol
- D. Dofetilide (Correct Answer)
- E. Diltiazem
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Dofetilide***
- **Dofetilide** is a **Class III antiarrhythmic** that blocks potassium channels (IKr) and **prolongs the QT interval**, making it the drug described in the stem.
- It is **FDA-approved for conversion and maintenance of sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation**, matching this patient's treatment history.
- The QT shortening observed during stress testing is **normal physiologic behavior** seen with all drugs—the QT interval naturally decreases as heart rate increases (the corrected QT, or QTc, accounts for this).
- Dofetilide carries a significant **risk of torsades de pointes**, especially with QT prolongation, which is why the stem emphasizes QT monitoring.
*Lidocaine*
- **Lidocaine** is a **Class IB antiarrhythmic** that primarily shortens or has minimal effect on the QT interval.
- It is used for **ventricular arrhythmias** (especially in acute MI), **not for atrial fibrillation**.
- Does not match the described QT-prolonging treatment.
*Flecainide*
- **Flecainide** is a **Class IC antiarrhythmic** that primarily slows conduction by blocking sodium channels.
- It **does not significantly prolong the QT interval**—it may widen the QRS complex but doesn't affect ventricular repolarization substantially.
- While it can be used for atrial fibrillation, it doesn't match the QT-prolonging drug described.
*Carvedilol*
- **Carvedilol** is a **non-selective beta-blocker** with alpha-1 blocking properties used for rate control in atrial fibrillation and heart failure.
- Beta-blockers **do not prolong the QT interval**; they may slightly shorten it or have no effect.
- Does not match the stem description.
*Diltiazem*
- **Diltiazem** is a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** used for rate control in atrial fibrillation.
- It **does not prolong the QT interval**—calcium channel blockers affect AV nodal conduction but not ventricular repolarization.
- Does not match the drug described in the stem.
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 12 hours after ingesting 30 tablets of an unknown drug in a suicide attempt. The tablets belonged to her father, who has a chronic heart condition. She has had nausea and vomiting. She also reports blurring and yellowing of her vision. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 51/min, and blood pressure is 108/71 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows diffuse tenderness with no guarding or rebound. Bowel sounds are normal. An ECG shows prolonged PR-intervals and flattened T-waves. Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following electrolyte abnormalities?
- A. Increased serum K+ (Correct Answer)
- B. Decreased serum K+
- C. Decreased serum Na+
- D. Increased serum Na+
- E. Increased serum Ca2+
Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) Explanation: ***Increased serum K+***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **digoxin toxicity**, including **nausea, vomiting, blurry and yellow vision, bradycardia**, and ECG changes like **prolonged PR interval** and **flattened T-waves**.
- **Digoxin inhibits the Na+/K+-ATPase pump**, leading to an increase in extracellular potassium as potassium cannot enter the cells.
*Decreased serum K+*
- While hypokalemia can exacerbate digoxin toxicity by increasing digoxin binding to the Na+/K+-ATPase, digoxin overdose itself typically causes **hyperkalemia** due to its direct effect on the pump.
- ECG changes like **flattened T-waves** can be seen in hypokalemia, but the overall clinical picture, especially the history of overdose and bradycardia, points more strongly to digoxin toxicity with hyperkalemia.
*Decreased serum Na+*
- **Hyponatremia** is not a characteristic feature of acute digoxin overdose.
- Digoxin primarily affects potassium and calcium channels, with less direct impact on sodium levels, unless related to fluid status changes which are not indicated here.
*Increased serum Na+*
- **Hypernatremia** is not typically associated with digoxin toxicity.
- Digoxin's mechanism of action does not directly lead to increased serum sodium; rather, it primarily inhibits the Na+/K+-ATPase.
*Increased serum Ca2+*
- Digoxin **increases intracellular calcium** by inhibiting the Na+/K+-ATPase, which indirectly leads to increased Na+/Ca2+ exchanger activity.
- However, this primarily affects intracellular levels and **does not typically result in increased serum calcium**.
More Secondary arrhythmias (electrolyte, drug-induced) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.